Abstract
In the title compound, C17H18N8, the imidazolidine ring adopts an envelope conformation with the substituents at the N atoms in trans positions with respect to the central ring. The dihedral angle between the two benzotriazole rings is 71.65 (10)°. In the crystal, non-classical C—H⋯N interactions link the molecules into helical chains along the b axis. The crystal packing is further stabilized by weak C—H⋯π interactions.
Related literature
For related structures, see: Rivera et al. (2011a ▶,b
▶). For the synthesis of the title compound, see: Rivera et al. (2004 ▶); Katriztky et al. (1990 ▶). For ring conformations, see Cremer & Pople (1975 ▶). For bond-length data, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶). For the anomeric effect, see: Dabbagh et al. (2002 ▶); Selámbaron et al. (2001 ▶); Zefirov & Shekhtman (1971 ▶); Hendrickson (1961 ▶).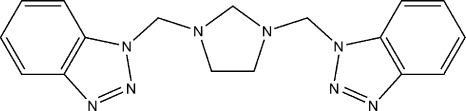
Experimental
Crystal data
C17H18N8
M r = 334.4
Monoclinic,

a = 11.8609 (6) Å
b = 4.6429 (2) Å
c = 14.4712 (8) Å
β = 93.053 (4)°
V = 795.78 (7) Å3
Z = 2
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 0.74 mm−1
T = 120 K
0.43 × 0.18 × 0.10 mm
Data collection
Agilent Xcalibur diffractometer with an Atlas (Gemini ultra Cu) detector
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2010 ▶) T min = 0.378, T max = 1
10081 measured reflections
1609 independent reflections
1541 reflections with I > 3σ(I)
R int = 0.030
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.027
wR(F 2) = 0.073
S = 1.52
1609 reflections
226 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.09 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.11 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Agilent, 2010 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis PRO; program(s) used to solve structure: SIR2002 (Burla et al., 2003 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: JANA2006 (Petříček et al., 2006 ▶); molecular graphics: DIAMOND (Brandenburg & Putz, 2005 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: JANA2006.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812000232/bt5768sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812000232/bt5768Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812000232/bt5768Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg3 is the centroid of the N6/N7/N8/C13/C12 aromatic ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C17—H17⋯N5i | 0.96 | 2.60 | 3.552 (2) | 173 |
| C11—H11b⋯Cg3ii | 0.96 | 2.86 | 3.394 (2) | 116 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the Dirección de Investigaciones, Sede Bogotá (DIB) de la Universidad Nacional de Colombia, for financial support of this work, as well as the Institutional research plan No. AVOZ10100521 of the Institute of Physics and the Praemium Academiae project of the Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic. DQ acknowledges the Vicerrectoría Académica de la Universidad Nacional de Colombia for a fellowship.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The anomeric effect is a stereoelectronic effect observed in various heterocyclic compounds and some acyclic structures with a great deal of importance due its implications on the molecular structure, conformational properties and reactivity of organic compounds (Zefirov & Shekhtman, 1971; Selámbaron, et al., 2001; Dabbagh, et al., 2002). Our investigations on the synthesis and structural studies of heterocyclic compounds have evidenced the occurrence of a n(N)→σ* (C—N) electron delocalization (Rivera et al., 2011a, 2011b). In this article, we discussed the crystal structure of the title compound, which can be synthetized by a three component condensation between ethylenediamine, formaldehyde and benzotriazole (Katriztky et al., 1990) or using a novel methodology involving a Mannich type reaction between the aminal cage 1,3,6,8-tetrazatricyclo[4.4.1.13,8]dodecane and benzotriazole (Rivera et al., 2004). By recrystallization from ethanol we obtained suitable crystals for X-rays analysis.
The molecular structure and atom-numbering scheme for (I) are shown in Fig. 1. The anomeric effect is evidenced by the C—N bond lengths, which are longer as C11—N6 [1.484 (2) Å] and shorter as N2—C11 [1.433 (2) Å] than the expected bond length of 1.469 Å (Allen et al., 1987). Moreover, this effect is confirmed by the bond angles around N2 with a Σα = 339.43 (13) which are distorted from a normal tetrahedral geometry in a five-membered ring (Hendrickson, 1961), whereas for N1 the bond lenghts and angles are within normal ranges. These results are in a good agreement with the crystal structures of related structures (Rivera et al., 2011a, 2011b).
