Abstract
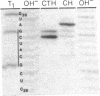
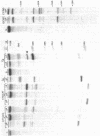
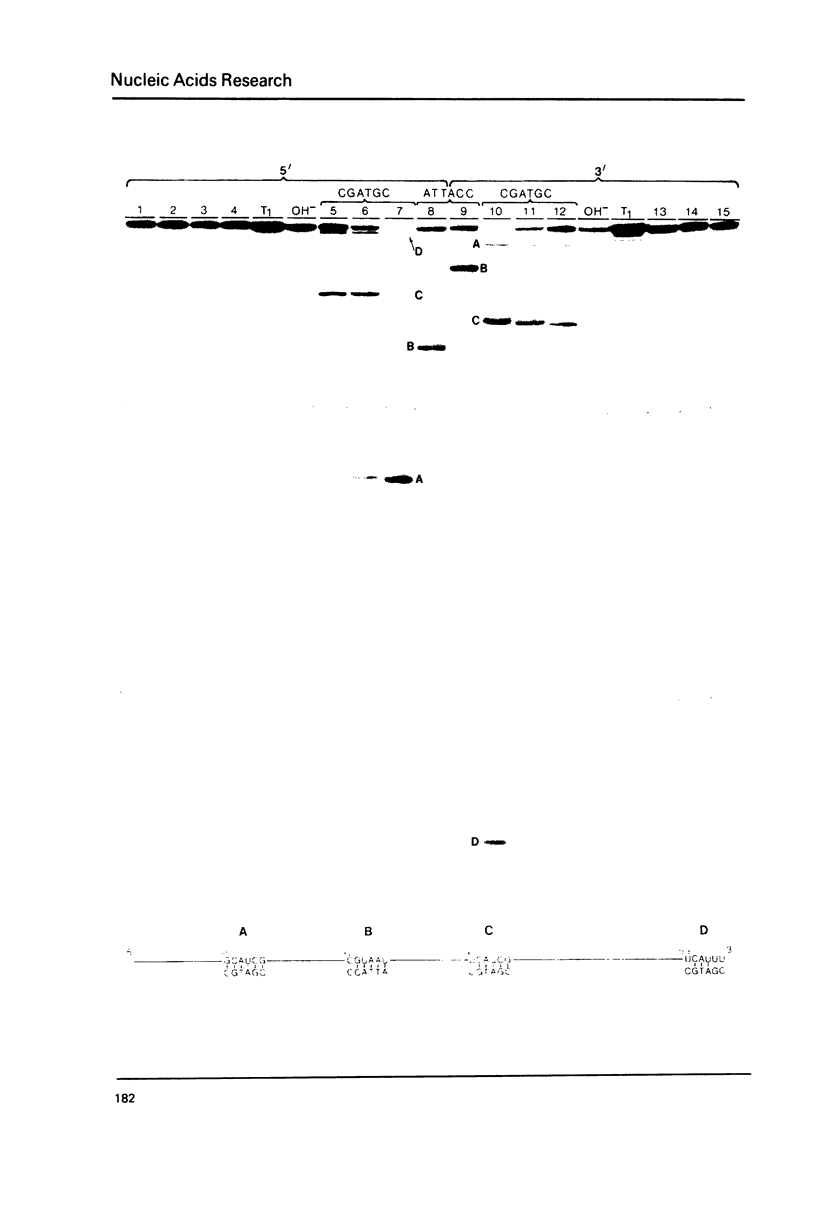
The hybridization of a DNA oligonucleotide a specific tetramer or longer) will direct a cleavage by RNase H (EC 3.1.4.34) to a specific site in RNA. The resulting fragments can then be labeled at their 5' or 3' ends, purified, and sequenced directly. This procedure is demonstrated with two RNA molecules of known sequence: 5.8S rRNA from yeast (158 nucleotides) and satellite tobacco necrosis virus (STNV) RNA (1240 nucleotides).
