Abstract
Background
In this study, we established a hypothetical tumor-lodds-metastasis (TLM) and tumor-ratio-metastasis (TRM) staging system. Moreover, we compared them with the 7th edition of American Joint Committee on Cancer tumor-nodes-metastasis (AJCC TNM) staging system in gastric cancer patients after D2 resection.
Methods
A total of 1000 gastric carcinoma patients receiving treatment in our center were selected for the analysis. Finally, 730 patients who received D2 resection were retrospectively studied. Patients were staged using the TLM, TRM and the 7th edition AJCC TNM system. Survival analysis was performed with a Cox regression model. We used two parameters to compare the TNM, TRM and TLM staging system, the −2log likelihood and the hazard ratio.
Results
The cut points of lymph node ratio (LNR) were set as 0, 0–0.3, 0.3–0.6, 0.6–1.0. And for the log odds of positive lymph nodes (LODDS), the cut points were established as≤−0.5, −0.5-0, 0-0.5, >0.5. There were significant differences in survival among patients in different LODDS classifications for each pN or LNR groups. When stratified by the LODDS classifications, the prognosis was highly homologous between those in the according pN or LNR classifications. Multivariate analysis showed that TLM staging system was better than the TRM or TNM system for the prognostic evaluation.
Conclusions
The TLM system was superior to the TRM or TNM system for prognostic assessment of gastric adenocarcinoma patients after D2 resection.
Introduction
Approximately one million people are diagnosed each year with gastric cancer, making it the fourth most common cancer and the second leading cause of cancer related death worldwide with an estimated 800,000 deaths caused by the disease [1]. The incidence of gastric cancer varies widely according to geographic region and is particularly common in Asia [2]. Until now the prognosis for gastric adenocarcinoma patients stays poor and Tumor-Node-Metastasis (TNM) staging system has been proved to be a prognostic factor which can effectively predict the prognosis of gastric adenocarcinoma patients [3]. From January 1, 2010 on, the most recent revision of American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) TNM stage for carcinoma of gastric (the 7th edition) was put into use [4]. Our previous study has shown that the 7th edition of AJCC TNM staging system was more reasonable compared with the AJCC 6th system in predicting the survival of gastric cancer patients to a certain degree [5]. However, some authors pointed out that the value of the latest number-based pN classification in the AJCC TNM staging system was affected by the number of lymph nodes retrieved [6]–[13]. A new ratio-based lymph nodes system (rN) has been proposed, which was defined as the ratio of the metastatic lymph nodes and the total number of retrieved lymph nodes after the resection. Recently, some studies has indicated that the TRM (Tumor-Ratio-Metastasis) staging system can be an alternative to the traditional TNM staging system [14]. However, some authors concerned that almost half of the Asian patients would not benefit from the ratio-based classification system since the definition of the rN0 classification was congruent with the pN0 classification [13].
Log odds of positive lymph nodes (LODDS), is defined as the log of the ratio between numbers of positive lymph nodes and the numbers of negative lymph nodes. To avoid singularity, 0.5 is usually added to both the numbers of positive lymph nodes and negative lymph nodes, log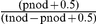 , in which the pnod is the number of positive lymph nodes and tnod means the total number of lymph nodes retrieved [15]. Sun et al. studied 2,547 gastric cancer patients and concluded that the LODDS system was more reliable than the Union Internationale Contre le Cancer (UICC) and AJCC pN system and the rN system for prognostic assessment [13]. Till now, there is no study focus on the prognostic significance of the tumor-lodds-metastasis (TLM) stage system for gastric cancer patients after D2 resection. The aim of our study is to compare the TLM, tumor-ratio-metastasis (TRM) and the 7th AJCC TNM staging system in prognostic assessment for carcinoma of the gastric after D2 resection in China.
, in which the pnod is the number of positive lymph nodes and tnod means the total number of lymph nodes retrieved [15]. Sun et al. studied 2,547 gastric cancer patients and concluded that the LODDS system was more reliable than the Union Internationale Contre le Cancer (UICC) and AJCC pN system and the rN system for prognostic assessment [13]. Till now, there is no study focus on the prognostic significance of the tumor-lodds-metastasis (TLM) stage system for gastric cancer patients after D2 resection. The aim of our study is to compare the TLM, tumor-ratio-metastasis (TRM) and the 7th AJCC TNM staging system in prognostic assessment for carcinoma of the gastric after D2 resection in China.
Results
Patient demographics
The median age of the 730 patients was 60 years (range 24–83 years). Among them, 522 were male and 208 were female. The overall 5-year survival for the whole group of patients was 55.4%, with median survival of 78.0 months. The median follow-up for the entire cohort was 48.0 months (range 3.0–175.0 months). The characteristics of the 730 gastric adenocarcinoma patients and the effect of clinical features on survival were summarized in Table 1. The total number of dissected lymph nodes was 12374, with an average of 17.0±11.4 (means±s.d.) dissected nodes per case (median 16.0, range 0–72). The mean number of metastatic nodes was 7.8±5.0 (median 4, range 0–70) in the overall series and 9.7±7.6 (median 7, range 1–70) in lymph nodes positive patients. The number of excised lymph nodes was less than 15 in 21.6% of patients who received resection.
