Abstract
The inner histone complex, extracted from chicken erythrocyte chromatin in 2 M NaCL AT pH 7.4, has been characterized by sedimentation equilibrium and sedimentation velocity. High speed sedimentation equilibrium studies indicate that in 2 M NaCl the inner histones are a weakly associating system with contributions from species ranging in molecular weight from dimer to octamer. The appearance of a single boundary (3.8S at 2 M NaCl) in sedimentation velocity studies conducted over a wide range of protein concentrations and ionic conditions indicates that the various histone oligomers present are in rapid equilibrium with one another. At higher salts the equilibrium is shifted to favor higher molecular weight species; in 4 M NaCl essentially all of the histone is octameric at protein concentrations above 0.2 mg/ml. The facile interconversion of histone oligomers suggests that small alterations in histone-histone interactions may be responsible for changes in nucleosome conformations during various biological processes.
Full text
PDF


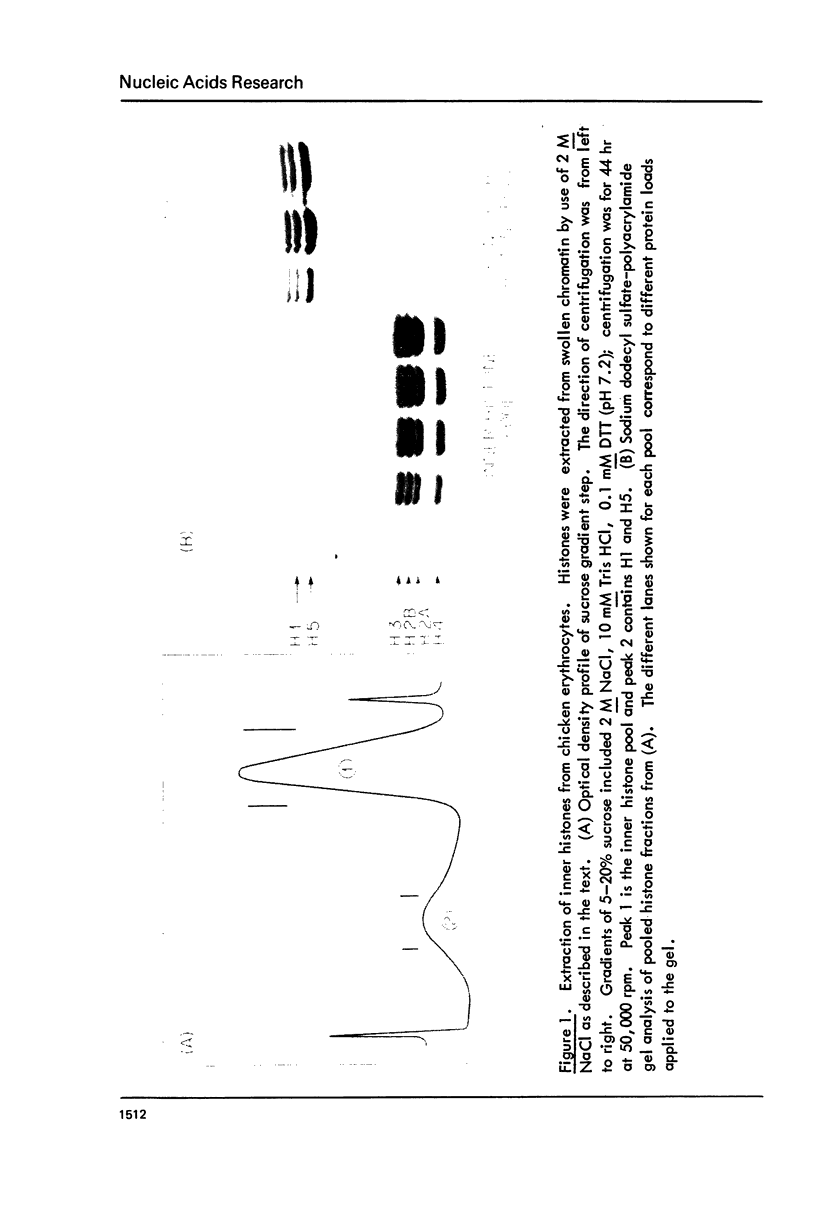

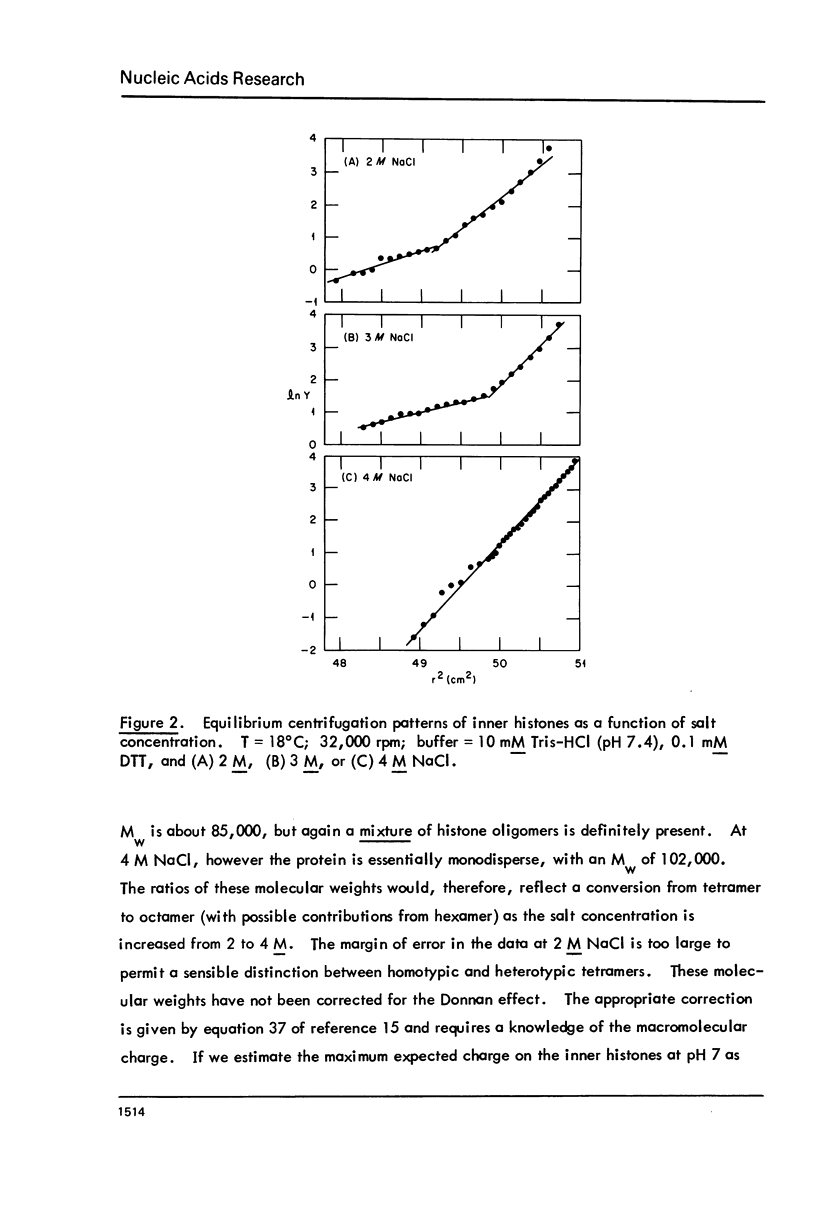
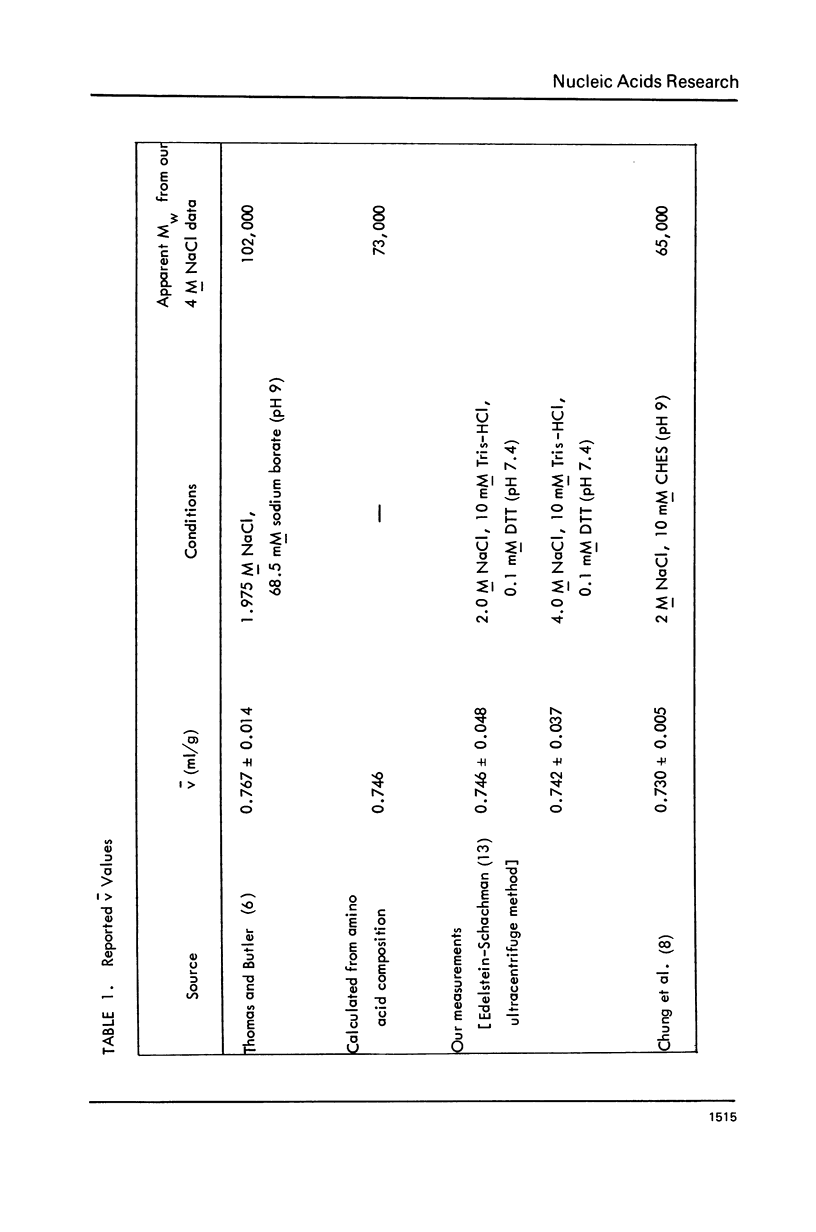
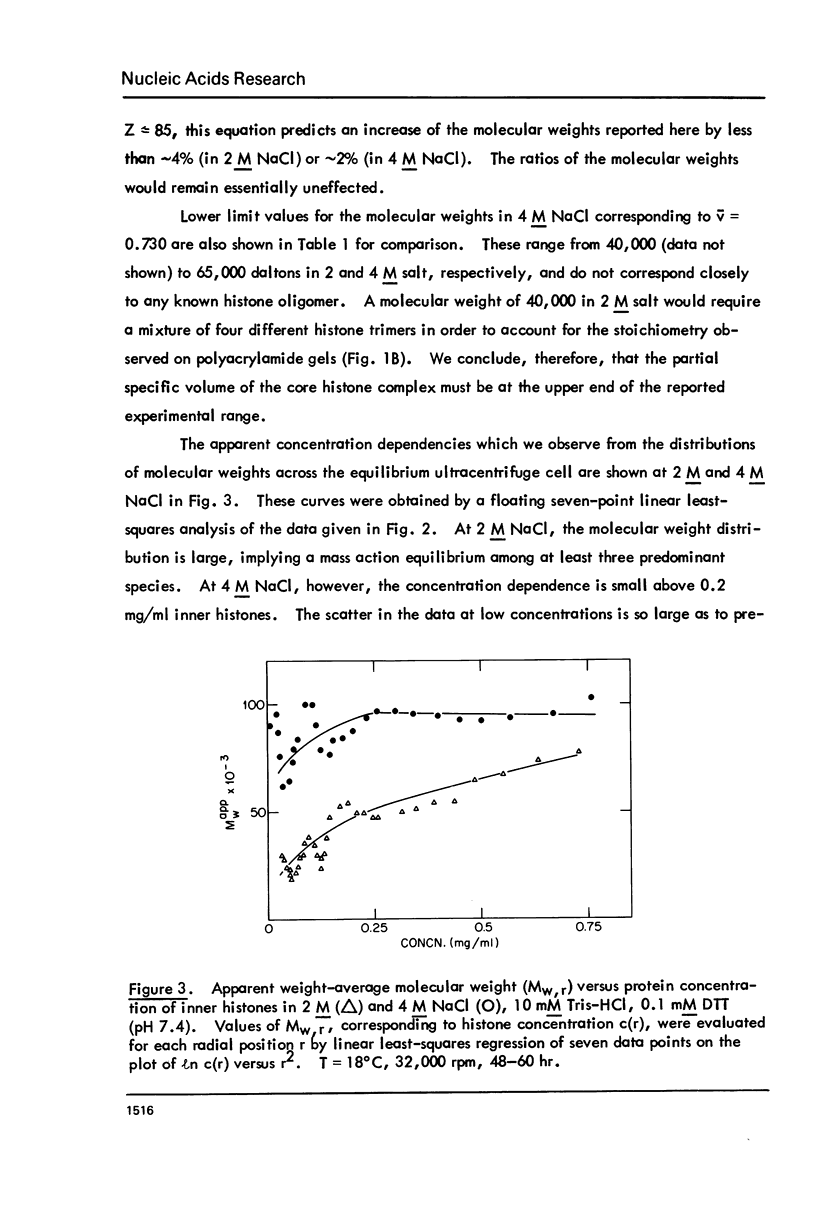



