Abstract
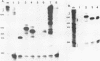
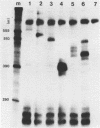
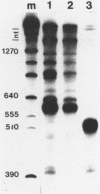
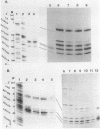
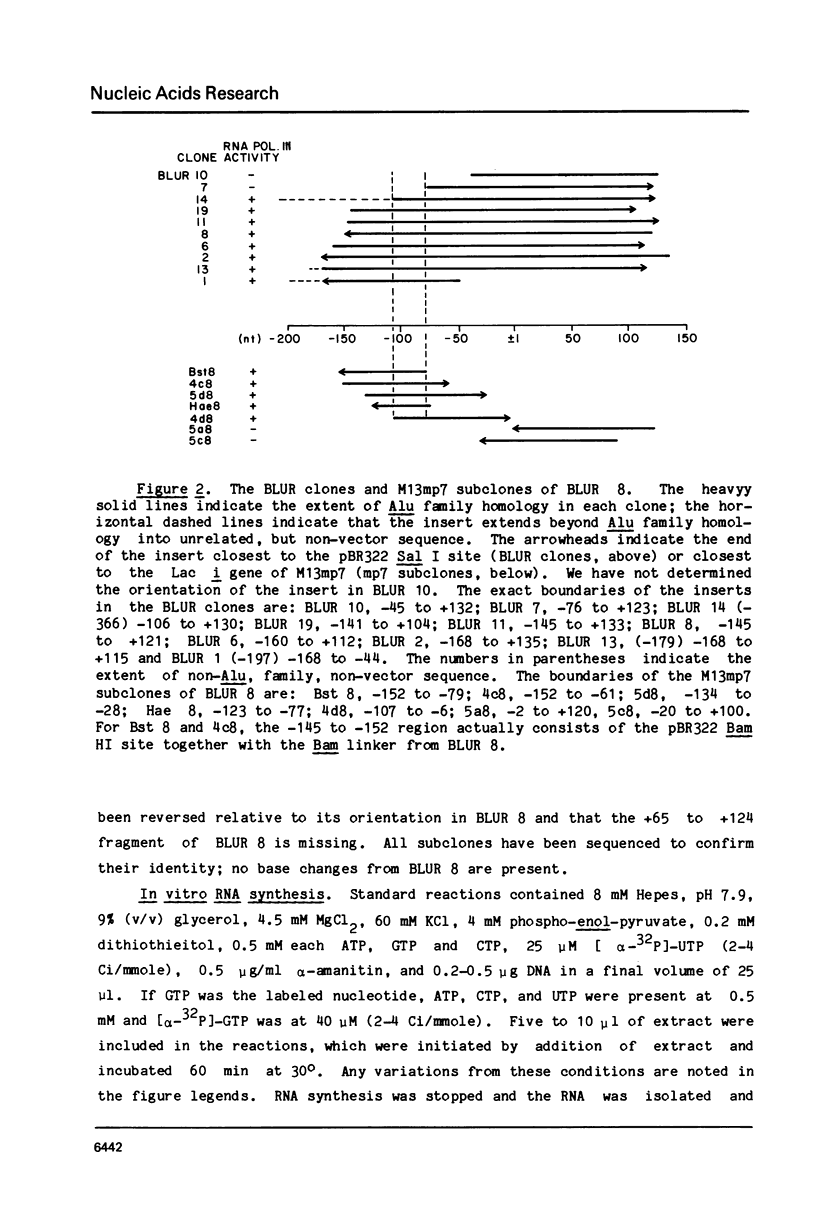
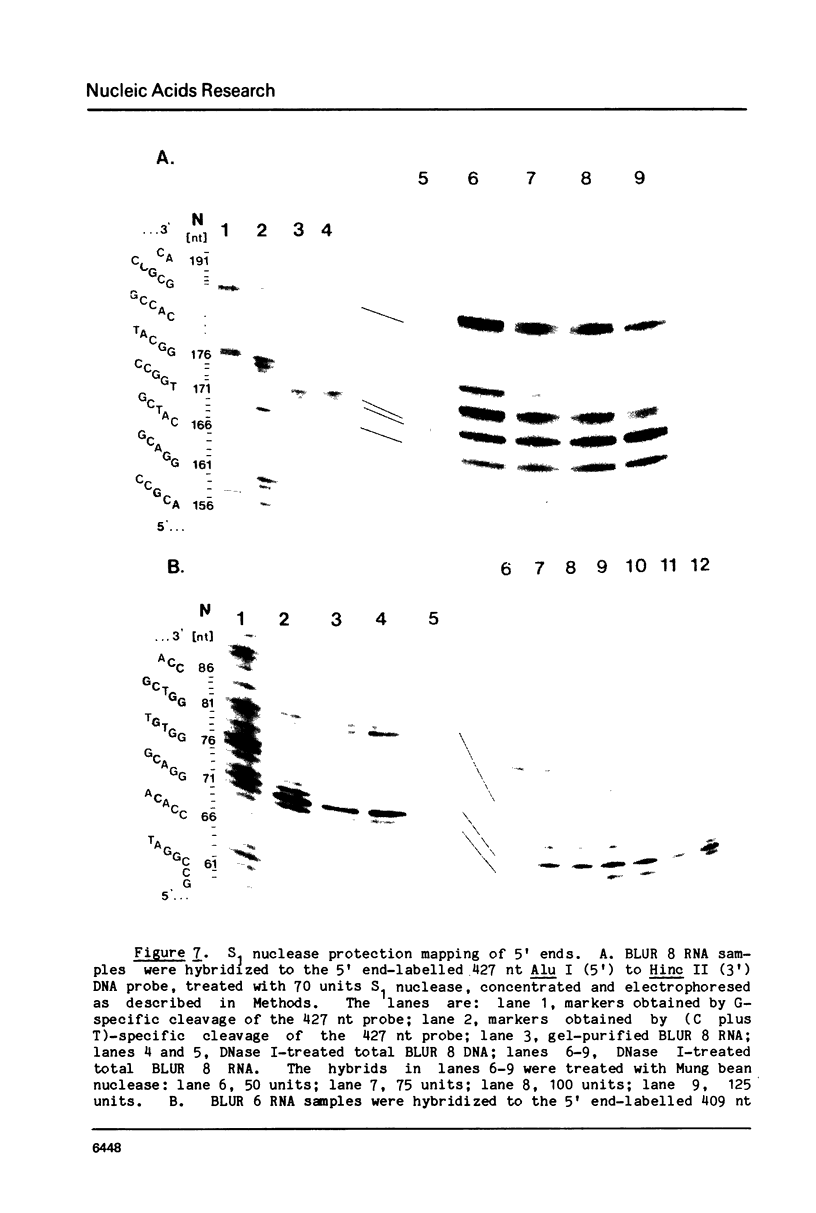
A series of clones that contain human Alu family elements are actively transcribed in soluble in vitro RNA polymerase III systems. The 5' ends of the in vitro transcripts are located about 170 nucleotides upstream of the eponymous Alu I site of the repeat, while a region associated with specifying of the initiation site for in vitro transcription lies in the region between 79 and 106 nucleotides upstream of the central Alu site. Thus, the RNA polymerase III transcription unit defined by the human Alu family is similar to other RNA polymerase III transcription units in possessing an internal region that is required for active transcription in vitro.
