Abstract
Since the report of a paralogous acetylcholinesterase (AChE, EC3.1.1.7) gene in the greenbug (Schizaphis graminum) in 2002, two different AChE genes (Ace1 and Ace2) have been identified in each of at least 27 insect species. However, the gene models of Ace1 and Ace2, and their molecular properties have not yet been comprehensively analyzed in any insect species. In this study, we sequenced the full-length cDNAs, computationally predicted the corresponding three-dimensional protein models, and profiled developmental stage and tissue-specific expression patterns of two Ace genes from the red flour beetle (Tribolium castaneum; TcAce1 and TcAce2), a globally distributed major pest of stored grain products and an emerging model organism. TcAce1 and TcAce2 encode 648 and 604 amino acid residues, respectively, and have conserved motifs including a choline-binding site, a catalytic triad, and an acyl pocket. Phylogenetic analysis show that both TcAce genes are grouped into two insect Ace clusters and TcAce1 is completely diverged from TcAce2, suggesting that these two genes evolve from their corresponding Ace gene lineages in insect species. In addition, TcAce1 is located on chromosome 5, whereas TcAce2 is located on chromosome 2. Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and quantitative real-time PCR analyses indicate that both genes are virtually transcribed in all the developmental stages and predominately expressed in the insect brain. Our computational analyses suggest that the TcAce1 protein is a robust acetylcholine (ACh) hydrolase and has susceptibility to sulfhydryl agents whereas the TcAce2 protein is not a catalytically efficient ACh hydrolase.
Introduction
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE, EC3.1.1.7) is an essential enzyme at the synapses of cholinergic neurons in the central and peripheral nervous systems in all animals. It catalyzes the hydrolysis of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh), thus terminating neurotransmission. AChE has long been of academic and industrial interest and studied extensively at the biochemical, biophysical, and molecular levels in mammals because this enzyme is a target of palliative Alzheimer drugs, nerve agents, and insecticides [1]. In insects, AChE has also been extensively studied because it serves as the target site for organophosphate and carbamate insecticides, and involves in insecticide resistance known as target-site insensitivity [2]–[8].
The first insect AChE gene (Ace) was sequenced from Drosophila melanogaster in 1986 [9]. After the first Ace paralogous gene was reported in the greenbug (Schizaphis graminum) in 2002 [10], the D. melanogaster Ace gene was designated as Ace orthologous gene. It is now clear that D. melanogaster has only one Ace gene as confirmed by its genome sequence [11], whereas most other insect species have two different Ace genes (i.e., Ace1 and Ace2) [12]. Ace1 commonly refers to the Ace paralogous (AP-Ace) gene and Ace2 the Ace orthologous (AO-Ace) gene in relation to the D. melanogaster Ace [8].
To date, the cDNAs encoding AChEs have been sequenced from at least 43 insect species. Among them, both Ace1 and Ace2 have been reported from each of 27 species, including Bombyx mandarina (GenBank accession numbers: EU262633 for BmAce1 and EU262632 for BmAce2); Sitobion avenae [13]; Rhopalosiphum padi [13]; Anopheles gambiae [14]; Liposcelis decolor (GenBank accession numbers: FJ647186 for LdeAce1 and FJ647187 for LdeAce2); Orchesella villosa [15]; Liposcelis entomophila (GenBank accession numbers: EU854149 for LeAce1 and EU854150 for LeAce2); Blattella germanica [16]; Bemisia tabaci [17]; Culex pipiens quinquefasciatus (GenBank accession numbers: XM_001847396 for CqAce1 and XM_001842175 CqAce2); Bombyx mori [18]; Acyrthosiphon pisum (GenBank accession numbers: XM_001948618 for ApAce1 and XM_001948953 for ApAce2); Nasonia vitripennis (GenBank accession numbers: XM_001600408 for NvAce1 and XM_001605518 for NvAce2); Pediculus humanus corporis [19]; Cydia pomonella [20]; Helicoverpa assulta [21]; Aedes albopictus (GenBank accession numbers: AB218421 for AaAce1 and AB218420 for AaAce2); Aphis gossypii [22]; Culex tritaeniorhynchus [23]; Myzus persicae [24]; Culex pipiens [25]; Plutella xylostella [26]–[28]; Chilo suppressalis [29]; Pediculus humanus capitis [19]; Aedes aegypti [30]; Liposcelis bostrychophila (GenBank accession numbers: FJ647185 for LbAce1 and EF362950 for LbAce2) and Alphitobius diaperinus [31]. The remaining insect species may also have two Ace genes but only one Ace gene (Ace1 or Ace2) has been documented.
