Abstract
The title compound, C20H28O3, was isolated during our investigation into the chemical composition and pharmacological activity of Centipeda cunninghamii (DC.) A. Braun & Asch. (Asteraceae). The enantiopure compound, a diterpene with a carbon skeleton, is composed of three six- and one five-membered rings in chair, twist-boat, half-chair and envelope conformations, respectively. Each molecule makes one intra- and one intermolecular O—H⋯O hydrogen bond in the crystal lattice, forming hydrogen-bonded chains along [010]. The absolute configuration of the compound was assigned on the basis of optical rotation measurements.
Related literature
For the characterization of related kaurane diterpenes, see: Reynolds et al. (1991 ▶); Piozzi et al. (1972 ▶). For literature on the occurrence of the 3S isomer of the title compound isolated from Ichthyothere terminalis and Pseudognaphalium cheiranthifolium, see: Bohlmann et al. (1982 ▶); Mendoza & Urzúa (1998 ▶). For the antibacterial activity of the 3S isomer, see: Mendoza et al. (1997 ▶). For phytopharmacological aspects of Centipeda cunninghamii, see: Campbell (1973 ▶); Cribb (1988 ▶); D’Amelio & Mirhom, (1998 ▶); Maiden (1975 ▶); Webb (1948 ▶). For optical rotation data of related compounds, see: Bohlmann et al. (1982 ▶); Brieskorn & Pöhlmann (1968 ▶); Reynolds et al. (1991 ▶).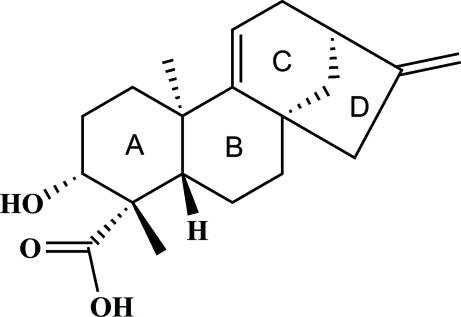
Experimental
Crystal data
C20H28O3
M r = 316.4
Monoclinic,
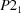
a = 8.064 (2) Å
b = 10.775 (3) Å
c = 10.462 (4) Å
β = 109.70 (2)°
V = 855.8 (5) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.08 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.30 × 0.25 × 0.10 mm
Data collection
Enraf–Nonius CAD-4 diffractometer
1586 measured reflections
1586 independent reflections
1254 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.000
1 standard reflections every 30 min intensity decay: none
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.044
wR(F 2) = 0.112
S = 1.05
1586 reflections
218 parameters
1 restraint
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.15 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.17 e Å−3
Data collection: CAD-4 Software (Enraf–Nonius, 1989 ▶); cell refinement: CAD-4 Software; data reduction: CAD-4 Software; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and Mercury (Macrae et al., 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: publCIF (Westrip, 2010 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812002206/qk2025sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812002206/qk2025Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O3—H1O3⋯O1i | 0.82 (5) | 1.83 (5) | 2.637 (4) | 169 (5) |
| O1—H1O1⋯O2 | 0.96 (7) | 1.94 (6) | 2.651 (4) | 129 (5) |
Symmetry code: (i) 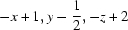 .
