This study investigates the role played by the Tel1ATM and Rad3ATR kinases in fission yeast telomere biology. Ishikawa and colleagues find that these kinases directly phosphorylate the telomere protein Ccq1 on residue Thr 93. Such phoshorylation is required for telomerase recruitment to telomeres, highlighting the importance of these kinases in telomere maintenance.
Keywords: telomere, telomerase, phosphorylation, PIKK, DNA damage checkpoint
Abstract
In fission yeast, the DNA damage sensor kinases Tel1ATM and Rad3ATR exist at telomeres and are required for telomere maintenance, but the biological role they play at telomeres is not known. Here we show that the telomere protein Ccq1 is phosphorylated at Thr 93 (threonine residue at amino acid 93) by Tel1ATM and Rad3ATR both in vitro and in vivo. A ccq1 mutant in which alanine was substituted for Thr 93 failed to recruit telomerase to telomeres and showed gradual shortening of telomeres. These results indicate that the direct phosphorylation of Ccq1 Thr 93 by Tel1 and Rad3 is involved in the recruitment of telomerase to elongate telomeres.
Telomeres are the chromatin positioned at the ends of linear genomic DNAs, protecting the DNA ends from degradation and fusion and ensuring the replication of the terminal DNAs (Palm and de Lange 2008). Telomere DNA length is determined by the balance between telomere attrition caused by the end replication problem and elongation caused primarily by telomerase. Maintenance of telomere length within a relatively narrow range must involve a feedback regulatory mechanism, but the molecular details are largely unknown.
A six-component protein complex called shelterin is conserved in mammalian cells (Palm and de Lange 2008), providing the structural basis of telomere function. In fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe, a shelterin-like complex also exists (Miyoshi et al. 2008). In this complex, Taz1 binds to double-stranded (ds) telomere DNAs, and Pot1 binds to the most terminal single-stranded (ss) telomere DNAs (Cooper et al. 1997; Baumann and Cech 2001). Other components—Rap1, Poz1, Ccq1, and Tpz1—act as a molecular bridge between Taz1 and Pot1 through protein–protein interactions (see Supplemental Fig. 5; Miyoshi et al. 2008). We reported that Taz1, Rap1, and Poz1 comprise a pathway that negatively regulates the elongation of telomere DNAs by telomerase. In contrast, Ccq1 positively regulates telomerase (Miyoshi et al. 2008; Tomita and Cooper 2008).
The fission yeast shelterin-like complex also plays essential roles in protecting the ends of genomic DNAs from activation of the DNA damage checkpoint (Miyoshi et al. 2008; Palm and de Lange 2008; Moser and Nakamura 2009), although, paradoxically, it is widely accepted that the DNA damage sensor kinases are required for telomere maintenance (Lustig and Petes 1986; Metcalfe et al. 1996; Smilenov et al. 1997; Naito et al. 1998; Vespa et al. 2005; Moser et al. 2009). For example, in S. pombe, we previously reported that cells deleted of Tel1 and Rad3 had very short telomeres (Naito et al. 1998), suggesting that a downstream target of Tel1 and Rad3 operates to regulate telomere length, although the target has not yet been identified. Fission yeast Tel1 and Rad3 are members of the family of protein kinases called PIKK (phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinase), to which mammalian ATM and ATR also belong. Since it has been recognized that Tel1 and Rad3 function similarly, although not identically, to ATM and ATR, respectively, in this study, we call them Tel1ATM and Rad3ATR.
In budding yeast, telomerase preferentially reacts with short telomeres (Teixeira et al. 2004; Bianchi and Shore 2007). It has been suggested that budding yeast cells measure telomere length indirectly by counting the number of ds-telomere DNA-binding proteins (Rap1 in budding yeast) instead of directly measuring the telomere DNA length (protein-counting model) (Marcand et al. 1997). It is not known whether a similar model applies to fission yeast. However, given that Ccq1 indirectly interacts with ds-telomere DNA-binding protein Taz1 and positively regulates telomerase, we hypothesized that Tel1 and Rad3 target Ccq1 to regulate telomerase.
Here we show that the phosphorylation of Ccq1 Thr 93 (threonine residue at amino acid 93) targeted by Tel1 and Rad3 mediates the recruitment of telomerase to maintain the telomere length.
