Abstract
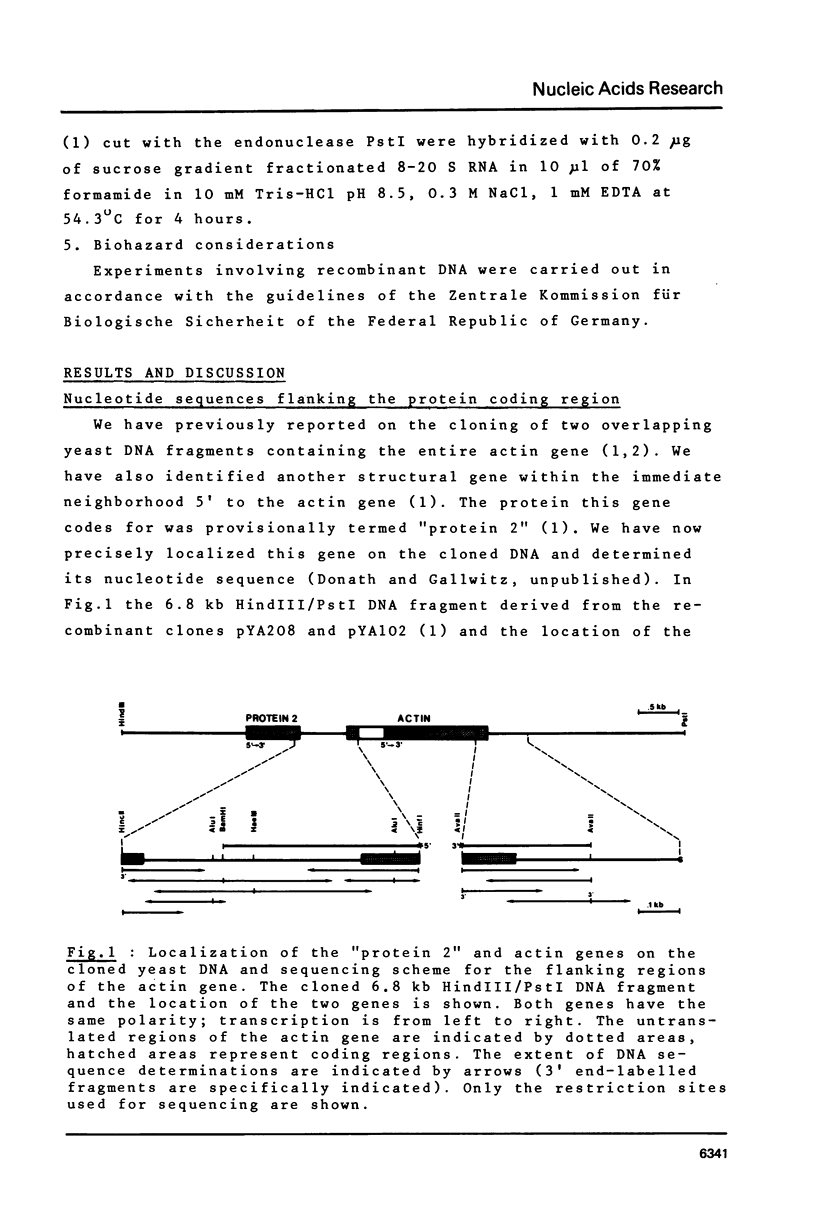
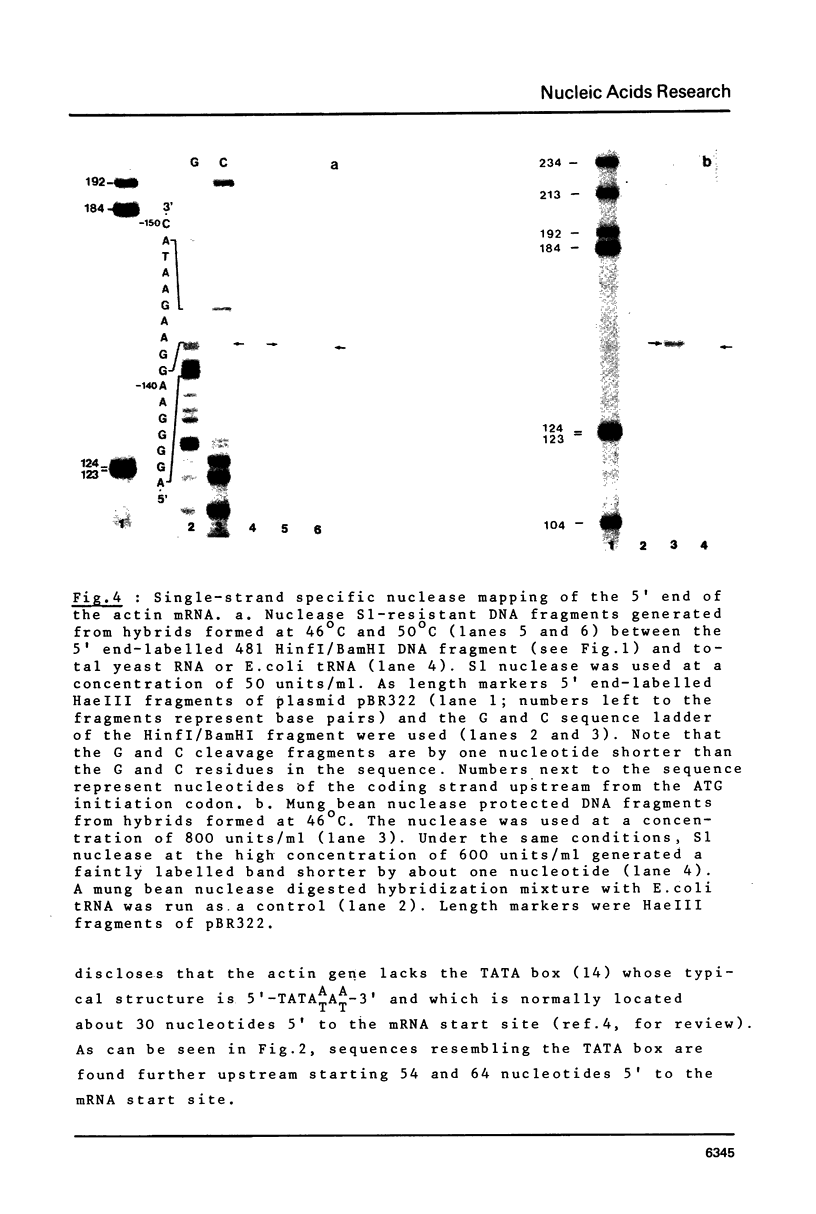
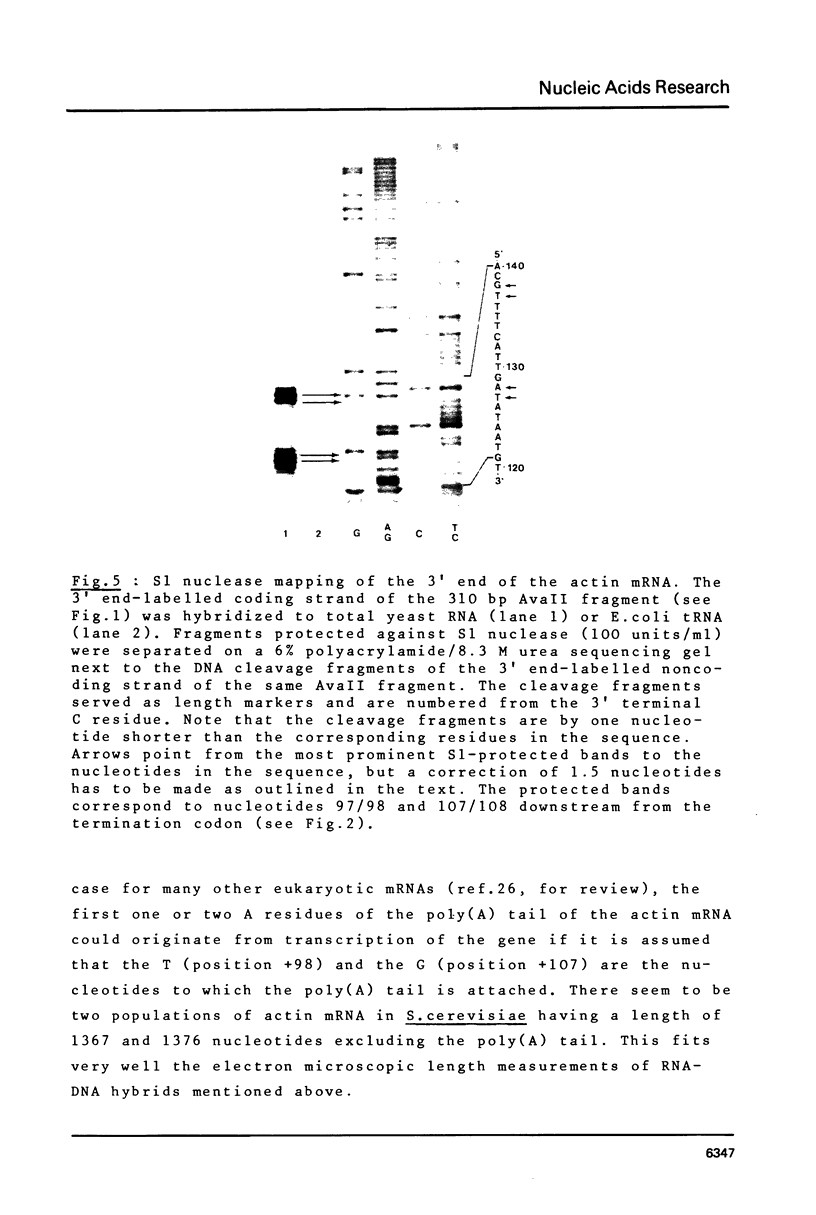
The 5' and 3' flanking regions of the yeast actin gene have been sequenced and the ends of the actin mRNA were determined by the single-strand nuclease mapping procedure. The mRNA starts with a pyrimidine residue 141 (or 140) nucleotides upstream from the initiation codon. The actin gene lacks a typical "TATA" box 30 base pairs upstream from the mRNA start site but it contains a region homologous to the canonical sequence 5'-GGCTCAATCT-3' which is found in several eukaryotic genes 70 to 80 bp upstream from the mRNA cap site. Judging from the S1 nuclease mapping, there are two populations of actin mRNA terminating 98 and 107 nucleotides downstream from the stop codon. The 3' termini are preceded by three AATAAA sequences found in most eukaryotic polyadenylated mRNAs.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker C. C., Herisse J., Courtois G., Galibert F., Ziff E. Messenger RNA for the Ad2 DNA binding protein: DNA sequences encoding the first leader and heterogenity at the mRNA 5' end. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):569–580. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90073-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., O'Hare K., Breathnach R., Chambon P. The ovalbumin gene-sequence of putative control regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):127–142. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Kloet S. R., Andrean B. A. Methylated nucleosides in polyadenylate-containing yeast messenger ribonucleic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 2;425(4):401–408. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dierks P., van Ooyen A., Mantei N., Weissmann C. DNA sequences preceding the rabbit beta-globin gene are required for formation in mouse L cells of beta-globin RNA with the correct 5' terminus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1411–1415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faye G., Leung D. W., Tatchell K., Hall B. D., Smith M. Deletion mapping of sequences essential for in vivo transcription of the iso-1-cytochrome c gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2258–2262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M., Shenk T. The sequence 5'-AAUAAA-3'forms parts of the recognition site for polyadenylation of late SV40 mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90521-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyrberg E. A., Bond B. J., Hershey N. D., Mixter K. S., Davidson N. The actin genes of Drosophila: protein coding regions are highly conserved but intron positions are not. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):107–116. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90506-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Seidel R. Molecular cloning of the actin gene from yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 11;8(5):1043–1059. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.5.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Sures I. Structure of a split yeast gene: complete nucleotide sequence of the actin gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2546–2550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon F., O'Hare K., Perrin F., LePennec J. P., Benoist C., Cochet M., Breathnach R., Royal A., Garapin A., Cami B. Organisation and sequences at the 5' end of a cloned complete ovalbumin gene. Nature. 1979 Mar 29;278(5703):428–434. doi: 10.1038/278428a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y., Sambrook J. F., Frisque R. J. Expression of early genes of origin-defective mutants of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3898–3902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Roeder R. G. Definition of a novel promoter for the major adenovirus-associated virus mRNA. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):231–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90171-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Identification of regulatory sequences in the prelude sequences of an H2A histone gene by the study of specific deletion mutants in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1432–1436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Spacer DNA sequences upstream of the T-A-T-A-A-A-T-A sequence are essential for promotion of H2A histone gene transcription in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7102–7106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld G. C., Shewmaker C. K., Jat P., Flavell R. A. Localization of DNA sequences necessary for transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in vitro. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):215–226. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90246-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haegeman G., Fiers W. Localization of the 5' terminus of late SV40 mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jul;5(7):2359–2371. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.7.2359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamlyn P. H., Browniee G. G., Cheng C. C., Gait M. J., Milstein C. Complete sequence of constant and 3' noncoding regions of an immunoglobulin mRNA using the dideoxynucleotide method of RNA sequencing. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1067–1075. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90290-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heindell H. C., Liu A., Paddock G. V., Studnicka G. M., Salser W. A. The primary sequence of rabbit alpha-globin mRNA. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):43–54. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90081-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C., Irminger J. C., Bucher P., Birnstiel M. L. Sea urchin histone mRNA termini are located in gene regions downstream from putative regulatory sequences. Nature. 1980 May 15;285(5761):147–151. doi: 10.1038/285147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. P., Holland M. J. Structural comparison of two nontandemly repeated yeast glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase genes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2596–2605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. P., Holland M. J. The primary structure of a glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9839–9845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland M. J., Holland J. P., Thill G. P., Jackson K. A. The primary structures of two yeast enolase genes. Homology between the 5' noncoding flanking regions of yeast enolase and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase genes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 10;256(3):1385–1395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D. J., Chambon P. The SV40 early region TATA box is required for accurate in vitro initiation of transcription. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):310–315. doi: 10.1038/290310a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery D. L., Hall B. D., Gillam S., Smith M. Identification and isolation of the yeast cytochrome c gene. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):673–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90250-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng R., Abelson J. Isolation and sequence of the gene for actin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3912–3916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sripati C. E., Groner Y., Warner J. R. Methylated, blocked 5' termini of yeast mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 25;251(10):2898–2904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Deletion mapping a eukaryotic promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4461–4465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]