Abstract
The title molecule, C14H18Cl2N2O2, lies on a crystallographic inversion center and the each 4-chlorobutanamide group adopts an anti-staggered conformation. In the crystal, adjacent molecules are linked through N—H⋯O contacts, forming infinite ribbons extending parallel to the a axis.
Related literature
For details and syntheses of chloroamides as precursors for new azamacrocycles see: Benaglia et al. (2005 ▶); Harte & Gunnlaugsson (2006 ▶); Humphrey & Chamberlin (1997 ▶); Mangalagiu et al. (2007 ▶); Zbancioc et al. (2012 ▶).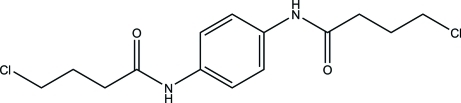
Experimental
Crystal data
C14H18Cl2N2O2
M r = 317.20
Triclinic,

a = 5.105 (5) Å
b = 6.876 (5) Å
c = 10.549 (5) Å
α = 97.735 (5)°
β = 93.214 (5)°
γ = 90.512 (5)°
V = 366.3 (5) Å3
Z = 1
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.45 mm−1
T = 200 K
0.25 × 0.2 × 0.2 mm
Data collection
Agilent Xcalibur Eos diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2011 ▶) T min = 0.914, T max = 1.000
2575 measured reflections
1446 independent reflections
1189 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.026
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.038
wR(F 2) = 0.092
S = 1.03
1446 reflections
91 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.23 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.26 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Agilent, 2011 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis PRO; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812001341/nk2130sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812001341/nk2130Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812001341/nk2130Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1⋯O1i | 0.88 | 2.10 | 2.941 (3) | 161 |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by PCAP FP7-PEOPLE-2009-IRSES (No. 246902) and the Development Fund, Sectoral Operational Programme "Increase of Economic Competitiveness", Priority Axis 2 (SOP IEC-A2-O2.1.2-2009-2, ID 570, COD SMIS-CSNR: 12473, Contract 129/2010-POLISILMET).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
With the aim of synthesizing new chloroamides as precursors for new azamacrocycles (Zbancioc et al., 2012), we report the synthesis and crystal structure of the title compound C14H18Cl2N2O2, which represents a diamide with aliphatic arms, consisting of two moieties of butyryl chloride and a phenylenediamine unit. Amides are important building blocks in preparative macrocycle chemistry (Harte & Gunnlaugsson, 2006), due to their spectroscopic proprieties as well as to their arms ability to coordinate to metal centers. The X-ray structure of the title compound with the atom numbering scheme is shown in Fig. 1. The molecule is assembled from two centro-symmetrically related units through the Ci at the center of the aromatic ring. The amide group is rotated by 32.4 (2)° in respect with the phenyl ring. The butyryl chloride fragment adopts an anti-staggered conformation. The main crystal structure motif arises from the parallel packing of the ribbon (Fig. 2) along the crystallographic a axis. The infinite ribbons are stabilized via intermolecular N1—H1···O1ii H-bond with N1—H1 = 0.88 Å, N1···O1ii = 2.941 (3) Å, [symmetry code ii: x–1, y, z], H1···O1ii = 2.10 Å and N1HO1 angle of 161°.
Experimental
p-Phenylenediamine (5 mmol, 0.54 g) was dissolved in sodium hydroxide solution (0.4 N, 50 ml) and 4-chlorobutyryl chloride (30 mmol, 3.4 ml) was added dropwise under stirring at 0° C for 1 h. Afterwards the mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight resulting in a white precipitate, which was separated by filtration, washed several times with water and dried in vacuum; yield 60%. The purity of N,N'-(1,4-phenylene)bis(4-chlorobutanamide) was confirmed by 1H and 13C NMR spectra.
1H NMR (DMSO-d6) δ (p.p.m.): 9.876 (s, 2NH), 7.492 (s, 4H, Ar), 3.675–3.708 (t, J = 6.8 Hz, 4H, CH2, adjacent to chlor), 2.433–2.469 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 4H, CH2, adjacent to amido), 1.988–2.057 (c, J = 6.8 Hz J = 7.2 Hz, 4H, CH2).
13C NMR (DMSO-d6) δ (p.p.m.): 169.72 (2 C, C═O), 134.46 (2 C, Ar), 119.37 (4 C, Ar), 44.97 (2 C, CH2, adjacent to chlor), 33.19 (2 C, CH2, adjacent to amido), 27.90 (2 C, CH2).