Results and Discussion
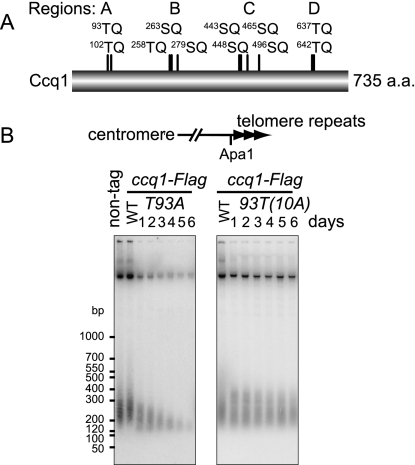
PIKK proteins phosphorylate serine or threonine residues preceding a glutamine residue (SQ/TQ motif). Fission yeast Ccq1 contains 11 SQ/TQ motifs (Fig. 1A). We observed gradual telomere shortening in a ccq1 mutant strain (ccq1-11A) producing Ccq1-11A-Flag in which alanine was substituted for serine or threonine residues in all of the 11 SQ/TQ motifs (Supplemental Fig. 1), suggesting that one or more of the SQ/TQ motifs of Ccq1 are required for the maintenance of telomere length. The 11 SQ/TQ motifs are clustered in four regions of the Ccq1 protein (regions A–D in Fig. 1A). We generated ccq1 mutants in which the SQ/TQ motifs present in individual regions were mutated to AQ and found that telomere shortening occurred only when we mutated residues Thr 93 and Thr 102 (threonine residue at amino acid 102) in region A (Supplemental Fig. 1). When Thr 93 and Thr 102 were individually replaced with alanine, ccq1 mutant cells producing Ccq1-T93A-Flag (ccq1-T93A), but not Ccq1-T102A-Flag (ccq1-T102A), showed gradual telomere shortening (Fig. 1B; Supplemental Fig. 1). Replacement of Thr 93 with aspartic acid or glutamic acid also resulted in gradual telomere shortening, suggesting that phosphorylation in a precise amino acid context is required for telomere maintenance (Supplemental Fig. 1). Conversely, when all SQ/TQ motifs except Thr 93 were mutated to AQ residues [ccq1-93T(10A)], the cells maintained telomere lengths similar to those in wild-type cells (Fig. 1B). These results strongly suggest that, of the 11 SQ/TQ motifs, Thr 93 plays a major role in telomere length homeostasis.
Figure 1.
Thr 93 of Ccq1 is required for telomere length homeostasis. (A) SQ/TQ motifs present in Ccq1. (B) Telomere length of cells expressing Ccq1-Flag, Ccq1-T93A-Flag, or Ccq1-93T(10A)-Flag. Established cultures at the earliest time point were referred to as day 1. Subsequently, cultures were collected every 24 h (see also Supplemental Fig. 1). Genomic DNAs were digested with ApaI, which cuts proximal to telomeres of chromosomes I and II (shown at the top), and were analyzed by Southern hybridization with a telomere DNA probe.
We cultured ccq1-T93A cells, ccq1Δ cells, and cells deleted for trt1+, which encodes the catalytic subunit of telomerase, for 12 d following the isolation of the respective strains. Aliquots of cells were harvested every day, counted, and monitored for telomere lengths and cell shapes (Supplemental Fig. 2A). Mutant ccq1-T93A clones showed gradual telomere shortening until days 5–7, when telomere signals were faint to undetectable. After this period, one strain regained telomere signals (T93A-1), but the other strain did not (T93A-2). ccq1Δ and trt1Δ cells underwent changes to telomere signals similarly to ccq1-T93A cells (Supplemental Fig. 2B). When we examined the estimated number of cell divisions calculated from the increase of cell numbers over 24-h intervals (see the Supplemental Material for details), all mutant cells showed retarded cell growth at the middle of the time course (Supplemental Fig. 2C), suggesting that ccq1-T93A, ccq1Δ, and trt1Δ cells underwent senescence. The increase of cell growth at later time points in some cells suggests the generation of survivor cells, although we do not know whether they bypassed senescence via homologous recombination or circular chromosome formation. We noted that ccq1Δ cells elongated their cell morphology immediately after the deletion of ccq1+. In contrast, both ccq1-T93A cells and trt1Δ cells showed normal cell length for a while after the establishment of mutants, and the cell length gradually increased only when the telomere length was extremely shortened (data not shown). Consistently, ccq1Δ cells showed retarded growth earlier (day 3 and thereafter) than ccq1-T93A cells and trt1Δ cells (day 5 and thereafter, when the telomere length became very short) (Supplemental Fig. 2B). These results suggest that ccq1-T93A cells retain a residual activity that partially protects telomeres from the DNA damage checkpoint, whereas telomeres are deprotected in ccq1Δ cells. It was reported that Ccq1 binds to histone deacetylase Clr3 (Sugiyama et al. 2007). In immunoprecipitation–immunoblotting experiments, we found that Ccq1-T93A-Flag associates with Clr3 (Supplemental Fig. 3). Taken together, ccq1-T93A is not a ccq1-null mutation; rather, it is a separation-of-function mutation that is specifically defective in telomere length homeostasis.