The imidazolidine ring adopts an envelope conformation on C1 as seen in the puckering parameters Q(2) = 0.3953 (17) Å and φ2 = 40.3 (2) ° (Cremer & Pople, 1975), with endocyclic bond angles between 103.06 (13) ° and 106.55 (13) °. The geometry of the N—C—C—N moiety is close to the planar in a syn-periplanar conformation evidenced by the N2—C2—C3—N1 torsion angle [3.05 (17) °]. The benzotriazolylmethyl substituents are arranged trans respect the imidazolidine ring, which is preferred because the nitrogen lone pairs are oriented anti-axial to avoid repulsion electronic repulsions. The benzotriazole rings makes an angle of 38.47 (10) ° and 78.88 (10) ° with the mean plane of imidazolidine ring. The dihedral angle between the two benzotriazole rings is 71.65 (10) °. Chains of molecules in the title compound are linked along the b direction by non-classical intermolecular hydrogen bonds C17—H17···N5 interactions [2.60 Å] which link neighboring molecules. The crystal packing is further stabilized by weak C—H···π interactions.
Experimental
For the originally reported synthesis, see: Rivera et al. (2004). Single crystals of the title compound (I) were grown from ethanol by recrystallization.
Refinement
All H atoms atoms were positioned geometrically and treated as riding on their parent atoms. The isotropic atomic displacement parameters of hydrogen atoms were evaluated as 1.2×Ueq of the parent atom. As the structure contains only light atoms, the Friedel-pair reflections were merged and the Flack parameter has not been determined.
Figures
Fig. 1.
A view of (I) with the numbering scheme.displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
Packing of the molecules of the title compound view along b axis.
Crystal data
| C17H18N8 | F(000) = 352 |
| Mr = 334.4 | Dx = 1.395 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21 | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.5418 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2yb | Cell parameters from 7090 reflections |
| a = 11.8609 (6) Å | θ = 3.1–66.9° |
| b = 4.6429 (2) Å | µ = 0.74 mm−1 |
| c = 14.4712 (8) Å | T = 120 K |
| β = 93.053 (4)° | Prism, colourless |
| V = 795.78 (7) Å3 | 0.43 × 0.18 × 0.10 mm |
| Z = 2 |
Data collection
| Agilent Xcalibur diffractometer with an Atlas (Gemini ultra Cu) detector | 1609 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Enhance Ultra (Cu) X-ray Source | 1541 reflections with I > 3σ(I) |
| mirror | Rint = 0.030 |
| Detector resolution: 10.3784 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 67.0°, θmin = 3.1° |
| Rotation method data acquisition using ω scans | h = −14→14 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2010) | k = −5→5 |
| Tmin = 0.378, Tmax = 1 | l = −17→16 |
| 10081 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 73 constraints |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.027 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.073 | Weighting scheme based on measured s.u.'s w = 1/(σ2(I) + 0.0016I2) |