Table 1. Demographics and univariate survival analysis results of the 730 gastric carcinoma patients.
| Factors | Numbers | 5 years OS (%) | P value |
| Gender | |||
| Male | 522 | 55.2 | |
| female | 208 | 56.0 | 0.544 |
| Age median 60 | |||
| <60 | 386 | 60.0 | |
| ≥60 | 344 | 50.2 | 0.004 |
| Tumor size | |||
| ≤5 cm | 470 | 61.5 | |
| >5 cm | 260 | 44.7 | <0.001 |
| Anemia | |||
| Yes | 127 | 60.6 | |
| No | 309 | 70.1 | 0.038 |
| Location of tumor | |||
| Proximal | 304 | 46.4 | |
| distal | 426 | 58.3 | <0.001 |
| Degree of differentiation | |||
| Well+Moderate | 200 | 54.1 | |
| Poor+signet ring cell | 530 | 45.8 | 0.007 |
| Total number of LN retrieved | |||
| <15 | 158 | 47.5 | |
| ≥15 | 572 | 60.2 | <0.001 |
| The 7th T stage (AJCC) | |||
| T1 | 144 | 91.8 | |
| T2 | 179 | 78.2 | |
| T3 | 133 | 57.8 | |
| T4 | 274 | 49.4 | <0.001 |
| The 7th N stage (AJCC) | |||
| N0 | 267 | 72.1 | |
| N1 | 113 | 63.7 | |
| N2 | 168 | 53.9 | |
| N3 | 182 | 26.8 | <0.001 |
| The R stage (LN) | |||
| R0 | 267 | 72.1 | |
| R1 | 195 | 65.6 | |
| R2 | 143 | 30.3 | |
| R3 | 125 | 13.0 | <0.001 |
| The L stage (LN) | |||
| LODDS1 | 305 | 71.2 | |
| LODDS2 | 174 | 47.9 | |
| LODDS3 | 142 | 25.9 | |
| LODDS4 | 109 | 14.8 | <0.001 |
| The 7th TNM stage (AJCC) | |||
| IA | 31 | 92.3 | |
| IB | 35 | 87.2 | |
| IIA | 32 | 74.2 | |
| IIB | 220 | 71.3 | |
| IIIA | 85 | 56.5 | |
| IIIB | 145 | 46.7 | |
| IIIC | 182 | 26.3 | <0.001 |
| The TRM stage | |||
| IA | 31 | 92.3 | |
| IB | 39 | 88.7 | |
| IIA | 40 | 83.9 | |
| IIB | 212 | 68.7 | |
| IIIA | 135 | 60.7 | |
| IIIB | 142 | 35.7 | |
| IIIC | 131 | 20.5 | <0.001 |
| The TLM stage | |||
| IA | 40 | 93.8 | |
| IB | 55 | 85.9 | |
| IIA | 35 | 78.3 | |
| IIB | 242 | 65.2 | |
| IIIA | 108 | 52.3 | |
| IIIB | 136 | 30.1 | |
| IIIC | 114 | 12.4 | <0.001 |
Abbreviations: AJCC, American Joint Committee on Cancer; TNM, Tumor-Node-Metastasis; TRM, Tumor-Ratio-Metastasis; TLM, Tumor-Lodds-Metastasis.
The classification of rN and LODDS intervals
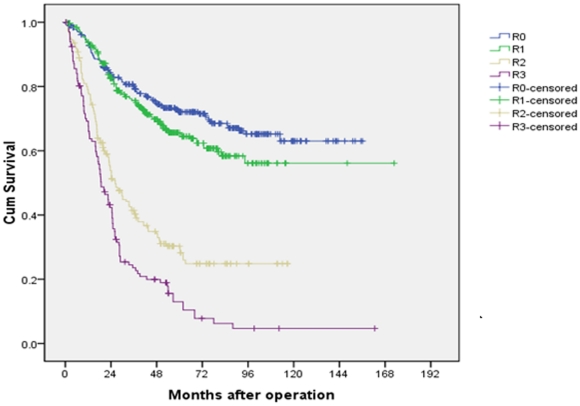
Table 2 listed the patient numbers and the 5-year survival rates of different groups according to the value of rN with an interval of 0.1 (ranging from 0 to 1.0). As shown, 4 groups were identified by combining patients with similar prognosis. Accordingly, a novel N classification, rN classification was established: R0 (rN = 0), R1 (0<rN≤0.3), R2 (0.3<rN≤0.6), R3 (0.6<rN≤1.0). The 5-year survival rates of R0, R1, R2 and R3 patients were 72.1%, 65.6%, 30.3% and 13.0%, respectively (P<0.001, Figure 1).