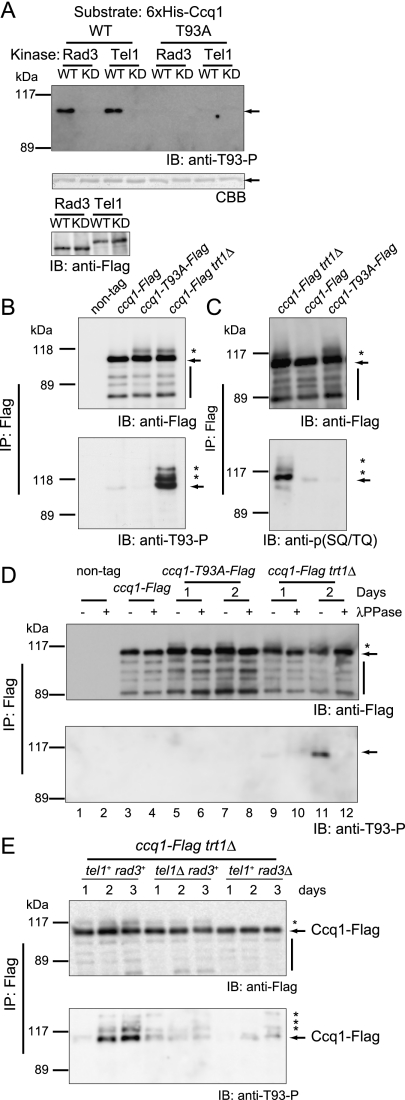
We raised a mouse monoclonal antibody (anti-T93-P antibody) against a phospho-peptide antigen [CLDHSENDFL(pT)QEVDEFPST] representing a short Ccq1 peptide sequence containing phosphorylated Thr 93. The antibody recognized affinity-purified wild-type 6xHis-tagged Ccq1 that had been incubated with immunoprecipitated wild-type Tel1 or Rad3, but not Ccq1 incubated with kinase-dead Tel1 or Rad3 (Fig. 2A). It did not recognize affinity-purified 6xHis-tagged Ccq1-T93A treated with wild-type Tel1 or Rad3. These results indicate that Thr 93 of Ccq1 is directly phosphorylated by Tel1 or Rad3 in vitro.
Figure 2.