.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Dr Kim Dastlick from the Institute of Molecular Biosciences at The University of Queensland for performing optical rotations, and the Chemical Analysis Laboratories, Bulleen, Victoria, for performing high resolution-mass spectrometric analyses. This research was supported by the Centre for Phytochemistry and Pharmacology at Southern Cross University and the University of New South Wales. KB is grateful to the Australian Federal Government for an Australian Postgraduate Award and to Bioactive Exports Pty. Ltd for financial assistance.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
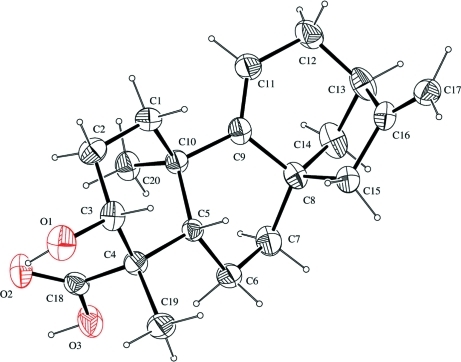
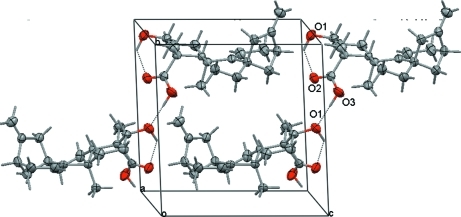
The title compound C20H28O3 [Fig. 1., systematic name (3R,4S,5S,8S,10R,13R)-3-hydroxykaura-9(11),16-dien-18-oic acid], a diterpene, was isolated during our investigation into the chemical composition and pharmacological activity of active components of Centipeda cunninghamii. The herb is native to Australia and New Zealand and has been utilized by the Aboriginals to treat infection (Campbell, 1973; Cribb, 1988; D'Amelio & Mirhom, 1998) and inflammation (Maiden, 1975; Webb, 1948). Compound (I) crystallizes in the monoclinic chiral space group P21. The carbon skeleton is composed of three six- and one five-membered rings in chair (ring A), twist-boat (ring B), half-chair (ring C) and envelope conformations (ring D). In the unit cell, two symmetry equivalent molecules make an intramolecular O—H···O bond between the 3-OH (O1) and the carbonyl oxygen (O2) and are linked by intermolecular O—H···O hydrogen bonds involving the carboxylic hydroxyl group (O3, donor) and the 3-OH group (O1, acceptor) into infinite chains extending parallel to the b axis (Fig. 2; Table 1).
The majority of the ent-kaurane diterpenes characteristically exhibit negative values for optical rotation with the exception of those that feature a double bond between C9 and C11. Piozzi and co-workers (Piozzi et al., 1972) have demonstrated that sequential catalytic hydrogenation of the exocyclic C16—C17 and the endocyclic C9—C11 double bonds in grandiflorenic acid [(4α)-kaura-9(11),16-dien-18-oic acid] transforms the optical rotation from +38 to +43° and subsequently to -80° in the saturated product. More recently Reynolds and co-workers (Reynolds et al., 1991) have analysed the solid state and solution characteristics of grandiflorenic acid, and have determined that the introduction of the C9—C11 double bond in grandiflorenic acid has a drastic effect on the molecular conformation and consequently on optical rotation, whereby the B ring adopts a boat conformation compared to the regular chair conformation in kaurenoic acid. In the case of compound (I) the observed rotation is [α]D22 + 30.8° (c 0.12, MeOH), which is in agreement with values for the methyl ester derivative of the 3S isomer, +15° (Bohlmann et al., 1982) and the closely related grandiflorenic acid +32.1° (Brieskorn & Pöhlmann, 1968) and + 46° (Reynolds et al., 1991) and establishes the 3R,4S,5S,8S,10R,13R absolute stereochemistry of compound (I). The 3S isomer of compound (I) has been obtained previously from Ichthyothere terminalis (Bohlmann et al., 1982) and Pseudognaphalium cheiranthifolium (Mendoza & Urzúa, 1998). The antibacterial activity of the 3S isomer has also been evaluated and is described in Mendoza et al. (1997).
Experimental
The whole, air-dried flowers of Centipeda cunninghamii (100 g) were extracted in 100% ethanol (1 L) overnight at ambient temperatures with stirring. The resulting extract was filtered and then partitioned with hexane (3 × 200 ml). The hexane soluble fraction (2.8 g, 2.8% yield w/w) was evaporated and then subjected to reverse phase preparative HPLC (Gilson preparative HPLC system; Phenomenex Luna C18 column, 5 µm, 50 mm × 21.2 mm; sample loading 50 - 100 mg/injection). The column was eluted using a stepwise gradient of H2O/CH3CN containing 0.05% CF3COOH (3:2 to 1:3 over 16.4 min; 1:3 isocratic for 3.6 min; then 1:3 to 1:9 over 1.0 min; then 1:9 isocratic for 7 minutes) at a flow rate of 15 ml/min. Crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction were obtained by slow evaporation of the H2O/CH3CN HPLC eluent of (I).