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Campbell A. M., Cotter R. I. The molecular weight of nucleosome protein by laser light scattering. FEBS Lett. 1976 Nov;70(1):209–211. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80759-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubochet J., Noll M. Nucleosome arcs and helices. Science. 1978 Oct 20;202(4365):280–286. doi: 10.1126/science.694532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein S. J., Schachman H. K. The simultaneous determination of partial specific volumes and molecular weights with microgram quantities. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jan 25;242(2):306–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eickbush T. H., Moudrianakis E. N. The histone core complex: an octamer assembled by two sets of protein-protein interactions. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 14;17(23):4955–4964. doi: 10.1021/bi00616a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon V. C., Knobler C. M., Olins D. E., Schumaker V. N. Conformational changes of the chromatin subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):660–663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M., Pardon J. F., Richards B. M. Structural investigations of chromatin core protein by nuclear magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1977 Jun 28;16(13):2853–2860. doi: 10.1021/bi00632a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T., Cary P. D., Crane-Robinson C., Bradbury E. M. Physical studies on the H3/H4 histone tetramer. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 1;15(11):2261–2267. doi: 10.1021/bi00656a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M. Differences and similarities in chromatin structure of Neurospora crassa and higher eucaryotes. Cell. 1976 Jul;8(3):349–355. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90146-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olins A. L., Carlson R. D., Wright E. B., Olins D. E. Chromatin nu bodies: isolation, subfractionation and physical characterization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Dec;3(12):3271–3291. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.12.3271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roark D. E., Geoghegan T. E., Keller G. H., Matter K. V., Engle R. L. Histone interactions in solution and susceptibility to denaturation. Biochemistry. 1976 Jul 13;15(14):3019–3025. doi: 10.1021/bi00659a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roark D. E., Yphantis D. A. Equilibrium centrifugation of nonideal systems. The Donnan effect in self-associating systems. Biochemistry. 1971 Aug 17;10(17):3241–3249. doi: 10.1021/bi00793a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. J., Jr, Prescott B., Olins D. E. Secondary structure of histones and DNA in chromatin. Science. 1977 Jul 22;197(4301):385–388. doi: 10.1126/science.560060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Butler P. J. Characterization of the octamer of histones free in solution. J Mol Biol. 1977 Nov;116(4):769–781. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90270-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Kornberg R. D. An octamer of histones in chromatin and free in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2626–2630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YPHANTIS D. A. EQUILIBRIUM ULTRACENTRIFUGATION OF DILUTE SOLUTIONS. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:297–317. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zama M., Bryan P. N., Harrington R. E., Olins A. L., Olins D. E. Conformational states of chromatin. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 1):31–41. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