The existence of two Ace genes in insects has attracted much attention to the study of their functions, particularly their roles in insecticide resistance [8], [32] and as targets for developing new insecticides [12], [33]–[37]. Beetles (coleopterans) are the most evolutionarily successful metazoans, accounting for 25% of all known animal species, far more than any other taxonomic orders [31]. Despite the diversity and economic importance of coleopterans, Ace genes have been reported from only two species: Leptinotarsa decemlineata [5], [6] and Alphitobius diaperinus [31]. Although T. castaneum (the red flour beetle) is one of the most notorious stored grain pests in the world and is now regarded as an emerging model organism, its Ace genes were only predicted from genomic sequence and detailed information on these genes has been limited.
In this paper, we report two Ace genes from T. castaneum. Our study of the two genes focuses on the genome organization, three-dimensional (3D) protein models, phylogenies, and expression patterns of the two genes at different developmental stages of the insect, in an effort to better understand the functions of the two genes and obtain insights into better strategies for insect pest control.
Results
AChE cDNA and deduced amino acid sequences
Based on the predicted sequences of two T. castaneum Ace genes in NCBI (XM_968369 and XM_965681), we designed specific primers (Table 1) to determine the full-length cDNAs of the two genes from the brain of T. castaneum. Each of several polymerase chain reaction (PCR) primer pairs was able to generate overlapping fragments for each gene and it was then possible to assemble them into its full-length cDNA of the protein coding region. The two deduced amino acid sequences show significant similarities to AChE1 (AP-AChE) and AChE2 (AO-AChE) proteins of other insects in GenBank according to our BLASTP analysis. Therefore, the two T. castaneum Ace genes are named TcAce1 (AP-Ace) and TcAce2 (AO-Ace), and their protein products are named TcAce1 and TcAce2, respectively. The TcAce1 cDNA contains 2148 base pairs (bp) and has an open reading frame (ORF) of 1944 bp, encoding a protein of 648 amino acid residues, whereas the TcAce2 cDNA contains 1,890 bp and has an ORF of 1,812 bp, encoding a protein of 604 residues. However, we were not able to obtain the 5′-untranslated region (5′-UTR) of the TcAce2 cDNA (Fig. 1).
Table 1. PCR primers used to amplify cDNA sequences of both TcAce1 and TcAce2 genes and to analyze their gene expressions.