(3R,4S,5S,8S,10R,13R)- 3-Hydroxykaura-9(11),16-dien-18-oic acid (I): Colourless needles (ACN/H2O) (26.5 mg, 1.0% yield w/w, not optimized); [α]D22 + 30.8° (c 0.12, MeOH); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CD3OD): δ 5.26 (1H, t, J = 3.3 Hz, H-11), 4.89 (1H, d, J = 1.1 Hz, H-17a), 4.77 (1H, br s, H-17b), 3.17 (1H, dd, J = 4.4, 12.1 Hz, H-3), 2.74 (1H, br s, H-13), 2.61 (1H, br d, J = 14.8 Hz, H-15a), 2.44 - 2.40 (1H, m, H-12a), 2.41 - 2.35 (1H, m, H-6a), 2.29 - 2.16 (1H, m, H-2a), 2.20 - 2.16 (1H, m, H-15b), 2.04 (1H, m, H-1a), 1.99 - 1.95 (1H, m. H-7a), 1.99 - 1.95 (1H, m, H-12b), 1.93 – 1.85 (1H, m, H-6 b), 1.68 - 1.74 (1H, m, H-2 b), 1.65 – 1.62 (1H, m, H-5), 1.63 - 1.60 (1H, m, H-14a), 1.51 - 1.47 (1H, m, H-7 b), 1.51 - 1.47 (1H, m, H-14b), 1.38 - 1.32 (1H, m, H-1 b), 1.36 (3H, s, H-19), 1.10 (3H, s, H-20); Lit. (3S isomer as the methyl ester derivative, see Bohlmann et al., 1982); 13C NMR (126 MHz, CD3OD): δ 180.1 (C, C-18), 159.6 (C, C-16), 157.3 (C, C-9), 116.3 (CH, C-11), 106.2 (CH2, C-17), 79.4 (CH, C-3), 51.5 (CH2, C-15), 51.3 (C, C-4), 47.0 (CH, C-5), 46.2 (CH2, C-14), 43.6 (C, C-8), 42.8 (CH, C-13), 40.4 (CH2, C-1), 39.7 (C, C-10), 39.1 (CH2, C-12), 31.0 (CH2, C-7), 29.9 (CH2, C-2), 24.6 (CH3, C-19), 24.4 (CH3, C-20), 19.8 (CH2, C-6); (+)-LRAPCIMS m/z (rel. int.): 316 [M+H+, 0%], 299 (100), 271 (59), 253 (93), 225 (6); (+)-HRAPCIMS m/z (rel. int): 317.2109 calcd for C20H29O3, 317.2118 (Δ0.0009 a.m.u.).
Refinement
C-bonded H-atoms were positioned geometrically (C–H = 0.93–0.98 Å) and refined as riding with Uiso(H) = xUeq(C), where x = 1.5 for methyl and x = 1.2 for the rest. The two O-bonded H-atoms were fully refined. The absolute configuration was assigned by comparison of a similar moiety using NMR spectral data and optical rotation, see section Comment. No Friedel pairs were measured and the refined Flack absolute structure parameter, 1(2), was inconclusive.
Figures
Fig. 1.
View of (I) with atom numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids for non-H atoms are drawn at the 40% probability level.
Fig. 2.
Packing diagram of (I) viewed down the a axis depicting intra and inter molecular O—H···O hydrogen bonding.
