Abstract
A fraction of the cellular nicking-closing (NC) enzyme cosediments with SV40 chromatin isolated after Triton X-100 treatment of infected cells nuclei. Extraction of viral DNA according to the Hirt procedure by treatment of infected cells with sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) followed by sedimentation in sucrose gradient to separate the DNA from the bulk of detergent also revealed NC activity associated with DNA. Reconstitution experiments showed that only prebinding of the NC enzyme to DNA protects it against irreversible inactivation by SDS. These results suggest that a fraction of the cellular NC activity is indeed associated with the viral chromosome in vivo.
Full text
PDF


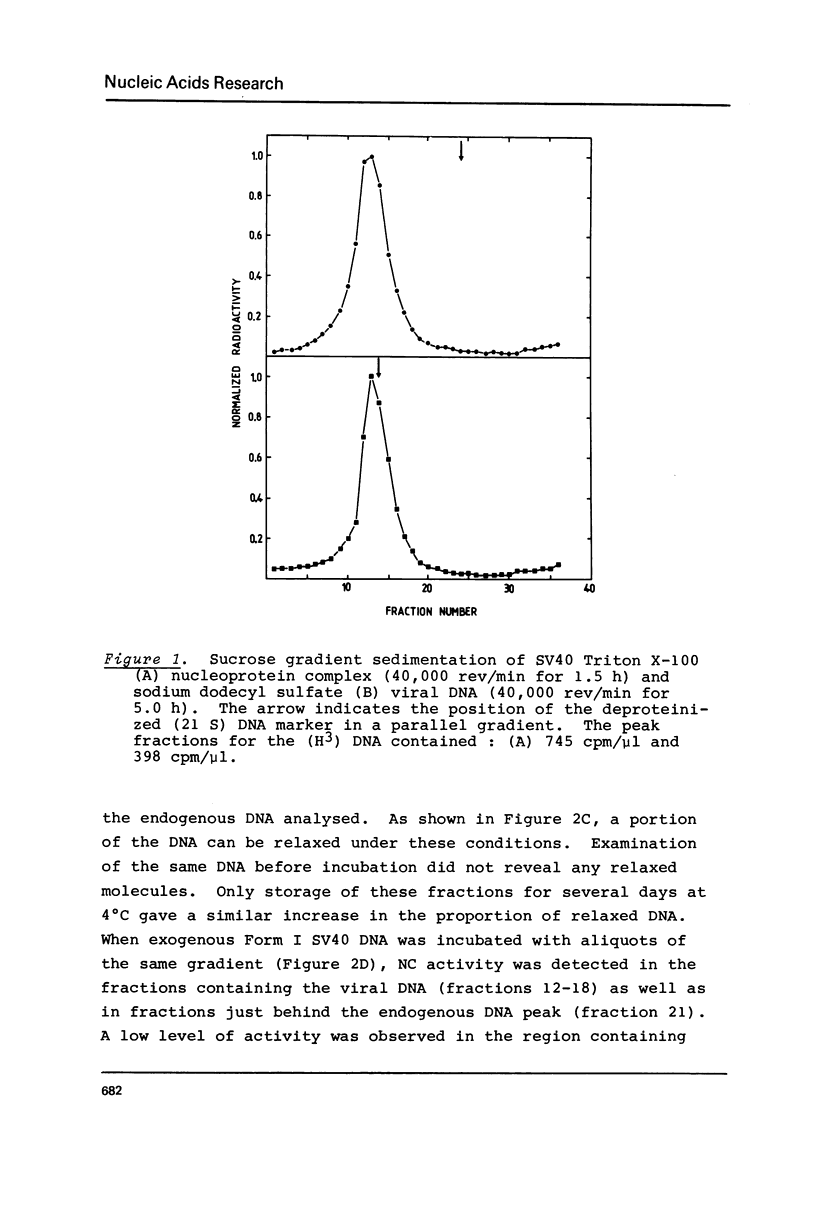





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Champoux J. J., Dulbecco R. An activity from mammalian cells that untwists superhelical DNA--a possible swivel for DNA replication (polyoma-ethidium bromide-mouse-embryo cells-dye binding assay). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):143–146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champoux J. J. Proteins that affect DNA conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:449–479. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.002313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremisi C., Pignatti P. F., Croissant O., Yaniv M. Chromatin-like structures in polyoma virus and simian virus 10 lytic cycle. J Virol. 1975 Jan;17(1):204–211. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.1.204-211.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germond J. E., Hirt B., Oudet P., Gross-Bellark M., Chambon P. Folding of the DNA double helix in chromatin-like structures from simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1843–1847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germond J. E. Simian virus 40 DNA extracted from infected cells with sodium deoxycholate no longer reflects its in vivo superhelix density. J Virol. 1978 Jun;26(3):681–685. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.3.681-685.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. H., Miller H. I., Hendler S. Isolation of a polyoma-nucleoprotein complex from infected mouse-cell cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):1032–1036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.1032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht R., Thielmann H. W. DNA-relaxing enzyme from Micrococcus luteus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Dec;4(12):4235–4247. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.12.4235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W., Müller U., Eicken I., Wendel I., Zentgraf H. Biochemical and ultrastructural analysis of SV40 chromatin. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 1):227–244. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen A., Levine A. J. SV40 nucleoprotein complex activity unwinds superhelical turns in SV40 DNA. Nature. 1974 May 24;249(455):343–344. doi: 10.1038/249343a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsubota Y., Waqar M. A., Burke J. F., Milavetz B. I., Evans M. J., Kowalski D., Huberman J. A. Association of enzymes with replicating and nonreplicating simian virus 40 chromosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):693–704. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Champoux J. J. Interaction of the DNA untwisting enzyme with the SV40 nucleoprotein complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Feb;5(2):623–635. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.2.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





