Abstract
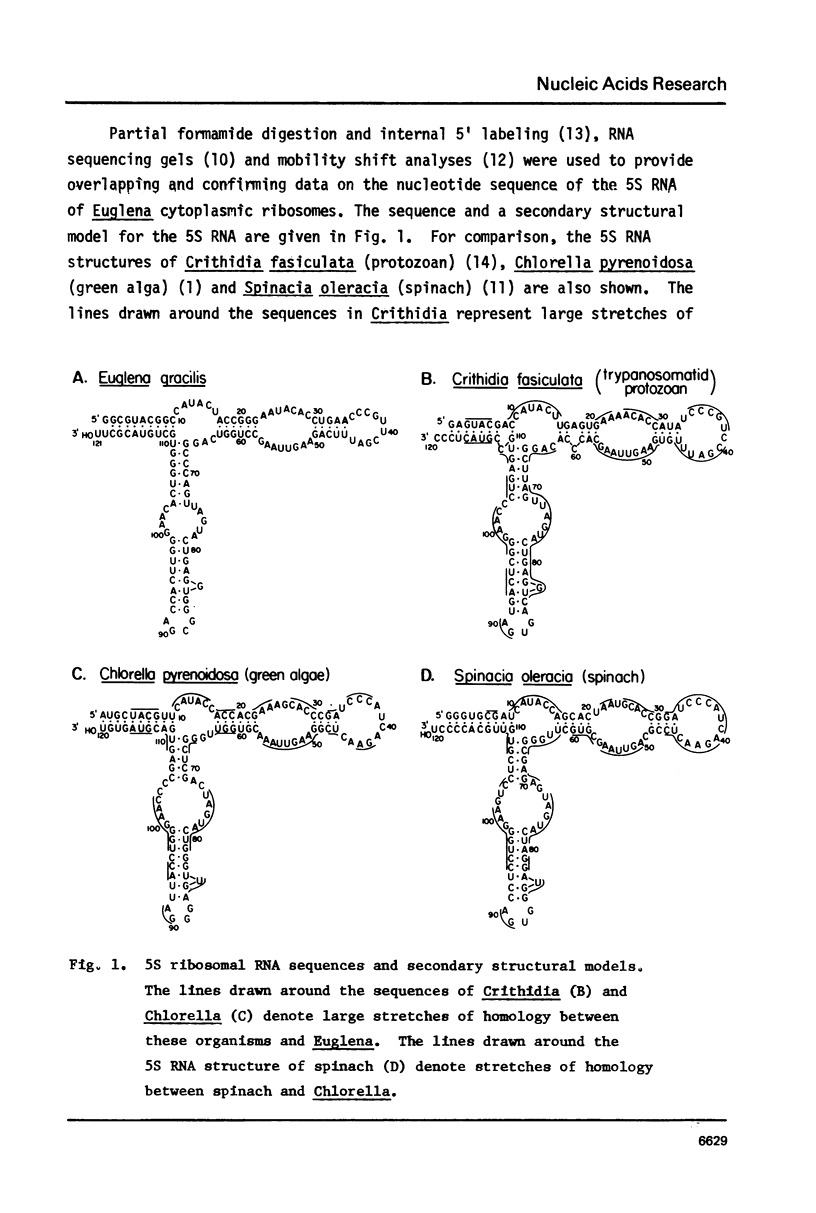
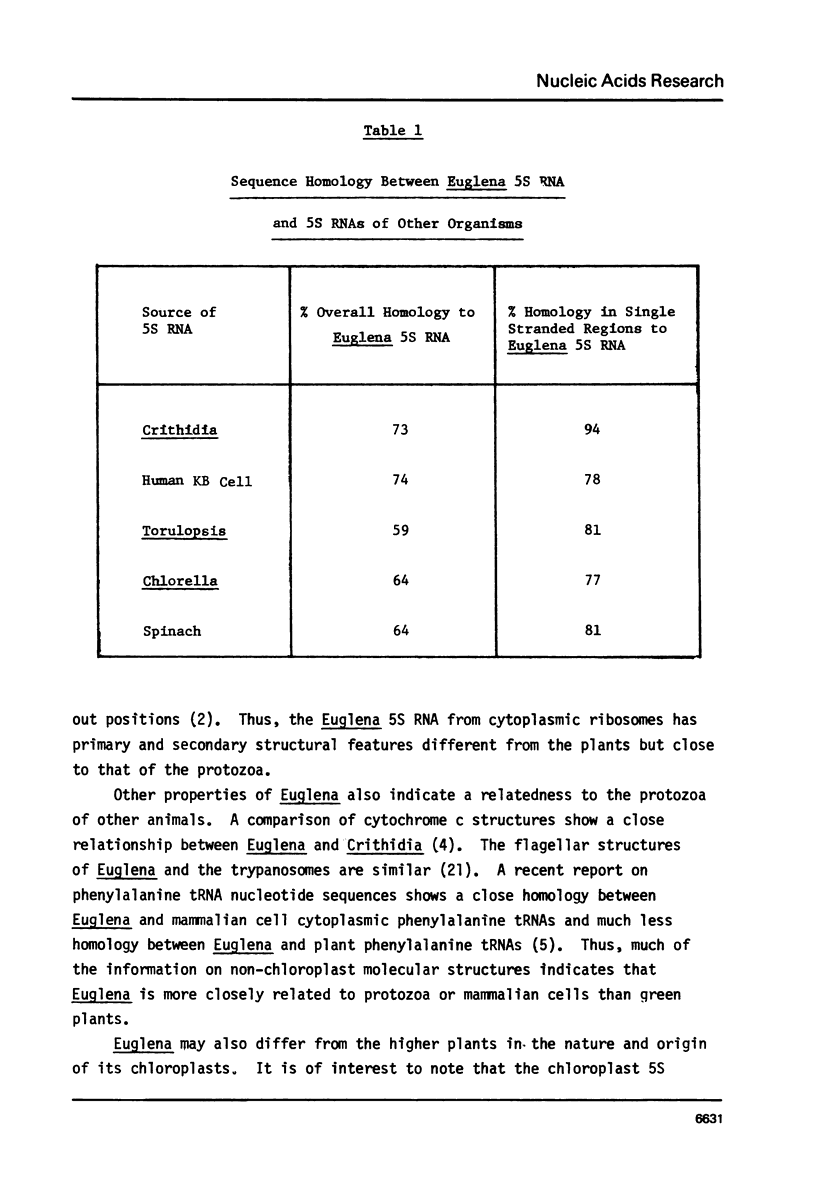
The complete nucleotide sequence of the major species of cytoplasmic 5S ribosomal RNA of Euglena gracilis has been determined. The sequence is: 5' GGCGUACGGCCAUACUACCGGGAAUACACCUGAACCCGUUCGAUUUCAGAAGUUAAGCCUGGUCAGGCCCAGUUAGUAC UGAGGUGGGCGACCACUUGGGAACACUGGGUGCUGUACGCUUOH3'. This sequence can be fitted to the secondary structural models recently proposed for eukaryotic 5S ribosomal RNAs (1,2). Several properties of the Euglena 5S RNA reveal a close phylogenetic relationship between this organism and the protozoa. Large stretches of nucleotide sequences in predominantly single-stranded regions of the RNA are homologous to that of the trypanosomatid protozoan Crithidia fasticulata. There is less homology when compared to the RNAs of the green alga Chlorella or to the RNAs of the higher plants. The sequence AGAAC near position 40 that is common to plant 5S RNAs is CGAUU in both Euglena and Crithidia. The Euglena 5S RNA has secondary structural features at positions 79-99 similar to that of the protozoa and different from that of the plants. The conclusions drawn from comparative studies of cytochrome c structures which indicate a close phylogenetic relatedness between Euglena and the trypanosomatid protozoa are supported by the comparative data with 5S ribosomal RNAs.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beale S. I., Foley T., Dzelzkalns V. delta-Aminolevulinic acid synthase from Euglena gracilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1666–1669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. H., Hecker L. I., Brum C. K., Schnabel J. J., Heckman J. E., Silberklang M., RajBhandary U. L., Barnett W. E. The nucleotide sequence of Euglena cytoplasmic phenylalanine transfer RNA. Evidence for possible classifications of Euglena among the animal rather than the plant kingdom. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3199–3204. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlix J. L., Rochaix J. D. Nucleotide sequence and structure of cytoplasmic 5S RNA and 5.8S RNA of Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 25;9(6):1291–1299. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.6.1291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delihas N., Andersen J., Sprouse H. M., Dudock B. The nucleotide sequence of the chloroplast 5S ribosomal RNA from spinach. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2801–2805. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delihas N., Andersen J., Sprouse H. M., Kashdan M., Dudock B. The nucleotide sequence of spinach cytoplasmic 5 S ribosomal RNA. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7515–7517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer T. A., Bowman C. M. Nucleotide sequences of chloroplast 5S ribosomal ribonucleic acid in flowering plants. Biochem J. 1979 Dec 1;183(3):595–604. doi: 10.1042/bj1830595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann V. A. Collection of published 5S and 5.8S rRNA sequences and their precursors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):r31–r47. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.197-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori H., Osawa S. Evolutionary change in 5S RNA secondary structure and a phylogenic tree of 54 5S RNA species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):381–385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori H., Osawa S., Iwabuchi M. The nucleotide sequence of 5S rRNA from a cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 11;8(23):5535–5539. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.23.5535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Küntzel H., Heidrich M., Piechulla B. Phylogenetic tree derived from bacterial, cytosol and organelle 5S rRNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 25;9(6):1451–1461. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.6.1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa K., Takemura S. Structure and function of 5S ribosomal ribonucleic acid from Torulopsis utilis. II. Partial digestion with ribonucleases and derivation of the complete sequence. J Biochem. 1974 Nov;76(5):935–947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piechulla B., Hahn U., McLaughlin L. W., Küntzel H. Nucleotide sequence of 5S ribosomal RNA from Aspergillus nidulans and Neurospora crassa. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 25;9(6):1445–1450. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.6.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirtle R., Kashdan M., Pirtle I., Dudock B. The nucleotide sequence of a major species of leucine tRNA from bovine liver. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Feb 25;8(4):805–815. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. M., Dayhoff M. O. Origins of prokaryotes, eukaryotes, mitochondria, and chloroplasts. Science. 1978 Jan 27;199(4327):395–403. doi: 10.1126/science.202030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J., Vassilenko S. A different approach to RNA sequencing. Nature. 1978 Jul 6;274(5666):87–89. doi: 10.1038/274087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