Crystal data
| C20H28O3 | F(000) = 344 |
| Mr = 316.4 | Dx = 1.228 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2yb | Cell parameters from 11 reflections |
| a = 8.064 (2) Å | θ = 10–11° |
| b = 10.775 (3) Å | µ = 0.08 mm−1 |
| c = 10.462 (4) Å | T = 296 K |
| β = 109.70 (2)° | Block, colourless |
| V = 855.8 (5) Å3 | 0.30 × 0.25 × 0.10 mm |
| Z = 2 |
Data collection
| Enraf–Nonius CAD-4 diffractometer | Rint = 0.0000 |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 2.1° |
| graphite | h = −9→9 |
| ω–2θ scans | k = 0→12 |
| 1586 measured reflections | l = 0→12 |
| 1586 independent reflections | 1 standard reflections every 30 min |
| 1254 reflections with I > 2σ(I) | intensity decay: none |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.044 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.112 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0704P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.05 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 1586 reflections | Δρmax = 0.15 e Å−3 |
| 218 parameters | Δρmin = −0.17 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Absolute structure: deduced from optical rotation |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.3554 (4) | 0.4597 (3) | 0.9863 (3) | 0.0658 (8) | |
| O2 | 0.4220 (4) | 0.2189 (3) | 0.9850 (2) | 0.0620 (7) | |
| O3 | 0.5758 (4) | 0.1598 (3) | 0.8595 (3) | 0.0678 (9) | |
| C1 | 0.0447 (4) | 0.3543 (4) | 0.6459 (4) | 0.0521 (10) | |
| C2 | 0.1154 (5) | 0.3753 (4) | 0.7994 (4) | 0.0511 (9) | |
| C3 | 0.2956 (5) | 0.4335 (3) | 0.8438 (3) | 0.0473 (9) | |
| C4 | 0.4293 (4) | 0.3558 (3) | 0.8032 (3) | 0.0395 (8) | |
| C5 | 0.3551 (4) | 0.3369 (3) | 0.6461 (3) | 0.0359 (7) | |
| C6 | 0.4877 (5) | 0.2789 (4) | 0.5853 (3) | 0.0520 (9) | |
| C7 | 0.4047 (5) | 0.2222 (4) | 0.4458 (3) | 0.0572 (10) | |
| C8 | 0.2344 (4) | 0.2860 (4) | 0.3602 (3) | 0.0460 (8) | |
| C9 | 0.1005 (4) | 0.2857 (3) | 0.4348 (3) | 0.0435 (8) | |
| C10 | 0.1677 (4) | 0.2779 (3) | 0.5907 (3) | 0.0399 (8) | |
| C11 | −0.0703 (5) | 0.2924 (4) | 0.3625 (4) | 0.0587 (10) | |
| C12 | −0.1416 (5) | 0.3019 (4) | 0.2107 (4) | 0.0667 (12) | |
| C13 | 0.0059 (6) | 0.3158 (4) | 0.1511 (4) | 0.0609 (11) | |
| C14 | 0.1503 (6) | 0.2238 (4) | 0.2209 (4) | 0.0645 (11) | |
| C15 | 0.2579 (5) | 0.4187 (4) | 0.3156 (3) | 0.0499 (9) | |
| C16 | 0.0971 (5) | 0.4395 (4) | 0.1910 (3) | 0.0485 (9) | |
| C17 | 0.0429 (5) | 0.5449 (4) | 0.1297 (4) | 0.0567 (10) | |
| C18 | 0.4701 (4) | 0.2379 (3) | 0.8902 (3) | 0.0422 (8) | |
| C19 | 0.6049 (5) | 0.4288 (4) | 0.8399 (4) | 0.0578 (10) | |
| C20 | 0.1658 (5) | 0.1410 (4) | 0.6329 (4) | 0.0518 (9) | |
| H1A | 0.0241 | 0.4344 | 0.6009 | 0.062* | |
| H1B | −0.0679 | 0.3121 | 0.6225 | 0.062* | |
| H1O1 | 0.353 (7) | 0.381 (6) | 1.029 (6) | 0.11 (2)* | |
| H1O3 | 0.598 (6) | 0.104 (5) | 0.916 (5) | 0.070 (14)* | |
| H2A | 0.0352 | 0.4289 | 0.8251 | 0.061* | |
