Abstract
Background
Shiga toxin (stx) genes have been transferred to numerous bacteria, one of which is E. coli O157:H7. It is a common belief that stx gene is transferred by bacteriophages, because stx genes are located on lambdoid prophages in the E. coli O157:H7 genome. Both E. coli O157:H7 and non-pathogenic E. coli are highly enriched in cattle feedlots. We hypothesized that strong UV radiation in combination with high temperature accelerates stx gene transfer into non-pathogenic E. coli in feedlots.
Methodology/Principal Findings
E. coli O157:H7 EDL933 strain were subjected to different UV irradiation (0 or 0.5 kJ/m2) combination with different temperature (22, 28, 30, 32, and 37°C) treatments, and the activation of lambdoid prophages was analyzed by plaque forming unit while induction of Stx2 prophages was quantified by quantitative real-time PCR. Data showed that lambdoid prophages in E. coli O157:H7, including phages carrying stx2, were activated under UV radiation, a process enhanced by elevated temperature. Consistently, western blotting analysis indicated that the production of Shiga toxin 2 was also dramatically increased by UV irradiation and high temperature. In situ colony hybridization screening indicated that these activated Stx2 prophages were capable of converting laboratory strain of E. coli K12 into new Shiga toxigenic E. coli, which were further confirmed by PCR and ELISA analysis.
Conclusions/Significance
These data implicate that high environmental temperature in combination with UV irradiation accelerates the spread of stx genes through enhancing Stx prophage induction and Stx phage mediated gene transfer. Cattle feedlot sludge are teemed with E. coli O157:H7 and non-pathogenic E. coli, and is frequently exposed to UV radiation via sunlight, which may contribute to the rapid spread of stx gene to non-pathogenic E. coli and diversity of shiga toxin producing E. coli.
Introduction
Escherichia coli (E. coli) O157:H7 and non-O157 Shiga toxin producing E. coli (STEC) serotypes, most commonly O26, O111, and O103, are responsible for many food-borne diseases [1] and cause deadly diseases or even death in humans. Recently E. coli O104:H4 outbreak in Europe caused thousands of people sick, hundreds of serious hemolytic uremic syndrome and more than thirty death [2]. E. coli O157:H7 induces huge losses to the meat industry and is a threat to consumer health [3], [4].
Since the first STEC serotype, E. coli O157:H7, was discovered in 1982, more than 500 different serogroups of E. coli have been reported to produce Shiga toxin [5]. It is widely regarded that E. coli O157:H7 and other STEC obtained the Shiga toxin (stx) genes through horizontal gene transfer mediated by lambda phages, because stx genes are located in lambdoid prophages within E. coli O157:H7 genome [6], [7]. The lambdoid prophages in STEC genomes might be activated similar to lambda phages [7]. UV light activates SOS response, a post-replication DNA repair system, in bacterial cells which enhances the expression of RecA (DNA strand exchange and recombination protein with protease and nuclease activity), leading to the activation of lambda prophages [8]. It is reported that lambda prophage activation requires a threshold temperature of 20°C; below this temperature, lambda prophage cannot be activated, while the higher temperature may enhance its activation [9], [10]. Whether lambdoid prophages in STEC is sensitized similarly by temperature as lambda prophages, and whether there is a synergistic effect of UV light and elevated temperature on its activation has not been tested. However, this is an important question, because global warming increases environmental average temperature, which may accelerate phage activation and the spread of stx genes.
Cattle gastrointeninal tract are the natural reservoir of E. coli O157:H7. As a result, the sludge in cattle feedlots is densely populated with enteric bacteria including both E. coli O157:H7 and non-pathogenic E. coli [11], [12]. The extremely high dense population of generic E. coli in the feedlot sludge may provide abundant opportunities for the activated stx carrying phages to be integrated into the genome of non-toxin producing E. coli, generating new STEC. In addition, most feedlots are directly exposed to sunlight which contains a high level of solar UV irradiation. The objective of this study was to test whether high environmental temperature in combination with strong UV radiation provides an environment to generate new STEC, which may provide an explanation for the exploding increase of STEC strains.