| S = 1.52 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.005 |
| 1609 reflections | Δρmax = 0.09 e Å−3 |
| 226 parameters | Δρmin = −0.11 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints |
Special details
| Experimental. CrysAlisPro (Agilent, 2010) Empirical absorption correction using spherical harmonics, implemented in SCALE3 ABSPACK scaling algorithm. |
| Refinement. The refinement was carried out against all reflections. The conventional R-factor is always based on F. The goodness of fit as well as the weighted R-factor are based on F and F2 for refinement carried out on F and F2, respectively. The threshold expression is used only for calculating R-factors etc. and it is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement.The program used for refinement, Jana2006, uses the weighting scheme based on the experimental expectations, see _refine_ls_weighting_details, that does not force S to be one. Therefore the values of S are usually larger than the ones from the SHELX program. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| N1 | 0.21591 (11) | 0.2699 (3) | 0.93068 (9) | 0.0235 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.26794 (11) | 0.5272 (3) | 1.06164 (10) | 0.0238 (4) | |
| N3 | 0.09989 (11) | 0.3594 (3) | 0.79499 (9) | 0.0235 (4) | |
| N4 | −0.01384 (12) | 0.4004 (4) | 0.78915 (11) | 0.0290 (4) | |
| N5 | −0.05795 (11) | 0.2425 (4) | 0.72197 (10) | 0.0298 (5) | |
| N6 | 0.40908 (11) | 0.4060 (3) | 1.18741 (10) | 0.0239 (4) | |
| N7 | 0.50606 (11) | 0.2991 (4) | 1.15561 (10) | 0.0280 (4) | |
| N8 | 0.54874 (11) | 0.1110 (4) | 1.21481 (10) | 0.0279 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.31519 (14) | 0.3661 (4) | 0.98560 (11) | 0.0264 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.17294 (13) | 0.3532 (4) | 1.09029 (11) | 0.0248 (5) | |
| C3 | 0.13569 (13) | 0.1890 (4) | 1.00110 (11) | 0.0239 (5) | |
| C4 | 0.17205 (15) | 0.4928 (4) | 0.86759 (12) | 0.0263 (5) | |
| C5 | 0.12961 (13) | 0.1659 (4) | 0.73030 (11) | 0.0215 (5) | |
| C6 | 0.02769 (13) | 0.0916 (4) | 0.68333 (12) | 0.0253 (5) | |
| C7 | 0.02635 (16) | −0.1107 (4) | 0.61123 (12) | 0.0314 (5) | |
| C8 | 0.12773 (17) | −0.2263 (5) | 0.58977 (12) | 0.0354 (6) | |
| C9 | 0.23000 (15) | −0.1486 (5) | 0.63788 (12) | 0.0308 (5) | |
| C10 | 0.23362 (14) | 0.0484 (4) | 0.70895 (11) | 0.0251 (5) | |
| C11 | 0.34550 (15) | 0.6304 (4) | 1.13345 (12) | 0.0286 (5) | |
| C12 | 0.38817 (13) | 0.2843 (4) | 1.27059 (11) | 0.0228 (5) | |
| C13 | 0.47863 (13) | 0.0943 (4) | 1.28781 (12) | 0.0232 (5) | |
| C14 | 0.48715 (14) | −0.0715 (4) | 1.36880 (12) | 0.0270 (5) | |
| C15 | 0.40331 (15) | −0.0378 (4) | 1.42939 (13) | 0.0311 (5) | |
| C16 | 0.31195 (15) | 0.1530 (5) | 1.41080 (13) | 0.0329 (6) | |
| C17 | 0.30163 (14) | 0.3172 (4) | 1.33186 (12) | 0.0293 (5) | |
| H1a | 0.358632 | 0.493853 | 0.949314 | 0.0316* | |