| Primer name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Tm (°C) | Product size (bp) | Locationa |
| PCR for cDNA sequences | ||||
| TcAce1-Fb | CGGCCTGCTTACTAGTGATTCTAC | 60.66 | 1714 | 17-1730 |
| TcAce1-R | ACATCGAGGGTGAGAAACTCC | 60.50 | ||
| TcAce1S-F | CAACGACCGTTGTGCAAATA | 60.56 | 320 | N/A-219 |
| TcAce1S-R | CAGGGGATCATCTTCGGAGT | 61.39 | ||
| TcAce1E-F | CGTTTGGACACCCACTTTCT | 60.01 | 402 | 1665-N/A |
| TcAce1E-R | GTCGTGTTGATTTTGAATACCTCAC | 60.99 | ||
| TcAce2-F | AGACCTCATCACGCTGTTTG | 55.2 | 1034 | 750-1783 |
| TcAce2-R | CTGGGTTATCCCGAAGCTTG | 61.86 | ||
| TcAce2S-F | GTCGTAGAGGCGTCGTCGT | 61.44 | 1014 | N/A-895 |
| TcAce2S-R | TCTCCCCCGACATGTAACTC | 59.93 | ||
| TcAce2E-F | AACCAGTGACAGACGACGTG | 59.78 | 267 | 1627-N/A |
| TcAce2E-R | CGCAACCGATGCGTTTAATA | 61.86 | ||
| Quantitative real-time PCR | ||||
| TcAce1(Q)-F | CCGTTCGTCCCAGTCATTG | 55.3 | 121 | 1069-1189 |
| TcAce1(Q)-R | AGTAGTAGCCTTCTTCTGTGTTAG | 55.4 | ||
| TcAce2(Q)-F | AGACCTCATCACGCTGTTTG | 55.2 | 179 | 750-928 |
| TcAce2(Q)-R | CCTCCACCAGGACCTTCC | 54.9 | ||
| TcRps3-F | CCGTCGTATTCGTGAATTGAC | 54.8 | 130 | 279-408 |
| TcRps3-R | TCTAAGAGACTCTGCTTGTGC | 54.7 | ||
Product location refers to the PCR fragment corresponding to the Ace gene nucleotide sequence of T. castaneum from NCBI database (TcAce1: XM_968369; TcAce2: XM_965681). N/A refers to the sequence based on the genomic sequence in Beetlebase (http://beetlebase.org/).
F and R refer to forward and reverse primers, respectively.
Figure 1. The cDNA and deduced amino acid sequences of two Ace genes from Tribolium castaneum.
The amino acid sequences were numbered from the start of the mature proteins. The start codon ATG were bold and underlined, and the stop codon TAA at the end of the coding region were bold and marked with asterisks. The putative signal peptides of the deduced amino acid sequences were underlined with red dots. Potential N-linked glycosylation sites were bold and shaded. The sequences were deposited in the GenBank (accession numbers: HQ260968 for TcAce1 and HQ260969 for TcAce2).
TcAce1 and TcAce2 belong to typical Ace1- and Ace2-type genes, respectively, as judged by their sequence similarities with other known insect Aces (Fig. 2). The deduced amino acid sequences (TcAce1 and TcAce2) of TcAce1 and TcAce2 exhibit six and four N-glycosylation sites (N-X-S or N-X-T) [38], respectively (Fig. 1). Predicted isoelectric points (pI) and molecular masses of TcAce1 and TcAce2 are 6.58 and 5.39, and 72.81 and 68.15 kDa, respectively (http://www.scripps.edu/~cdputnam/protcalc.html). Both TcAce1 and TcAce2 are predicted to contain a cleavable signal peptide, which suggests that these proteins can be secreted and function in an extracellular environment. Both proteins have a C-terminal Cys residue (C617 in TcAce1 and C600 in TcAce2) that is likely to form an intermolecular disulfide bond. According to the analysis using PredGPI (http://gpcr.biocomp.unibo.it/predgpi/), TcAce1 appears to contain a GPI-anchor, which is linked to the C-terminal residue after a proteolytic cleavage at the ω site (D619 in TcAce1), whereas TcAce2 doesn't seem to contain a GPI-anchor. Both proteins have relatively high sequence identity (47% for TcAce1 and 59% for TcAce2) to the C-terminal residues 526–543 (i.e., QTCAFWNRFLPKLLSAT) of the recombinant mouse AChE (mAChE) [39], [40]. This level of sequence identity is identical or higher than the corresponding sequence identity (47%) between mAChE and D. melanogaster AChE (DmAChE). All these suggest that residues 589–605 in TcAce1 and residues 578–594 in TcAce2 are likely responsible for the formation of a dimeric four-helix bundle at the C-terminus as seen in mAChE [40] and DmAChE [41].
