Abstract
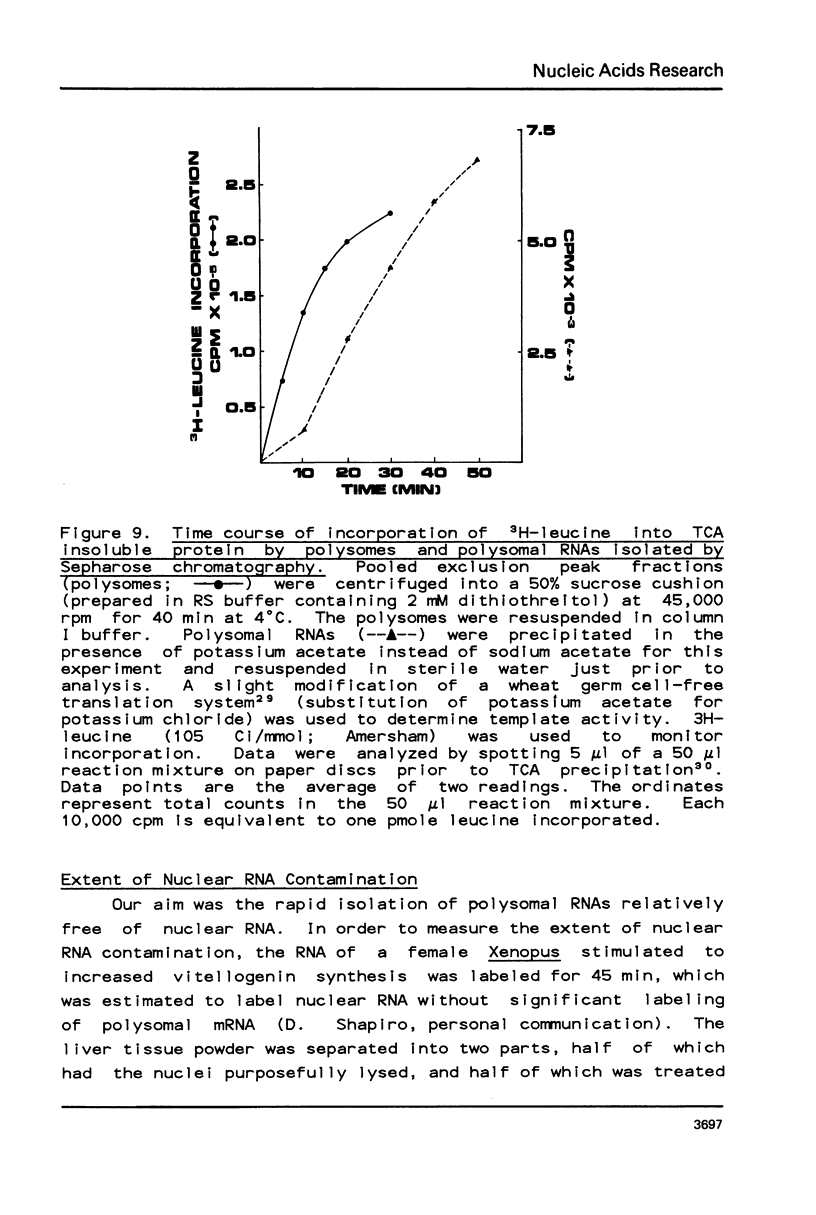
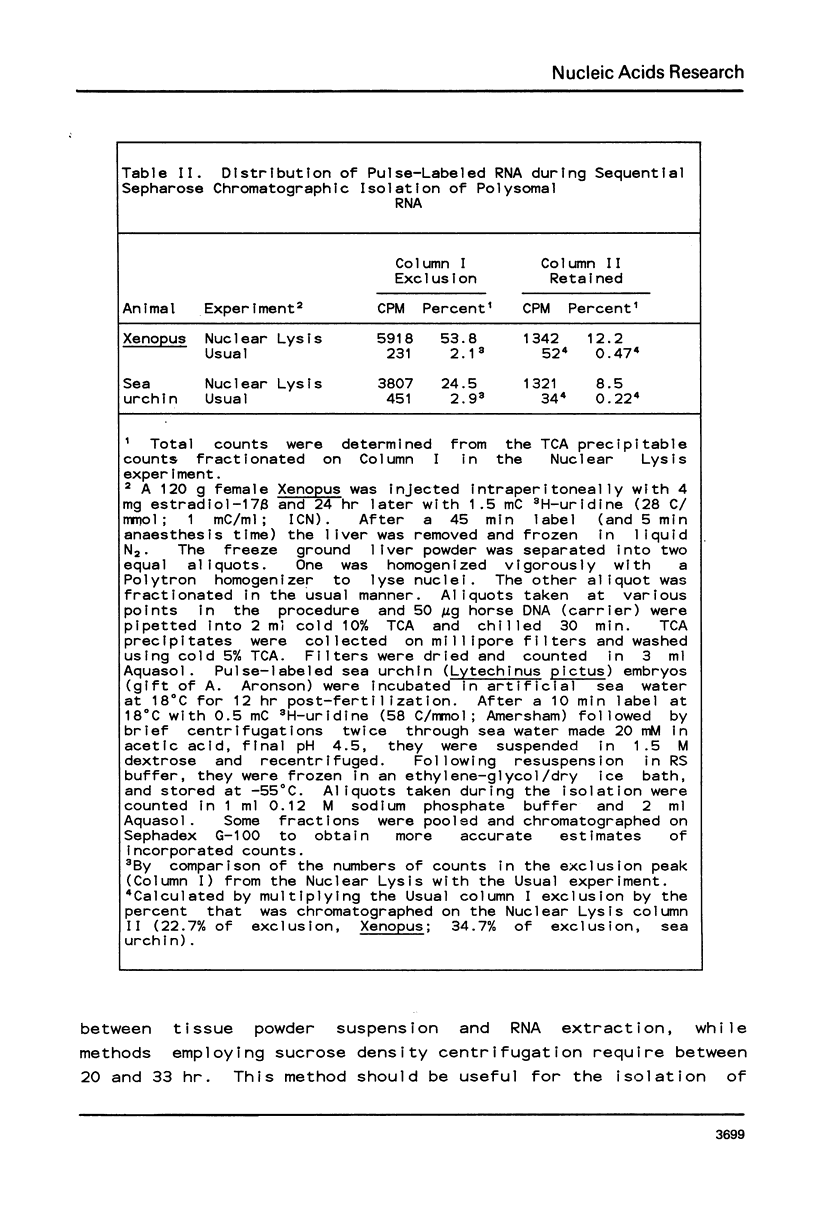
Analyses of sequence complexities, stage specific gene expression, and mRNA sequence divergence require polysomal RNA preparations relatively free of nuclear RNA contamination. Conventional procedures for the isolation of uncontaminated polysomal RNAs which rely on sucrose density centrifugations are laborious and unsuitable for large scale isolations. We describe here a method using sequential Sepharose chromatography for isolating polysomes and polysomal RNAs depleted for nuclear RNA. Polysomes and polysomal RNAs isolated from livers of Xenopus stimulated to produce vitellogenin were capable of directing protein synthesis in vitro and showed little evidence of degradation. The polysomal RNAs contained less than 0.5% of nuclear RNA.
Full text
PDF
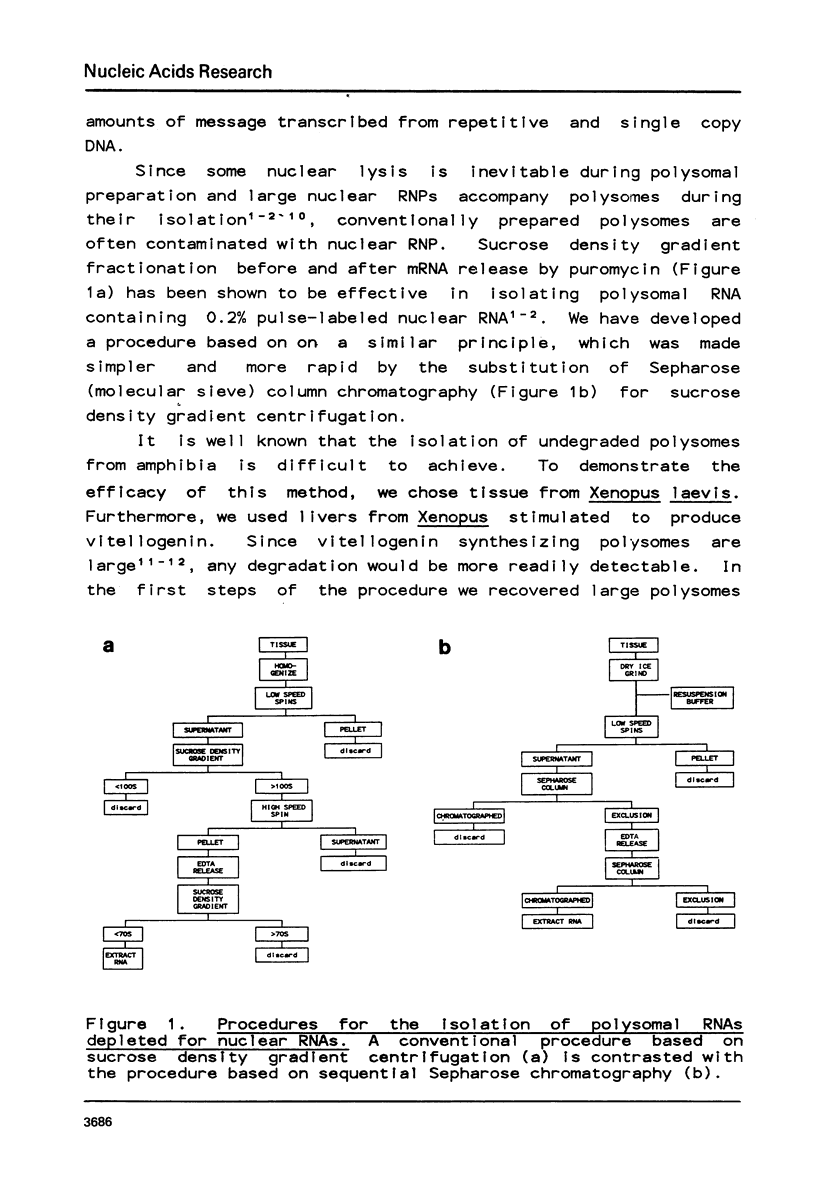

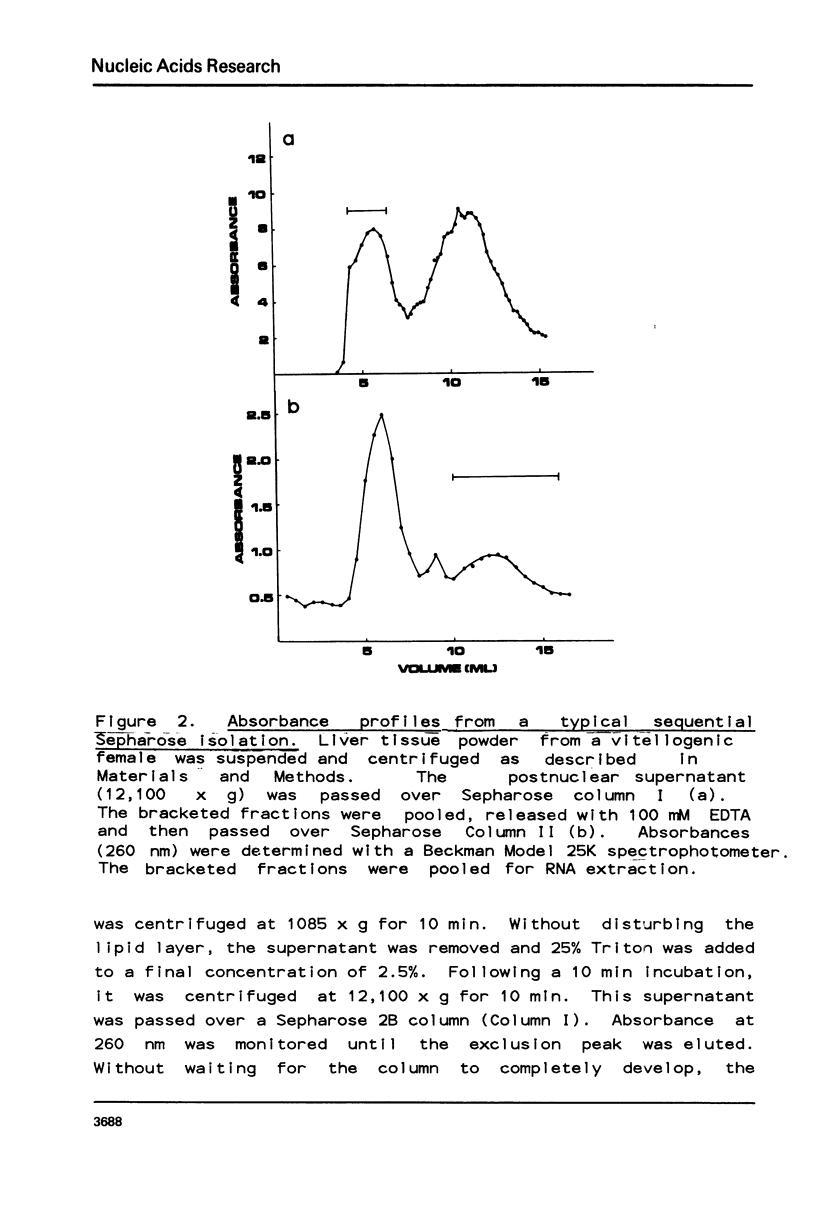

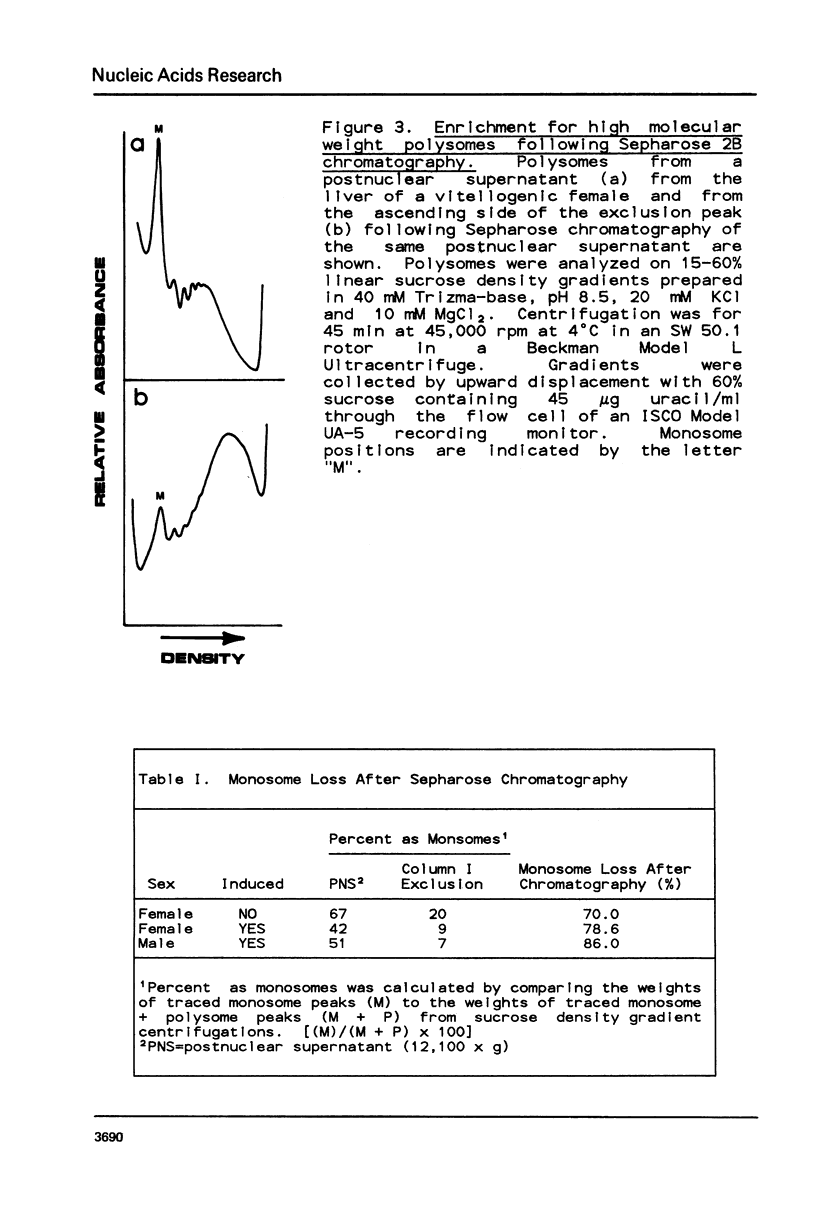
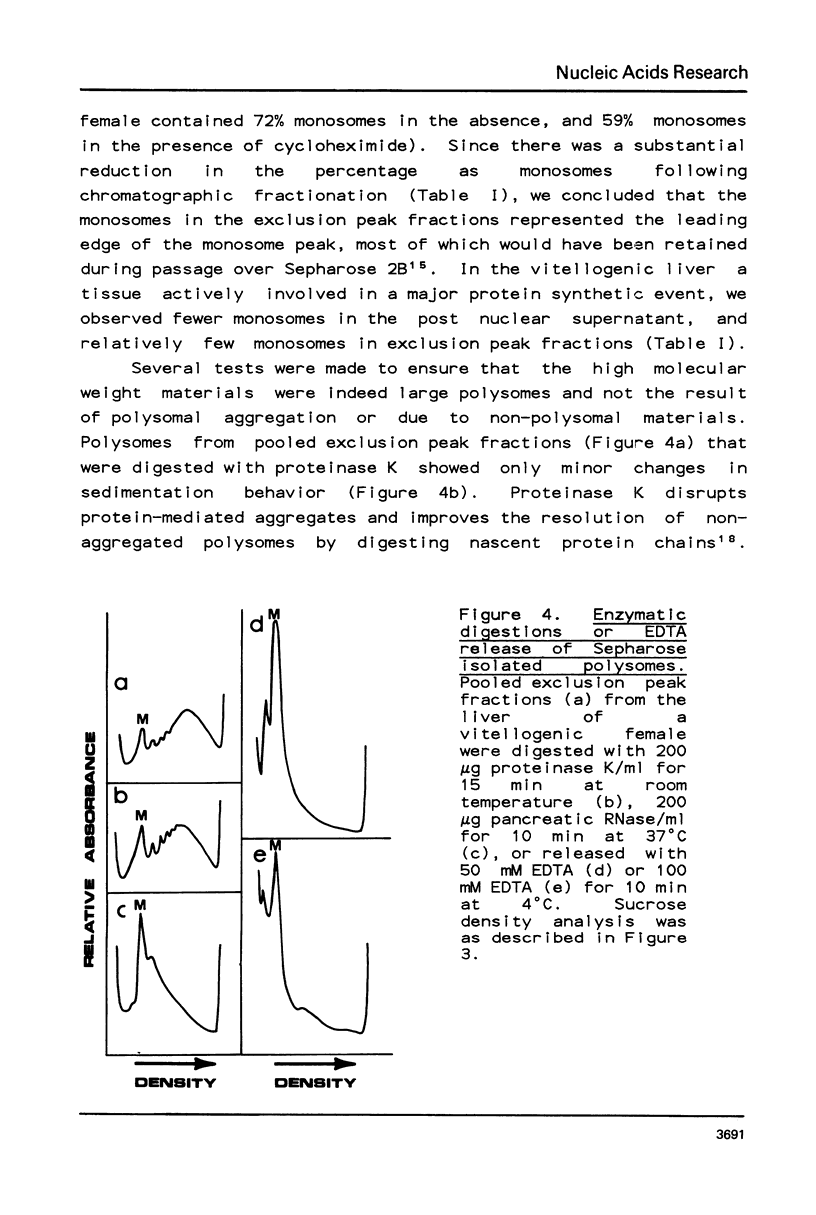

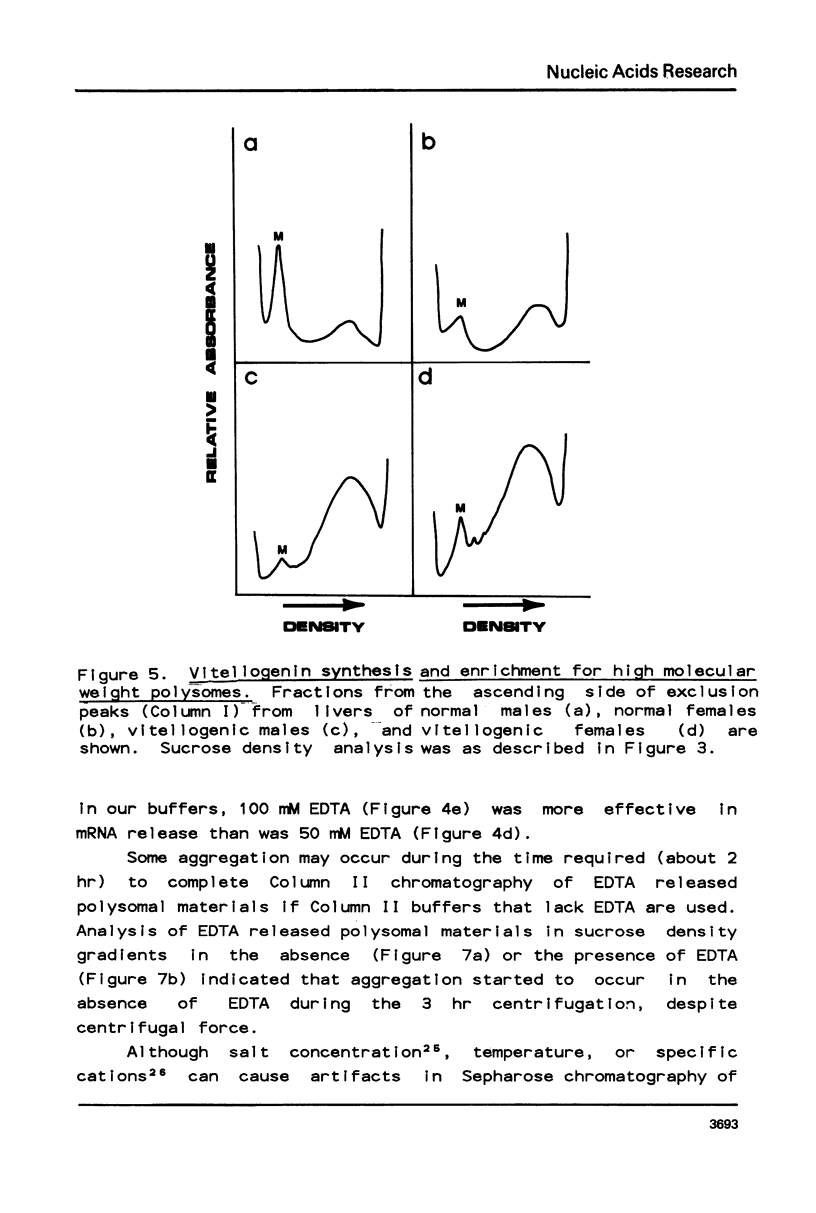
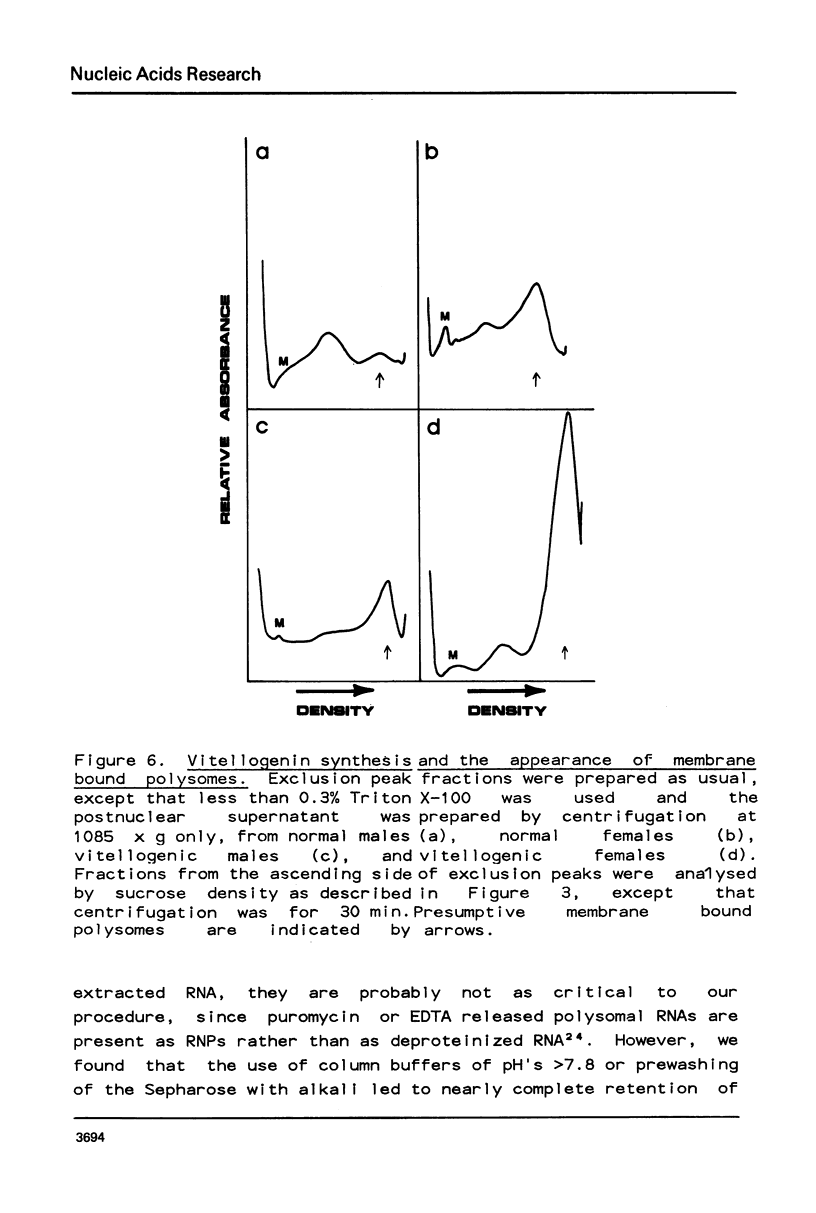