Materials and Methods
Bacterial strains
E. coli O157:H7 strains EDL933, 86-24, 493/89 and 9505 were obtained from the STEC center at Michigan State University. Wild-type laboratory strain, E. coli K12 MG1655, was obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (700926™, ATCC, Manassas, VA), which is used as sensitive hosts for induced phages generated by E. coli O157:H7 strains. E. coli strains were stored in Luria-Bertani (LB) medium containing 15% glycerol at −80°C, which were routinely grown in LB broth at 37°C overnight with aeration.
Bacterial activation and prophage induction
E. coli O157:H7 strains were activated from frozen glycerol stock by culturing in LB media overnight at 37°C with aeration and, then, 1∶100 inoculated into fresh LB medium. The inoculum was cultured at 37°C, 250 rpm till OD600 nm 0.6∼0.8 and, then the culture was divided into two parts. For UV induction, 10 ml of the E. coli O157:H7 culture was placed in a 100×15 mm petri dishes with lid off and exposed to UV radiation (0.5 kJ/m2) from top. The intensity of UV radiation was measured with a UVX Radiometer equipped with a UVX-25 probe (UVP, Inc., Upland, CA). Following UV radiation, cultures were maintained shaking for 6 h at different temperatures (22, 28, 30, 32, or 37°C). For controls untreated with UV irradiation, cultures were processed exactly the same except UV irradiation. After incubation, culture supernatants were used for analyzing phage titer, Stx2 bacteriophage abundance, and Stx2 protein content.
Phage enumeration
One ml of E. coli O157:H7 culture from different incubation temperature with/without UV radiation was transferred into 1.5 ml micro-centrifuge tubes. The supernatants were collected after centrifuging at 10,000× g for 5 min, and serially diluted with phage buffer containing 10 mM MgSO4 and 5 mM CaCl2. The appropriate phage suspension dilutions were used for phage forming unit (PFU) analysis. Briefly, 200 µl of phage suspension was mixed with 1 ml of plating host, MG1655 stationary phase culture and 5 ml of tempered top agar (0.7% in 10 mM MgSO4 and 10 mM CaCl2), and poured onto the bottom LB agar plate per previously published procedure [13], [14], [15]. Plates were incubated at 37°C for 24–48 h and the plaques were counted.
Quantitative PCR analysis of Stx2 bacteriophages
E. coli O157:H7 cultures from different incubation temperature with/without UV radiation were centrifuged (10 min at 10,000× g), and the supernatant was filtered through a sterile 0.22 µm filter (Millipore, Bedford, MA) to completely remove bacteria. One ml of the resulting filtrate was centrifuged at 35,000× g, 4°C for 60 min. The resulting phage pellet was dissolved in sterile ddH2O and treated with DNase Ι (2 units/µl) at 37°C for 2 h to digest possible E. coli O157:H7 genomic DNA contamination. The resulting phage preparation that only contain packaged phage DNA (phage protein coats protect phage DNA from DNase I) was incubated at 100°C for 10 min to inactivate DNase I and release phage DNA. The prepared phage DNA samples were stored at −20°C and used as a template for quantitative PCR (qPCR) analysis of Stx2 bacteriophages. PCR was conducted using primers specific to stx2 subunit A (Forward primer: CGTCACTCACTGGTTTCATCAT; Reverse primer: TCTGTATCTGCCTGAAGCGTAA; PCR product size is 133 bp) and SYBR Green master mix (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA). The specificity of primers was verified by spiking E. coli O157:H7 genomic DNA, showing that qPCR signal was directly proportional to the amount of genomic DNA added into the reaction. The amplification efficiency was 0.90–0.99. At the end of each run, dissociation melt curves were obtained to verify that only one PCR product was amplified; the size of amplicon was further confirmed by electrophoresis. Stx2 phage are known to carry only one stx2 gene copy, therefore the abundance of stx2 gene was extrapolated to the quantity of Stx2 bacteriophage in each sample.
Western blot analysis of Shiga toxin 2
Immunobloting analysis was conducted according to the procedures described previously [16], [17], [18]. Briefly, protein extractions from the whole bacterial suspension were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. The transferred nitrocellulose membranes were blocked with 5% milk in PBS, pH7.4 with 0.05% Tween-20, incubated with Stx2A mouse monoclonal antibody (1∶1000 dilution, Toxin Technology Inc., Sarasota, FL) and anti-mouse secondary antibody (Cell Signaling Tech., Boston, MA) consecutively. Blotted membranes were visualized using ECL™ Western blotting detection reagents (Amersham Bioscience, Piscataway, NJ). The density of bands was quantified by using the Quantity One software (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA).