| H1b | 0.355874 | 0.201865 | 1.010035 | 0.0316* | |
| H2a | 0.113022 | 0.477804 | 1.107635 | 0.0298* | |
| H2b | 0.199161 | 0.21839 | 1.136922 | 0.0298* | |
| H3a | 0.140331 | −0.014517 | 1.012342 | 0.0287* | |
| H3b | 0.060918 | 0.24844 | 0.980747 | 0.0287* | |
| H4a | 0.128774 | 0.628658 | 0.901023 | 0.0316* | |
| H4b | 0.233758 | 0.58913 | 0.840354 | 0.0316* | |
| H7 | −0.042768 | −0.165557 | 0.578371 | 0.0376* | |
| H8 | 0.129465 | −0.364408 | 0.540509 | 0.0424* | |
| H9 | 0.299061 | −0.236079 | 0.620438 | 0.037* | |
| H10 | 0.302981 | 0.101822 | 0.741735 | 0.0302* | |
| H11a | 0.30616 | 0.75146 | 1.174811 | 0.0343* | |
| H11b | 0.397607 | 0.762446 | 1.107664 | 0.0343* | |
| H14 | 0.54877 | −0.2024 | 1.381195 | 0.0325* | |
| H15 | 0.406631 | −0.146438 | 1.485921 | 0.0373* | |
| H16 | 0.254861 | 0.1683 | 1.45514 | 0.0395* | |
| H17 | 0.239268 | 0.445844 | 1.319532 | 0.0351* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| N1 | 0.0240 (6) | 0.0259 (8) | 0.0205 (7) | −0.0003 (6) | −0.0004 (5) | 0.0012 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0261 (7) | 0.0225 (7) | 0.0223 (7) | −0.0021 (6) | −0.0037 (5) | 0.0009 (6) |
| N3 | 0.0221 (6) | 0.0253 (7) | 0.0229 (7) | 0.0011 (6) | −0.0008 (5) | 0.0020 (6) |
| N4 | 0.0230 (7) | 0.0315 (8) | 0.0326 (8) | 0.0042 (7) | 0.0022 (6) | 0.0053 (7) |
| N5 | 0.0218 (7) | 0.0346 (9) | 0.0325 (8) | −0.0010 (6) | −0.0027 (5) | 0.0075 (7) |
| N6 | 0.0235 (6) | 0.0241 (8) | 0.0235 (7) | −0.0008 (6) | −0.0032 (5) | −0.0013 (6) |
| N7 | 0.0227 (6) | 0.0338 (9) | 0.0269 (7) | −0.0032 (6) | −0.0025 (5) | −0.0021 (7) |
| N8 | 0.0221 (7) | 0.0336 (9) | 0.0275 (7) | 0.0006 (6) | −0.0023 (5) | −0.0019 (7) |
| C1 | 0.0233 (7) | 0.0334 (10) | 0.0224 (8) | −0.0017 (8) | 0.0009 (6) | 0.0024 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0212 (7) | 0.0296 (9) | 0.0236 (8) | 0.0009 (7) | 0.0008 (6) | −0.0008 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0233 (8) | 0.0239 (9) | 0.0243 (8) | −0.0025 (7) | −0.0007 (6) | 0.0003 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0323 (8) | 0.0244 (9) | 0.0219 (8) | −0.0026 (8) | −0.0032 (6) | −0.0010 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0234 (7) | 0.0221 (9) | 0.0187 (7) | −0.0006 (7) | −0.0008 (6) | 0.0035 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0240 (8) | 0.0260 (9) | 0.0255 (8) | −0.0022 (7) | −0.0033 (6) | 0.0080 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0360 (9) | 0.0301 (10) | 0.0267 (9) | −0.0058 (8) | −0.0098 (7) | 0.0031 (8) |
| C8 | 0.0514 (11) | 0.0314 (10) | 0.0228 (8) | −0.0009 (9) | −0.0021 (7) | −0.0015 (8) |
| C9 | 0.0332 (8) | 0.0330 (11) | 0.0264 (8) | 0.0063 (8) | 0.0038 (6) | 0.0011 (8) |
| C10 | 0.0229 (8) | 0.0291 (10) | 0.0235 (8) | −0.0004 (7) | 0.0009 (6) | 0.0029 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0348 (9) | 0.0208 (9) | 0.0288 (9) | −0.0039 (8) | −0.0109 (7) | 0.0012 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0224 (7) | 0.0225 (9) | 0.0228 (8) | −0.0029 (7) | −0.0062 (6) | −0.0028 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0193 (7) | 0.0246 (9) | 0.0253 (8) | −0.0022 (7) | −0.0032 (6) | −0.0039 (7) |
