Abstract
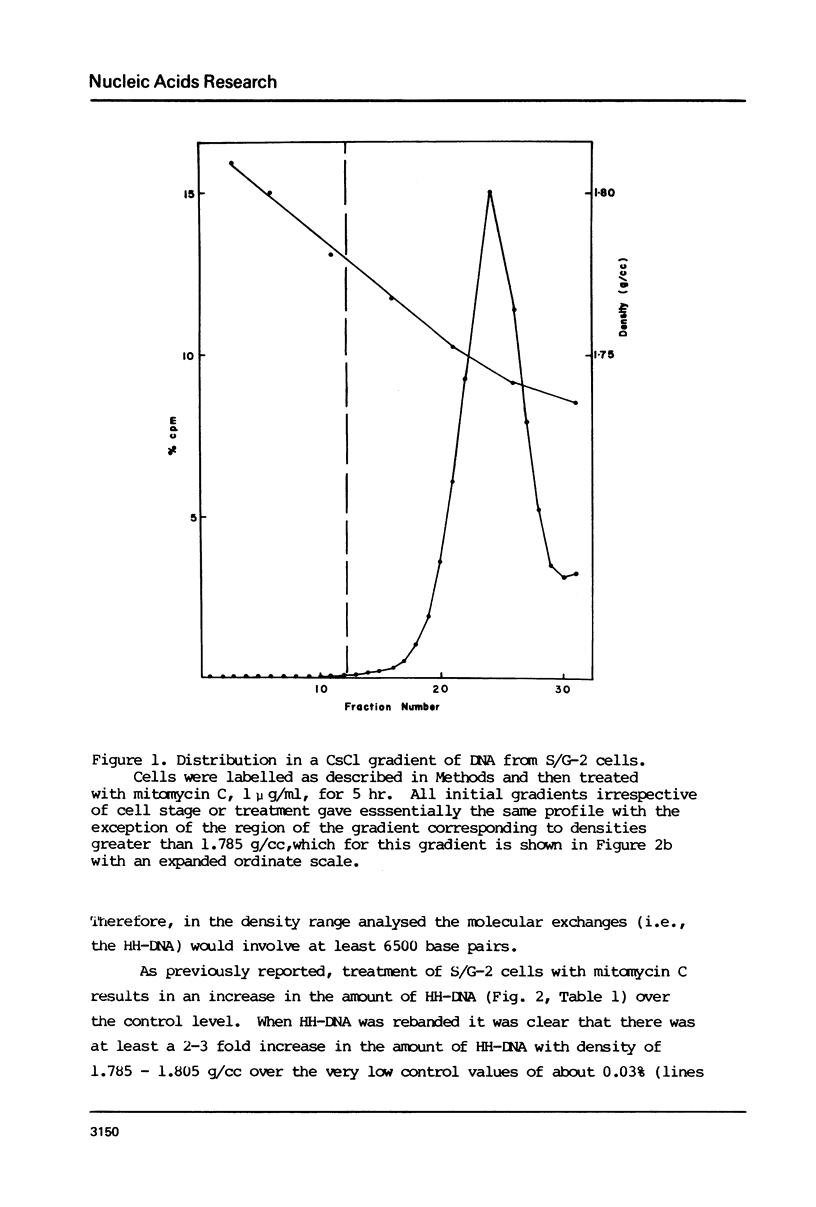
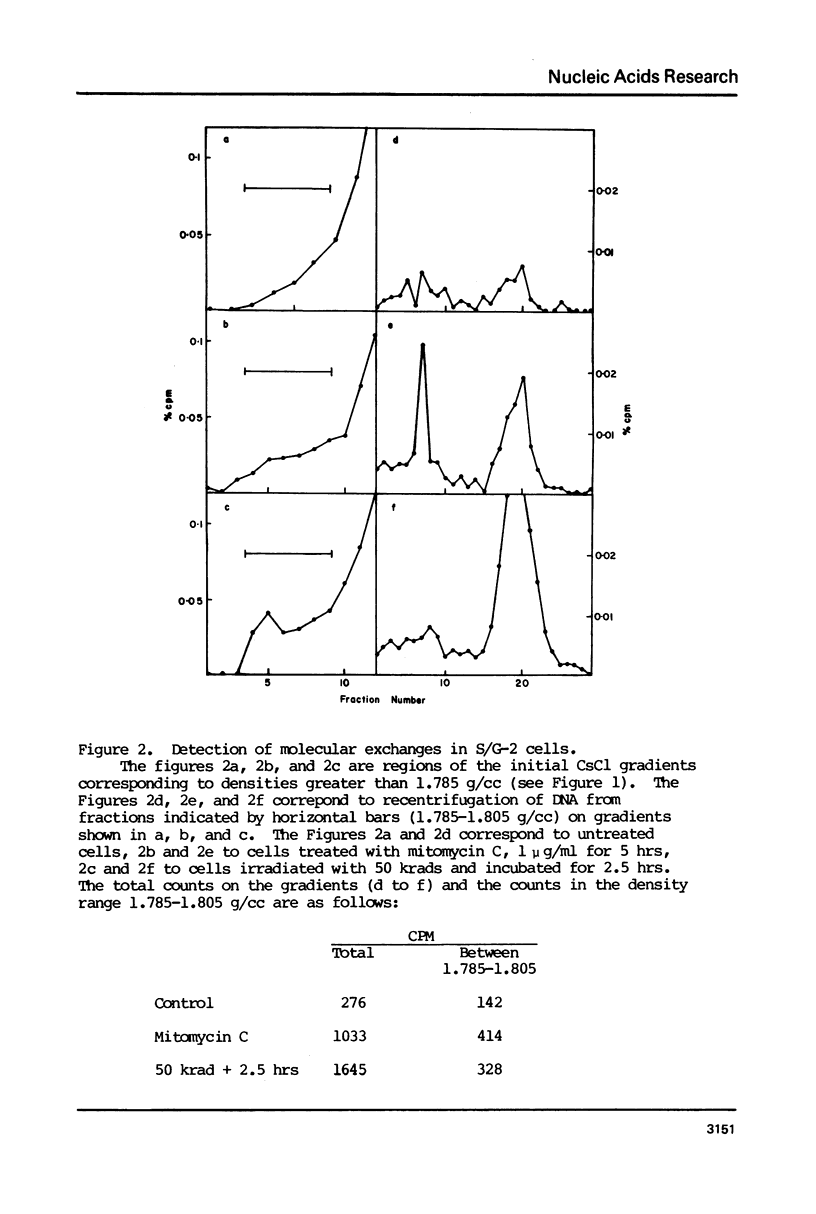
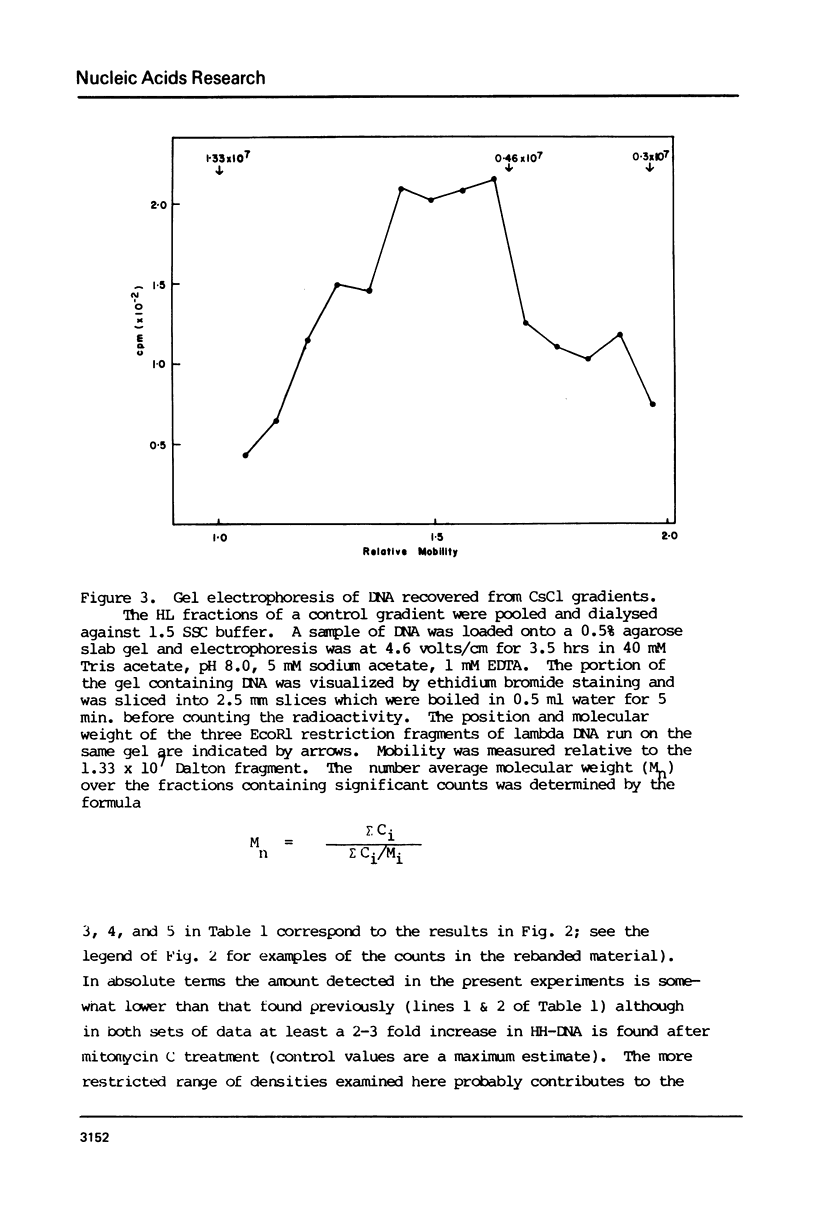
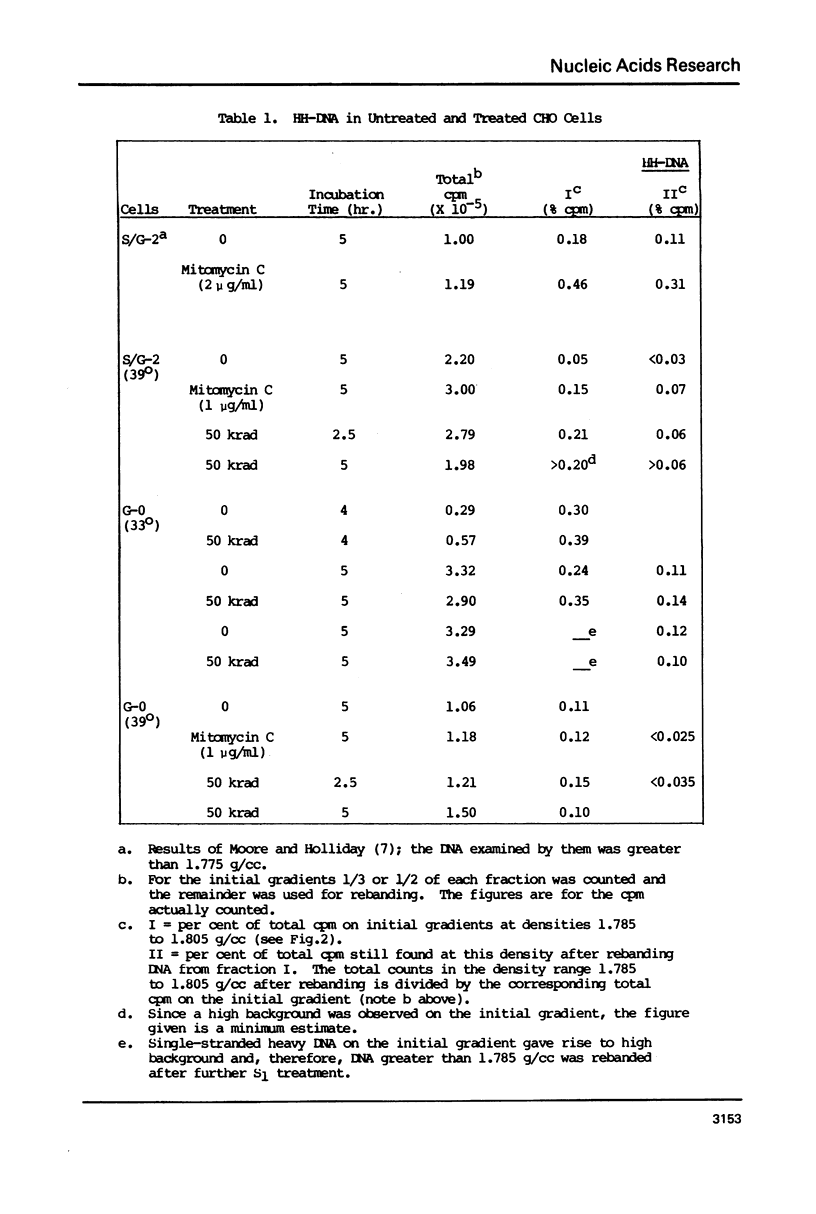
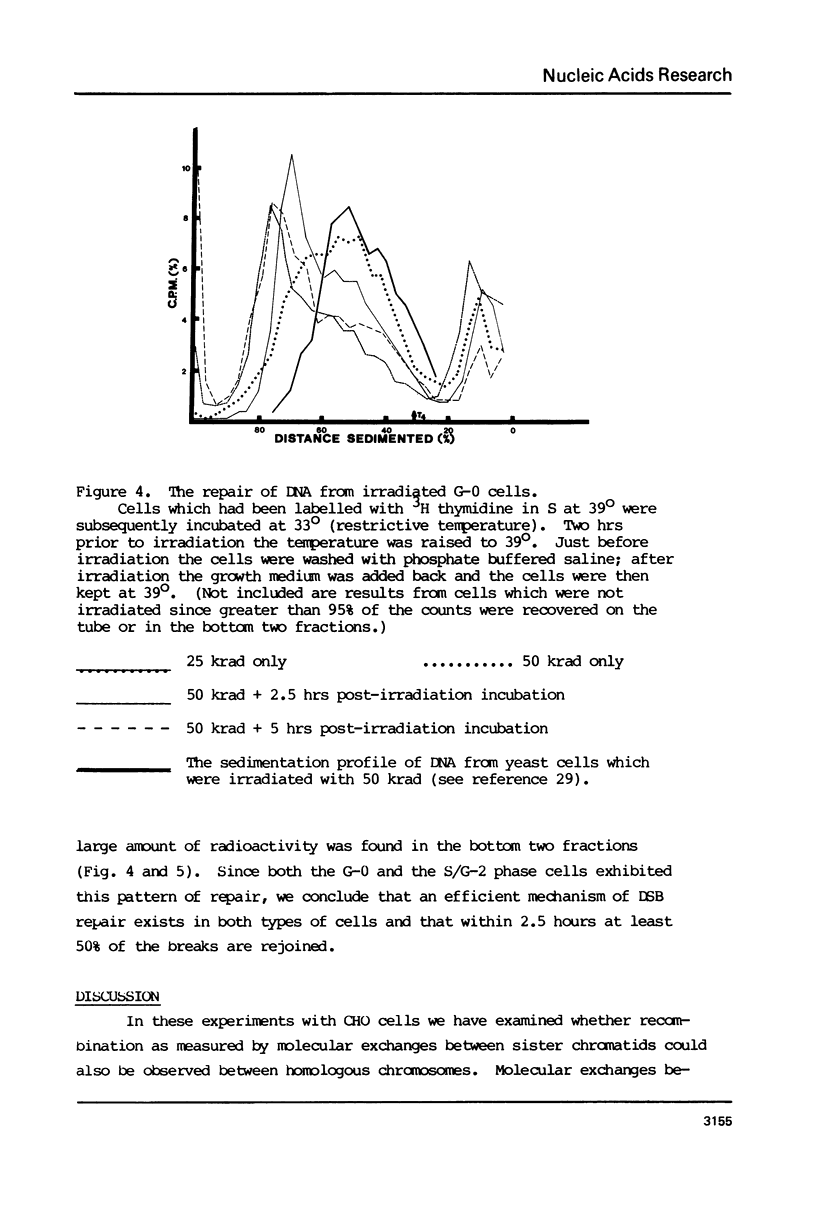
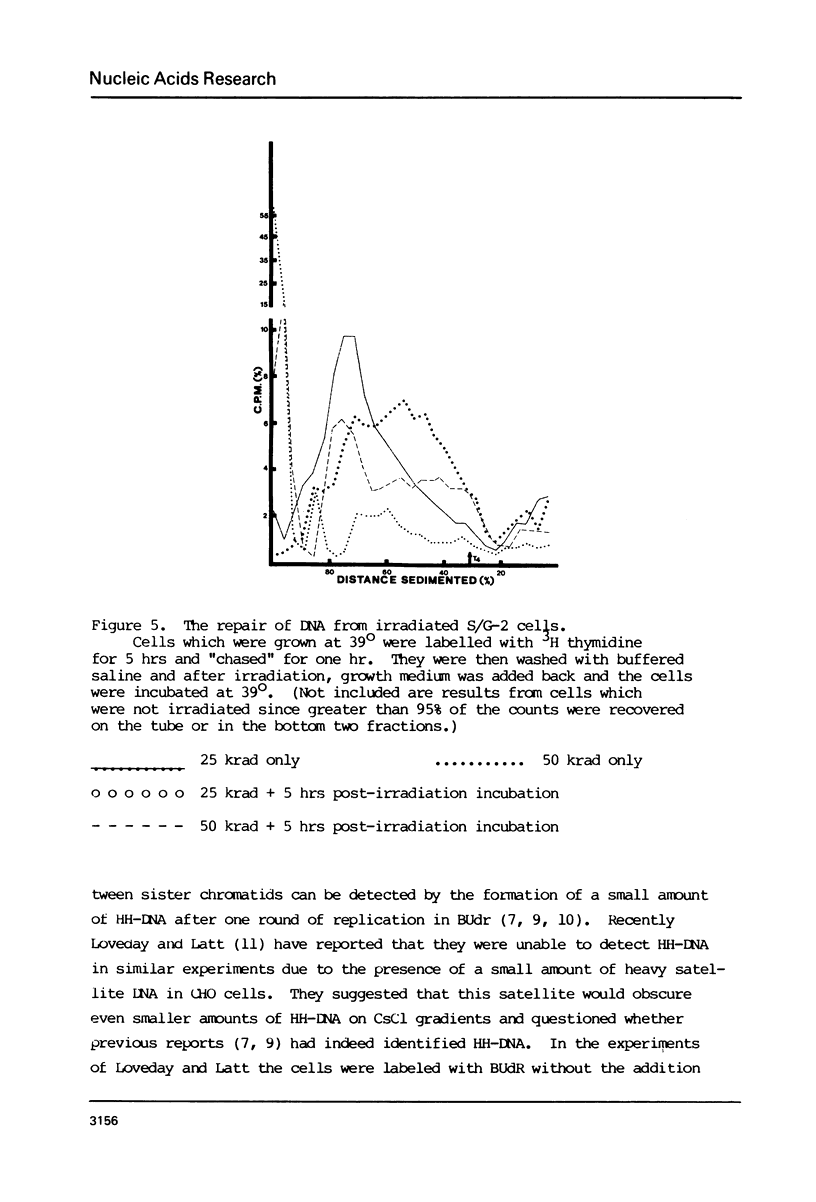
Molecular recombination and the repair of DNA double-strand breaks (DSB) have been examined in the G-0 and S phase of the cell cycle using a temperature-sensitive CHO cell line to test i) if there are cell cycle restrictions on the repair of DSB's' ii) the extent to which molecular recombination can be induced between either sister chromatids or homologous chromosomes and iii) whether repair of DSB's involves recombination (3). Mitomycin C (1-2 micrograms/ml) or ionizing radiation (50 krad) followed by incubation resulted in molecular recombination (hybrid DNA) in S phase cells. Approximately 0.03 to 0.10% of the molecules (number average molecular weight: 5.6 x 10(6) Daltons after shearing) had hybrid regions for more than 75% of their length. However, no recombination was detected in G-0 cells. Since the repair of DSB was observed in both stages with more than 50% of the breaks repaired in 5 hours, it appears that DSB repair in G-0 cells does not involve recombination between homologous chromosomes. The possibility is not excluded that repair in G-0 cells involves only small regions (less than 4 x 10(6) Daltons).
