Abstract
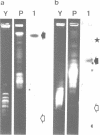
Cryptomonads are unicellular algae with chloroplasts surrounded by four membranes. Between the inner and the outer pairs of membranes is a narrow plasmatic compartment which contains a nucleus-like organelle called the nucleomorph. Using pulsed field gel electrophoresis it is shown that the nucleomorph of the cryptomonad Pyrenomonas salina contains three linear chromosomes of 195 kb, 225 kb and 240 kb all of which encode rRNAs. Thus, this vestigial nucleus has a haploid genome size of 660 kb, harboring the smallest eukaryotic genome known so far. From the cell nucleus of P. salina at least 20 chromosomes ranging from 230 kb to 3.000 kb were fractionated. Here, the rDNA was detected on a single chromosome of about 2.500 kb.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beverley S. M. Characterization of the 'unusual' mobility of large circular DNAs in pulsed field-gradient electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):925–939. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Olson M. V. An electrophoretic karyotype for yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3756–3760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBS S. P. Nuclear envelope-chloroplast relationships in algae. J Cell Biol. 1962 Sep;14:433–444. doi: 10.1083/jcb.14.3.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs S. P. The chloroplasts of some algal groups may have evolved from endosymbiotic eukaryotic algae. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;361:193–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb46519.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. W., Doolittle W. F. Has the endosymbiont hypothesis been proven? Microbiol Rev. 1982 Mar;46(1):1–42. doi: 10.1128/mr.46.1.1-42.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. W. The evolutionary origins of organelles. Trends Genet. 1989 Sep;5(9):294–299. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90111-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansmann P., Eschbach S. Isolation and preliminary characterization of the nucleus and the nucleomorph of a cryptomonad, Pyrenomonas salina. Eur J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;52(2):373–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara Y., Akiyama K., Isono K. The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer R. K., Schild D. Genetic map of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, edition 9. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Sep;49(3):181–213. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.3.181-213.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orbach M. J., Vollrath D., Davis R. W., Yanofsky C. An electrophoretic karyotype of Neurospora crassa. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1469–1473. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Matsumoto T., Niwa O., Klco S., Fan J. B., Yanagida M., Cantor C. R. An electrophoretic karyotype for Schizosaccharomyces pombe by pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4481–4489. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toloczyki C., Feix G. Occurrence of 9 homologous repeat units in the external spacer region of a nuclear maize rRNA gene unit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 25;14(12):4969–4986. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.12.4969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Resolution of DNA molecules greater than 5 megabases by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7865–7876. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whatley J. M. Chloroplast evolution--ancient and modern. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;361:154–165. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb46517.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]