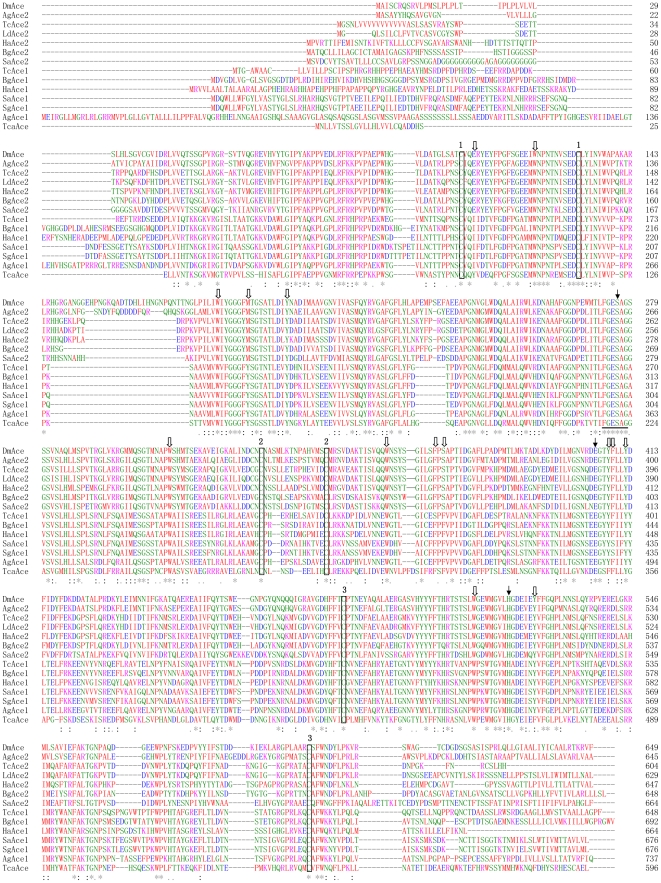
Figure 2. Alignment of deduced AChE protein sequences encoded by TcaAce (CAA27169, Torpedo californica Ace); TcAce1 (HQ260968, Tribolium castaneum Ace1, this paper); TcAce2 (HQ260969, T. castaneum Ace2, this paper); SaAce1 (AY819704, Sitobion avenae Ace1); SaAce2 (AY707319, S. avenae Ace2); DmAce (X05893, Drosophila melanogaster Ace); AgAce1 (XM_321792, Anopheles gambiae Ace1); AgAce2 (BN000067, A. gambiae Ace2); BgAce1 (DQ288249, Blattella germanica Ace1); BgAce2 (DQ288847, B. germanica Ace2); HaAce1 (DQ001323, Helicoverpa assulta Ace1); HaAce2 (AY817736, H. assulta Ace2); SgAce1 (AF321574, Schizaphis graminum Ace1) and LdAce2 (L41180, Leptinotarsa decemlineata Ace2).
Numbering of the amino acid sequences was from the N-terminus of mature proteins. Identical amino acids were indicated by asterisks and conservative substitutions by dots. The catalytic triad residues were marked with arrowhead. The number 1, 2, 3 on the boxed amino acids indicated the residues forming intramolecular disulfide bonds. The positions of aromatic residues lining the active site gorge in T. californica AChE were marked with block arrows. The cholinesterase signature sequence was underlined.
Chromosomal locations of TcAce1 and TcAce2
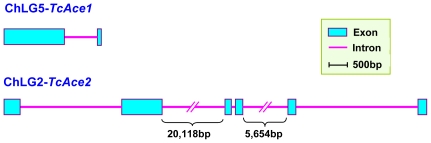
The exon-intron organizations of TcAce1 and TcAce2 were revealed by comparisons of the full-length cDNAs with their corresponding genomic sequences (http://beetlebase.org/). The lengths of TcAce1 and TcAce2 genomic DNA sequences are 2,986 bp and 32,243 bp, respectively. Genome structure analysis shows that the two genes are located on different chromosomes of T. castaneum; TcAce1 is located on chromosome 5, whereas TcAce2 on chromosome 2. TcAce1 has two exons and one intron, whereas TcAce2 has six exons and five introns (Fig. 3).
