Abstract
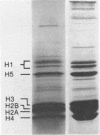
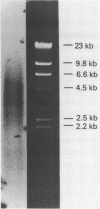
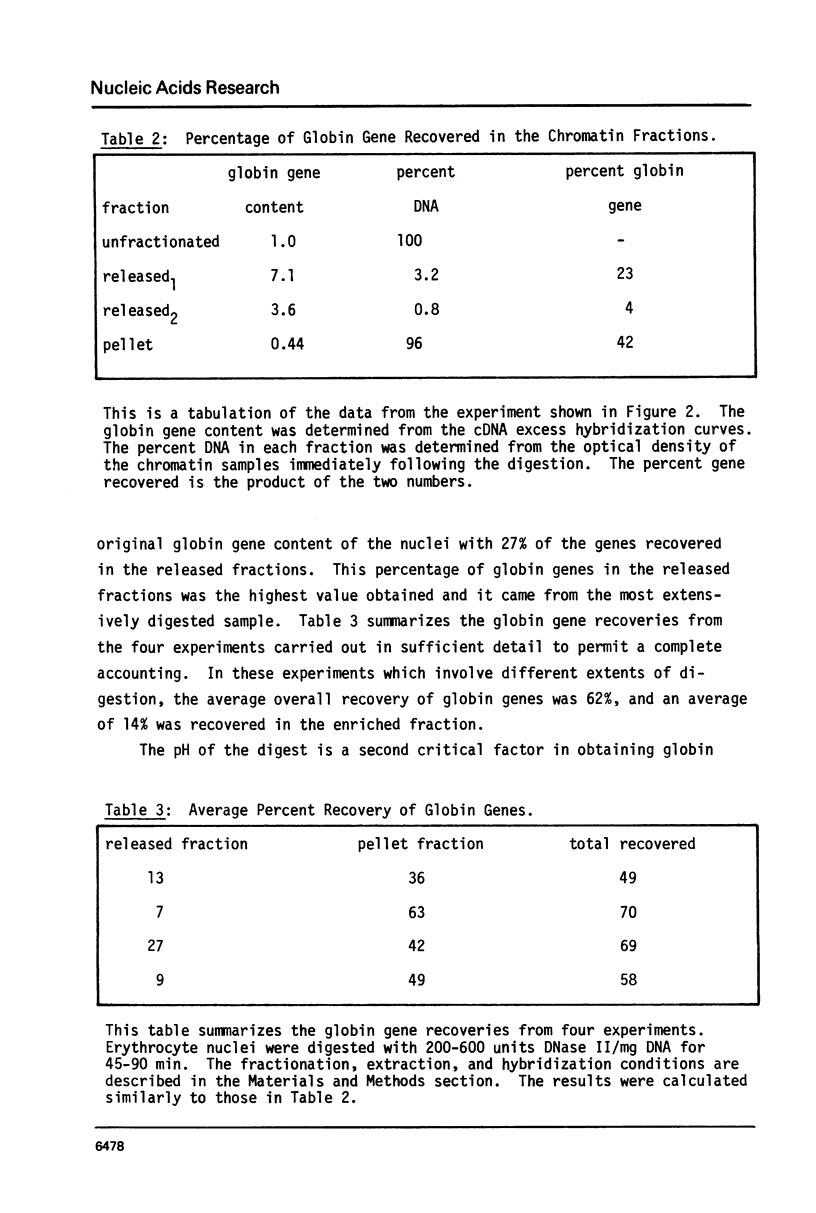
Mild digestion of chicken erythrocyte nuclei with deoxyribonuclease II results in the release of a chromatin fraction which is 4- to 13-fold enriched for the globin coding sequences when compared to total chicken DNA. The remaining nuclear pellet is depleted in these sequences. A maximum of 25% of the globin genes have been recovered in the released fraction. The addition of 5 mM sodium butyrate to the digestion buffer is required to obtain reproducible globin gene enrichment. The released fraction contains equimolar amounts of the four core histones and a subset of the nonhistone chromosomal proteins. The globin genes are released as large chromatin fragments which exceed the 1.6 kilobase size of the transcribed portion of the gene.