Tel1- and Rad3-dependent phosphorylation of Thr 93 of Ccq1 in vitro and in vivo. (A) In vitro kinase assay. 6xHis-tagged wild-type Ccq1 (WT) and Ccq1-T93A (T93A) (calculated molecular mass is 86.8 kDa) were affinity-purified and incubated with immunoprecipitated wild-type (WT) or kinase-dead (KD) 3xFlag-tagged Rad3 and Tel1 (278.1 and 331.7 kDa, respectively). Ccq1 proteins were examined in immunoblotting experiments using anti-T93-P antibody (top panel) or Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) staining (middle panel). (Bottom panel) Relative amounts of immunoprecipitated 3xFlag-tagged Rad3 and Tel1 were similar. Arrows indicate the position of 6xHis-tagged Ccq1 proteins. (IB) Immunoblotting. (B) Anti-T93-P antibody detects Ccq1 in trt1+ cells. Anti-Flag-immunoprecipitated Ccq1-Flag (87.4 kDa) and Ccq1-T93A-Flag were immunoblotted with indicated antibodies. (C) Anti-phospho-SQ/TQ antibody detects Ccq1 in trt1+ cells. Anti-Flag-immunoprecipitated Ccq1-Flag and Ccq1-T93A-Flag were analyzed as in B using indicated antibodies. (D) Phosphorylation of Ccq1 in vivo. Total cell extracts were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag-antibody, treated with (+) or without (−) λPPase, and analyzed in immunoblotting experiments using anti-Flag or anti-T93-P antibody. Cells were either wild-type trt1+ (lanes 1–8) or trt1Δ (lanes 9–12). (E) Tel1- and Rad3-dependent phosphorylation of Ccq1 in vivo. Anti-Flag-immunoprecipitated Ccq1 proteins of trt1Δ cells in a tel1Δ or rad3Δ background were analyzed in immunoblotting experiments using anti-Flag or anti-T93-P antibody. See detailed culture conditions in the Materials and Methods. (B–E) In addition to the primary band corresponding to Ccq1-Flag protein (arrows), slower-migrating smeared Ccq1-Flag signals were observed (asterisks). Bars indicate degradation products of Ccq1-Flag protein. (IP) Immunoprecipitation; (IB) immunoblotting. (A–E) Ccq1 migrates in gels slower than expected from the calculated molecular mass.
We next explored whether phosphorylation of Thr 93 is involved in telomere length homeostasis in vivo. When Ccq1-Flag was immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibody from trt1+ ccq1-Flag cells, the phosphorylated form was detected, albeit weakly, by the anti-T93-P antibody (Fig. 2B, lane 2). The antibody did not detect immunoprecipitated Ccq1-T93A-Flag (Fig. 2B, lane 3), although the T93A mutation by itself profoundly reduced telomere length in the trt1+ background (Fig. 1B). Similar results were obtained using a commercially available anti-phosphorylated SQ/TQ antibody [anti-p(SQ/TQ) antibody] (Fig. 2C). These results indicate that a small but detectable fraction of Ccq1 in wild-type cells is phosphorylated at Thr 93. We then deleted trt1+ in the ccq1-Flag background and found that anti-T93-P antibody readily detected immunoprecipitated Ccq1-Flag prepared from cells at day 2 after the establishment of clones but barely detected signals from cells at day 1, and this was sensitive to λ protein phosphatase (λPPase) treatment (Fig. 2D, lanes 11,12). Taken together, these results indicate that Thr 93 is phosphorylated in vivo, and the antibody specifically recognizes the in vivo phosphorylation of Thr 93. The signal intensities with anti-T93-P antibody and anti-p(SQ/TQ) antibody were much stronger in trt1Δ cells compared with trt1+ cells (Fig. 2B [lanes 2,4], C [lanes 1,2], D [arrows and asterisks]), which can be explained by the fact that most trt1Δ cells had short telomeres, while only a small fraction of trt1+ cells presumably possessed short telomeres at any given time point. The mobility of Ccq1 in the gel was noticeably retarded in trt1Δ cells and Ccq1-T93A-Flag-expressing cells (Fig. 2B,C, asterisks), and this retardation was sensitive to λPPase treatment and rad3+ deletion (Fig. 2D, lanes 5–12; Supplemental Fig. 4), suggesting that Ccq1 is heavily phosphorylated at multiple sites, in addition to Thr 93, by a Rad3-dependent pathway in vivo when telomeres are shortened. Recall, however, that the telomere length was not shortened in Ccq-93T(10A)-Flag-expressing cells (Fig. 1B). These results indicate that the Ccq-93T(10A)-Flag is fully functional with regard to telomere length homeostasis and that phosphorylation at SQ/TQ sites other than Thr 93 does not play a major role in telomere length control. We investigated the contributions of Tel1 and Rad3 to Thr 93 phosphorylation in trt1Δ cells. Heterozygous diploid strains for ccq1-Flag/ccq1+ trt1Δ/trt1+ in the tel1Δ/tel1+ or rad3Δ/rad3+ background were sporulated, and resulting haploid cells, ccq1-Flag trt1Δ, ccq1-Flag trt1Δ tel1Δ, and ccq1-Flag trt1Δ rad3Δ were selected. Immunoprecipitated Ccq1-Flag from a lysate of each respective strain was analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-T93-P antibody. The intensity of the phosphorylation signal at Thr 93 was diminished in tel1Δ cells and only minimally detected in rad3Δ cells (Fig. 2E), suggesting that Tel1 and Rad3 phosphorylate Thr 93 in vivo and that Rad3 plays a relatively major role.