| H2B | 0.1212 | 0.2965 | 0.8455 | 0.061* | |
| H3A | 0.2844 | 0.5133 | 0.7966 | 0.057* | |
| H5 | 0.3378 | 0.4215 | 0.6096 | 0.043* | |
| H6A | 0.5700 | 0.3427 | 0.5799 | 0.062* | |
| H6B | 0.5545 | 0.2152 | 0.6467 | 0.062* | |
| H7A | 0.3802 | 0.1353 | 0.4561 | 0.069* | |
| H7B | 0.4886 | 0.2262 | 0.3977 | 0.069* | |
| H11 | −0.1504 | 0.2912 | 0.4089 | 0.070* | |
| H12A | −0.2197 | 0.3730 | 0.1847 | 0.080* | |
| H12B | −0.2097 | 0.2281 | 0.1736 | 0.080* | |
| H13 | −0.0373 | 0.3044 | 0.0524 | 0.073* | |
| H14A | 0.2340 | 0.2154 | 0.1732 | 0.077* | |
| H14B | 0.1024 | 0.1429 | 0.2294 | 0.077* | |
| H15A | 0.2618 | 0.4781 | 0.3863 | 0.060* | |
| H15B | 0.3652 | 0.4260 | 0.2937 | 0.060* | |
| H17A | −0.0600 | 0.5480 | 0.0549 | 0.068* | |
| H17B | 0.1071 | 0.6171 | 0.1610 | 0.068* | |
| H19A | 0.6417 | 0.4530 | 0.9336 | 0.087* | |
| H19B | 0.5881 | 0.5014 | 0.7839 | 0.087* | |
| H19C | 0.6936 | 0.3771 | 0.8250 | 0.087* | |
| H20A | 0.0491 | 0.1080 | 0.5929 | 0.078* | |
| H20B | 0.2006 | 0.1356 | 0.7300 | 0.078* | |
| H20C | 0.2464 | 0.0942 | 0.6021 | 0.078* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.094 (2) | 0.0543 (18) | 0.0541 (17) | −0.0171 (15) | 0.0310 (15) | −0.0191 (14) |
| O2 | 0.0852 (18) | 0.0558 (16) | 0.0539 (14) | 0.0077 (16) | 0.0353 (14) | 0.0151 (14) |
| O3 | 0.0799 (19) | 0.0664 (19) | 0.0635 (19) | 0.0311 (16) | 0.0324 (16) | 0.0300 (16) |
| C1 | 0.0394 (19) | 0.061 (2) | 0.054 (2) | 0.0037 (18) | 0.0125 (16) | 0.0050 (19) |
| C2 | 0.053 (2) | 0.046 (2) | 0.060 (2) | 0.0081 (18) | 0.0275 (18) | −0.0023 (18) |
| C3 | 0.067 (2) | 0.0321 (18) | 0.047 (2) | −0.0034 (17) | 0.0240 (17) | −0.0033 (16) |
| C4 | 0.0405 (18) | 0.0345 (18) | 0.0401 (18) | −0.0065 (15) | 0.0094 (14) | −0.0001 (15) |
| C5 | 0.0370 (16) | 0.0337 (16) | 0.0352 (16) | 0.0009 (14) | 0.0100 (13) | 0.0038 (14) |
| C6 | 0.0451 (18) | 0.066 (2) | 0.0468 (19) | 0.0127 (19) | 0.0179 (16) | 0.0072 (19) |
| C7 | 0.070 (2) | 0.056 (2) | 0.052 (2) | 0.020 (2) | 0.0293 (18) | 0.008 (2) |
| C8 | 0.055 (2) | 0.0439 (19) | 0.0368 (17) | 0.0057 (18) | 0.0120 (15) | 0.0002 (16) |
| C9 | 0.053 (2) | 0.0355 (16) | 0.0396 (17) | −0.0086 (17) | 0.0127 (15) | −0.0014 (15) |
| C10 | 0.0408 (18) | 0.0368 (18) | 0.0406 (18) | −0.0055 (16) | 0.0119 (15) | −0.0012 (15) |
| C11 | 0.052 (2) | 0.065 (2) | 0.051 (2) | −0.020 (2) | 0.0080 (18) | 0.004 (2) |
| C12 | 0.063 (2) | 0.070 (3) | 0.048 (2) | −0.025 (2) | −0.0063 (19) | 0.004 (2) |
| C13 | 0.085 (3) | 0.054 (3) | 0.0337 (18) | 0.001 (2) | 0.0073 (19) | −0.0051 (16) |
| C14 | 0.095 (3) | 0.047 (2) | 0.047 (2) | 0.007 (2) | 0.019 (2) | −0.0020 (19) |
| C15 | 0.052 (2) | 0.055 (2) | 0.0442 (19) | −0.0005 (18) | 0.0193 (16) | 0.0042 (18) |
| C16 | 0.059 (2) | 0.049 (2) | 0.0421 (19) | 0.0009 (18) | 0.0233 (16) | 0.0043 (17) |
| C17 | 0.049 (2) | 0.058 (2) | 0.065 (2) | 0.0036 (19) | 0.0203 (17) | 0.009 (2) |
| C18 | 0.0398 (17) | 0.0418 (18) | 0.0397 (17) | −0.0048 (16) | 0.0061 (15) | −0.0008 (16) |
