Abstract
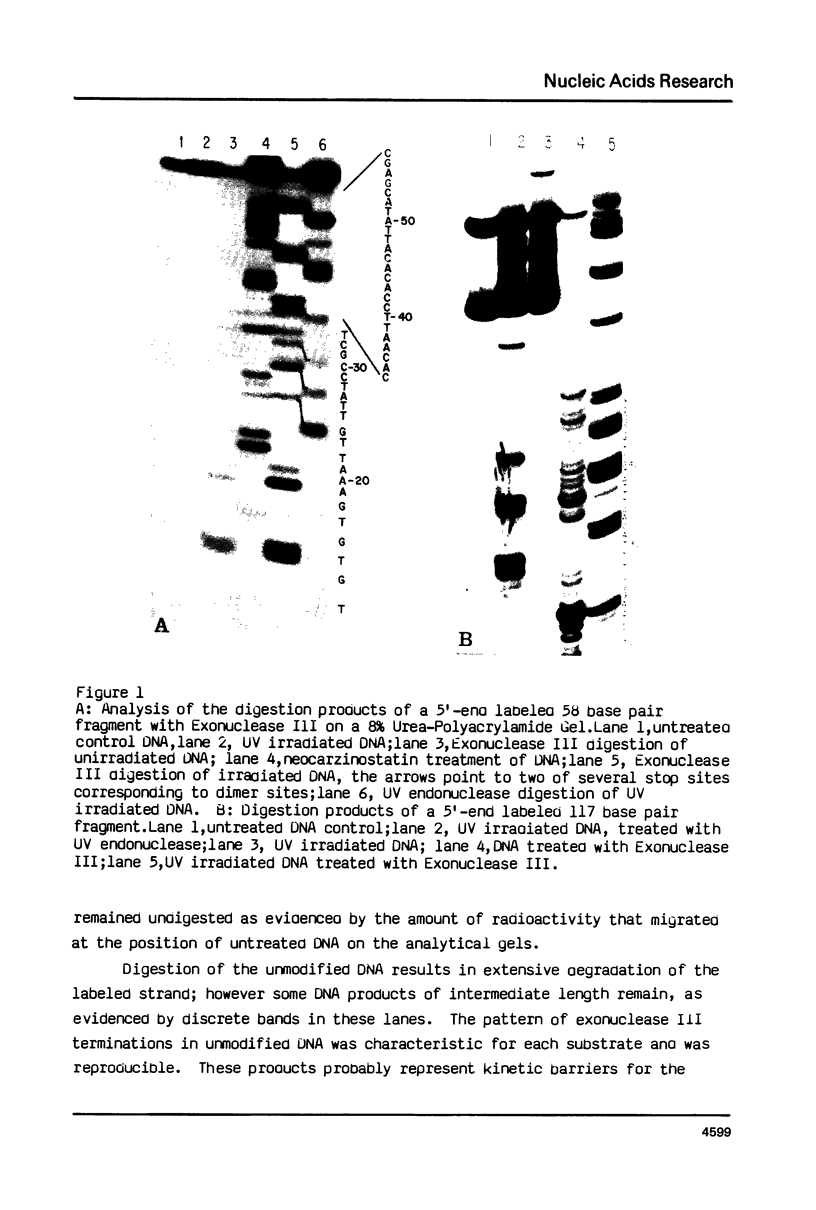
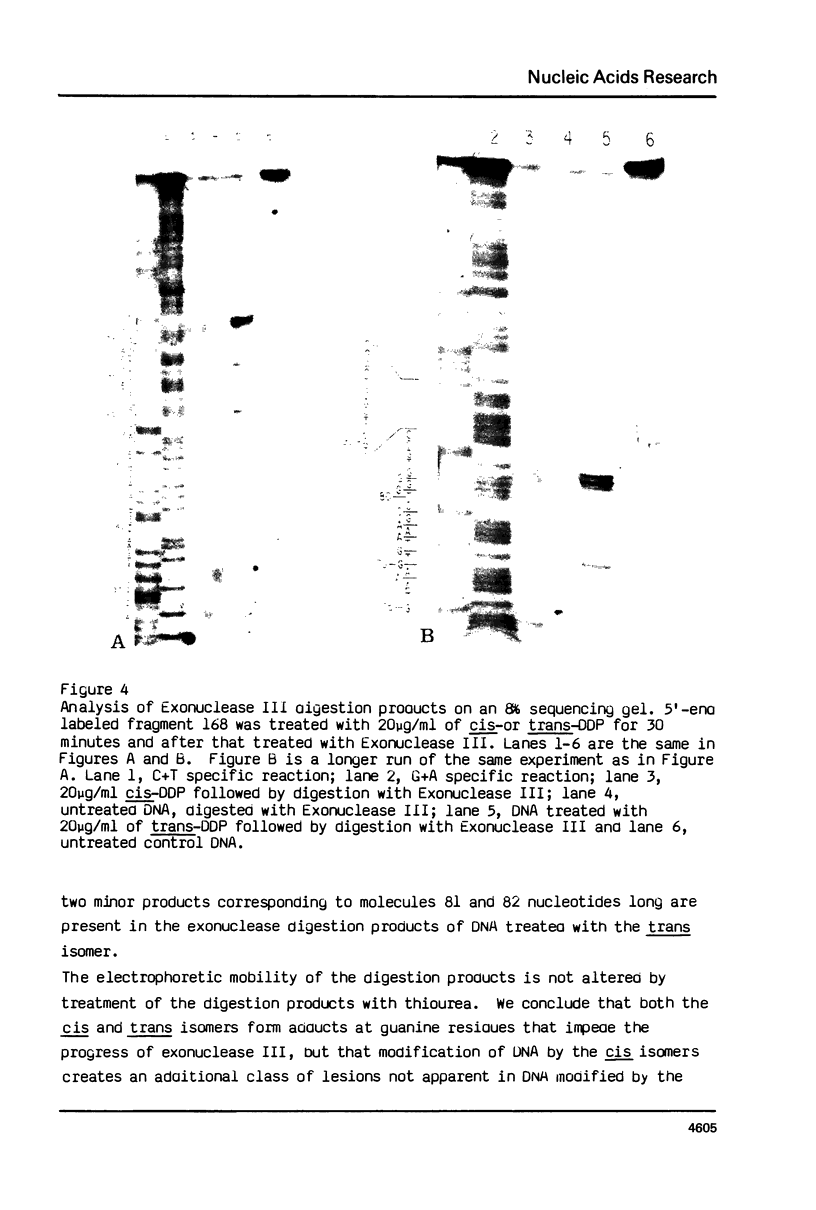
A method to detect chemically stable lesions in DNA has been developed using Exonuclease III, a double strand specific nuclease, to digest 5'-end labeled DNA. The products, when analyzed on high resolution DNA sequencing gels, reveal the sites of DNA modification. Cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers induced by UV irradiation can be localized by comparison of the fragments produced by Exonuclease III digestion with fragments obtained after digestion of the DNA with UV specific endonuclease. The experiments demonstrate the Exonuclease III stops one base away from the cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers. Similar experiments with cis- and trans-dichlorodiammine-platinum (II) showed that modification of DNA by these agents also impede Exonuclease III digestion. In general the same stop sites were found for cis-and trans-platinum adducts. They occur at sites of guanine bases. Additional stop sites were found for cis-platinum at sites of adjacent guanine bases. These results are in agreement with the model that cis-platinum forms intrastrand guanine-guanine dimers, whereas trans-platinum does not.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berkner K. L., Folk W. R. Polynucleotide kinase exchange reaction: quantitave assay for restriction endonuclease-generated 5'-phosphoroyl termini in DNA. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 25;252(10):3176–3184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin V., Haseltine W. A. Reduction of adriamycin to a semiquinone-free radical by NADPH cytochrome P-450 reductase produces DNA cleavage in a reaction mediated by molecular oxygen. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4747–4756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron V., Uhlenbeck O. C. 3'-Phosphatase activity in T4 polynucleotide kinase. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 15;16(23):5120–5126. doi: 10.1021/bi00642a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. L., Bauer W. R., Barton J. K., Lippard S. J. Binding of cis- and trans-dichlorodiammineplatinum(II) to DNA: evidence for unwinding and shortening of the double helix. Science. 1979 Mar 9;203(4384):1014–1016. doi: 10.1126/science.370979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Andrea A. D., Haseltine W. A. Modification of DNA by aflatoxin B1 creates alkali-labile lesions in DNA at positions of guanine and adenine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4120–4124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filipski J., Kohn K. W., Prather R., Bonner W. M. Thiourea reverses cross-links and restores biological activity in DNA treated with dichlorodiaminoplatinum (II). Science. 