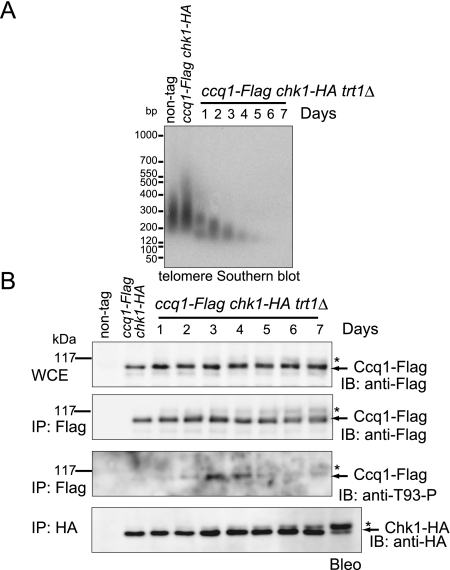
We examined the time course of Thr 93 phosphorylation during telomere shortening after the removal of trt1+. A heterozygous diploid strain with ccq1-Flag/ccq1+ trt1Δ/trt1+ chk1-HA/chk1+ was sporulated, and haploid cells with ccq1-Flag chk1-HA trt1Δ were selected. During 7 d of growth in culture after the establishment of mutants, telomere DNA length gradually shortened and was barely visible on days 6 and 7 (Fig. 3A). We found that Ccq1-Flag immunoprecipitates were positive with anti-T93-P antibody on days 3 and 4; the phosphorylation was barely apparent after day 5, when telomeres were extremely shortened (Fig. 3B, arrows and asterisks). A simple interpretation of these results is that Ccq1 is phosphorylated at Thr 93 transiently on days 3 and 4, when the telomere length is moderately reduced. We found that activated Chk1 (asterisks in Fig. 3B, anti-HA blot) was first perceptible on day 2 and steadily increased thereafter until day 7. It was reported that even when telomeres are recognized as DNA damage and Rad3 is activated, Chk1 is not activated as long as Ccq1 is localized at the telomere (Carneiro et al. 2010). If we assume that Ccq1 phosphorylation at Thr 93 occurs only when telomeres are moderately shortened, as suggested by Figure 3B, an interesting possibility arises: Telomeres undergoing gradual shortening first phosphorylate Ccq1 Thr 93 transiently to recruit telomerase, and then fully activate Chk1 to elicit a DNA damage response (DDR) when telomeres become critically shortened (Supplemental Fig. 5). In this scenario, Rad3 and Tel1 regulate Ccq1 and Chk1 differentially to achieve different tasks. Alternatively, we noticed that a fraction of Ccq1-Flag migrated slowly in gels (asterisks in Fig. 3B, anti-Flag blot). Such a broad distribution of Ccq1-Flag in a gel might have made it difficult to be detected with anti-T93-P antibody. In this case, both Ccq1 Thr 93 and Chk1 are phosphorylated by Tel1 and Rad3 when telomeres are shortened, as manifestations of DDR. Future studies are necessary to differentiate these two possibilities.
Figure 3.
Kinetics of phosphorylation of Ccq1 during telomere shortening. (A) Telomere length was analyzed by Southern hybridization for cells with ccq1-Flag, chk1-HA, and trt1Δ background collected at indicated time points following the establishment of the strain. For the culture conditions, see the Materials and Methods. (B) Whole-cell extracts (WCEs) and anti-Flag- or anti-HA-immunoprecipitates from the cells collected in A were analyzed by immunoblotting experiments using anti-Flag, anti-T93-P, or anti-HA antibody. Ccq1-Flag-expressing and Chk1-HA-expressing (60.3 kDa) cells with trt1+ were treated with bleomycin (Bleo) as a positive control of Chk1 phosphorylation. In addition to the major band corresponding to Ccq1-Flag protein or Chk1-HA (arrows), slower-migrating smeared Ccq1-Flag or Chk1-HA signals were observed (asterisks).