Horizontal transfer of stx2 gene from E. coli O157:H7 to non-pathogenic E. coli
Wild type laboratory E. coli K12 MG1655 was electropolated with the pKNOCK plasmid which carries a Kanamycin resistant gene [19]. MG1655 (KanR) carrying kanamycin resistance was activated from frozen glycerol stock by culturing in LB media overnight at 37°C with aeration. The activated overnight culture was 1∶100 inoculated into fresh LB medium and cultured at 37°C, 250 rpm till OD600 nm≅0.6, when 10% (V/V) of the phage preparation obtained from EDL933 was added. MG1655 and phage preparation mixture was incubated at 37°C for 6 h.
In situ colony hybridization to screen newly converted STEC
The newly converted STEC was screened by in situ colony hybridization using DIG labeled stx2 probes. Briefly, the MG1655 (KanR) and phage co-culture prepared above was 10-fold serial diluted and plated to LB with 50 µg/ml Kanamycin (LBKan50) plates. Colonies in plates with 200∼250 colonies were lifted with sterile nitrocellulose (NC) membrane. The NC membrane was inverted and transferred to freshly prepared LBKan50 plates, and incubated at 37°C for 3 h. After incubation, the NC membrane was dried, saturated with 10% SDS, transferred to denaturing solution (0.5 N NaOH, 1.5 M NaCl), neutralizing solution (1.5 M NaCl, 0.5 M Tris Cl pH7.4) and 2× saline-sodium citrate (SSC) washing solution following the published protocols [20]. Then, the membrane was baked at 80°C for 2 h to cross-link DNA to NC membrane and hybridized with DIG label stx2 probes synthesized using a PCR DIG Probe Synthesis Kit (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) according to the manufacture's instruction. The positive colonies carrying stx2 gene was detected using DIG Nucleic Acid Detection Kit (Roche).
PCR confirmation of newly converted STEC
E. coli O157:H7 EDL933 strain, MG1655 (KanR) and potential positive STEC strains were activated from frozen glycerol stock by culturing in LB media overnight at 37°C with aeration, where EDL933 served as a positive control while MG1655 (KanR) served as a negative control. Overnight culture (200 µl) was centrifuged for 3 min at 10,000× g, the pellet was washed with sterile ddH2O twice, then re-suspended in 200 µl sterile ddH2O and boiled for 15 min. This crude DNA extract (1 µl) from each strain was used as a template DNA in 25 µl PCR reaction containing 200 µM dNTP, 200 nM each primer and 1 unit of Taq polymerase (NEB, Ipswich, MA). Stx2 primer sequences (Forward primer: GGCACTGTCTGAAACTGCTCC; Reverse primer: TCGCCAGTTATCTGACATTCTG; Product size = 255 bp) and O157 primer sequences (Forward primer: CGGACATCCATGTGATATGG; Reverse primer: TTGCCTATGTACAGCTAATCC; Product size = 259 bp) were synthesized according to the published sequences [21]. PCR reaction mixtures were electrophoresed on 2% (W/V) agarose gel and stained with ethidium bromide.
Examination of Stx production by ELISA
Stx production of newly converted STEC was analyzed by ELISA using the ProSpecT Shiga Toxin E. coli (STEC) Microplate Assay kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Lenexa, KS).
E. coli O157 serotyping
E. coli O157:H7, MG1655 (KanR) and potential positive STEC strains were activated from frozen glycerol stock by culturing in LB media overnight at 37°C with aeration. Overnight cultures were boiled at 100°C for 30 min then used for O157 serotyping using an E. coli O157:H7 Latex test kit according to the manual instruction (RIM E. coli O157:H7 Latex test, Thermo Fisher Scientific).
Statistics
Data were analyzed using GLM (General Linear Model of Statistical Analysis System, SAS, 2000). Differences in mean values were compared by Tukey multiple comparison, and mean ± standard errors of mean (SEM) is reported. Statistical significance was considered as P<0.05. All data are given as means ± SEM of three independent experiments.