Table 2. Overall survival rates of gastric cancer patients with D2 resection according to the value of lymph nodes ratio (rN) with the interval of 0.1 (ranging from 0 to 1).
| No. | 5-YSR(%) | Pa | |
| rN = 0 | 267 | 72.1 | 0.039 |
| 0<rN≤0.1 | 66 | 68.0 | 0.897 |
| 0.1<rN≤0.2 | 70 | 67.3 | 0.921 |
| 0.2<rN≤0.3 | 59 | 67.5 | 0.007 |
| 0.3<rN≤0.4 | 62 | 40.2 | 0.373 |
| 0.4<rN≤0.5 | 52 | 33.9 | 0.677 |
| 0.5<rN≤0.6 | 29 | 32.9 | 0.021 |
| 0.6<rN≤0.7 | 33 | 24.4 | 0.418 |
| 0.7<rN≤0.8 | 39 | 21.3 | 0.092 |
| 0.8<rN≤0.9 | 22 | 12.7 | 0.597 |
| 0.9<rN≤1.0 | 31 | 10.2 |
5-YSR, 5-year survival rate.
Compared between adjacent groups.
Figure 1. Survival curves of gastric cancer patients with D2 resection according to rN stage.
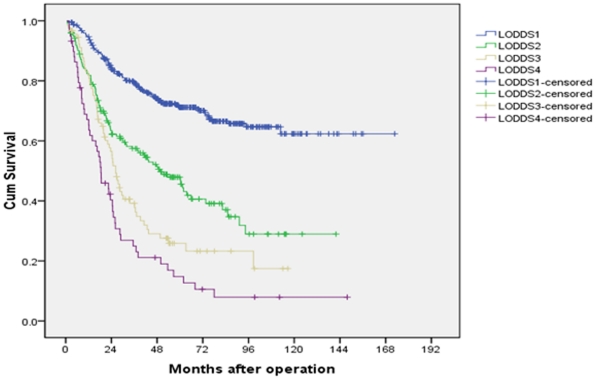
The value of LODDS ranged from −2.05 to 1.93. Table 3 listed the patient numbers and the 5-year survival rates of different groups according to the value of LODDS with an interval of 0.5. Since only three patients with a LODDS smaller than −2.00, we combined patients in the group LODDS≤−2.00 and patients in the group −2.00<LODDS≤−1.50 together. As shown, we identified 4 groups by combining patients with similar prognosis. Another novel N classification, LODDS classification was then established: LODDS1 (LODDS≤−0.5), LODDS2 (0.5<LODDS≤0), LODDS3 (0<LODDS≤0.5), LODDS4 (0.5<LODDS). The 5-year survival rates of LODDS1, LODDS2, LODDS3 and LODDS4 patients were 71.2%, 47.9%, 25.9% and 14.8%, respectively (P<0.001, Figure 2).
Table 3. Overall survival rates of gastric cancer patients with D2 resection according to the value of LODDS with the interval of 0.5 (ranging from −2.05 to 1.93).
| No. | 5-YSR(%) | Pa | |
| LODDS≤−1.5 | 96 | 75.7 | 0.418 |
| −1.5<LODDS≤−1.0 | 123 | 73.4 | 0.270 |
| −1.0<LODDS≤−0.5 | 86 | 65.3 | <0.001 |
| −0.5<LODDS≤0 | 174 | 47.9 | 0.009 |
| 0<LODDS≤0.5 | 142 | 25.9 | 0.005 |
| 0.5<LODDS≤1.0 | 48 | 12.2 | 0.342 |
| 1.0<LODDS≤1.5 | 28 | 17.0 | 0.437 |
| LODDS>1.5 | 33 | 11.0 |
5-YSR, 5-year survival rate.
Compared between adjacent groups.
Figure 2. Survival curves of gastric cancer patients with D2 resection according to LODDS stage.
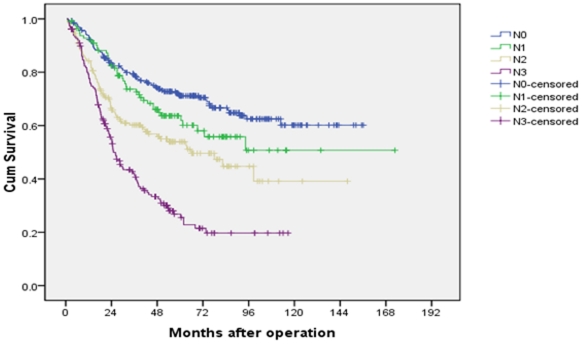
The 5-year survival rates of N0, N1, N2 and N3 (AJCC N classification) patients were 72.1%, 63.7%, 53.9% and 26.8%, respectively (P<0.001, Figure 3).