Refinement
The H atoms were positioned geometrically and refined using a riding model with C—H = 0.95–0.99 Å and with Uiso(H) = 1.2 times Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of C14H18Cl2N2O2. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at 50% probability level. H atoms are presented as small spheres of arbitrary radius. Symmetry code: (i) –x, –y+1, –z+1.
Fig. 2.
Part of the crystal structure of C14H18Cl2N2O2. Molecular chains generated by N—H···O hydrogen bonds are shown by dashed lines. H atoms not involved in intermolecular bonding have been omitted.
Crystal data
| C14H18Cl2N2O2 | Z = 1 |
| Mr = 317.20 | F(000) = 166 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.438 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 5.105 (5) Å | Cell parameters from 1244 reflections |
| b = 6.876 (5) Å | θ = 3.0–29.4° |
| c = 10.549 (5) Å | µ = 0.45 mm−1 |
| α = 97.735 (5)° | T = 200 K |
| β = 93.214 (5)° | Prism, clear light yellow |
| γ = 90.512 (5)° | 0.25 × 0.2 × 0.2 mm |
| V = 366.3 (5) Å3 |
Data collection
| Agilent Xcalibur Eos diffractometer | 1446 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1189 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.026 |
| Detector resolution: 16.1593 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 26.0°, θmin = 3.0° |
| ω scans | h = −5→6 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2011) | k = −8→7 |
| Tmin = 0.914, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −12→8 |
| 2575 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.038 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.092 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.03 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0387P)2 + 0.0691P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 1446 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 91 parameters | Δρmax = 0.23 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.26 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.29972 (11) | −0.27268 (9) | 1.02884 (5) | 0.0434 (2) | |
| O1 | 0.4276 (2) | 0.1286 (2) | 0.67205 (14) | 0.0337 (4) | |
| C5 | 0.0022 (3) | 0.3420 (3) | 0.57107 (17) | 0.0189 (4) | |
| C6 | −0.1885 (3) | 0.4863 (3) | 0.58668 (18) | 0.0201 (4) | |
| H6 | −0.3186 | 0.4768 | 0.6466 | 0.024* | |
| N1 | −0.0077 (3) | 0.1862 (2) | 0.64528 (14) | 0.0207 (4) | |
| H1 | −0.1645 | 0.1441 | 0.6607 | 0.025* | |
| C2 | 0.3081 (3) | −0.2263 (3) | 0.77558 (18) | 0.0241 (4) | |
| H2A | 0.2956 | −0.2923 | 0.6860 | 0.029* | |
| H2B | 0.4926 | −0.1826 | 0.7966 | 0.029* | |
| C1 | 0.2360 (4) | −0.3719 (3) | 0.86319 (19) | 0.0309 (5) | |
| H1A | 0.3385 | −0.4927 | 0.8437 | 0.037* | |
| H1B | 0.0476 | −0.4077 | 0.8477 | 0.037* | |
| C4 | 0.2010 (3) | 0.0948 (3) | 0.69526 (18) | 0.0206 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.1331 (3) | −0.0471 (3) | 0.78585 (18) | 0.0229 (4) | |
| H3A | −0.0520 | −0.0909 | 0.7674 | 0.027* | |
| H3B | 0.1498 | 0.0214 | 0.8748 | 0.027* | |
| C7 | 0.1922 (3) | 0.3575 (3) | 0.48302 (17) | 0.0199 (4) | |
| H7 | 0.3238 | 0.2610 | 0.4710 | 0.024* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0626 (4) | 0.0419 (3) | 0.0274 (3) | 0.0172 (3) | 0.0011 (3) | 0.0104 (2) |
| O1 | 0.0155 (7) | 0.0434 (9) | 0.0481 (9) | 0.0006 (6) | 0.0023 (6) | 0.0278 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0161 (8) | 0.0198 (9) | 0.0210 (10) | −0.0022 (7) | −0.0029 (7) | 0.0060 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0154 (8) | 0.0251 (10) | 0.0203 (9) | −0.0005 (7) | 0.0031 (7) | 0.0045 (8) |