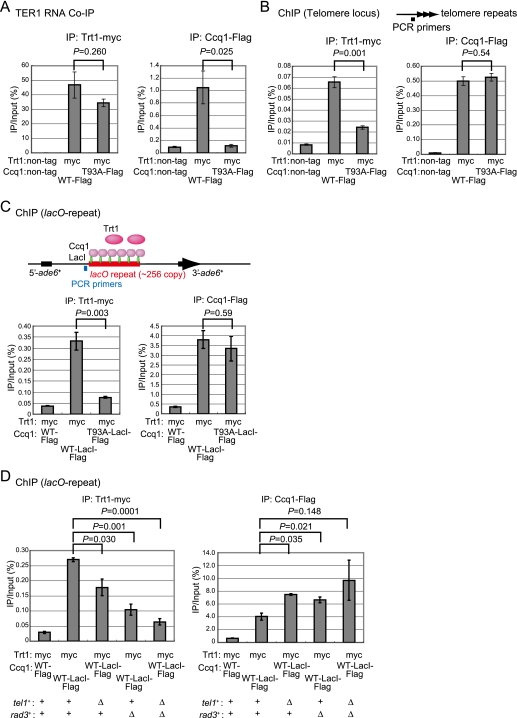
We previously reported that telomerase activity was coimmunoprecipitated with Ccq1 (Miyoshi et al. 2008). We found that Trt1-myc was coimmunoprecipitated with the telomerase template RNA TER1 in Ccq1-T93A-Flag-expressing cells as efficiently as in wild-type Ccq1-Flag-expressing cells (Fig. 4A), indicating that the Trt1-TER1 telomerase core enzyme is formed in Ccq1-T93A-Flag-expressing cells. In contrast, the coimmunoprecipitation of Ccq1 and TER1 observed in wild-type Ccq1-Flag-expressing cells was almost eliminated in Ccq1-T93A-Flag-expressing cells, as demonstrated by RT–qPCR experiments using three independent TER1-specific RT primers (Fig. 4A; Supplemental Fig. 6). In ChIP (chromatin immunoprecipitation) experiments, both wild-type Ccq1-Flag and Ccq1-T93A-Flag were similarly localized at telomeres (Fig. 4B). In contrast, localization of Trt1-myc at telomeres was significantly less in Ccq1-T93A-Flag-expressing cells than in wild-type Ccq1-Flag-expressing cells (Fig. 4B). We ectopically tethered Ccq1-LacI-Flag fusion protein to lacO repeats inserted at the ade6 locus. We found that wild-type Ccq1-LacI-Flag, but not T93A Ccq1-LacI-Flag, recruited Trt1-myc to the ade6 locus, indicating that Ccq1 is sufficient for telomerase recruitment, independent of telomeric DNA (Fig. 4C). The Trt1 recruitment was moderately inefficient in tel1Δ or rad3Δ cells and mostly eliminated in tel1Δ rad3Δ double-mutant cells (Fig. 4D). We noticed that Ccq1 occupancy at lacO repeats was greater in tel1Δ or rad3Δ mutants compared with tel1+ rad3+, the reason for which we do not know at present. Ccq1-T93D-Flag or T93E-LacI-Flag did not recruit Trt1-myc (Supplemental Fig. 7), consistent with the results that ccq1-T93D- or T93E-Flag cells showed gradual telomere shortening (Supplemental Fig. 1). Taken together, these results suggest that Ccq1 recruits telomerase via Tel1- and Rad3-dependent phosphorylation of Ccq1 Thr 93.
Figure 4.