Figure 3. Survival curves of gastric cancer patients with D2 resection according to AJCC 7th N stage.
The Kaplan-Meier plots shown a good discriminatory ability among each group in these three N classifications.
Table 4 listed the 5-year survival rates of patients with different pN and rN classifications, stratified by LODDS. As shown, for patients in each of the pN or rN classification, significant differences in survival could always be observed among patients in different LODDS classification. For patients in each LODDS classification, prognosis was highly homologous between those in different pN or rN classifications. These results indicated that the LODDS classification is superior to the pN and rN classifications for prognostic assessment.
Table 4. Overall survival rates with different pN and rN classifications stratified by the LODDS staging system.
| LODDS1 | LODDS2 | LODDS3 | LODDS4 | P a | |||||
| No | 5-YSR(%) | No. | 5-YSR(%) | No. | 5-YSR(%) | No. | 5-YSR(%) | ||
| N stage | |||||||||
| N0 | 209 | 71.1 | 48 | 61.8 | 10 | 42.6 | - | - | 0.035 |
| N1 | 51 | 68.0 | 39 | 55.2 | 23 | 33.3 | - | - | 0.04 |
| N2 | 37 | 77.2 | 59 | 49.2 | 40 | 29.1 | 32 | 18.2 | <0.001 |
| N3 | 8 | 75.0 | 28 | 38.8 | 69 | 24.7 | 77 | 13.6 | 0.005 |
| P b | 0.796 | 0.396 | 0.872 | 0.892 | |||||
| R stage | |||||||||
| R0 | 205 | 70.3 | 54 | 60.4 | 8 | 42.0 | - | - | 0.009 |
| R1 | 100 | 71.3 | 85 | 51.6 | 10 | 29.4 | - | - | 0.026 |
| R2 | - | - | 35 | 47.3 | 78 | 28.7 | 30 | 15.4 | 0.018 |
| R3 | - | - | - | - | 46 | 26.3 | 79 | 14.8 | 0.003 |
| P c | 0.827 | 0.497 | 0.329 | 0.920 | |||||
Abbreviations: LODDS, Log Odds of Positive Lymph Nodes; No, number of patients; 5-YSRs, 5-year survival rate.
Comparison of overall survival rates between different LODDS groups.
Comparison of overall survival rates between different pN groups.
Comparison of overall survival rates between different rN groups.
Univariate and multivariate analyses of 5-year overall survival
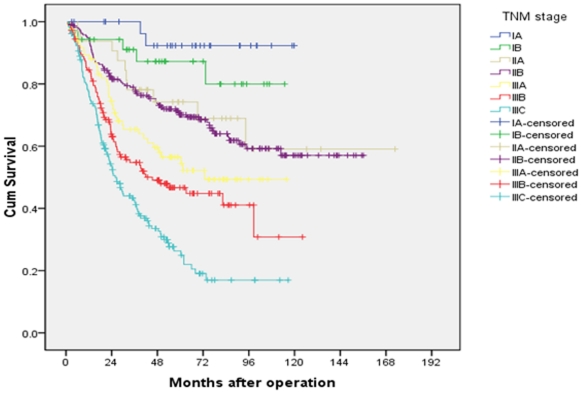
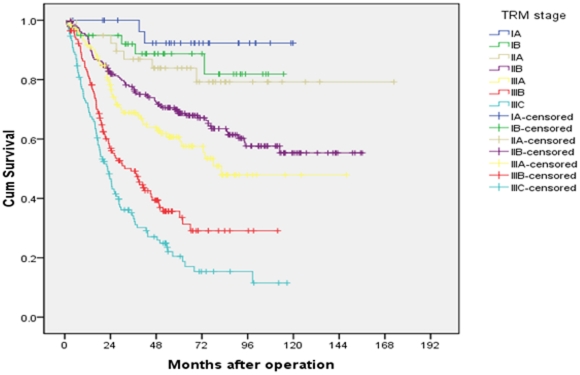
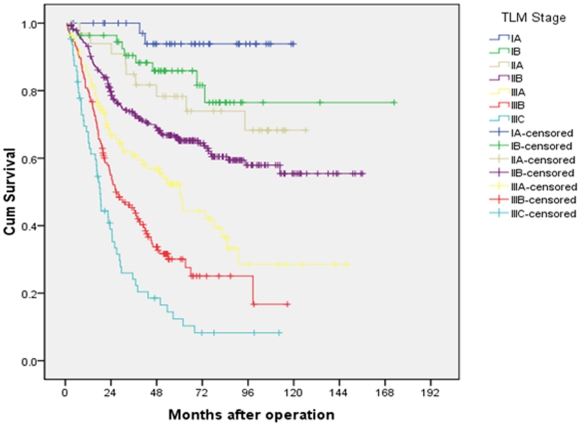
Both univariate and multivariate analyses were used to evaluate factors relating to 5-year overall survival. The items of age, tumor size, status of anemia, location of tumor, degree of differentiation, total number of lymph nodes retrieved, pT classification, pN classification, rN classification, LODDS and three staging systems were significantly related to 5-year overall survival (Table 1). In the AJCC 7th TNM staging system the 5-year overall survival rates of patients from stage IA to stage IIIC were 92.3% vs 87.2% vs 74.2% vs 71.3% vs 56.5% vs 46.7% vs 26.3%, respectively (P<0.001, Figure 4). There was similar survival curves between stages IIA and IIB. While in the TRM and TLM staging systems, no overlapping survival curve was found in the seven subgroups (Figures 5 and 6). The 5-years survival rates of patients from stage IA to stage IIIC in the TRM staging system were 92.3% vs 88.7% vs 83.9% vs 68.7% vs 60.7% vs 35.7% vs 20.5% (P<0.001). In the TLM staging system, the survival rates were 93.8% vs 85.9% vs 78.3% vs 65.2% vs 52.3% vs 30.1% vs 12.4%, respectively (P<0.001).