Results
Rates of lambdoid prophage activation differed among E. coli O157:H7 strains
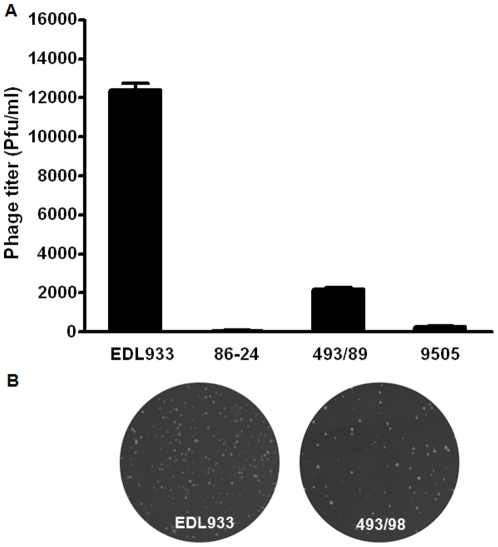
Four different E. coli O157:H7 strains, EDL933, 86-24, 493/89, and 5905, were selected to test the spontaneous activation of lambdoid prophages. As measured by the formation of phage plagues, EDL933 strain had the highest rate of spontaneous activation of prophages, 493/89 stain was the second, and the 86-24 strain had the lowest (Figure 1). Therefore, we chose EDL933 strain for further studies.
Figure 1. Spontaneous lambdoid prophage induction in E. coli O157:H7 strains.
(A) Statistical data of prophage induction (Means ± SEM, n = 3). (B) Representative pictures of plaque forming units of E. coli O157:H7 strains EDL933 and 493/98.
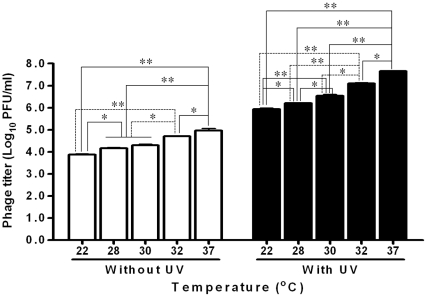
UV radiation and high temperature enhanced activation of lambdoid prophages
The UV radiation dramatically increased the release of lambdoid prophages (Figure 2). Meanwhile, induction of prophage was affected by temperature (Figure 2). For EDL933 strain, when temperature increased from 22 to 37°C, the inducation of prophages was enhanced (Figure 2). We can also see that temperature and UV irradiation had synergistic effects on lambdoid prophage activation (Figure 2).
Figure 2. Effects of UV radiation and temperature on lambdoid prophage induction of E. coli O157:H7 EDL933 strain.
**: P<0.01; **: P<0.05. (Mean ± SEM; n = 3).
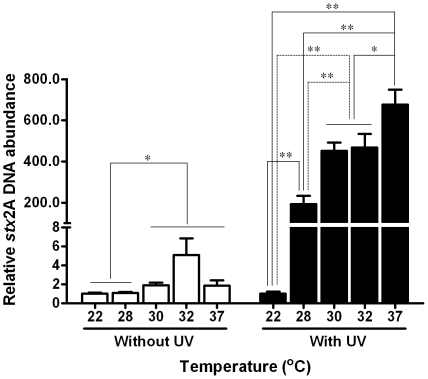
Synergistic effects of temperature and UV irradiation on induction of Stx2 prophages
We further studied the induction of Stx2 prophages under different temperature and UV irradiation combination by quantitative PCR using primers specific to stx2 gene subunit A. Since Stx2 phage contains one copy of stx2 gene, the abundance of stx2 gene subunit A was referred to the quantity of induced Stx2 phages. At all test temperature except 22°C, UV irradiation dramatically enhanced the induction of Stx2 prophages (Figure 3). In non-UV treated control, induction of Stx2 prophage at 28°C was not different from that at 22°C, however, induction of Stx2 prophage was significantly higher at 30, 32 and 37°C compared to that at 22°C. In the UV treated group, induction of Stx2 prophage increased several hundred folds when temperature increased from 22°C to 28, 30, 32 or 37°C (Figure 3); the induction of Stx2 phage was the highest at 37°C, followed by 30 and 32°C (Figure 3). These results indicated that there were synergistic effects between UV irradiation and environmental temperature on Stx2 prophage induction.