Figure 3. Schematic diagram of the organization of two Ace genes from Tribolium castaneum.
The full lengths of the two genomic sequences were 2,986 bp for TcAce1 and 32,243 bp for TcAce2. Genome structure showed that two different Ace genes in T. castaneum located on different chromosomes. TcAce1 located on chromosome 5 and TcAce2 on chromosome 2. TcAce1 has two exons and one intron, whereas TcAce2 has six exons and five introns.
Phylogenetic relationship of T. castaneum AChE to other AChEs
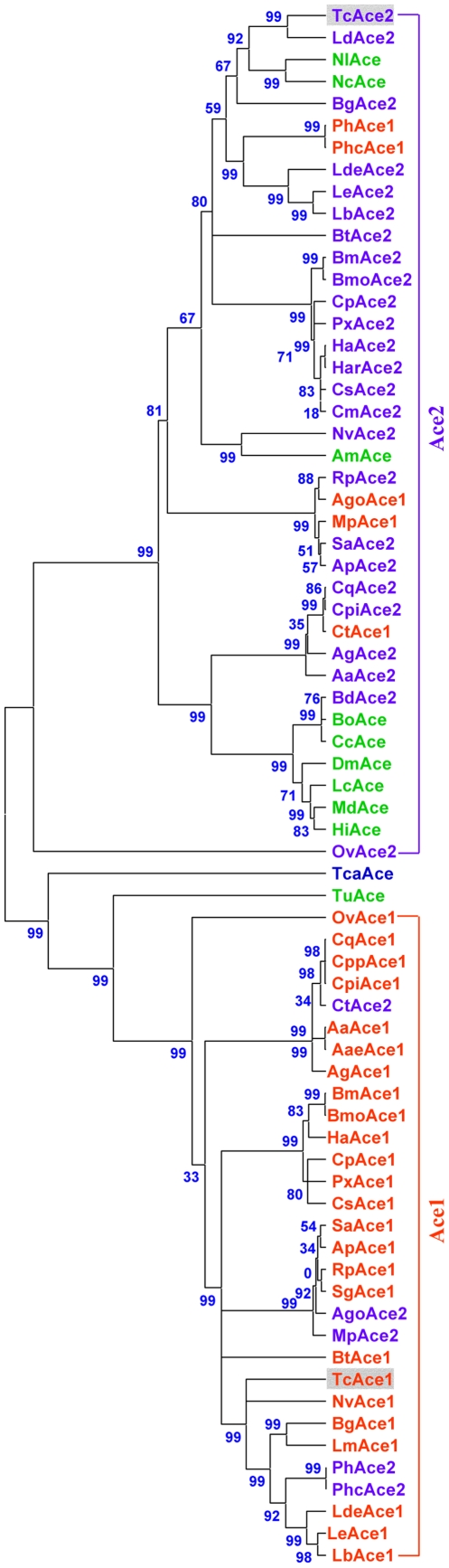
The phylogenetic tree of the deduced amino acid sequences of AChEs from the Pacific electric ray (Torpedo californica), twospotted spider mite (Tetranychus urticae), and all the insect species available in GenBank was generated using the neighbor-joining method. Phylogenetic analysis suggests that there are two major groups (Ace1 and Ace2); TcAce1 and TcAce2 belong to the Ace1- and Ace2-type genes, respectively (Fig. 4). As expected, the cDNA-deduced TcAce1 has high protein sequence identities to BgAce1 (70%), HaAce1 (64%), AgAce1 (61%), SaAce1 (57%), and SgAce1 (57%). The cDNA-deduced TcAce2 has high protein sequence identities to LdAce2 (84%), HaAce2 (69%), BgAce2 (68%), AgAce2 (60%), SaAce2 (57%), and DmAce (55%) (Table 2). TcAce1 and TcAce2 exhibited 39% and 38% protein sequence identities to T. californica AChE, respectively. However, the protein sequence identities of Ace1 and Ace2 in the same insect species are 36% (between TcAce1 and TcAce2), 31% (between SaAce1 and SaAce2), 35% (between AgAce1 and AgAce2), 35% (between BgAce1 and BgAce2), and 32% (between HaAce1 and HaAce2) (Table 2).
