Abstract
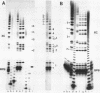
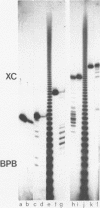
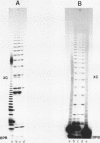
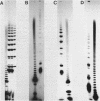
Nature and stability of secondary structures formed from DNA-fragments during electrophoresis in urea containing polyacrylamide-gels were investigated. Duplices and especially hairpin loops were found to be surprisingly stable. Polyacrylamide-gels containing high concentrations of formamide effectively melt these structures. Such gels will improve nucleotide sequence analysis in regions of dyad symmetry that often cause 'band compressions' under standard electrophoresis conditions.
Full text
PDF




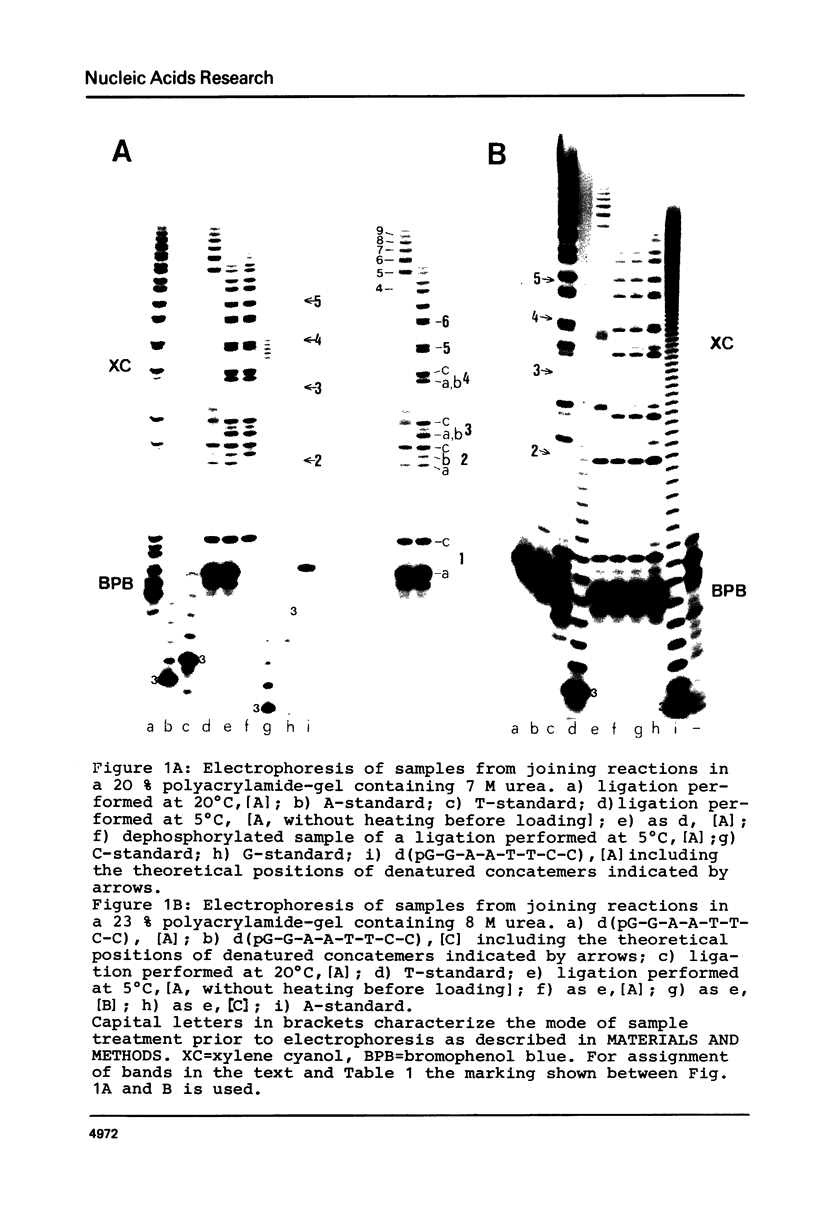
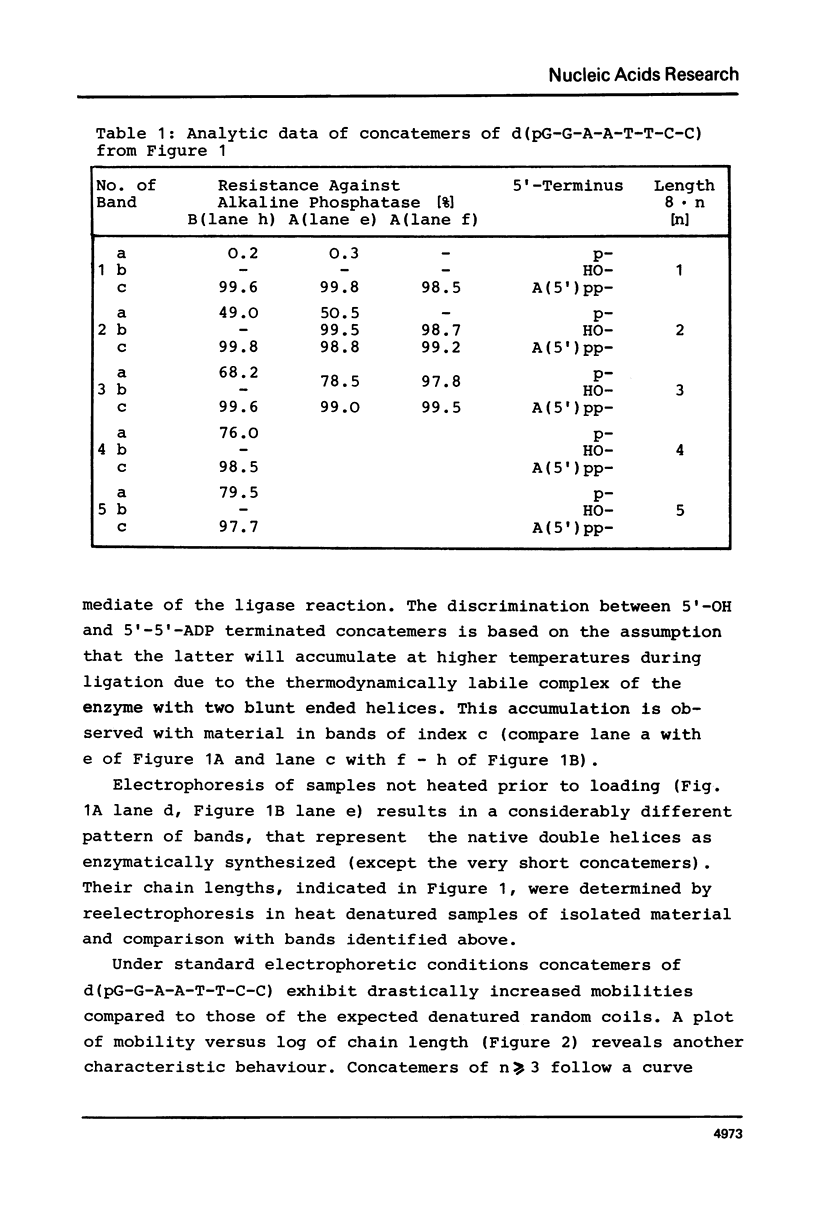
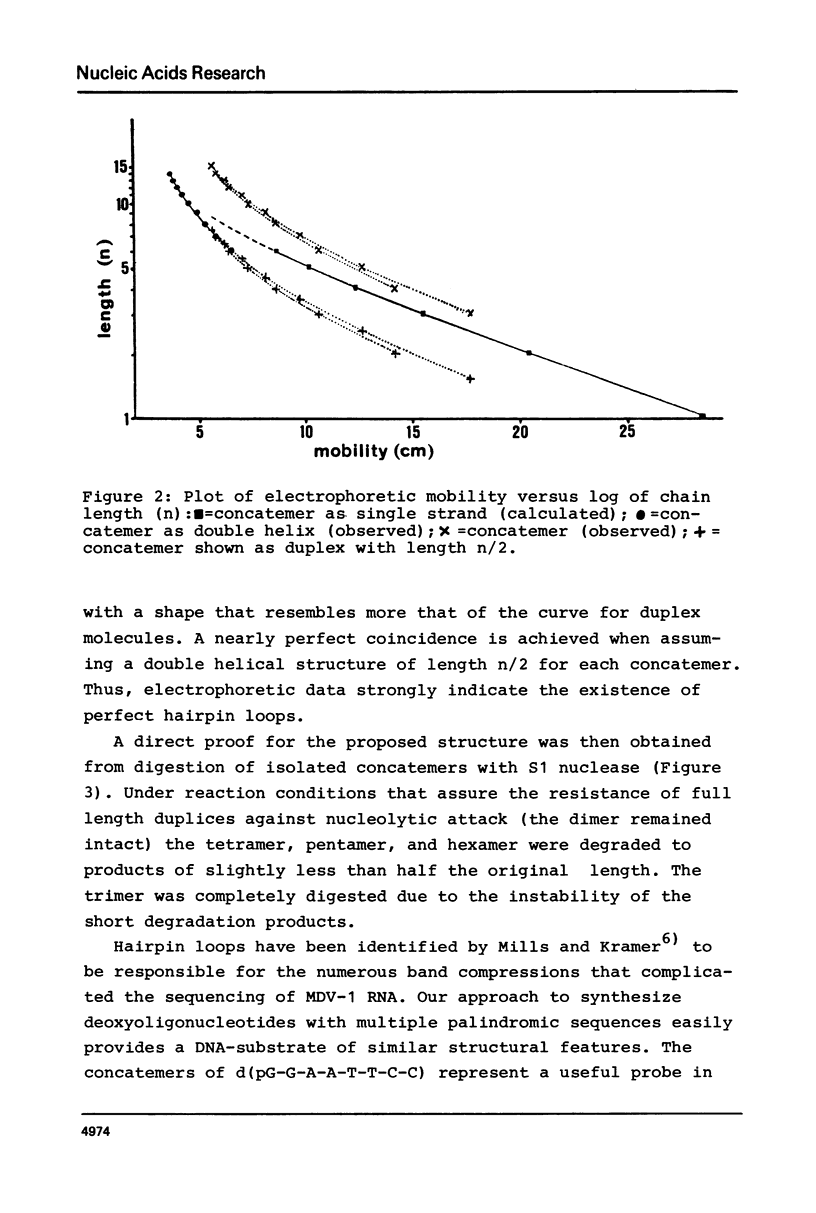

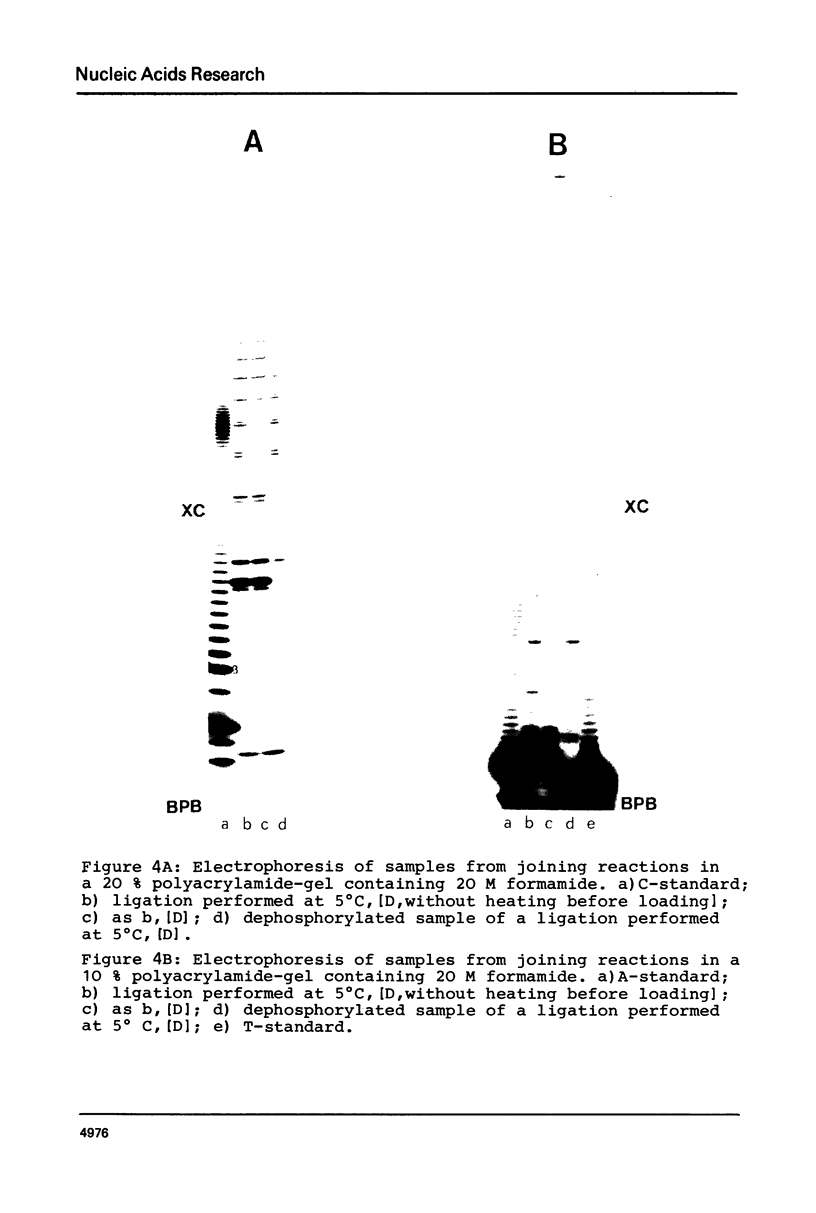


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Deugau K. V., van de Sande J. H. T4 polynucleotide ligase catalyzed joining of short synthetic DNA duplexes at base-paired ends. Biochemistry. 1978 Feb 21;17(4):723–729. doi: 10.1021/bi00597a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank R., Köster H. DNA chain length markers and the influence of base composition on electrophoretic mobility of oligodeoxyribonucleotides in polyacrylamide-gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979;6(6):2069–2087. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.6.2069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer F. R., Mills D. R. RNA sequencing with radioactive chain-terminating ribonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5334–5338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D. R., Kramer F. R. Structure-independent nucleotide sequence analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2232–2235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. A rapid method for determining sequences in DNA by primed synthesis with DNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. The use of thin acrylamide gels for DNA sequencing. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]