Full text
PDF















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baralle F. E., Shoulders C. C., Goodbourn S., Jeffreys A., Proudfoot N. J. The 5' flanking region of human epsilon-globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Oct 10;8(19):4393–4404. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.19.4393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Pictet R., Rutter W. J. Analysis of the regions flanking the human insulin gene and sequence of an Alu family member. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 25;8(18):4091–4109. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.18.4091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bina-Stein M., Thoren M., Salzman N., Thomspon J. A. Rapid sequence determination of late simian virus 40 16S mRNA leader by using inhibitors of reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):731–735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. Nucleotide sequences in Xenopus 5S DNA required for transcription termination. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90522-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Sakonju S., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: II. The 3' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coggins L. W., Grindlay G. J., Vass J. K., Slater A. A., Montague P., Stinson M. A., Paul J. Repetitive DNA sequences near three human beta-type globin genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 11;8(15):3319–3333. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.15.3319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P. L., Schmid C. W. An electron microscope study of the DNA sequence organization of the human genome. J Mol Biol. 1976 Sep 25;106(3):773–790. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90264-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C. H., Jagadeeswaran P., Wang R. R., Weissman S. M. Structural analysis of templates and RNA polymerase III transcripts of Alu family sequences interspersed among the human beta-like globin genes. Gene. 1981 Mar;13(2):185–196. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C., Biro P. A., Choudary P. V., Elder J. T., Wang R. R., Forget B. G., de Riel J. K., Weissman S. M. RNA polymerase III transcriptional units are interspersed among human non-alpha-globin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5095–5099. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. T., Pan J., Duncan C. H., Weissman S. M. Transcriptional analysis of interspersed repetitive polymerase III transcription units in human DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 11;9(5):1171–1189. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.5.1171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowlkes D. M., Shenk T. Transcriptional control regions of the adenovirus VAI RNA gene. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90351-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrman S. A., Van Beveren C., Verma I. M. Identification of a RNA polymerase II initiation site in the long terminal repeat of Moloney murine leukemia viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5411–5415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilfoyle R., Weinmann R. Control region for adenovirus VA RNA transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3378–3382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstetter H., Kressman A., Birnstiel M. L. A split promoter for a eucaryotic tRNA gene. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):573–585. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90348-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houck C. M., Rinehart F. P., Schmid C. W. A ubiquitous family of repeated DNA sequences in the human genome. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 15;132(3):289–306. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90261-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W. R., Toomey T. P., Leinwand L., Duncan C. H., Biro P. A., Choudary P. V., Weissman S. M., Rubin C. M., Houck C. M., Deininger P. L. Ubiquitous, interspersed repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1398–1402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp G., Beckmann J. S., Johnson P. F., Fuhrman S. A., Abelson J. Transcription and processing of intervening sequences in yeast tRNA genes. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):221–236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90109-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koski R. A., Clarkson S. G., Kurjan J., Hall B. D., Smith M. Mutations of the yeast SUP4 tRNATyr locus: transcription of the mutant genes in vitro. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):415–425. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90352-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krayev A. S., Kramerov D. A., Skryabin K. G., Ryskov A. P., Bayev A. A., Georgiev G. P. The nucleotide sequence of the ubiquitous repetitive DNA sequence B1 complementary to the most abundant class of mouse fold-back RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 25;8(6):1201–1215. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.6.1201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan J., Elder J. T., Duncan C. H., Weissman S. M. Structural analysis of interspersed repetitive polymerase III transcription units in human DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 11;9(5):1151–1170. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Brown D. D. A specific transcription factor that can bind either the 5S RNA gene or 5S RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4170–4174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichel R., Benecke B. J. Reinitiation of synthesis of small cytoplasmic RNA species K and L in isolated HeLa cell nuclei in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 25;8(2):225–234. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.2.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. M., Houck C. M., Deininger P. L., Friedmann T., Schmid C. W. Partial nucleotide sequence of the 300-nucleotide interspersed repeated human DNA sequences. Nature. 1980 Mar 27;284(5754):372–374. doi: 10.1038/284372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: I. The 5' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J., Matsui T., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors are required for the accurate transcription of purified genes by RNA polymerase III. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11986–11991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague K. U., Larson D., Morton D. 5' flanking sequence signals are required for activity of silkworm alanine tRNA genes in homologous in vitro transcription systems. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telford J. L., Kressmann A., Koski R. A., Grosschedl R., Müller F., Clarkson S. G., Birnstiel M. L. Delimitation of a promoter for RNA polymerase III by means of a functional test. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2590–2594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thimmappaya B., Jones N., Shenk T. A mutation which alters initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase III on the Ad5 chromosome. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):947–954. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90207-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil P. A., Luse D. S., Segall J., Roeder R. G. Selective and accurate initiation of transcription at the Ad2 major late promotor in a soluble system dependent on purified RNA polymerase II and DNA. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):469–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M. An abundant cytoplasmic 7S RNA is complementary to the dominant interspersed middle repetitive DNA sequence family in the human genome. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):209–218. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]