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Corry P. M., Cole A. Double strand rejoining in mammalian DNA. Nat New Biol. 1973 Sep 26;245(143):100–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crane M. S., Thomas D. B. Cell-cycle, cell-shape mutant with features of the Go state. Nature. 1976 May 20;261(5557):205–208. doi: 10.1038/261205a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deaven L. L., Petersen D. F. The chromosomes of CHO, an aneuploid Chinese hamster cell line: G-band, C-band, and autoradiographic analyses. Chromosoma. 1973;41(2):129–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00319690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber R. A., Unrau P. Isolation of cold-sensitive Chinese hamster cells. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Jun 19;138(3):233–242. doi: 10.1007/BF00269350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hittelman W. N., Rao P. N. Premature chromosome condensation. I. Visualization of x-ray-induced chromosome damage in interphase cells. Mutat Res. 1974 May;23(2):251–258. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(74)90145-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner K. M., Ruddle F. H. Study of mitomycin C-induced chromosomal exchange. Chromosoma. 1976 Jun 30;56(1):1–13. doi: 10.1007/BF00293724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAFER E. Radiation effects and mitotic recombination in diploids of Aspergillus nidulans. Genetics. 1963 Jan;48:27–45. doi: 10.1093/genetics/48.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato H. Induction of sister chromatid exchanges by UV light and its inhibition by caffeine. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Dec;82(2):383–390. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90356-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasin F., Hutchinson F. Repair of DNA double-strand breaks in Escherichia coli, which requires recA function and the presence of a duplicate genome. J Mol Biol. 1977 Oct 15;116(1):81–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90120-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman A. R., Stevens S. The production and repair of double strand breaks in cells from normal humans and from patients with ataxia telangiectasia. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 3;474(1):49–60. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(77)90213-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann A. R., Ormerod M. G. Double-strand breaks in the DNA of a mammalian cell after x-irradiation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Oct 15;217(2):268–277. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90526-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobban P. E., Kaiser A. D. Enzymatic end-to end joining of DNA molecules. J Mol Biol. 1973 Aug 15;78(3):453–471. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90468-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loveday K. S., Latt S. A. Search for DNA interchange corresponding to sister chromatid exchanges in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Nov;5(11):4087–4104. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.11.4087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonell M. W., Simon M. N., Studier F. W. Analysis of restriction fragments of T7 DNA and determination of molecular weights by electrophoresis in neutral and alkaline gels. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 15;110(1):119–146. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meneghini R., Hanawalt P. T4-endonuclease V-sensitive sites in DNA from ultraviolet-irradiated human cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 2;425(4):428–437. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. D., Holliday R. Evidence for the formation of hybrid DNA during mitotic recombination in Chinese hamster cells. Cell. 1976 Aug;8(4):573–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90225-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray N. E., Murray K. Manipulation of restriction targets in phage lambda to form receptor chromosomes for DNA fragments. Nature. 1974 Oct 11;251(5475):476–481. doi: 10.1038/251476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ormerod M. G., Lehmann A. R. The release of high molecular weight DNA from a mammalian cell (L-5178Y). Attachment of the DNA to the nuclear membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jan 28;228(2):331–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry P., Evans H. J. Cytological detection of mutagen-carcinogen exposure by sister chromatid exchange. Nature. 1975 Nov 13;258(5531):121–125. doi: 10.1038/258121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROMAN H., JACOB F. A comparison of spontaneous and ultraviolet-induced allelic recombination with reference to the recombination of outside markers. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1958;23:155–160. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1958.023.01.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick M. A., Martin P. The repair of double-strand breaks in the nuclear DNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its genetic control. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Jan 16;143(2):119–129. doi: 10.1007/BF00266917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick M. A. Similar responses to ionizing radiation of fungal and vertebrate cells and the importance of DNA doublestrand breaks. J Theor Biol. 1978 Apr 6;71(3):339–346. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(78)90164-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick M. A. The repair of double-strand breaks in DNA; a model involving recombination. J Theor Biol. 1976 Jun;59(1):97–106. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(76)80025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommelaere J., Miller-Faurès A. Detection by density equilibrium centrifugation of recombinant-like DNA molecules in somatic mammalian cells. J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 15;98(1):195–218. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommelaere J., Susskind M., Errera M. Chromosome and chromatid exchanges in Chinese hamster cells. Chromosoma. 1973;41(3):243–257. doi: 10.1007/BF00344019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sgaramella V., Van de Sande J. H., Khorana H. G. Studies on polynucleotides, C. A novel joining reaction catalyzed by the T4-polynucleotide ligase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1468–1475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siciliano M. J., Siciliano J., Humphrey R. M. Electrophoretic shift mutants in Chinese hamster ovary cells: evidence for genetic diploidy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1919–1923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarrant G. M., Holliday R. A search for allelic recombination in Chinese hamster cell hybrids. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Nov 18;156(3):273–279. doi: 10.1007/BF00267182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters R., Regan J. D. Recombination of UV-induced pyrimidine dimers in human fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Oct 4;72(3):803–807. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80204-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimm B. H. Anomalies in sedimentation. IV. Decrease in sedimentation coefficients of chains at high fields. Biophys Chem. 1974 Apr;1(4):279–291. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(74)80014-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann F. K. Induction of mitotic gene conversion by mutagens. Mutat Res. 1971 Mar;11(3):327–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