Figure 3. Quantitative PCR quantification of Stx2 prophage induction in the E. coli O157:H7 EDL933 strain with/without UV radiation at different temperatures.
**: P<0.01; **: P<0.05. (Mean ± SEM; n = 3).
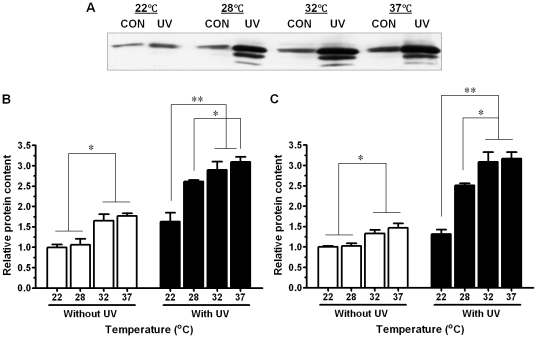
Effects of UV radiation and temperature on Shiga toxin 2 production
Consistent with the enhanced Stx2 prophages induction, UV treatment and elevated temperature increased the protein content of Stx2 (Figure 4). As for Stx2 prophages induction, there was synergistic effect between UV and temperature on Stx2 production (Figure 4). Interestingly, western blotting analysis detected three bands of Stx2A subunit in samples treated UV irradiation, while only single band (MW = 37 kD) in non-UV treated samples. The reason for these two lower MW bands appeared in the UV treated group is unclear (Figure 4).
Figure 4. Effects of UV radiation and temperature on Shiga toxin 2 protein content in E. coli O157:H7 EDL933 strain.
(A) Representative Stx2A western blotting band. (B) Relative Stx2A protein content including only the major band. (C) Relative Stx2A protein content including all three bands. **: P<0.01; **: P<0.05. (Mean ± SEM; n = 3).
Horizontal gene transfer of stx2 gene from Stx2 phage to non-pathogenic E. coli
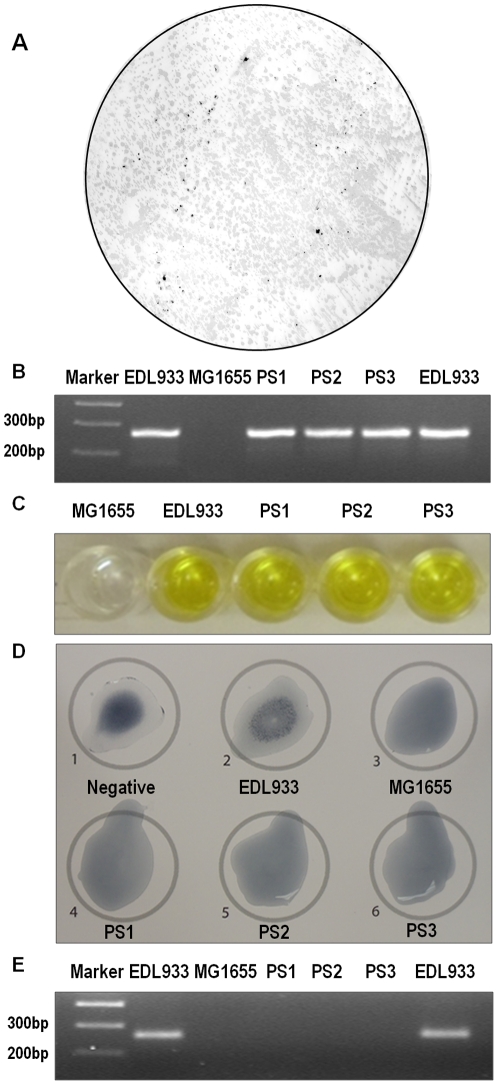
To test whether induced Stx2 phage has the ability to convert non-pathogenic E. coli to STEC, phage preparation following EDL933 induction was incubated with an E. coli K12 strain MG1655 (KanR). As shown in Figure 5A, a number of stx2 positive colonies were detected by in situ colony hybridization. To further confirm, three positive colonies were selected which were designated as PS1–3. PCR analysis indicated that PS1–3 contained stx2 gene (Figure 5B). ELISA analysis further confirmed that PS1–3 produced Stxs (Figure 5C). O157 agglutination assay indicated that PS1–3 as well as MG1655 (KanR) were O157 negative. We further analyzed the presence of O157 gene by PCR using primers specific to O157 gene. As indicated in Figure 5E, O157 gene was only detected in E. coli O157:H7, but not in MG1665 (KanR) and PS1–3. All these indicated that PS1–3 were newly generated STEC through horizontal gene transfer.