| C19 | 0.052 (2) | 0.057 (2) | 0.058 (2) | −0.017 (2) | 0.0090 (18) | 0.0025 (19) |
| C20 | 0.064 (2) | 0.042 (2) | 0.046 (2) | −0.0102 (18) | 0.0138 (17) | −0.0012 (17) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C3 | 1.432 (4) | C8—C15 | 1.536 (5) |
| O1—H1O1 | 0.96 (7) | C8—C14 | 1.538 (5) |
| O2—C18 | 1.198 (4) | C9—C11 | 1.331 (5) |
| O3—C18 | 1.312 (4) | C9—C10 | 1.537 (4) |
| O3—H1O3 | 0.82 (5) | C10—C20 | 1.541 (5) |
| C1—C2 | 1.529 (5) | C11—C12 | 1.499 (5) |
| C1—C10 | 1.544 (5) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C1—H1A | 0.9700 | C12—C13 | 1.525 (6) |
| C1—H1B | 0.9700 | C12—H12A | 0.9700 |
| C2—C3 | 1.505 (5) | C12—H12B | 0.9700 |
| C2—H2A | 0.9700 | C13—C16 | 1.511 (6) |
| C2—H2B | 0.9700 | C13—C14 | 1.516 (6) |
| C3—C4 | 1.534 (5) | C13—H13 | 0.9800 |
| C3—H3A | 0.9800 | C14—H14A | 0.9700 |
| C4—C18 | 1.532 (5) | C14—H14B | 0.9700 |
| C4—C19 | 1.551 (5) | C15—C16 | 1.514 (5) |
| C4—C5 | 1.562 (4) | C15—H15A | 0.9700 |
| C5—C6 | 1.549 (5) | C15—H15B | 0.9700 |
| C5—C10 | 1.559 (4) | C16—C17 | 1.305 (6) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9800 | C17—H17A | 0.9300 |
| C6—C7 | 1.514 (5) | C17—H17B | 0.9300 |
| C6—H6A | 0.9700 | C19—H19A | 0.9600 |
| C6—H6B | 0.9700 | C19—H19B | 0.9600 |
| C7—C8 | 1.527 (5) | C19—H19C | 0.9600 |
| C7—H7A | 0.9700 | C20—H20A | 0.9600 |
| C7—H7B | 0.9700 | C20—H20B | 0.9600 |
| C8—C9 | 1.531 (5) | C20—H20C | 0.9600 |
| C3—O1—H1O1 | 105 (4) | C9—C10—C1 | 109.0 (3) |
| C18—O3—H1O3 | 107 (3) | C20—C10—C1 | 109.5 (3) |
| C2—C1—C10 | 114.4 (3) | C9—C10—C5 | 108.8 (2) |
| C2—C1—H1A | 108.7 | C20—C10—C5 | 112.7 (3) |
| C10—C1—H1A | 108.7 | C1—C10—C5 | 107.9 (3) |
| C2—C1—H1B | 108.7 | C9—C11—C12 | 124.1 (4) |
| C10—C1—H1B | 108.7 | C9—C11—H11 | 118.0 |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 107.6 | C12—C11—H11 | 118.0 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 111.4 (3) | C11—C12—C13 | 111.5 (3) |
| C3—C2—H2A | 109.3 | C11—C12—H12A | 109.3 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 109.3 | C13—C12—H12A | 109.3 |
| C3—C2—H2B | 109.3 | C11—C12—H12B | 109.3 |
| C1—C2—H2B | 109.3 | C13—C12—H12B | 109.3 |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 108.0 | H12A—C12—H12B | 108.0 |
| O1—C3—C2 | 110.8 (3) | C16—C13—C14 | 102.7 (3) |
| O1—C3—C4 | 112.0 (3) | C16—C13—C12 | 110.4 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 112.5 (3) | C14—C13—C12 | 108.5 (3) |
| O1—C3—H3A | 107.1 | C16—C13—H13 | 111.6 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 107.1 | C14—C13—H13 | 111.6 |
| C4—C3—H3A | 107.1 | C12—C13—H13 | 111.6 |
| C18—C4—C3 | 108.6 (3) | C13—C14—C8 | 101.2 (3) |
| C18—C4—C19 | 106.2 (3) | C13—C14—H14A | 111.5 |
| C3—C4—C19 | 108.8 (3) | C8—C14—H14A | 111.5 |
| C18—C4—C5 | 116.5 (3) | C13—C14—H14B | 111.5 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 107.9 (3) | C8—C14—H14B | 111.5 |
