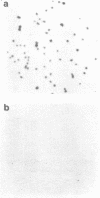
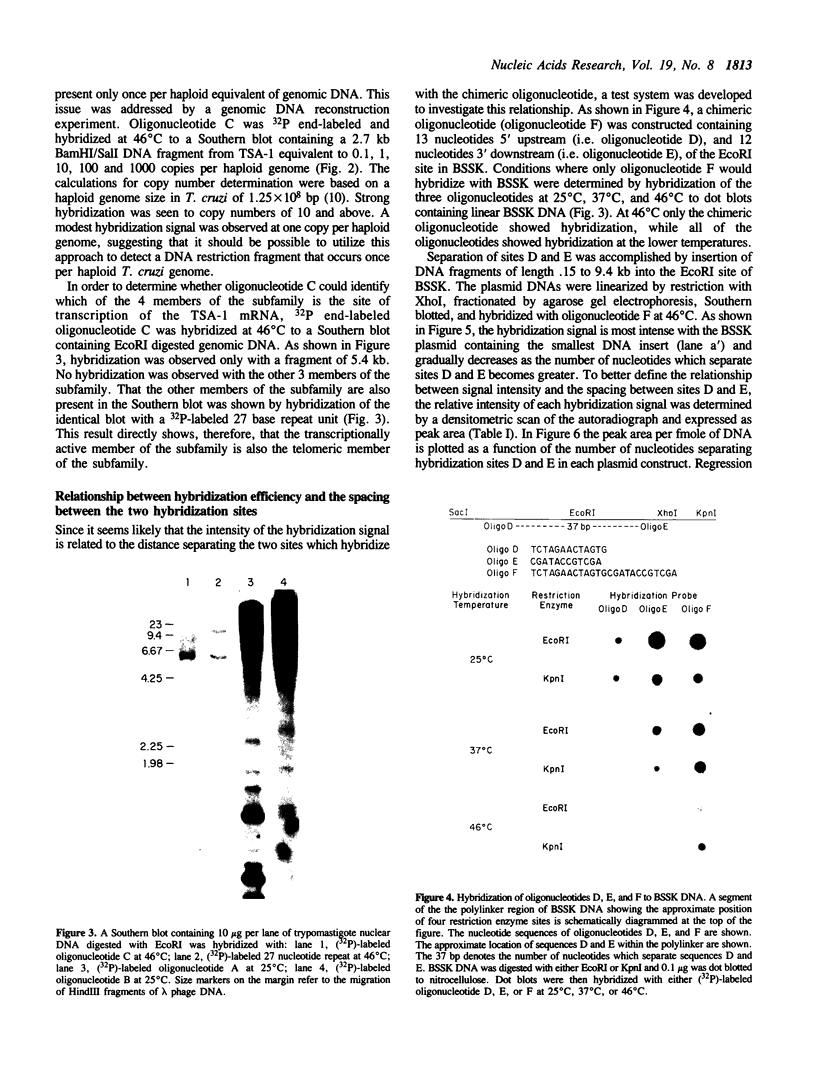
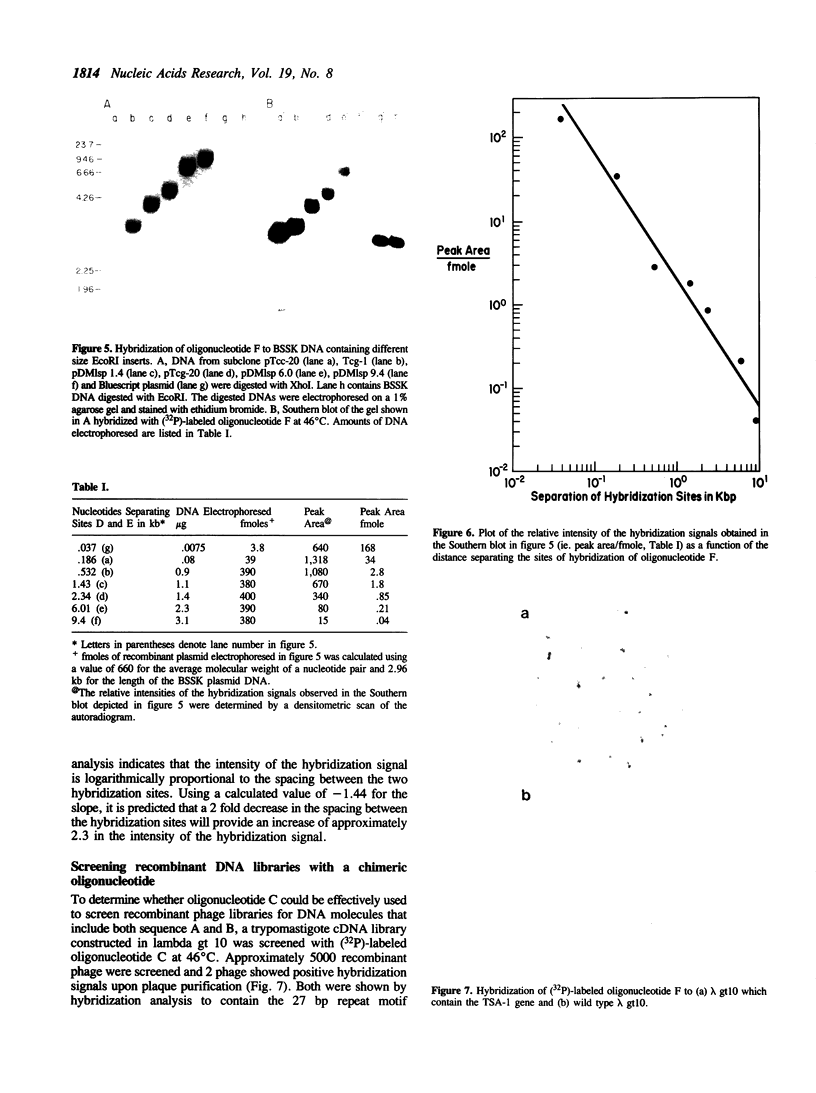
Abstract
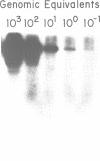
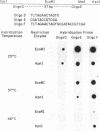
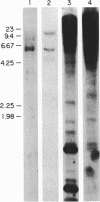
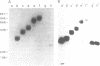
A chimeric oligonucleotide was constructed using DNA sequences from two distal regions of a cDNA which encodes a major surface antigen (TSA-1) of Trypanosoma cruzi. Conditions were found that allowed the chimeric oligonucleotide to hybridize only to a 5.4 kb EcoRI fragment in a Southern blot of total genomic DNA. The 5.4 kb EcoRI genomic DNA fragment has previously been shown to be located at a telomeric site, thus the studies described here directly demonstrate that the TSA-1 gene is telomeric in location. It is also shown that the chimeric oligonucleotide can be used to selectively identify recombinant lambda phage which harbor the TSA-1 gene using standard library screening procedures. Since these studies demonstrate that a chimeric oligonucleotide can be used to identify in both Southern blots and library screens a single member among the more than sixty members of the TSA-1 gene family, it seems likely that chimeric oligonucleotides may be of general use in studies involving repetitive DNA sequence families.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abuin G., Colli W., de Souza W., Alves M. J. A surface antigen of Trypanosoma cruzi involved in cell invasion (Tc-85) is heterogeneous in expression and molecular constitution. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Jul;35(3):229–237. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90209-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alves M. J., Abuin G., Kuwajima V. Y., Colli W. Partial inhibition of trypomastigote entry into cultured mammalian cells by monoclonal antibodies against a surface glycoprotein of Trypanosoma cruzi. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1986 Oct;21(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(86)90081-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews N. W., Katzin A. M., Colli W. Mapping of surface glycoproteins of Trypanosoma cruzi by two-dimensional electrophoresis. A correlation with the cell invasion capacity. Eur J Biochem. 1984 May 2;140(3):599–604. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08144.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard C. A., Wrightsman R. A., Manning J. E. Identification of monoclonal antibodies against the trypomastigote stage of Trypanosoma cruzi by use of iminobiotinylated surface polypeptides. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1985 Aug;16(2):199–212. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(85)90087-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard C. A., Wrightsman R. A., Manning J. E. Stage and strain specific expression of the tandemly repeated 90 kDa surface antigen gene family in Trypanosoma cruzi. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Apr;28(3):227–234. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender W., Spierer P., Hogness D. S. Chromosomal walking and jumping to isolate DNA from the Ace and rosy loci and the bithorax complex in Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 25;168(1):17–33. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80320-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brener Z. Biology of Trypanosoma cruzi. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1973;27:347–382. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.27.100173.002023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fouts D. L., Manning J. E., Fox G. M., Schmid C. W. A complex repeated DNA sequence within the Drosophila transposable element copia. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):7053–7064. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.7053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Chatterjee R. N., Bunick D., Manning J. E., Lucchesi J. C. The LSP1-alpha gene of Drosophila melanogaster exhibits dosage compensation when it is relocated to a different site on the X chromosome. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1191–1196. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03491.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzin A. M., Colli W. Lectin receptors in Trypanosoma cruzi. An N-acetyl-D-glucosamine-containing surface glycoprotein specific for the trypomastigote stage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jan 19;727(2):403–411. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90425-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kooter J. M., van der Spek H. J., Wagter R., d'Oliveira C. E., van der Hoeven F., Johnson P. J., Borst P. The anatomy and transcription of a telomeric expression site for variant-specific surface antigens in T. brucei. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):261–272. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90153-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanar D. E., Levy L. S., Manning J. E. Complexity and content of the DNA and RNA in Trypanosoma cruzi. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1981 Sep;3(5):327–341. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(81)90006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. S., Fouts D. L., Manning J. E. The 85-kd surface antigen gene of Trypanosoma cruzi is telomeric and a member of a multigene family. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3911–3916. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08571.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. S., Wrightsman R. A., Manning J. E. Cloning of a major surface-antigen gene of Trypanosoma cruzi and identification of a nonapeptide repeat. Nature. 1986 Aug 7;322(6079):566–568. doi: 10.1038/322566a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C., Davidson N. On the probability of ring closure of lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(2):469–482. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C., Davidson N. Thermodynamic and kinetic studies on the interconversion between the linear and circular forms of phage lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jan;15(1):111–123. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80213-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zingales B., Andrews N. W., Kuwajima V. Y., Colli W. Cell surface antigens of Trypanosoma cruzi: possible correlation with the interiorization process in mammalian cells. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1982 Aug;6(2):111–124. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(82)90069-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]