Figure 5. Confirmation tests on newly converted STEC.
(A) Representative picture of in situ colony hybridization with DIG labeled stx2A probe; (B) PCR confirmation of stx2A gene in newly converted STEC strains (PS1–PS3); (C) ELISA detection of Shiga toxins; (D) O157 serotyping of newly converted STEC; (E) PCR confirmation of O157 gene was absent in newly converted STEC strains (PS1–PS3).
Discussion
Shiga toxin genes are mainly responsible for the pathogenesis of E. coli O157:H7 through Stx-induced renal endothelial injury [22]. E. coli O157:H7 and non-O157 STEC serotypes are responsible for many food-borne diseases [1]. Beef product recalls due to E. coli O157:H7 contamination cause huge losses to beef industry. Further, the runoffs from cattle farms contaminate vegetables causing additional safety concerns. Therefore, it is important to prevent E. coli O157:H7 and other STEC contamination and propagation. Very recently, European toll in the outbreak of a rare STEC strain, E. coli O104:H4, in Germany and France had risen to 855 cases of HUS, 2,987 cases of acute gastroenteritis and 35 deaths, highlighting the seriousness of food safety problems associated with STECs [2].
Cattle gastrointestinal tract is the primary reservoir of E. coli O157:H7 and non-O157 STEC [23], and fecal shedding of E. coli O157:H7 is the major source of this pathogen [24]. The prevalence of E. coli O157:H7 in the intestinal tracts of feedlot cattle is alarmingly high, ranging from around 10 to 20% [11], [25]. Due to the high rate of E. coli O157:H7 shedding in feces, feedlot sludge is highly contaminated with E. coli O157:H7. In addition, other STEC such as members of the O26, O91, O103, O111, O118, O145, and O166 serogroups are increasingly detected in beef feedlots, which also have been isolated from beef and associated human cases [23]. These STECs co-exist with extremely dense populations of enteric bacteria in feces, which accumulate in the feedlot sludge. The abundance of both STEC and non-STEC, in combination with the high moisture content of feedlot sludge, may provide an ideal environment for horizontal transfer of stx genes from STEC to non-pathogenic E. coli.
Shiga toxin genes likely were captured by STEC through horizontal gene transfer [26]. There are 18 lambdoid prophages identified in the E. coli O157:H7 genome. Both stx1 and stx2 genes locate in lambdoid prophages, with stx2 gene in prophage 5 and stx1 gene in prophage 15 [6], [7]. Though these prophages are defective in certain genes required for phage induction and propagation individually, a very recent study shows that as a pool, these prophages can compensate each other's defects and generate active phages carrying stx2 genes [7]. We tested the spontaneous induction of phages in four different E. coli O157:H7 strains, EDL933, 86-24, 493/89, and 5905, and the EDL933 strain had the highest rate of spontaneous induction of prophages while the 86-24 strain had the lowest. The difference in phage activation may be due to the different degree of lambdoid prophage degeneration; high degree of degeneration reduces and abolishes the ability of lambdoid prophages to be activated [27].
It has been demonstrated earlier that lambda prophage activation is temperature dependent; higher temperature decreases the stability of phage CII protein, promoting the lytic cycle of prophages [9]. The lytic pathway is blocked when temperature below 20°C [10]. In this study, similar temperature-dependent induction of lambdoid prophages was observed. In addition, we also observed that lambdoid prophages in E. coli O157:H7 were dramatically induced by UV radiation at a level comparable to the radiation of sunlight in western high plains. More importantly, we observed synergistic effects between temperature and UV radiation on lambdoid prophage induction, including stx2 prophages.