| C14 | 0.0262 (8) | 0.0241 (9) | 0.0299 (9) | 0.0014 (7) | −0.0066 (6) | 0.0000 (7) |
| C15 | 0.0322 (9) | 0.0317 (11) | 0.0289 (9) | −0.0030 (8) | −0.0028 (7) | 0.0043 (8) |
| C16 | 0.0292 (8) | 0.0394 (11) | 0.0303 (9) | −0.0009 (8) | 0.0039 (7) | −0.0004 (9) |
| C17 | 0.0238 (8) | 0.0336 (11) | 0.0302 (9) | 0.0041 (8) | −0.0013 (6) | −0.0026 (8) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| N1—C1 | 1.455 (2) | C4—H4b | 0.96 |
| N1—C3 | 1.479 (2) | C5—C6 | 1.398 (2) |
| N1—C4 | 1.458 (2) | C5—C10 | 1.398 (2) |
| N2—C1 | 1.466 (2) | C6—C7 | 1.403 (3) |
| N2—C2 | 1.464 (2) | C7—C8 | 1.368 (3) |
| N2—C11 | 1.433 (2) | C7—H7 | 0.96 |
| N3—N4 | 1.3604 (19) | C8—C9 | 1.413 (3) |
| N3—C4 | 1.458 (2) | C8—H8 | 0.96 |
| N3—C5 | 1.357 (2) | C9—C10 | 1.376 (3) |
| N4—N5 | 1.305 (2) | C9—H9 | 0.96 |
| N5—C6 | 1.377 (2) | C10—H10 | 0.96 |
| N6—N7 | 1.355 (2) | C11—H11a | 0.96 |
| N6—C11 | 1.484 (2) | C11—H11b | 0.96 |
| N6—C12 | 1.364 (2) | C12—C13 | 1.401 (2) |
| N7—N8 | 1.307 (2) | C12—C17 | 1.400 (2) |
| N8—C13 | 1.381 (2) | C13—C14 | 1.402 (2) |
| C1—H1a | 0.96 | C14—C15 | 1.369 (3) |
| C1—H1b | 0.96 | C14—H14 | 0.96 |
| C2—C3 | 1.543 (2) | C15—C16 | 1.414 (3) |
| C2—H2a | 0.96 | C15—H15 | 0.96 |
| C2—H2b | 0.96 | C16—C17 | 1.373 (3) |
| C3—H3a | 0.96 | C16—H16 | 0.96 |
| C3—H3b | 0.96 | C17—H17 | 0.96 |
| C4—H4a | 0.96 | ||
| C1—N1—C3 | 103.48 (12) | N3—C5—C10 | 132.45 (15) |
| C1—N1—C4 | 112.04 (14) | C6—C5—C10 | 123.13 (15) |
| C3—N1—C4 | 112.98 (13) | N5—C6—C5 | 108.33 (15) |
| C1—N2—C2 | 105.19 (14) | N5—C6—C7 | 131.54 (15) |
| C1—N2—C11 | 117.30 (13) | C5—C6—C7 | 120.12 (16) |
| C2—N2—C11 | 116.94 (13) | C6—C7—C8 | 117.14 (16) |
| N4—N3—C4 | 121.83 (14) | C6—C7—H7 | 121.4291 |
| N4—N3—C5 | 110.05 (13) | C8—C7—H7 | 121.4287 |
| C4—N3—C5 | 127.90 (14) | C7—C8—C9 | 122.02 (18) |
| N3—N4—N5 | 108.94 (14) | C7—C8—H8 | 118.9882 |
| N4—N5—C6 | 108.26 (13) | C9—C8—H8 | 118.9897 |
| N7—N6—C11 | 119.68 (14) | C8—C9—C10 | 122.01 (17) |
| N7—N6—C12 | 110.21 (14) | C8—C9—H9 | 118.9967 |
| C11—N6—C12 | 130.08 (14) | C10—C9—H9 | 118.9971 |
| N6—N7—N8 | 109.17 (13) | C5—C10—C9 | 115.58 (15) |
| N7—N8—C13 | 108.11 (14) | C5—C10—H10 | 122.2124 |
| N1—C1—N2 | 103.65 (13) | C9—C10—H10 | 122.2126 |
| N1—C1—H1a | 109.4707 | N2—C11—N6 | 115.81 (15) |
| N1—C1—H1b | 109.4711 | N2—C11—H11a | 109.4718 |
| N2—C1—H1a | 109.4712 | N2—C11—H11b | 109.4704 |
| N2—C1—H1b | 109.4715 | N6—C11—H11a | 109.4709 |
| H1a—C1—H1b | 114.7236 | N6—C11—H11b | 109.4712 |
| N2—C2—C3 | 103.06 (13) | H11a—C11—H11b | 102.2888 |
| N2—C2—H2a | 109.4714 | N6—C12—C13 | 104.13 (14) |
| N2—C2—H2b | 109.4715 | N6—C12—C17 | 133.44 (16) |
| C3—C2—H2a | 109.4717 | C13—C12—C17 | 122.43 (16) |
| C3—C2—H2b | 109.4711 | N8—C13—C12 | 108.38 (15) |
| H2a—C2—H2b | 115.2 | N8—C13—C14 | 130.61 (16) |
