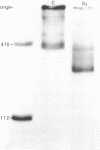
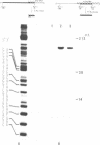
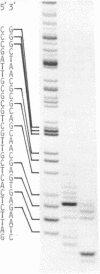
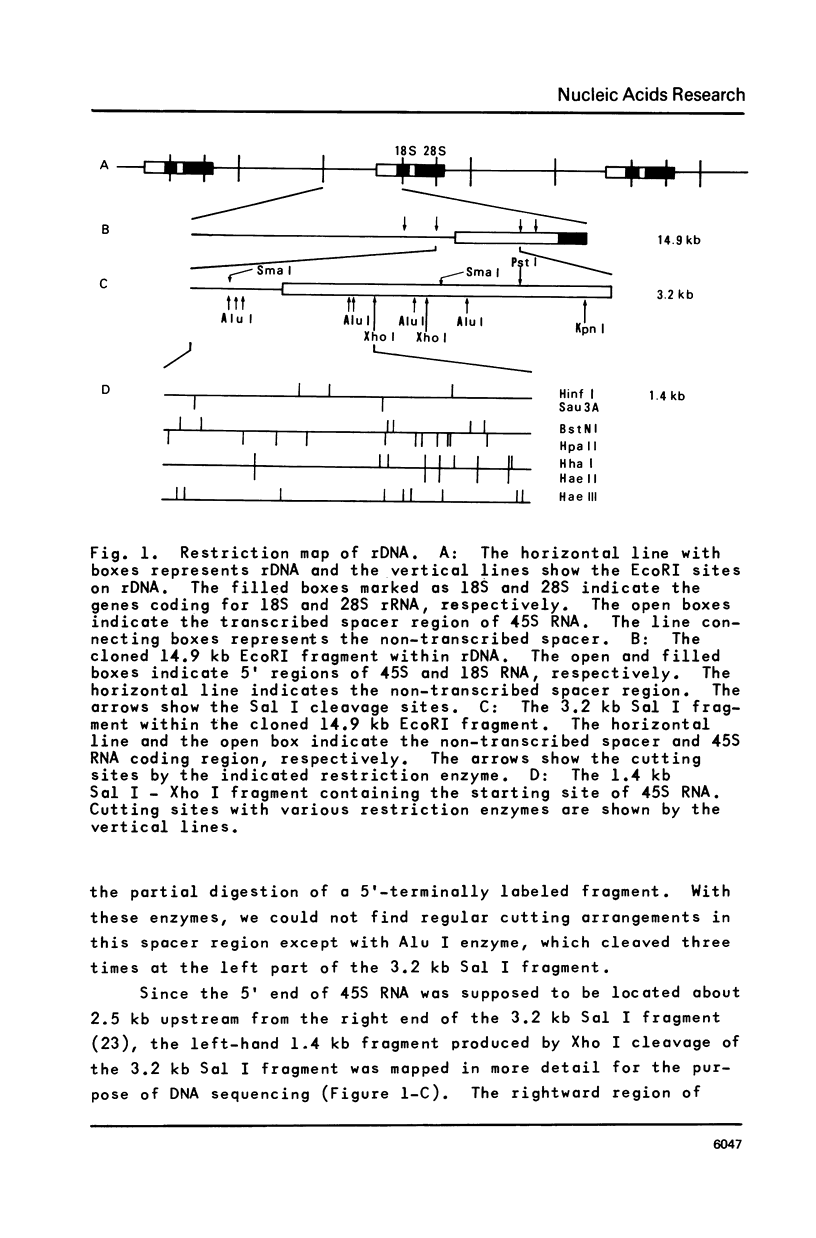
Abstract
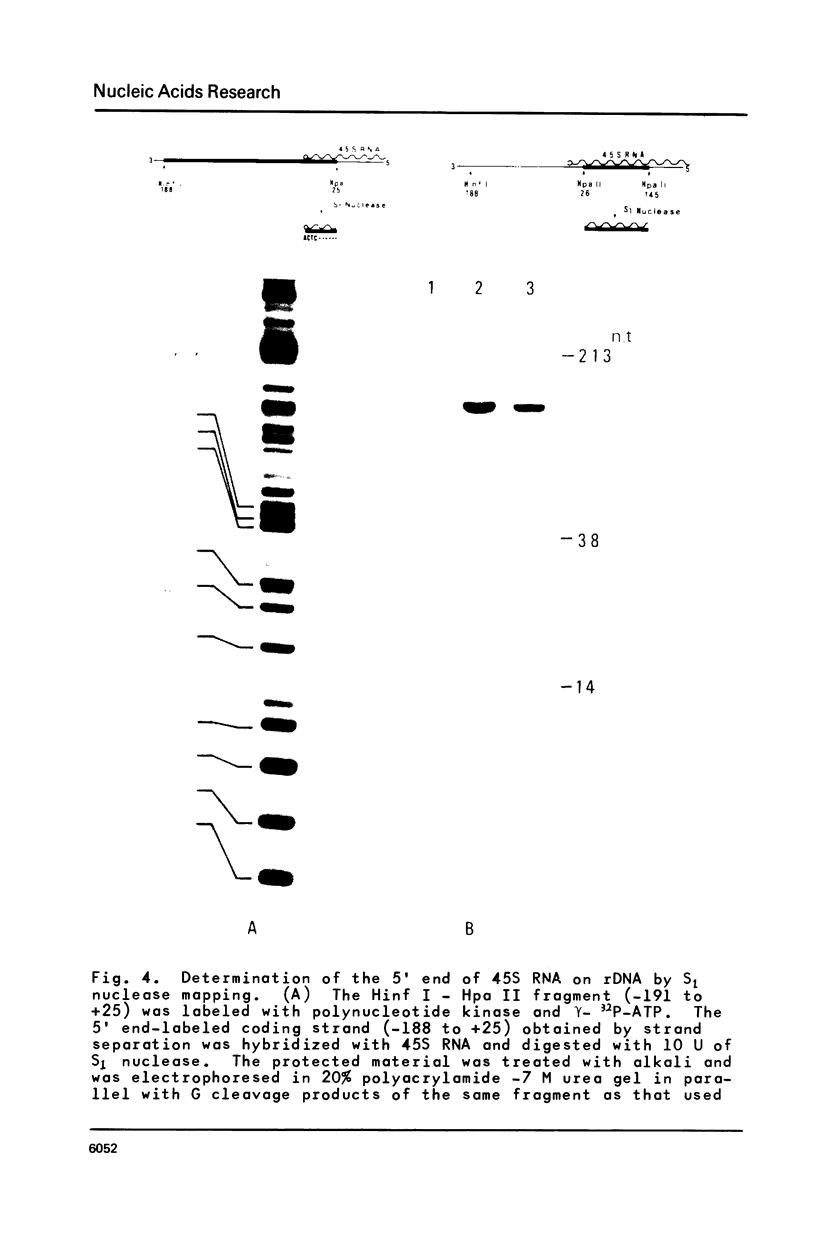
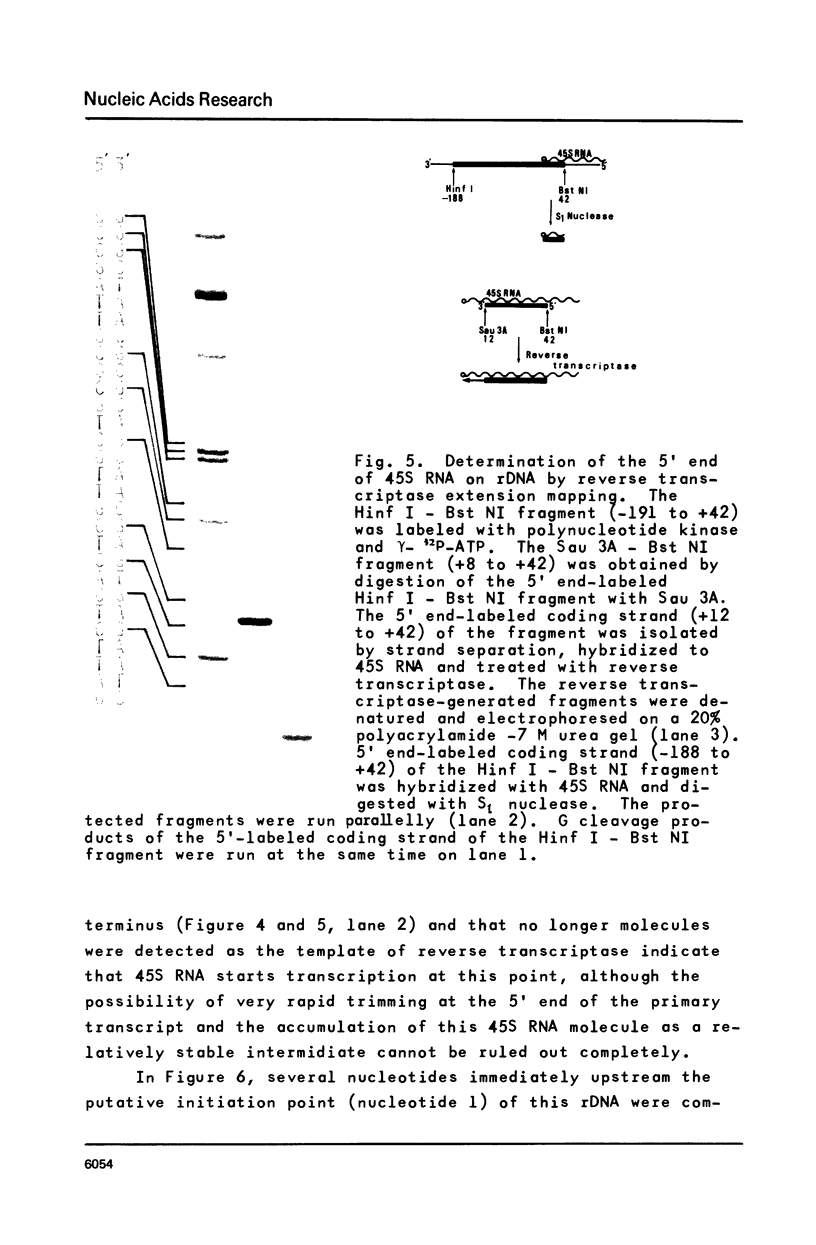
Approximately one kilobase pairs surrounding and upstream the transcription initiation site of a cloned ribosomal DNA (rDNA) of the mouse were sequenced. The putative transcription initiation site was determined by two independent methods: one nuclease S1 protection and the other reverse transcriptase elongation mapping using isolated 45S ribosomal RNA precursor (45S RNA) and appropriate restriction fragments of rDNA. Both methods gave an identical result; 45S RNA had a structure starting from ACTCTTAG---. Characteristically, mouse rDNA had many T clusters (greater than or equal to 5) upstream the initiation site, the longest being 21 consecutive T's. A pentadecanucleotide, TGCCTCCCGAGTGCA, appeared twice within 260 nucleotides upstream the putative initiation site. No such characteristic sequences were found downstream this site. Little similarity was found in the upstream of the transcription initiation site between the mouse, Xenopus laevis and Saccharomyces cerevisiae rDNA.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnheim N. Characterization of mouse ribosomal gene fragments purified by molecular cloning. Gene. 1979 Oct;7(2):83–96. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN D. D., LITTNA E. RNA SYNTHESIS DURING THE DEVELOPMENT OF XENOPUS LAEVIS, THE SOUTH AFRICAN CLAWED TOAD. J Mol Biol. 1964 May;8:669–687. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80116-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batts-Young B., Lodish H. F. Triphosphate residues at the 5' ends of rRNA precursor and 5S RNA from Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):740–744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baulieu E. E. Some aspects of the mechanism of action of steroid hormones. Mol Cell Biochem. 1975 Jun 30;7(3):157–174. doi: 10.1007/BF01731406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bina-Stein M., Thoren M., Salzman N., Thomspon J. A. Rapid sequence determination of late simian virus 40 16S mRNA leader by using inhibitors of reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):731–735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M., Speirs J., Purdom I., Jones K., Loening U. E. Properties and composition of the isolated ribosomal DNA satellite of Xenopus laevis. Nature. 1968 Aug 3;219(5153):454–463. doi: 10.1038/219454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boseley P., Moss T., Mächler M., Portmann R., Birnstiel M. Sequence organization of the spacer DNA in a ribosomal gene unit of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):19–31. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90291-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. D., Littna E. Synthesis and accumulation of DNA-like RNA during embryogenesis of Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1966 Sep;20(1):81–94. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90119-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. D., Weber C. S. Gene linkage by RNA-DNA hybridization. II. Arrangement of the redundant gene sequences for 28 s and 18 s ribosomal RNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jun 28;34(3):681–697. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90189-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambon P. Eukaryotic nuclear RNA polymerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:613–638. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.003145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currier T. C., Nester E. W. Isolation of covalently closed circular DNA of high molecular weight from bacteria. Anal Biochem. 1976 Dec;76(2):431–441. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90338-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Soellner C., Scholz I. Characterization of a cloned ribosomal fragment from mouse which contains the 18S coding region and adjacent spacer sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Apr;6(4):1351–1369. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.4.1351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Woodland H. R. The influence of the cytoplasm on the nucleus during cell differentiation, with special reference to RNA synthesis during amphibian cleavage. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1969 Apr 15;173(1030):99–111. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1969.0042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J. EFFECTS OF PUROMYCIN ON RNA SYNTHESIS IN MAMMALIAN CELLS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:436–446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi Y., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Effect of cycloheximide on the synthesis and processing of 5S RNA in HeLa cells. J Biochem. 1977 Feb;81(2):451–459. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi K., Matsuhisa T., Kitao A., Sakamoto Y. Selective suppression of nucleolar RNA metabolism in the absence of protein synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Sep 24;166(2):388–393. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90226-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemenz R., Geiduschek E. P. The 5' terminus of the precursor ribosomal RNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jun 25;8(12):2679–2689. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.12.2679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klootwijk J., de Jonge P., Planta R. J. The primary transcript of the ribosomal repeating unit in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jan;6(1):27–39. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Heterogeneity of 5' -termini of nucleolar 45S, 32S and 28S RNA in mouse hepatoma. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Jan;4(1):229–240. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.1.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konkel D. A., Maizel J. V., Jr, Leder P. The evolution and sequence comparison of two recently diverged mouse chromosomal beta--globin genes. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):865–873. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90138-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konkel D. A., Tilghman S. M., Leder P. The sequence of the chromosomal mouse beta-globin major gene: homologies in capping, splicing and poly(A) sites. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1125–1132. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90040-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T., Onishi T., Muramatsu M. Nucleolar DNA-dependent RNA polymerase from rat liver. 1. Purification and subunit structure. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Dec 11;71(2):351–360. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb11121.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishima Y., Kominami R., Honjo T., Muramatsu M. Cloning and determination of a putative promoter region of a mouse ribosomal deoxyribonucleic acid fragment. Biochemistry. 1980 Aug 5;19(16):3780–3786. doi: 10.1021/bi00557a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishima Y., Matsui T., Muramatsu M. The mechanism of decrease in nucleolar RNA synthesis by protein synthesis inhibition. J Biochem. 1979 Mar;85(3):807–818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyahara E., Abe H., Yamana K. Differential inhibition of 28S-18S RNA and 5S RNA synthesis in the cycloheximide-treated Xenopus laevis embryonic cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Sep 10;40(5):1070–1075. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90903-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T., Birnstiel M. L. The putative promoter of a Xenopus laevis ribosomal gene is reduplicated. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 24;6(12):3733–3743. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.12.3733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu M., Shimada N., Higashinakagawa T. Effect of cycloheximide on the nucleolar RNA synthesis in rat liver. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):91–106. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90047-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niles E. G. Isolation of a high specific activity 35S ribosomal RNA precursor from Tetrahymena pyriformis and identification of its 5' terminus, pppAp. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4839–4844. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka Y., Leder P. The complete sequence of a chromosomal mouse alpha--globin gene reveals elements conserved throughout vertebrate evolution. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):875–882. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90139-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H., Sollner-Webb B., Wahn H. L. Sites of transcription initiation in vivo on Xenopus laevis ribosomal DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5402–5406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Roeder R. G. Purification and subunit structure of deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase I from the mouse myeloma, MOPC 315. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5898–5906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabak H. F., Flavell R. A. A method for the recovery of DNA from agarose gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jul;5(7):2321–2332. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.7.2321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M., White R. L., Davis R. W. Hybridization of RNA to double-stranded DNA: formation of R-loops. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2294–2298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S., Maxam A. M., Tizard R., Bernard O., Gilbert W. Sequence of a mouse germ-line gene for a variable region of an immunoglobulin light chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1485–1489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela P., Bell G. I., Venegas A., Sewell E. T., Masiarz F. R., DeGennaro L. J., Weinberg F., Rutter W. J. Ribosomal RNA genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. II. Physical map and nucleotide sequence of the 5 S ribosomal RNA gene and adjacent intergenic regions. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 25;252(22):8126–8135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B. Secondary structure maps of ribosomal RNA and DNA. I. Processing of Xenopus laevis ribosomal RNA and structure of single-stranded ribosomal DNA. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 25;89(2):379–395. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90526-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems M., Penman M., Penman S. The regulation of RNA synthesis and processing in the nucleolus during inhibition of protein synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1969 Apr;41(1):177–187. doi: 10.1083/jcb.41.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziff E. B., Evans R. M. Coincidence of the promoter and capped 5' terminus of RNA from the adenovirus 2 major late transcription unit. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1463–1475. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]