| C19—C4—C5 | 108.7 (3) | H14A—C14—H14B | 109.4 |
| C6—C5—C10 | 113.6 (3) | C16—C15—C8 | 104.0 (3) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 114.4 (3) | C16—C15—H15A | 111.0 |
| C10—C5—C4 | 115.1 (2) | C8—C15—H15A | 111.0 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 104.0 | C16—C15—H15B | 111.0 |
| C10—C5—H5 | 104.0 | C8—C15—H15B | 111.0 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 104.0 | H15A—C15—H15B | 109.0 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 114.6 (3) | C17—C16—C13 | 125.5 (3) |
| C7—C6—H6A | 108.6 | C17—C16—C15 | 126.8 (4) |
| C5—C6—H6A | 108.6 | C13—C16—C15 | 107.7 (3) |
| C7—C6—H6B | 108.6 | C16—C17—H17A | 120.0 |
| C5—C6—H6B | 108.6 | C16—C17—H17B | 120.0 |
| H6A—C6—H6B | 107.6 | H17A—C17—H17B | 120.0 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 113.7 (3) | O2—C18—O3 | 120.7 (3) |
| C6—C7—H7A | 108.8 | O2—C18—C4 | 124.7 (3) |
| C8—C7—H7A | 108.8 | O3—C18—C4 | 114.4 (3) |
| C6—C7—H7B | 108.8 | C4—C19—H19A | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7B | 108.8 | C4—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| H7A—C7—H7B | 107.7 | H19A—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 110.5 (3) | C4—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—C15 | 114.8 (3) | H19A—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—C15 | 109.7 (3) | H19B—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—C14 | 112.5 (3) | C10—C20—H20A | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—C14 | 108.7 (3) | C10—C20—H20B | 109.5 |
| C15—C8—C14 | 100.2 (3) | H20A—C20—H20B | 109.5 |
| C11—C9—C8 | 118.8 (3) | C10—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| C11—C9—C10 | 122.3 (3) | H20A—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—C10 | 118.9 (3) | H20B—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| C9—C10—C20 | 108.8 (3) | ||
| C10—C1—C2—C3 | 54.8 (4) | C2—C1—C10—C20 | 72.3 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—O1 | 176.4 (3) | C2—C1—C10—C5 | −50.7 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −57.4 (4) | C6—C5—C10—C9 | −55.0 (4) |
| O1—C3—C4—C18 | 55.0 (3) | C4—C5—C10—C9 | 170.5 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C18 | −70.5 (3) | C6—C5—C10—C20 | 65.7 (4) |
| O1—C3—C4—C19 | −60.1 (4) | C4—C5—C10—C20 | −68.7 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C19 | 174.4 (3) | C6—C5—C10—C1 | −173.2 (3) |
| O1—C3—C4—C5 | −177.9 (3) | C4—C5—C10—C1 | 52.3 (4) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 56.6 (3) | C8—C9—C11—C12 | −0.8 (6) |
| C18—C4—C5—C6 | −67.3 (4) | C10—C9—C11—C12 | 179.1 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 170.3 (3) | C9—C11—C12—C13 | −5.6 (6) |
| C19—C4—C5—C6 | 52.5 (4) | C11—C12—C13—C16 | −67.3 (5) |
| C18—C4—C5—C10 | 66.8 (4) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 44.5 (5) |
| C3—C4—C5—C10 | −55.6 (3) | C16—C13—C14—C8 | 42.4 (4) |
| C19—C4—C5—C10 | −173.4 (3) | C12—C13—C14—C8 | −74.4 (4) |