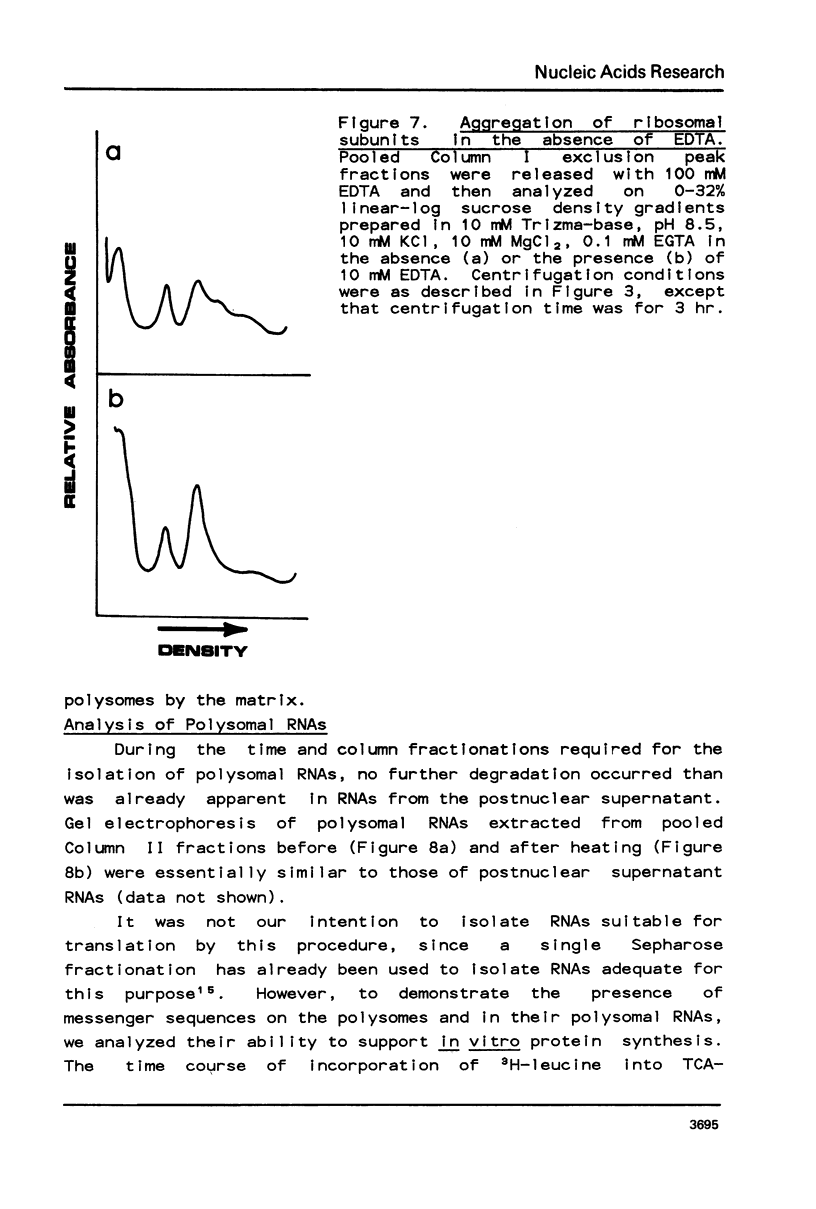
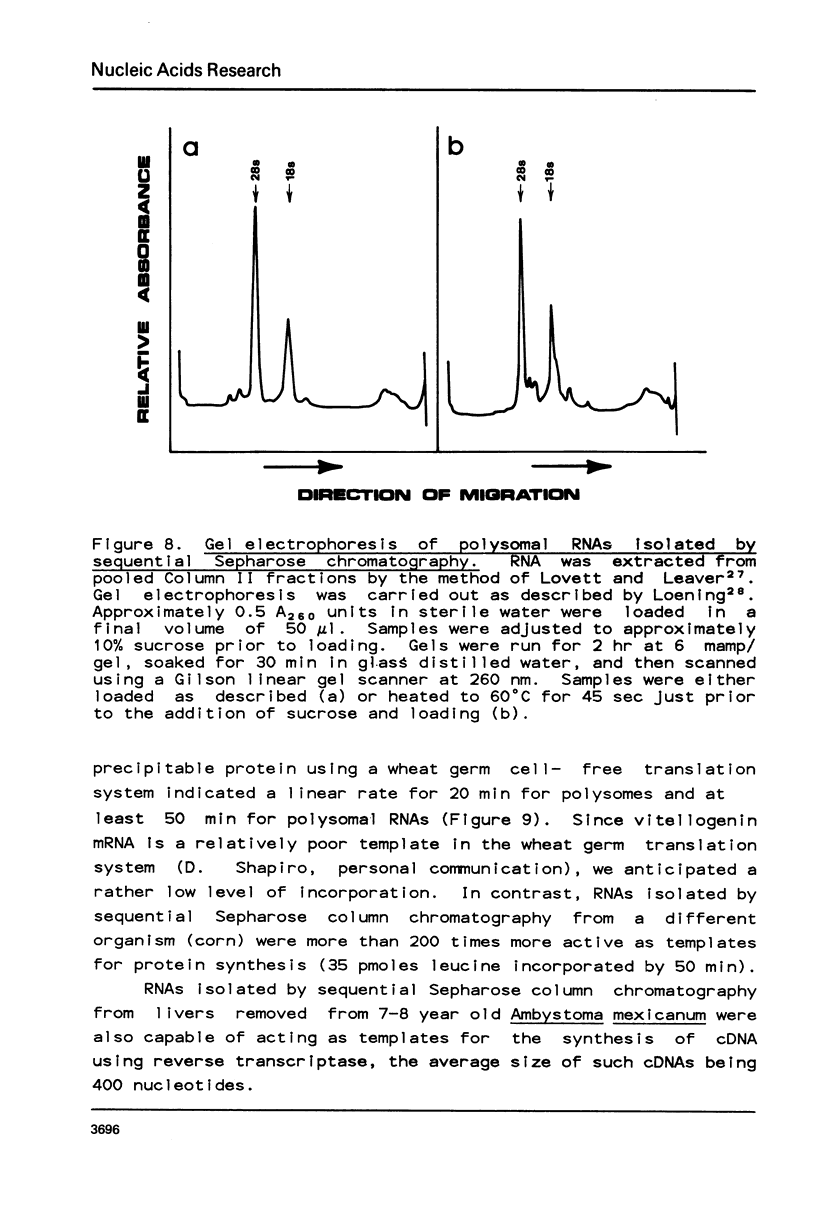



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angerer R. C., Davidson E. H., Britten R. J. Single copy DNA and structural gene sequence relationships among four sea urchin species. Chromosoma. 1976 Jul 8;56(3):213–226. doi: 10.1007/BF00293186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. V., Farmer S. R., Green C. D., Henshaw E. C., Tata J. R. Characterization of polysomes from Xenopus liver synthesizing vitellogenin and translation of vitellogenin and albumin messenger RNA's in vitro. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Feb 2;62(1):161–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G. Release, identification, and isolation of messenger RNA from mammalian ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):832–835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eschenfeldt W. H., Patterson R. J. Polysome isolation of sepharose column chromatography. Prep Biochem. 