Abstract
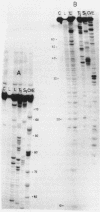
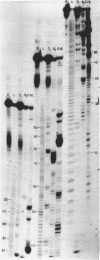
Rat liver 5S rRNA and 5.8S rRNA were end-labelled with 32P at 5'-end or 3'-end of the polynucleotide chain and partially digested with single-strand specific S1 nuclease and double-strand specific endonuclease from the cobra Naja naja oxiana venom. The parallel use of these two structure-specific enzymes in combination with rapid sequencing technique allowed the exact localization of single-stranded and double-stranded regions in 5S RNA and 5.8 S RNA. The most accessible regions to S1 nuclease in 5S RNA are regions 33-42, 74-78, 102-103 and in 5.8 S RNA 16-20, 26-29, 34-36, 74-80 and a region around 125-130. The cobra venom endonuclease cleaves the following areas in 5S RNA: 7-8, 17-20, 28-30, 49-51, 56-57, 60-64, 69-70, 81-82, 95-97, 106-112. In 5.8S RNA the venom endonuclease cleavage sites are 4-7, 10-13, 21-22, 33-35, 43-45, 51-55, 72-74, 85-87, 98-99, 105-106, 114-115, 132-135. According to these results the tRNA binding sequences proposed by Nishikawa and Takemura [(1974) FEBS Lett. 40, 106-109], in 5S RNA are located in partly single-stranded region, but in 5.8S RNA in double-stranded region.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aubert M., Scott J. F., Reynier M., Monier R. Rearrangement of the conformation of Escherichia coli 5S RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):292–299. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azad A. A., Lane B. G. A possible role for 5 S rRNA as a bridge between ribosomal subunits. Can J Biochem. 1973 Dec;51(12):1669–1672. doi: 10.1139/o73-224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber C., Nichols J. L. Conformational studies on wheat embryo 5S RNA using nuclease S1 as a probe. Can J Biochem. 1978 May;56(5):357–364. doi: 10.1139/o78-057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benhamou J., Jourdan R., Jordan B. R. Sequence of Drosophila 5S RNA synthesized by cultured cells and by the insect at different developmental stages. Homogeneity of the product and homologies with other 5S RNA's at the level of primary and secondary structure. J Mol Evol. 1977 May 13;9(3):279–298. doi: 10.1007/BF01796116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branlant C., Krol A., Machatt A., Ebel J. P. The secondary structure of the protein L1 binding region of ribosomal 23S RNA. Homologies with putative secondary structures of the L11 mRNA and of a region of mitochondrial 16S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):293–307. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron V., Uhlenbeck O. C. 3'-Phosphatase activity in T4 polynucleotide kinase. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 15;16(23):5120–5126. doi: 10.1021/bi00642a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann V. A. Structure and function of 5S and 5.8 S RNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1976;18:45–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forget B. G., Weissman S. M. The nucleotide sequence of ribosomal 5 S ribonucleic acid from KB cells. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3148–3165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kel've M. B., Metspalu A. Kh, Lind A. Ia, Saarma M. Iu, Villems R. L. Konformatsionnye izomery 5S RNK ribosom pecheni krysy. Mol Biol (Mosk) 1978 May-Jun;12(3):695–699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. M., Maden B. E. Chemical modification studies and the secondary structure of HeLa cell 5.8S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Oct 10;8(19):4521–4534. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.19.4521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan M. S., Maden B. E. Conformation of mammalian 5.8 S ribosomal RNA: S1 nuclease as a probe. FEBS Lett. 1976 Dec 15;72(1):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80823-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luoma G. A., Marshall A. G. Lasar Raman evidence for a new cloverleaf secondary structure for eucaryotic 5 S RNA. J Mol Biol. 1978 Oct 15;125(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90256-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luoma G. A., Marshall A. G. Laser Raman evidence for new cloverleaf secondary structures for eukaryotic 5.8S RNA and prokaryotic 5S RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4901–4905. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metspalu A., Saarma M., Villems R., Ustav M., Lind A. Interaction of 5-S RNA, 5.8-S RNA and tRNA with rat-liver ribosomal proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Nov 2;91(1):73–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb20938.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metspalu A., Toots I., Saarma M., Villems R. The ternary complex consisting of rat liver ribosomal 5 S RNA, 5.8 S RNA and protein L5. FEBS Lett. 1980 Sep 22;119(1):81–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nazar R. N., Sitz T. O., Busch H. Structural analyses of mammalian ribosomal ribonucleic acid and its precursors. Nucleotide sequence of ribosomal 5.8 S ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 25;250(22):8591–8597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa K., Takemura S. Nucleotide sequence of 5 S RNA from Torulopsis utilis. FEBS Lett. 1974 Mar 15;40(1):106–109. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80904-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa K., Takemura S. Structure and function of 5S ribosomal ribonucleic acid from Torulopsis utilis. III. Detection of single-stranded regions by digestion with nuclease S1. J Biochem. 1977 Apr;81(4):995–1003. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata K., Terao K., Uchiumi T. Stimulation by aminoacyl-tRNA of the GTPase and ATPase activities of rat liver 5S RNA protein particles in the presence of EF-2. J Biochem. 1980 Feb;87(2):517–524. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlakis G. N., Jordan B. R., Wurst R. M., Vournakis J. N. Sequence and secondary structure of Drosophila melanogaster 5.8S and 2S rRNAs and of the processing site between them. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 20;7(8):2213–2238. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.8.2213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M. The nucleotide sequence of Saccharomyces cerevisiae 5.8 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3860–3875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. The use of thin acrylamide gels for DNA sequencing. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinagawa M., Padmanabhan R. Inhibition of a nuclease contaminant in the commercial preparations of Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jun;95(2):458–464. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90756-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitz T. O., Kuo S. C., Nazar R. N. Multimer forms of eukaryotic 5.8S ribosomal RNA. Biochemistry. 1978 Dec 26;17(26):5811–5815. doi: 10.1021/bi00619a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulbrich N., Lin A., Wool I. G. Identification by affinity chromatography of the eukaryotic ribosomal proteins that bind to 5.8 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8641–8645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulbrich N., Wool I. G. Identification by affinity chromatography of the eukaryotic ribosomal proteins that bind to 5 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):9049–9052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasilenko S. K., Ryte V. C. [Isolation of highly purified ribonuclease from cobra (Naja oxiana) venom]. Biokhimiia. 1975 May-Jun;40(3):578–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigne R., Jordan B. R., Monier R. A common conformational feature in several prokaryotic and eukaryotic 5 S RNAs: a highly exposed, single-stranded loop around position 40. J Mol Biol. 1973 May 15;76(2):303–311. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90393-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villems R., Saarma M., Metspalu A., Toots I. New aspects of the eukaryotic ribosomal subunit interaction. FEBS Lett. 1979 Nov 1;107(1):66–68. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80464-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt V. M. Purification and further properties of single-strand-specific nuclease from Aspergillus oryzae. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Feb 15;33(1):192–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02669.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrede P., Woo N. H., Rich A. Initiator tRNAs have a unique anticodon loop conformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3289–3293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrede P., Wurst R., Vournakis J., Rich A. Conformational changes of yeast tRNAPhe and E. coli tRNA2Glu as indicated by different nuclease digestion patterns. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9608–9616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurst R. M., Vournakis J. N., Maxam A. M. Structure mapping of 5'-32P-labeled RNA with S1 nuclease. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 17;17(21):4493–4499. doi: 10.1021/bi00614a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]