For the propagation of stx gene, those activated lambdoid prophages carrying stx2 genes must be integrated into the genome of non-STEC. Indeed, we demonstrated that induced Stx2 prophages were able to convert a non-pathogenic E. coli into STEC. In a previous study, lysogenic infection of Stx phages was also detected in a pig farm [28].
In recent decades, climate change characterized by global warming significantly increases environmental temperature. It is expected that temperature will continue to increase during this century. In addition, most cattle feedlots are not or only partially shaded, and exposed to sunlight. High temperature in combination with UV radiation, plus the abundant STEC and other enteric bacteria in cattle sludge, may provide an ideal reservoir for the generation of new STEC from non-STEC. New pathogens, once generated, could rapidly propagate to other regions through cattle transportation, and beef and food distribution, threatening the health of Americans and even globally.
In summary, following the first identification of STEC, E. coli O157:H7, in 1982, stx genes have spread to more than 500 serogroups of E. coli, and other bacteria [5]. If no preventive strategies are taken, stx genes are expected to spread further. Our data demonstrate that high temperature and UV radiation comparable to the environment of cattle feedlots cause induction of lambdoid prophages carrying stx genes, which can convert non-pathogenic E. coli into STECs. Our observation provides a possible explanation for the widely spreading of stx genes in the last decades.
Footnotes
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Funding: Funding was provided by USDA AFRI 2010-65201-20599, Agricultural Experiment Station at University of Wyoming, and NIH-INBRE P20RR016474. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Fey PD, Wickert RS, Rupp ME, Safranek TJ, Hinrichs SH. Prevalence of non-O157:H7 shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in diarrheal stool samples from Nebraska. Emerg Infect Dis. 2000;6:530–533. doi: 10.3201/eid0605.000513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.RKI. Final presentation and evaluation of the epidemiological findings in the EHEC O104:H4 outbreak, Germany 2011. 2011. Robert Koch-Institute, September 2011. http://edoc.rki.de/documents/rki_ab/reQHS31jDrGxc/PDF/23NXL3JomOyAA.pdf.
- 3.Lim JY, Li J, Sheng H, Besser TE, Potter K, et al. Escherichia coli O157:H7 colonization at the rectoanal junction of long-duration culture-positive cattle. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007;73:1380–1382. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02242-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cobbold RN, Hancock DD, Rice DH, Berg J, Stilborn R, et al. Rectoanal junction colonization of feedlot cattle by Escherichia coli O157:H7 and its association with supershedders and excretion dynamics. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007;73:1563–1568. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01742-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Allison HE. Stx-phages: drivers and mediators of the evolution of STEC and STEC-like pathogens. Future Microbiol. 2007;2:165–174. doi: 10.2217/17460913.2.2.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.O'Brien AD, Newland JW, Miller SF, Holmes RK, Smith HW, et al. Shiga-like toxin-converting phages from Escherichia coli strains that cause hemorrhagic colitis or infantile diarrhea. Science. 1984;226:694–696. doi: 10.1126/science.6387911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Asadulghani M, Ogura Y, Ooka T, Itoh T, Sawaguchi A, et al. The defective prophage pool of Escherichia coli O157: prophage-prophage interactions potentiate horizontal transfer of virulence determinants. PLoS Pathog. 2009;5:e1000408. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ennis DG, Fisher B, Edmiston S, Mount DW. Dual role for Escherichia coli RecA protein in SOS mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985;82:3325–3329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gabig M, Obuchowski M, Srutkowska S, Wegrzyn G. Regulation of replication of lambda phage and lambda plasmid DNAs at low temperature. Mol Gen Genet. 1998;258:494–502. doi: 10.1007/s004380050760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Obuchowski M, Shotland Y, Koby S, Giladi H, Gabig M, et al. Stability of CII is a key element in the cold stress response of bacteriophage lambda infection. J Bacteriol. 1997;179:5987–5991. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.19.5987-5991.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Alam MJ, Zurek L. Seasonal prevalence of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in beef cattle feces. J Food Prot. 2006;69:3018–3020. doi: 10.4315/0362-028x-69.12.3018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Fegan N, Vanderlinde P, Higgs G, Desmarchelier P. The prevalence and concentration of Escherichia coli O157 in faeces of cattle from different production systems at slaughter. J Appl Microbiol. 2004;97:362–370. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2004.02300.