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berkower I., Leis J., Hurwitz J. Isolation and characterization of an endonuclease from Escherichia coli specific for ribonucleic acid in ribonucleic acid-deoxyribonucleic acid hybrid structures. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 10;248(17):5914–5921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbon P., Ehresmann C., Ehresmann B., Ebel J. P. The sequence of Escherichia coli ribosomal 16 S RNA determined by new rapid gel methods. FEBS Lett. 1978 Oct 1;94(1):152–156. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80926-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. M., Jr, Klein W. H. In vitro translation of STNV-RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1974;30:754–761. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)30074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlix J. L. Stimultaneous purification of Escherichia coli termination factor rho, RNAase III and RNAase H. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Feb 21;51(2):369–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb03937.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domingo E., Sabo D., Taniguchi T., Weissmann C. Nucleotide sequence heterogeneity of an RNA phage population. Cell. 1978 Apr;13(4):735–744. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90223-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England T. E., Uhlenbeck O. C. 3'-terminal labelling of RNA with T4 RNA ligase. Nature. 1978 Oct 12;275(5680):560–561. doi: 10.1038/275560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiers W., Contreras R., Duerinck F., Haegeman G., Iserentant D., Merregaert J., Min Jou W., Molemans F., Raeymaekers A., Van den Berghe A. Complete nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage MS2 RNA: primary and secondary structure of the replicase gene. Nature. 1976 Apr 8;260(5551):500–507. doi: 10.1038/260500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuke M. Allocation of 15 RNase T1-resistant large oligonucleotides of MS2 RNA. J Biochem. 1976 Apr;79(4):731–737. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haberkern R. C., Cantoni G. L. Studies on a calf thymus ribonuclease specific for ribonucleic acid-deoxyribonucleic acid hybrids. Biochemistry. 1973 Jun 19;12(13):2389–2395. doi: 10.1021/bi00737a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausen P., Stein H. Ribonuclease H. An enzyme degrading the RNA moiety of DNA-RNA hybrids. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Jun;14(2):278–283. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00287.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry C. M., Ferdinand F. J., Knippers R. A hydridase from Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Feb 5;50(3):603–611. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91287-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horst J., Fraenkel-Conrat H., Mandeles S. Terminal heterogeneity at both ends of the satellite tobacco necrosis virus ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1971 Dec 7;10(25):4748–4752. doi: 10.1021/bi00801a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W., Crouch R. Degradation of DNA RNA hybrids by ribonuclease H and DNA polymerases of cellular and viral origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3360–3364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. W., Browning K. S., Heckman J. E., RajBhandary U. L., Clark J. M., Jr Nucleotide sequence of the 5' terminus of satellite tobacco necrosis virus ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 3;18(7):1361–1366. doi: 10.1021/bi00574a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightfoot D. Thermodynamics of a stable yeast 5.8S rRNA hairpin helix. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Oct;5(10):3565–3577. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.10.3565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockard R. E., Alzner-Deweerd B., Heckman J. E., MacGee J., Tabor M. W., RajBhandary U. L. Sequence analysis of 5'[32P] labeled mRNA and tRNA using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jan;5(1):37–56. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans D., Smith H. O. Restriction endonucleases in the analysis and restructuring of dna molecules. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:273–293. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.001421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A. Direct chemical method for sequencing RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1760–1764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M. Preparation of RNA and ribosomes from yeast. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;12:45–64. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60951-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M. The nucleotide sequence of Saccharomyces cerevisiae 5.8 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3860–3875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. The use of thin acrylamide gels for DNA sequencing. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberklang M., Gillum A. M., RajBhandary U. L. The use of nuclease P1 in sequence analysis of end group labeled RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Dec;4(12):4091–4108. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.12.4091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoncsits A., Brownlee G. G., Brown R. S., Rubin J. R., Guilley H. New rapid gel sequencing method for RNA. Nature. 1977 Oct 27;269(5631):833–836. doi: 10.1038/269833a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J., Vassilenko S. A different approach to RNA sequencing. Nature. 1978 Jul 6;274(5666):87–89. doi: 10.1038/274087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavrianopoulos J. G., Chargaff E. Purification and properties of ribonuclease H of calf thymus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):1959–1963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavrianopoulos J. G., Chargaff E. Simplified method for purification of ribonuclease H from calf thymus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4140–4144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavrianopoulos J. G., Gambino-Giuffrida A., Chargaff E. Ribonuclease H of calf thymus: substrate specificity, activation, inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1087–1091. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H., Hausen P. Enzyme from calf thymus degrading the RNA moiety of DNA-RNA Hybrids: effect on DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Science. 1969 Oct 17;166(3903):393–395. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3903.393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. pBR322 restriction map derived from the DNA sequence: accurate DNA size markers up to 4361 nucleotide pairs long. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Aug;5(8):2721–2728. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.8.2721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]