| C10—C5—C6—C7 | 26.2 (5) | C7—C8—C14—C13 | −171.1 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 161.1 (3) | C9—C8—C14—C13 | 66.3 (4) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 30.5 (5) | C15—C8—C14—C13 | −48.7 (4) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | −56.6 (4) | C7—C8—C15—C16 | 156.9 (3) |
| C6—C7—C8—C15 | 68.0 (4) | C9—C8—C15—C16 | −78.1 (3) |
| C6—C7—C8—C14 | −178.2 (3) | C14—C8—C15—C16 | 36.2 (3) |
| C7—C8—C9—C11 | −154.9 (4) | C14—C13—C16—C17 | 161.6 (4) |
| C15—C8—C9—C11 | 77.6 (4) | C12—C13—C16—C17 | −82.9 (5) |
| C14—C8—C9—C11 | −31.1 (5) | C14—C13—C16—C15 | −19.9 (4) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | 25.3 (4) | C12—C13—C16—C15 | 95.6 (4) |
| C15—C8—C9—C10 | −102.2 (3) | C8—C15—C16—C17 | 167.9 (3) |
| C14—C8—C9—C10 | 149.1 (3) | C8—C15—C16—C13 | −10.5 (4) |
| C11—C9—C10—C20 | 85.3 (5) | C3—C4—C18—O2 | −8.6 (4) |
| C8—C9—C10—C20 | −94.8 (4) | C19—C4—C18—O2 | 108.2 (4) |
| C11—C9—C10—C1 | −34.0 (5) | C5—C4—C18—O2 | −130.6 (4) |
| C8—C9—C10—C1 | 145.8 (3) | C3—C4—C18—O3 | 176.3 (3) |
| C11—C9—C10—C5 | −151.5 (4) | C19—C4—C18—O3 | −66.9 (4) |
| C8—C9—C10—C5 | 28.3 (4) | C5—C4—C18—O3 | 54.3 (4) |
| C2—C1—C10—C9 | −168.8 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O3—H1O3···O1i | 0.82 (5) | 1.83 (5) | 2.637 (4) | 169 (5) |
| O1—H1O1···O2 | 0.96 (7) | 1.94 (6) | 2.651 (4) | 129 (5) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: QK2025).
References
- Bohlmann, F., Jakupovic, J., Schuster, A., King, R. M. & Robinson, H. (1982). Phytochemistry, 21, 2317–2327.
- Brieskorn, C. H. & Pöhlmann, E. (1968). Tetrahedron Lett. 54, 5661–5664.
- Campbell, A. (1973). Aust. J. Pharm. 54, 894–900.
- Cribb, A. B. (1988). Wild Medicines in Australia Collins: Sydney.
- D’Amelio, F. S. & Mirhom, Y. W. (1998). World Patent WO9838971.
- Enraf–Nonius (1989). CAD-4 Software Enraf–Nonius, Delft, The Netherlands.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Maiden, J. H. (1975). The Useful Native Plants of Australia (including Tasmania) Melbourne: Compendium; Sydney: Turner and Henderson.
- Mendoza, L. & Urzúa, A. (1998). Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 26, 469–471.
- Mendoza, L., Wilkens, M. & Urzúa, A. (1997). J. Ethnopharmacol. 58, 85–88. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Piozzi, F., Passannanti, S., Marino, M. L. & Spiro, V. (1972). Can. J. Chem. 62, 109–112.
- Reynolds, W. F., Lough, A. J., Sawyer, J. F., Enriquez, R. G., Ortiz, B. & Walls, F. (1991). Acta Cryst. C47, 973–977.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Webb, L. J. (1948). Guide to Medicinal and Poisonous Plants of Queensland Melbourne: Council for Scientific and Industrial Research.
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812002206/qk2025sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812002206/qk2025Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report