Figure 4. Survival curves of gastric cancer patients with D2 resection according to AJCC TNM staging system.
Figure 5. Survival curves of gastric cancer patients with D2 resection according to TRM staging system.
Figure 6. Survival curves of gastric cancer patients with D2 resection according to TLM staging system.
For the multivariable regression analysis, we firstly set up a model including age, status of anemia, size of tumor, tumor location, degree of differentiation, total number of lymph nodes retrieved and AJCC 7th TNM staging system. Then we set up a second model which was identical to the first one except that the AJCC 7th TNM staging system was replaced by the TRM staging system. In the third model we used the TLM staging system to replace the TRM system. We used two parameters to compare the TNM, TRM and TLM staging system, the −2log likelihood and the hazard ratio (HR). The higher the HR, the better the system. While the smaller the −2log likelihood, the better the system. Though in the three multivariable regression analysis systems, TNM, TRM and TLM were all independent factors for the overall survival (P<0.001 for these three parameters, Table 5). We found that the −2log likelihood of these three staging system were 1393.437, 1386.707 and 1382.555 for the TNM, TRM and TLM staging system, respectively. While the HRs were 1.366, 1.463 and 1.504 for the TNM, TRM and TLM staging system, respectively. Therefore we considered the TLM system was superior to the TRM and TNM system (Table 5).
Table 5. Three steps multivariate analysis of overall survival in gastric carcinoma.
| Factors | Characteristics | Multivariate Analysis 1 | Multivariate Analysis 2 | Multivariate Analysis 3 | |||||||
| Unfavorable | Favorable | Hazard ratio | 95%CI | P value | Hazard ratio | 95%CI | P value | Hazard ratio | 95%CI | P value | |
| Age | ≥60 | <60 | 1.016 | 1.000–1.032 | 0.056 | 1.258 | 0.881–1.796 | 0.206 | 1.302 | 0.913–1.858 | 0.145 |
| Anemia | Yes | No | 1.509 | 0.975–2.335 | 0.065 | 1.692 | 1.099–2.606 | 0.017 | 1.710 | 1.110–2.635 | 0.015 |
| Size | ≥5 cm | <5 cm | 1.512 | 1.059–2.158 | 0.023 | 1.542 | 1.082–2.198 | 0.017 | 1.544 | 1.084–2.200 | 0.016 |
| Location | Proximal | Distal | 0.730 | 0.497–1.073 | 0.109 | 0.742 | 0.509–1.081 | 0.120 | 0.753 | 0.515–1.100 | 0.142 |
| Degree of differentiation | Poor+signet ring cell | Well+Moderate | 0.599 | 0.379–0.946 | 0.028 | 0.588 | 0.375–0.924 | 0.021 | 0.569 | 0.362–0.895 | 0.015 |
| Total number of LN retrieved | <15 | ≥15 | 0.702 | 0.478–1.032 | 0.072 | 0.865 | 0.600–1.246 | 0.437 | 1.395 | 0.668–1.395 | 0.850 |
| AJCC 7th TNM stage | III+IV | I+II | 1.366 | 1.166–1.601 | <0.001 | ||||||
| TRM stage | III+IV | I+II | 1.463 | 1.286–1.664 | <0.001 | ||||||
| TLM stage | III+IV | I+II | 1.504 | 1.320–1.713 | <0.001 | ||||||
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; LN, lymph node; AJCC, American Joint Committee on Cancer; TNM, Tumor-Node-Metastasis; TRM, Tumor-Ratio-Metastasis; TLM, Tumor-Lodds-Metastasis.