| N1 | 0.0148 (7) | 0.0222 (8) | 0.0269 (9) | −0.0006 (6) | 0.0014 (6) | 0.0102 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0237 (9) | 0.0244 (10) | 0.0254 (10) | 0.0034 (8) | 0.0017 (8) | 0.0073 (8) |
| C1 | 0.0379 (11) | 0.0248 (11) | 0.0307 (12) | 0.0049 (8) | −0.0020 (9) | 0.0075 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0173 (9) | 0.0206 (10) | 0.0243 (10) | 0.0012 (7) | −0.0004 (7) | 0.0046 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0184 (8) | 0.0252 (10) | 0.0272 (10) | 0.0042 (7) | 0.0042 (8) | 0.0104 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0158 (8) | 0.0212 (9) | 0.0230 (10) | 0.0023 (7) | 0.0000 (7) | 0.0047 (8) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cl1—C1 | 1.799 (2) | C2—C3 | 1.524 (3) |
| O1—C4 | 1.222 (2) | C2—H2A | 0.9900 |
| C5—C7 | 1.393 (2) | C2—H2B | 0.9900 |
| C5—C6 | 1.397 (3) | C1—H1A | 0.9900 |
| C5—N1 | 1.412 (2) | C1—H1B | 0.9900 |
| C6—C7i | 1.381 (3) | C4—C3 | 1.505 (3) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9500 | C3—H3A | 0.9900 |
| N1—C4 | 1.359 (2) | C3—H3B | 0.9900 |
| N1—H1 | 0.8800 | C7—C6i | 1.381 (3) |
| C2—C1 | 1.508 (3) | C7—H7 | 0.9500 |
| C7—C5—C6 | 118.79 (17) | Cl1—C1—H1A | 109.4 |
| C7—C5—N1 | 123.01 (16) | C2—C1—H1B | 109.4 |
| C6—C5—N1 | 118.20 (16) | Cl1—C1—H1B | 109.4 |
| C7i—C6—C5 | 121.48 (17) | H1A—C1—H1B | 108.0 |
| C7i—C6—H6 | 119.3 | O1—C4—N1 | 122.99 (17) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.3 | O1—C4—C3 | 122.17 (16) |
| C4—N1—C5 | 126.45 (15) | N1—C4—C3 | 114.81 (15) |
| C4—N1—H1 | 116.8 | C4—C3—C2 | 112.75 (15) |
| C5—N1—H1 | 116.8 | C4—C3—H3A | 109.0 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 113.03 (16) | C2—C3—H3A | 109.0 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 109.0 | C4—C3—H3B | 109.0 |
| C3—C2—H2A | 109.0 | C2—C3—H3B | 109.0 |
| C1—C2—H2B | 109.0 | H3A—C3—H3B | 107.8 |
| C3—C2—H2B | 109.0 | C6i—C7—C5 | 119.73 (17) |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 107.8 | C6i—C7—H7 | 120.1 |
| C2—C1—Cl1 | 111.34 (14) | C5—C7—H7 | 120.1 |
| C2—C1—H1A | 109.4 | ||
| C7—C5—C6—C7i | 0.1 (3) | C5—N1—C4—C3 | 171.72 (16) |
| N1—C5—C6—C7i | −179.67 (15) | O1—C4—C3—C2 | −37.8 (2) |
| C7—C5—N1—C4 | 35.9 (3) | N1—C4—C3—C2 | 144.32 (17) |
| C6—C5—N1—C4 | −144.38 (18) | C1—C2—C3—C4 | −178.27 (15) |
| C3—C2—C1—Cl1 | −67.01 (19) | C6—C5—C7—C6i | −0.1 (3) |
| C5—N1—C4—O1 | −6.1 (3) | N1—C5—C7—C6i | 179.66 (16) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y+1, −z+1.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···O1ii | 0.88 | 2.10 | 2.941 (3) | 161 |
Symmetry codes: (ii) x−1, y, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: NK2130).
References
- Agilent (2011). CrysAlis PRO Aglient Technologies Ltd, Yarnton, England.
- Benaglia, M., Guizzetti, S., Rigamonti, C. & Puglisi, A. (2005). Tetrahedron, 61, 12100–12106.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Harte, A. J. & Gunnlaugsson, T. (2006). Tetrahedron Lett. 47, 6321–6324.
- Humphrey, J. M. & Chamberlin, A. R. (1997). Chem. Rev. 97, 2243–2266. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Mangalagiu, I. I., Balan, A. M. & Florea, O. J. (2007). J Phys. Conf. Ser. 61, 482–483.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Zbancioc, G., Florea, O., Jones, P. G. & Mangalagiu, I. I. (2012). Ultrasonics Sonochem. 19, 399–403. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812001341/nk2130sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812001341/nk2130Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812001341/nk2130Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