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Los JM, Los M, Wegrzyn A, Wegrzyn G. Hydrogen peroxide-mediated induction of the Shiga toxin-converting lambdoid prophage ST2-8624 in Escherichia coli O157:H7. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2010;58:322–329. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2009.00644.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.McDonald JE, Smith DL, Fogg PC, McCarthy AJ, Allison HE. High-throughput method for rapid induction of prophages from lysogens and its application in the study of Shiga Toxin-encoding Escherichia coli strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010;76:2360–2365. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02923-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yan Y, Shi Y, Cao D, Meng X, Xia L, et al. Prevalence of Stx phages in environments of a pig farm and lysogenic infection of the field E. coli O157 isolates with a recombinant converting Phage. Curr Microbiol. 2010;62:458–464. doi: 10.1007/s00284-010-9729-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Zhu MJ, Ford SP, Means WJ, Hess BW, Nathanielsz PW, et al. Maternal nutrient restriction affects properties of skeletal muscle in offspring. J Physiol. 2006;575:241–250. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.112110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Zhu MJ, Han B, Tong J, Ma C, Kimzey JM, et al. AMP-activated protein kinase signalling pathways are down regulated and skeletal muscle development impaired in fetuses of obese, over-nourished sheep. J Physiol. 2008;586:2651–2664. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.149633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zhu MJ, Ma Y, Long NM, Du M, Ford SP. Maternal obesity markedly increases placental fatty acid transporter expression and fetal blood triglycerides at midgestation in the ewe. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010;299:R1224–1231. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00309.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Alexeyev MF. The pKNOCK series of broad-host-range mobilizable suicide vectors for gene knockout and targeted DNA insertion into the chromosome of gram-negative bacteria. Biotechniques. 1999;26:824–826, 828. doi: 10.2144/99265bm05. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kirii Y, Danbara H, Komase K, Arita H, Yoshikawa M. Detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by colony hybridization with biotinylated enterotoxin probes. J Clin Microbiol. 1987;25:1962–1965. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.10.1962-1965.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Paton AW, Paton JC. Detection and characterization of Shiga toxigenic Escherichia coli by using multiplex PCR assays for stx1, stx2, eaeA, enterohemorrhagic E. coli hlyA, rfbO111, and rfbO157. J Clin Microbiol. 1998;36:598–602. doi: 10.1128/jcm.36.2.598-602.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ray PE, Liu XH. Pathogenesis of Shiga toxin-induced hemolytic uremic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol. 2001;16:823–839. doi: 10.1007/s004670100660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hussein HS. Prevalence and pathogenicity of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in beef cattle and their products. J Anim Sci. 2007;85:E63–72. doi: 10.2527/jas.2006-421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Elder RO, Keen JE, Siragusa GR, Barkocy-Gallagher GA, Koohmaraie M, et al. Correlation of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157 prevalence in feces, hides, and carcasses of beef cattle during processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97:2999–3003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.060024897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.LeJeune JT, Besser TE, Rice DH, Berg JL, Stilborn RP, et al. Longitudinal study of fecal shedding of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in feedlot cattle: predominance and persistence of specific clonal types despite massive cattle population turnover. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004;70:377–384. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.1.377-384.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Furst S, Scheef J, Bielaszewska M, Russmann H, Schmidt H, et al. Identification and characterisation of Escherichia coli strains of O157 and non-O157 serogroups containing three distinct Shiga toxin genes. J Med Microbiol. 2000;49:383–386. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-49-4-383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ogura Y, Ooka T, Iguchi A, Toh H, Asadulghani M, et al. Comparative genomics reveal the mechanism of the parallel evolution of O157 and non-O157 enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:17939–17944. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0903585106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Yan Y, Shi Y, Cao D, Meng X, Xia L, et al. Prevalence of Stx phages in environments of a pig farm and lysogenic infection of the field E. coli O157 isolates with a recombinant converting Phage. Curr Microbiol. 2010;62:458–464. doi: 10.1007/s00284-010-9729-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]