Discussion
For decades, the involvement of regional lymph nodes with cancer in malignant diseases has been considered as one of the most important prognostic factors. Other information pertaining to the total numbers of lymph nodes and negative lymph nodes has become the focus of studies in these years [15]. LNR and LODDS were two new indices that have been considered important and promising recently. The superiority of LNR as a prognostic classification in various malignancies, including gastric cancer, compared to the pN classification which is basing on the absolute number of metastasis lymph nodes (MLN) in predicting prognosis of gastric cancer patients [10], [12], [14].
There is little data on the study of LODDS. Considering its unique statistical characteristic, LODDS has the potential to become a superior prognostic index. Our study shown that the LODDS classification was superior to the pN and rN classifications for prognostic assessment. In an analysis of the prognostic factors related to lymph nodes in 24,477 colon cancer patients extracted from the SEER database, Wang et al. [15] concluded that LODDS was a better prognostic factor than LNR. Vinh-Hung et al. [16] and Yildirm et al [17] both reached another conclusion that the estimated LODDS provided similar result to those with LNR basing on the analysis of node positive breast cancer patients. There were several reasons that made LODDS classification superior to the rN and pN classification. Sun et al. [13] proposed that it might because of its potential of discriminating patients with the same ratio of nodes metastasis but different survival. Wang et al. [14] considered that LODDS was a function of the number of negative lymph nodes, whereas LNR was a function of total number of lymph nodes. In our study, we compared the overall survival rates of patients in different pN, rN and LODDS classifications and we observed that all the three N classifications were all significant different in predicting the survival. Moreover, we found that the significant differences in survival could always be found for patients in each of the pN or rN classifications when stratifying by LODDS. However, prognosis was highly homologous for patients in each of the LODDS classifications when stratifying by the pN or rN classifications. It is one evidence showing that the superiority of LODDS over the LNR or the AJCC N stage in gastric cancer.
Wang et al. [14] analyzed 1343 cases of gastric cancer patients who underwent D2 resection and clasified the cut points of LNR as 0, 0–0.3, 0.3–0.6 and >0.6. They concluded that the TRM staging system may be considered as an alternative to the 7th TNM system. While in some other reports the best cut points of LNR differed. In the study carried out by Bando et al. [18], it was 0, 0–0.1, 0.1–0.25 and ≥0.25. Sun et al. [13] analyzed 2547 cases of gastric cancer patients and classified the best cut points of LNR as 0, 1–0.2, 0.21–0.5 and >0.5. The intervals of N ratio classification were determined in our study by comparing the overall survival rates according to the rN with an initial interval of 0.1 and combing patients with similar prognosis. The intervals of LODDS were also determined by using the best cutoff approach and considering the patients' survival (log-rank statistic) with an initial interval of 0.5 as the dependent variable. According to this, in our manuscript, the cut points of lymph node ratio were set as 0, 0–0.3, 0.3–0.6, 0.6–1.0. And for the log odds of positive lymph nodes (LODDS), the cut points were established as≤−0.5, −0.5-0, 0-0.5, >0.5. Only 4 groups were identified by combining patients with similar prognosis which is comparible with the N classification in the AJCC 7th staging system. While Sun et al. [13] established the LODDS classifications as ≤−1.5, −1.5<LODDS≤−1.0, −1.0<LODDS≤−0.5, −0.5<LODDS≤0 and >0.
Basing on the superiority of LODDS to LNR and the pN classification, we therefore combined the pT stage and the two new N classifications (LODDS and rN) together to form the hypothetical TLM, TRM staging system and then compared them with the AJCC TNM staging system. The main finding of the present study is that the new TLM staging system is superior to the TRM or TNM staging system for prognostic prediction by using Cox regression multivariate analysis. Though the Kaplan-Meier plot shown a good discriminatory ability among stages IA through IIIC with all the three staging systems, we found that there was no significant difference between patients with stage IIA and IIB, P = 0.589. which was similar to our previous study [5]. The implementation of TLM staging system led to the identification of subgroups of patients prognostically more significantly than those classified by the TNM or TRM system. Though in the three multivariable regression analysis systems, TNM, TRM and TLM were all independent factors for the overall survival (P<0.001 for these three parameters. Table 5). We found that the −2log likelihood of the TLM staging system was the lowest and the HRs of the TLM staging system was the highest. Therefore we considered the TLM system was superior to the TRM and TNM system.
In our study, all the patients received D2 lymphadenectomy with R0 resection, and the majority of patients (78.4%) had more than 15 lymph nodes retrieved. Therefore we did not discuss the effect of lymph node number retrieved on the three staging systems.
The authors are not aware of any other studies addressing the superiority of TLM staging system in gastric cancer in China. In this investigation performed with 730 gastric adenocarcinoma we came to the following conslusions: 1) LODDS is superior to pN or rN classifications in predicting the 5-year overall survival rates of gastric adenocarcinoma patients. 2) The TLM staging system was better than the TRM or TNM.in predicting the overall survival of patients with gastric adenocarcinoma after D2 resection. Incorporating LODDS into the staging system of gastric cancer will enable clinicians to more accurately predict the prognosis of patients. The limitation of current study is in its retrospective analysis setting and from a single-institution experience. The impact of various treatments related outcome could not be evaluated fully in this study. External validation by using other large database for evaluating the prognostic effect of LODDS and TLM system must be taken prior to the recommendation for its practical usage.