Thr 93 of Ccq1 plays a role in recruitment of telomerase to telomeres. (A) Coimmunoprecipitation of TER1 RNA was performed for Trt1-myc- and Ccq1-Flag- or Ccq1-T93A-Flag-expressing cells using anti-myc or anti-Flag antibody as indicated. Coimmunoprecipitated TER1 RNA was reverse-transcribed and quantified by real-time PCR using TER1 RNA-specific primers (see primer positions in Supplemental Fig. 6A). (B) The association of Trt1-myc with telomeres is significantly impaired by Ala substitution for Thr 93. ChIP assay was performed for the same cells in A using anti-myc or anti-Flag antibody. The immunoprecipitated DNA was quantified by real-time PCR using subtelomeric primers. (C) Ccq1 is sufficient for telomerase recruitment, independent of telomeric DNA. A ChIP assay using anti-myc or anti-Flag antibody was performed for cells with ∼256 lacO repeats inserted at the ade6 locus (Yamamoto and Hiraoka 2003) expressing Trt1-myc and either one of Ccq1-Flag, Ccq1-WT-LacI-Flag, or Ccq1-T93A-LacI-Flag. LacI binds lacO repeat DNAs. The immunoprecipitated DNA was quantified by real-time PCR using primer sets amplifying a sequence proximal to the lacO-repeats. (D) Telomerase recruitment by Ccq1 is dependent on Tel1 and Rad3. A ChIP assay as in C using tel1+ and/or rad3+ deletion cells expressing Trt1-myc and Ccq1-WT-LacI-Flag was performed. Data are the means ± SEM of the results of three independent experiments.
When we compared the predicted amino acid sequences of Ccq1 in three other Schizosaccharomyces species, we found that the 93TQ motif of S. pombe Ccq1 is conserved in two other Schizosaccharomyces species but not in Schizosaccharomyces japonicus (Supplemental Fig. 8). S. japonicus Ccq1 may have an SQ/TQ motif functionally equivalent to 93TQ in S. pombe (for example, 56SQ). Alternatively, S. japonicus recruits telomerase in a manner distinct from that in S. pombe.
Collectively, we demonstrate that Tel1ATM and Rad3ATR phosphorylate Ccq1 Thr 93 to recruit telomerase. It remains to formally elucidate the biological significance of the Ccq1 phosphorylation. The phosphorylation may operate in wild-type cells as a homeostatic control mechanism to maintain the telomere length. Alternatively, it may occur only in global DDR, as in the case of deletion of the trt1+ gene. However, we prefer the former possibility because the telomere length of a population of cells becomes consistently reduced in the ccq1-T93A (and otherwise wild-type) background. In budding yeast, it was reported that telomerase extends only a small fraction of telomeres at a given time point in wild-type cells (<10% of telomeres with wild-type lengths) (Teixeira et al. 2004). If we assume that fission yeast telomerase reacts to telomeres with similar frequencies, this accounts for our detection of a low level of Ccq1 Thr 93 phosphorylation in trt1+ cells. In mammalian cells, although an apparent mammalian homolog of fission yeast Ccq1 has not been identified, it has been reported that a reduced ATR activity leads to telomere instability (McNees et al. 2010). It was suggested that the effect was not caused by a failure of telomerase recruitment to short telomeres in these settings, but future study is required to address whether mammalian cells regulate telomerase recruitment similarly, as revealed in this study. After we submitted this manuscript, we found that similar results were published by others (Moser et al. 2011).
Materials and methods
Strains, media, and general techniques for fission yeast
S. pombe strains used in this study are listed in Supplemental Table 1. Cells were grown in YES, SD, and EMM media supplemented with amino acids as required. Growth medium as well as basic genetic and biochemical techniques for fission yeast have been described elsewhere (Alfa et al. 1993). Checkpoint activation was elicited by adding 5 μg/mL bleomycin hydrochloride (Wako) to exponentially growing cultures for 1 h. Culture conditions of Figures 2E and 3 are as follows: Heterozygous diploids were sporulated, and the haploid cells were selected on EMM selection medium for 3 d. Colonies were picked and incubated on YES liquid medium for 2 d, and cultures were collected (day 1). Subsequently, cultures were sampled every 24 h.
Acknowledgments
We thank T.M. Nakamura, P. Baumann, A. Yamamoto, and H. Niki for plasmids and strains; M. Nozaki and N. Nozaki (MAB Institute, Inc., Sapporo, Japan) for preparing the phospho-specific antibody; T. Miyoshi, M. Saito, A. Nabetani, and J. Hejna for discussion; M. Tamura for technical support; and A. Katayama, F. Maekawa, A. Shirabuchi, and E. Yamazaki for secretarial work. This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Cancer Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan (to F.I.) and Kyoto University Start-up Grant-in-Aid for young scientists (to H.Y.).