1979 Apr 13;204(4389):181–183. doi: 10.1126/science.571145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunberg S. M., Haseltine W. A. Use of an indicator sequence of human DNA to study DNA damage by methylbis(2-chloroethyl)amine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6546–6550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseltine W. A., Gordon L. K., Lindan C. P., Grafstrom R. H., Shaper N. L., Grossman L. Cleavage of pyrimidine dimers in specific DNA sequences by a pyrimidine dimer DNA-glycosylase of M. luteus. Nature. 1980 Jun 26;285(5767):634–641. doi: 10.1038/285634a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseltine W. A., Lindan C. P., D'Andrea A. D., Johnsrud L. The use of DNA fragments of defined sequence for the study of DNA damage and repair. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):235–248. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseltine W. A., Lo K. M., D'Andrea A. D. Preferred sites of strand scission in DNA modified by andi-diol epoxide of benzo[a]pyrene. Science. 1980 Aug 22;209(4459):929–931. doi: 10.1126/science.7403858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T. DNA glycosylases, endonucleases for apurinic/apyrimidinic sites, and base excision-repair. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1979;22:135–192. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60800-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansy S., Rosenberg B., Thomson A. J. Binding of cis- and trans-dichlorodiammineplatinum(II) to nucleosides. I. Location of the binding sites. J Am Chem Soc. 1973 Mar 7;95(5):1633–1640. doi: 10.1021/ja00786a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON C. C., LEHMAN I. R., KORNBERG A. A DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID PHOSPHATASE-EXONUCLEASE FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI. II. CHARACTERIZATION OF THE EXONUCLEASE ACTIVITY. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jan;239:251–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. J., Pascoe J. M. Cross-linking of complementary strands of DNA in mammalian cells by antitumour platinum compounds. Nature. 1972 Feb 4;235(5336):282–284. doi: 10.1038/235282a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shooter K. V., Howse R., Merrifield R. K., Robins A. B. The interaction of plantinum II compounds with bacteriophages T7 and R17. Chem Biol Interact. 1972 Oct;5(5):289–307. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(72)90069-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone P. J., Kelman A. D., Sinex F. M. Specific binding of antitumour drug cis-Pt(NH3)2C12 to DNA rich in guanine and cytosine. Nature. 1974 Oct 25;251(5477):736–737. doi: 10.1038/251736a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yajko D. M., Weiss B. Mutations simultaneously affecting endonuclease II and exonuclease III in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):688–692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]