Methods
Ethics Statement
All patients provided written informed consent for their information to be stored in the hospital database; we obtained separate consent for use of research. Study approval was obtained from independent ethics committees at Cancer Center of Sun Yat-Sen University. The study was undertaken in accordance with the ethical standards of the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki.
Patients
Between January 1996 and January 2006, the medical records of 1000 pathology-proven gastric adenocarcinoma patients who were diagnosed and received treatment in the Cancer Center of Sun Yat-Sen University were retrospectively analyzed. Eligibility criteria were: (1) patients aged between 18 and 75 years of age, (2) patients receiving D2 resection carried out by experienced surgeons in our hospital following the Japanese Gastric Cancer Association (JGCA) guidelines [19], without macroscopic or microscopic residual tumor, (3) patients with a ≥3 months postoperative survival time and (4) patients without a history of other prior malignancy. Finally, 730 patients were included for the analysis.
The intervals of rN classification were determined by comparing overall survival rates according to rN with an initial interval of 0.1 and combining patients with similar prognosis (Table 2). Similarly, LODDS classification intervals were determined by comparing overall survival rates according to the value of LODDS with an initial interval of 0.5 and combing patients with similar prognosis (Table 3).
To make the study compatible with the 7th edition of AJCC TNM staging system, we proposed another two staging systems on the basis of rN and LODDS classifications respectively. Considering that no patients with distant metastasis were included in this study, there is no stage IV patients in these three staging systems. The TRM staging system is as follows: IA, T1R0; IB, T1R1, T2R0; IIA, T1R2, T2R1, T3R0; IIB, T1R3, T2R2, T3R1, T4aR0; IIIA, T2R3, T3R2, T4aR1; IIIB, T3R3, T4aR2, T4bR0, T4bR1; IIIC, T4aR3, T4bR2, T4bR3. The TLM staging system is as follows: IA, T1L1; IB, T1L2, T2L1; IIA, T1L3, T2L2, T3L1; IIB, T1L4, T2L3, T3L2, T4aL1; IIIA, T2L4, T3L3, T4aL2; IIIB, T3L4, T4aL3, T4bL1, T4bL2; IIIC, T4aL4, T4bL3, T4bR4.
Clinical data collected for subsequent analysis included gender (male or female), age at diagnosis (<60 or ≥60. The median age was 60.), tumor size (≤5 cm or >5 cm), anemia (yes or no), primary tumor site (proximal or distal), degree of differentiation (well+moderate differentiated carcinoma or poor+signet ring cell differentiated carcinoma), total number of lymph nodes retrieved (<15 or ≥15), pT stage (7th AJCC classification), pN stage (7th AJCC classification), rN stage, LODDS stage, TNM stage (7th AJCC classification), TRM stage and TLM stage (Table 1).
During the study period we did not have a standardized protocol for postoperative chemotherapy and (or) radiotherapy. Adjuvant therapy was suggested to all patients with T3–T4 classification or positive lymph node involvement; however, only 548 (75.1%) patients completed the adjuvant treatments. No patients received the adjuvant radiotherapy. Until July 2011, there were 321 patients died from the disease.
Statistical analysis
All statistical analysis were performed by Statistical Package of Social Sciences 13.0 software. P value<0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. The Kaplan-Meier method was used to estimate the 5-year overall survival. For patients who remained alive, data were censored at the date of the last contact. Kaplan-Meier analysis with log-rank testing was used for univariate analysis. Overall survival rates were compared with different pN and rN classification when stratifying by LODDS and with different LODDS when stratifying by pN or rN classification. For the multivariate analysis, we firstly set up a model including age, status of anemia, size of tumor, tumor location, degree of differentiation, total number of lymph nodes retrieved and AJCC 7th TNM staging system. Then we set up a second model which was identical to the first one except that the AJCC 7th TNM staging system was replaced by the TRM staging system. In the third model we used the TLM staging system to replace the TRM system. We used two parameters to compare the TNM, TRM and TLM staging system, the −2log likelihood and the hazard ratio (HR). The higher the HR, the better the system. While the smaller the −2log likelihood, the better the system.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully thank the staff members in the Department of Medical Oncology and GI Surgery Oncology at Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center for their suggestion and assistance.