| N1—C3—C2 | 106.55 (13) | C12—C13—C14 | 121.01 (15) |
| N1—C3—H3a | 109.4715 | C13—C14—C15 | 116.76 (16) |
| N1—C3—H3b | 109.4715 | C13—C14—H14 | 121.6205 |
| C2—C3—H3a | 109.4712 | C15—C14—H14 | 121.6212 |
| C2—C3—H3b | 109.4712 | C14—C15—C16 | 121.66 (17) |
| H3a—C3—H3b | 112.2427 | C14—C15—H15 | 119.1684 |
| N1—C4—N3 | 109.01 (15) | C16—C15—H15 | 119.1674 |
| N1—C4—H4a | 109.4712 | C15—C16—C17 | 122.64 (17) |
| N1—C4—H4b | 109.4703 | C15—C16—H16 | 118.6785 |
| N3—C4—H4a | 109.4717 | C17—C16—H16 | 118.6776 |
| N3—C4—H4b | 109.4721 | C12—C17—C16 | 115.49 (16) |
| H4a—C4—H4b | 109.9289 | C12—C17—H17 | 122.2546 |
| N3—C5—C6 | 104.42 (14) | C16—C17—H17 | 122.2552 |
| N2—C2—C3—N1 | 3.05 (17) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| Cg3 is the centroid of the N6/N7/N8/C13/C12 aromatic ring. |
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C17—H17···N5i | 0.96 | 2.60 | 3.552 (2) | 173 |
| C11—H11b···Cg3ii | 0.96 | 2.86 | 3.394 (2) | 116 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, y+1/2, −z+2; (ii) x, y+1, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BT5768).
References
- Agilent (2010). CrysAlis PRO Agilent Technologies, Yarnton, Oxfordshire, England.
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Brandenburg, K. & Putz, H. (2005). DIAMOND Crystal Impact, Bonn, Germany.
- Burla, M. C., Camalli, M., Carrozzini, B., Cascarano, G. L., Giacovazzo, C., Polidori, G. & Spagna, R. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst. 36, 1103.
- Cremer, D. & Pople, J. A. (1975). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 97, 1354–1358.
- Dabbagh, H. A., Modarresi-Alam, A. R., Tadjarodi, A. & Taeb, A. (2002). Tetrahedron, 58, 2621–2625.
- Hendrickson, J. B. (1961). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 83, 4537–4547.
- Katriztky, A. R., Pilarski, B. & Urogdi, L. (1990). J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, pp. 541–547.
- Petříček, V., Dušek, M. & Palatinus, L. (2006). JANA2006 Institute of Physics, Praha, Czech Republic.
- Rivera, A., Maldonado, M., Casas, J. L., Dušek, M. & Fejfarová, K. (2011a). Acta Cryst. E67, o990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Rivera, A., Núñez, M. E., Maldonado, M. & Joseph-Nathan, P. (2004). Heterocycl. Commun. 10, 77–80.
- Rivera, A., Pacheco, D. J., Ríos-Motta, J., Pojarová, M. & Dušek, M. (2011b). Acta Cryst. E67, o3071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Selámbaron, J., Monge, S., Carré, F., Fruchier, A., Roque, J. P. & Pavia, A. A. (2001). Carbohydr. Res. 330, 43–51. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Zefirov, N. S. & Shekhtman, N. M. (1971). Russ. Chem. Rev. 40, 315–329.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812000232/bt5768sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812000232/bt5768Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812000232/bt5768Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