Full text
PDF





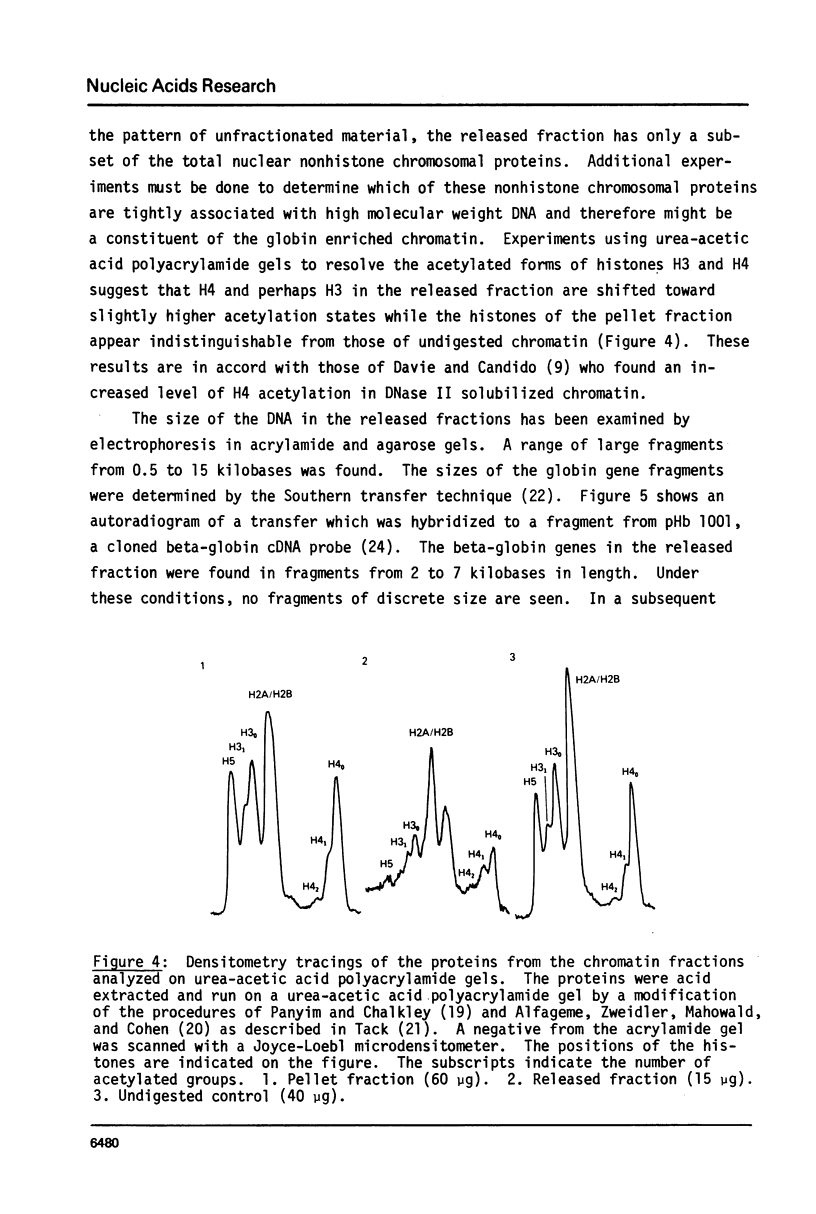





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albanese I., Weintraub H. Electrophoretic separation of a class of nucleosomes enriched in HMG 14 and 17 and actively transcribed globin genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jun 25;8(12):2787–2805. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.12.2787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alfageme C. R., Zweidler A., Mahowald A., Cohen L. H. Histones of Drosophila embryos. Electrophoretic isolation and structural studies. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 25;249(12):3729–3736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellard M., Gannon F., Chambon P. Nucleosome structure III: the structure and transcriptional activity of the chromatin containing the ovalbumin and globin genes in chick oviduct nuclei. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):779–791. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom K. S., Anderson J. N. Fractionation of hen oviduct chromatin into transcriptionally active and inactive regions after selective micrococcal nuclease digestion. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90090-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boffa L. C., Vidali G., Mann R. S., Allfrey V. G. Suppression of histone deacetylation in vivo and in vitro by sodium butyrate. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 25;253(10):3364–3366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Candido E. P., Reeves R., Davie J. R. Sodium butyrate inhibits histone deacetylation in cultured cells. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90305-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cousens L. S., Gallwitz D., Alberts B. M. Different accessibilities in chromatin to histone acetylase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 10;254(5):1716–1723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davie J. R., Candido E. P. Acetylated histone H4 is preferentially associated with template-active chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3574–3577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgieva E. I., Pashev I. G., Tsanev R. G. Distribution of high mobility group and other acid-soluble proteins in fractionated chromatin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jan 29;652(1):240–244. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(81)90228-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginder G. D., Wood W. I., Felsenfeld G. Isolation and characterization of recombinant clones containing the chicken adult beta-globin gene. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8099–8102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesfeld J. M., Butler P. J. Structure of transcriptionally-active chromatin subunits. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Sep;4(9):3155–3173. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.9.3155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesfeld J. M., Garrard W. T., Bagi G., Wilson R. F., Bonner J. Partial purification of the template-active fraction of chromatin: a preliminary report. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2193–2197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesfeld J. M., Murphy R. F., Bonner J. Structure of transcriptionally active chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4404–4408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesfeld J. M., Partington G. A. Distribution of messenger RNA-coding sequences in fractionated chromatin. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):953–962. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90160-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould H. J., Hamlyn P. H. The molecular weight of rabbit globin messenger RNA's. FEBS Lett. 1973 Mar 15;30(3):301–304. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80674-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrick D., Tolstoshev P., Randlett D. Enrichment for the globin coding region in a chromatin fraction from chick reticulocytes by endonuclease digestion. Gene. 1977;2(3-4):147–158. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(77)90014-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy E., Axel R. Analysis of DNA of isolated chromatin subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3978–3982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau A. F., Ruddon R. W., Collett M. S., Faras A. J. Distribution of the globin gene in active and inactive chromatin fractions from Friend erythroleukemia cells. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Feb;111(2):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90170-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau A. F., Ruddon R. W. Proteins of transcriptionally active and inactive chromatin from Friend erythroleukemia cells. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Jun;107(1):35–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90383-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy-Wilson B., Gjerset R. A., McCarthy B. J. Acetylation and phosphorylation of Drosophila histones. Distribution of acetate and phosphate groups in fractionated chromatin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 2;475(1):168–175. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(77)90351-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longacre S. S., Rutter W. J. Isolation of chicken hemoglobin mRNA and synthesis of complementary DNA. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2742–2752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D., Oudet P., Chambon P. Structure of transcribing chromatin. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1980;24:1–55. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60670-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyim S., Chalkley R. High resolution acrylamide gel electrophoresis of histones. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Mar;130(1):337–346. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry M., Chalkley R. The effect of histone hyperacetylation on the nuclease sensitivity and the solubility of chromatin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3313–3318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry M., Nelson D., Moore M., Chalkley R. Histone deacetylation in nuclei isolated from hepatoma tissue culture cells. Inhibition by sodium butyrate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 27;561(2):517–525. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(79)90159-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandeen G., Wood W. I., Felsenfeld G. The interaction of high mobility proteins HMG14 and 17 with nucleosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 11;8(17):3757–3778. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.17.3757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealy L., Chalkley R. The effect of sodium butyrate on histone modification. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):115–121. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Camerini-Otero R. D., Felsenfeld G. Chromatin structure as probed by nucleases and proteases: evidence for the central role of histones H3 and H4. Cell. 1976 Sep;9(1):179–193. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalder J., Larsen A., Engel J. D., Dolan M., Groudine M., Weintraub H. Tissue-specific DNA cleavages in the globin chromatin domain introduced by DNAase I. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):451–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90631-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt V. M. Purification and further properties of single-strand-specific nuclease from Aspergillus oryzae. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Feb 15;33(1):192–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02669.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Dube S. K., Bonner J. Localization of the globin gene in the template active fraction of chromatin of Friend leukemia cells. Science. 1977 Dec 16;198(4322):1166–1168. doi: 10.1126/science.270812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Groudine M. Chromosomal subunits in active genes have an altered conformation. Science. 1976 Sep 3;193(4256):848–856. doi: 10.1126/science.948749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Van Lente F. Dissection of chromosome structure with trypsin and nucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4249–4253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbrod S., Weintraub H. Isolation of actively transcribed nucleosomes using immobilized HMG 14 and 17 and an analysis of alpha-globin chromatin. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):391–400. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90134-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M., Felsenfeld G. Analysis of in vitro transcription of duck reticulocyte chromatin using mercury-substituted ribonucleoside triphosphates. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 15;16(23):5135–5145. doi: 10.1021/bi00642a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]