1975;5(3):247–255. doi: 10.1080/00327487508061575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galau G. A., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. A measurement of the sequence complexity of polysomal messenger RNA in sea urchin embryos. Cell. 1974 May;2(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg R. B., Galau G. A., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Nonrepetitive DNA sequence representation in sea urchin embryo messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3516–3520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg R. B., Hoschek G., Kamalay J. C., Timberlake W. E. Sequence complexity of nuclear and polysomal RNA in leaves of the tobacco plant. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):123–131. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90307-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. R., Perry R. P. Hybridization properties of DNA sequences directing the synthesis of messenger RNA and heterogeneous nuclear RNA. J Cell Biol. 1971 Sep;50(3):774–786. doi: 10.1083/jcb.50.3.774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hough-Evans B. R., Wold B. J., Ernst S. G., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Appearance and persistence of maternal RNA sequences in sea urchin development. Dev Biol. 1977 Oct 1;60(1):258–277. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90123-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson A. O., Larkins B. A. Influence of Ionic Strength, pH, and Chelation of Divalent Metals on Isolation of Polyribosomes from Tobacco Leaves. Plant Physiol. 1976 Jan;57(1):5–10. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabat D., Rich A. The ribosomal subunit--polyribosome cycle in protein synthesis of embryonic skeletal muscle. Biochemistry. 1969 Sep;8(9):3742–3749. doi: 10.1021/bi00837a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohne D. E., Byers M. J. Amplification and evolution of deoxyribonucleic acid sequences expressed as ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1973 Jun 19;12(13):2373–2378. doi: 10.1021/bi00737a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkins B. A., Tsai C. Y. Dissociation of polysome aggregates by protease k. Plant Physiol. 1977 Oct;60(4):482–485. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.4.482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin B. Units of transcription and translation: the relationship between heterogeneous nuclear RNA and messenger RNA. Cell. 1975 Jan;4(1):11–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90128-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening U. E. The fractionation of high-molecular-weight ribonucleic acid by polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1967 Jan;102(1):251–257. doi: 10.1042/bj1020251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett J. S., Leaver C. J. High-molecular-weight artifacts in RNA extracted from Blastocladiella at elevated temperatures. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Dec 16;195(2):319–327. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90639-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcu K., Dudock B. Characterization of a highly efficient protein synthesizing system derived from commercial wheat germ. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Nov;1(11):1385–1397. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.11.1385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A., Efron D., Weeks D. P. The wheat embryo cell-free system. Methods Enzymol. 1974;30:749–754. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)30073-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D. Rate of ovalbumin messenger ribonucleic acid synthesis in the oviduct of estrogen-primed chicks. J Biol Chem. 1973 Dec 10;248(23):8260–8270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman S., Vesco C., Penman M. Localization and kinetics of formation of nuclear heterodisperse RNA, cytoplasmic heterodisperse RNA and polyribosome-associated messenger RNA in HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1968 May 28;34(1):49–60. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90234-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., Kelley D. E. Messenger RNA-protein complexes and newly synthesized ribosomal subunits: analysis of free particles and components of polyribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 14;35(1):37–59. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(68)80035-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrović S. L., Ivanus J. J., Rakić L. M. Selective retention and filtration of brain nucleic acids in agarose gels. J Neurochem. 1974 Mar;22(3):327–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb07595.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrović S. L., Petrović J. S., Novaković M. B. Retention of ribosomal ribonucleic acids in agarose gels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 10;308(2):317–323. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90161-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roskam W. G., Gruber M., Ab G. Estradiol-induced synthesis of vitellogenin. II. Immunochemical characterization of vitellogenin polysomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 2;435(1):91–94. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90195-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. J., Baker H. J. Purification and characterization of Xenopus laevis vitellogenin messenger RNA. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 10;252(15):5244–5250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. J., Baker H. J., Stitt D. T. In vitro translation and estradiol-17beta induction of Xenopus laevis vitellogenin messenger RNA. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 25;251(10):3105–3111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skipper J. K., Hamilton T. H. Regulation by estrogen of the vitellogenin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2384–2388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai P. C., Wallace B. J., Herzog E. L., Davis B. D. Properties of initiation-free polysomes of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1973 Feb;12(4):609–615. doi: 10.1021/bi00728a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold B. J., Klein W. H., Hough-Evans B. R., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Sea urchin embryo mRNA sequences expressed in the nuclear RNA of adult tissues. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):941–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90348-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