Footnotes
Supplemental material is available for this article.
Article is online at http://www.genesdev.org/cgi/doi/10.1101/gad.177873.111.
References
- Alfa C, Fantes P, Hyams J, McLeod M, Warbrick E 1993. Experiments with fission yeast: A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York [Google Scholar]
- Baumann P, Cech TR 2001. Pot1, the putative telomere end-binding protein in fission yeast and humans. Science 292: 1171–1175 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi A, Shore D 2007. Increased association of telomerase with short telomeres in yeast. Genes Dev 21: 1726–1730 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carneiro T, Khair L, Reis CC, Borges V, Moser BA, Nakamura TM, Ferreira MG 2010. Telomeres avoid end detection by severing the checkpoint signal transduction pathway. Nature 467: 228–232 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper JP, Nimmo ER, Allshire RC, Cech TR 1997. Regulation of telomere length and function by a Myb-domain protein in fission yeast. Nature 385: 744–747 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustig AJ, Petes TD 1986. Identification of yeast mutants with altered telomere structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci 83: 1398–1402 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcand S, Gilson E, Shore D 1997. A protein-counting mechanism for telomere length regulation in yeast. Science 275: 986–990 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNees CJ, Tejera AM, Martinez P, Murga M, Mulero F, Fernandez-Capetillo O, Blasco MA 2010. ATR suppresses telomere fragility and recombination but is dispensable for elongation of short telomeres by telomerase. J Cell Biol 188: 639–652 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalfe JA, Parkhill J, Campbell L, Stacey M, Biggs P, Byrd PJ, Taylor AM 1996. Accelerated telomere shortening in ataxia telangiectasia. Nat Genet 13: 350–353 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi T, Kanoh J, Saito M, Ishikawa F 2008. Fission yeast Pot1-Tpp1 protects telomeres and regulates telomere length. Science 320: 1341–1344 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser BA, Nakamura TM 2009. Protection and replication of telomeres in fission yeast. Biochem Cell Biol 87: 747–758 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser BA, Subramanian L, Khair L, Chang YT, Nakamura TM 2009. Fission yeast Tel1(ATM) and Rad3(ATR) promote telomere protection and telomerase recruitment. PLoS Genet 5: e1000622 doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000622 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser BA, Chang YT, Kosti J, Nakamura TM 2011. Tel1(ATM) and Rad3(ATR) kinases promote Ccq1–Est1 interaction to maintain telomeres in fission yeast. Nat Struct Mol Biol 18: 1408–1413 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naito T, Matsuura A, Ishikawa F 1998. Circular chromosome formation in a fission yeast mutant defective in two ATM homologues. Nat Genet 20: 203–206 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palm W, de Lange T 2008. How shelterin protects mammalian telomeres. Annu Rev Genet 42: 301–334 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smilenov LB, Morgan SE, Mellado W, Sawant SG, Kastan MB, Pandita TK 1997. Influence of ATM function on telomere metabolism. Oncogene 15: 2659–2665 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama T, Cam HP, Sugiyama R, Noma K, Zofall M, Kobayashi R, Grewal SI 2007. SHREC, an effector complex for heterochromatic transcriptional silencing. Cell 128: 491–504 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira MT, Arneric M, Sperisen P, Lingner J 2004. Telomere length homeostasis is achieved via a switch between telomerase-extendible and -nonextendible states. Cell 117: 323–335 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita K, Cooper JP 2008. Fission yeast Ccq1 is telomerase recruiter and local checkpoint controller. Genes Dev 22: 3461–3474 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vespa L, Couvillion M, Spangler E, Shippen DE 2005. ATM and ATR make distinct contributions to chromosome end protection and the maintenance of telomeric DNA in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev 19: 2111–2115 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto A, Hiraoka Y 2003. Monopolar spindle attachment of sister chromatids is ensured by two distinct mechanisms at the first meiotic division in fission yeast. EMBO J 22: 2284–2296 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]