Footnotes
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Funding: This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China grant 30672408 Guangzhou Bureau of Science and Technology grant 2006Z3-E0041 and Sun Yat-sen University 985 Program Initiation Fund (China). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Kamangar F, Dores GM, Anderson WF. Patterns of cancer incidence, mortality, and prevalence across five continents: defining priorities to reduce cancer disparities in different geographic regions of the world. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:2137–2150. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.05.2308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Moore MA, Eser S, Igisinov N, Igisinov S, Mohagheghi MA, et al. Cancer epidemiology and control in North-Western and Central Asia - past, present and future. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2010;2:17–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ichikura T, Tomimatsu S, Uefuji K, Kimura M, Uchida T, et al. Evaluation of the New American Joint Committee on Cancer/International Union against cancer classification of lymph node metastasis from gastric carcinoma in comparison with the Japanese classification. Cancer. 1999;86:553–558. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0142(19990815)86:4<553::aid-cncr2>3.0.co;2-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Edge SB, Compton CC. The American Joint Committee on Cancer: the 7th Edition of the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual and the Future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17:1471–1474. doi: 10.1245/s10434-010-0985-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Qiu MZ, Wang ZQ, Zhang DS, Liu Q, Luo HY, et al. Comparison of 6th and 7th AJCC TNM Staging Classification for Carcinoma of the Stomach in China. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011;18:1869–1876. doi: 10.1245/s10434-010-1542-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yoo CH, Noh SH, Kim YI, Min JS. Comparison of prognostic significance of nodal staging between old (4th ed.) and new (5th ed.) UICC TNM classification for gastric carcinoma. International Union Against Cancer. World J Surg. 1999;23:492–497. doi: 10.1007/pl00012337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Nio Y, Yamasawa K, Yamaguchi K, Itakura M, Omori H, et al. Problems in the N-classification of the new 1997 UICC TNM stage classification for gastric cancer: an analysis of over 10 years' outcome of Japanese patients. Anticancer Res. 2003;23:697–705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Shen JY, Kim S, Cheong JH, Kim YI, Hyung WJ, et al. The impact of total retrieved lymph nodes on staging and survival of patients with pT3 gastric cancer. Cancer. 2007;110:745–751. doi: 10.1002/cncr.22837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bouvier AM, Haas O, Piard F, Roignot P, Bonithon-Kopp C, et al. How many nodes must be examined to accurately stage gastric carcinomas? Results from a population based study. Cancer. 2002;94:2862–2866. doi: 10.1002/cncr.10550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lee HK, Yang HK, Kim WH, Lee KU, Choe KJ, et al. Influence of the number of lymph nodes examined on staging of gastric cancer. Br J Surg. 2001;88:1408–1412. doi: 10.1046/j.0007-1323.2001.01875.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ichikura T, Ogawa T, Chochi K, Kawabata T, Sugasawa H, et al. Minimum number of lymph nodes that should be examined for the International Union Against Cancer/American Joint Committee on Cancer TNM classification of gastric carcinoma. World J Surg. 2003;27:330–333. doi: 10.1007/s00268-002-6730-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sun Z, Zhu GL, Lu C, Guo PT, Huang BJ, et al. The impact of N-ratio in minimizing stage migration phenomenon in gastric cancer patients with insufficient number or level of lymph node retrieved: results from a Chinese mono-institutional study in 2159 patients. Ann Oncol. 2009;20:897–905. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdn707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sun Z, Xu Y, Li de M, Wang ZN, Zhu GL, et al. Log odds of positive lymph nodes: a novel prognostic indicator superior to the number-based and the ratio-based N category for gastric cancer patients with R0 resection. Cancer. 2010;116:2571–2580. doi: 10.1002/cncr.24989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wang W, Xu DZ, Li YF, Guan YX, Sun XW, et al. Tumor–ratio–metastasis staging system as an alternative to the 7th edition UICC TNM system in gastric cancer after D2 resection–results of a single-institution study of 1343 Chinese patients. Ann Oncol. 2011;22:2049–2056. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdq716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wang J, Hassett JM, Dayton MT, Kulaylat MN. The prognostic superiority of log odds of positive lymph nodes in stage III colon cancer. J Gastrointest Surg. 2008;12:1790–1796. doi: 10.1007/s11605-008-0651-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Vinh-Hung V, Verschraegen C, Promish DI, Cserni G, Van de Steene J, et al. Ratios of involved nodes in early breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2004;6:R680–688. doi: 10.1186/bcr934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Yildirim E, Berberoglu U. Lymph node ratio ismore valuable than level III involvement for prediction of outcome in node-positive breast carcinoma patients. World J Surg. 2007;31:276–289. doi: 10.1007/s00268-006-0487-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bando E, Yonemura Y, Taniguchi K, Fushida S, Fujimura T, et al. Outcome of ratio of lymph node metastasis in gastric carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2002;9:775–784. doi: 10.1007/BF02574500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Japanese Gastric Cancer Association. Japanese Classification of Gastric Carcinoma—2nd English Edition. Gastric Cancer. 1998;1:10–24. doi: 10.1007/s101209800016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]