Figure 4. Rooted phylogenetic tree of deduced Ace amino acid sequences from the Pacific electric ray (Torpedo californica), two-spotted spider mite (Tetranychus urticae) and 43 insect species constructed by the neighbor-jointing method.
The name is made up of a species abbreviation (first letter of the genus followed by the first one or two letters of the specific name). Sequences used: TcaAce (CAA27169, T. californica Ace); TcAce1 (HQ260968, Tribolium castaneum Ace1, this paper); TcAce2 (HQ260969, T. castaneum Ace2, this paper); BmAce1(EU262633, Bombyx mandarina Ace1); BmAce2 (EU262632, B. mandarina Ace2); SaAce1 (AY819704, Sitobion avenae Ace1); SaAce2 (AY707319, S. avenae Ace2); RpAce1 (AY667435, Rhopalosiphum padi Ace1); RpAce2 (AY707318, R. padi Ace2); DmAce (X05893, Drosophila melanogaster Ace); AgAce1 (XM_321792, Anopheles gambiae Ace1); AgAce2 (BN000067, A. gambiae Ace2); LdeAce1 (FJ647186, Liposcelis decolor Ace1); LdeAce2 (FJ647187, L. decolor Ace2); OvAce1 (FJ228227, Orchesella villosa Ace1); OvAce2 (FJ228228, O. villosa Ace2); LeAce1 (EU854149, Liposcelis entomophila Ace1); LeAce2 (EU854150, L. entomophila Ace2); BgAce1 (DQ288249, Blattella germanica Ace1); BgAce2 (DQ288847, B. germanica Ace2); BtAce1 (EF675188, Bemisia tabaci Ace1); BtAce2 (EF675190, B. tabaci Ace2); CqAce1 (XM_001847396, Culex quinquefasciatus Ace1); CqAce2 (XM_001842175, C. quinquefasciatus Ace2); BmoAce1 (NP_001037380 Bombyx mori Ace1); BmoAce2 (NP_001108113 B. mori Ace2); ApAce1 (XM_001948618, Acyrthosiphon pisum Ace1); ApAce2 (XM_001948953, A. pisum Ace2); NvAce1 (XM_001600408, Nasonia vitripennis Ace1); NvAce2 (XM_001605518, N. vitripennis Ace2); PhAce1 (AB266605, Pediculus humanus corporis Ace1); PhAce2 (AB266606, P. humanus corporis Ace2); CpAce1 (DQ267977, Cydia pomonella Ace1); CpAce2 (DQ267976, C. pomonella Ace2); HaAce1 (DQ001323, Helicoverpa assulta Ace1); HaAce2 (AY817736, H. assulta Ace2); AaAce1 (AB218421, Aedes albopictus Ace1); AaAce2 (AB218420, A. albopictus Ace2); AgoAce1 (AF502081, Aphis gossypii Ace1); AgoAce2 (AF502082, A. gossypii Ace2); CtAce1 (AB122151, Culex tritaeniorhynchus Ace1); CtAce2 (AB122152, C. tritaeniorhynchus Ace2); SgAce1 (AF321574, Schizaphis graminum Ace1); MpAce1 (AF287291, Myzus persicae Ace1); MpAce2 (AY147797, M. persicae Ace2); CpiAce1 (AJ489456, Culex pipiens Ace1); CpiAce2 (AM159193, C. pipiens Ace2); MdAce (AY134873, Musca domestica Ace); PxAce1 (AY970293, Plutella xylostella Ace1); PxAce2 (AY061975, P. xylostella Ace2); CsAce1 (EF453724, Chilo suppressalis Ace1); CsAce2 (EF470245, C. suppressalis Ace2); CmAce2 (FN538987, Cnaphalocrocis medinalis Ace2); PhcAce1 (AB266614, Pediculus humanus capitis Ace1); PhcAce2 (AB266615, P. humanus capitis Ace2); TuAce (AY188448, T. urticae Ace); AaeAce1 (EF209048, Aedes aegypti Ace1); LmAce1 (EU231603, Locusta migratoria manilensis Ace1); LbAce1 (FJ647185, Liposcelis bostrychophila Ace1); LbAce2 (EF362950, L. bostrychophila Ace2); NlAce (FM866396, Nilaparvata lugens Ace); CcAce (EU130781, Ceratitis captitata Ace); AmAce (AB181702, Apis mellifera Ace); BdAce2 (AY155500, Bactrocera dorsalis Ace2); HiAce (AY466160, Haematobia irritans Ace); CppAce1 (AY762905, Culex pipiens pallens Ace1); HarAce2 (AF369793, Helicoverpa armigera Ace2); BoAce (AF452052; Bactrocera oleae Ace); LcAce (U88631, Lucilia cuprina Ace); NcAce (AF145235, Nephotettix cincticeps Ace); LdAce2 (L41180, Leptinotarsa decemlineata Ace2).
Table 2. Percent identities of amino acid residues among the AChEs of Tribolium castaneum, Torpedo californica and other seven insect species.
| Name | Tca | TcAce1 | SaAce1 | AgAce1 | BgAce1 | SgAce1 | HaAce1 | DmAce | TcAce2 | SaAce2 | AgAce2 | BgAce2 | LdAce2 | HaAce2 |
| Tca | — | 39 | 38 | 42 | 40 | 38 | 39 | 35 | 38 | 37 | 37 | 38 | 37 | 37 |
| TcAce1 | — | 57 | 61 | 70 | 57 | 64 | 31 | 36 | 31 | 34 | 36 | 34 | 34 | |
| SaAce1 | — | 51 | 59 | 96 | 55 | 32 | 36 | 31 | 33 | 34 | 33 | 34 | ||
| AgAce1 | — | 57 | 51 | 59 | 34 | 37 | 33 | 35 | 39 | 35 | 36 | |||
| BgAce1 | — | 59 | 62 | 33 | 36 | 33 | 33 | 35 | 36 | 34 | ||||
| SgAce1 | — | 55 | 32 | 36 | 30 | 33 | 34 | 34 | 33 | |||||
| HaAce1 | — | 31 | 35 | 30 | 32 | 35 | 34 | 32 | ||||||
| DmAce | — | 55 | 48 | 62 | 51 | 53 | 51 | |||||||
| TcAce2 | — | 57 | 60 | 68 | 84 | 69 | ||||||||
| SaAce2 | — | 50 | 53 | 55 | 52 | |||||||||
| AgAce2 | — | 55 | 57 | 56 | ||||||||||
| BgAce2 | — | 63 | 60 | |||||||||||
| LdAce2 | — | 66 | ||||||||||||
| HaAce2 | — |
NOTE: TcaAce, Torpedo californica; TcAce, Tribolium castaneum; SaAce, Sitobion avenae; DmAce, Drosophila melanogaster; AgAce, Anopheles gambiae; BgAce, Blattella germanica; HaAce, Helicoverpa assulta; SgAce, Schizaphis graminum; LdAce, Leptinotarsa decemlineata.
It is worth noting that, per the present nomenclature, the reported PhAce1, PhcAce1, AgoAce1, MpAce1 and CtAce1 in the Ace2 group should change to PhAce2, PhcAce2, AgoAce2, MpAce2 and CtAce2, respectively, whereas the reported PhAce2, PhcAce2, AgoAce2, MpAce2 and CtAce2 in the Ace1 group should be named PhAce1, PhcAce1, AgoAce1, MpAce1 and CtAce1, respectively (Fig. 4).
Three-dimensional models
TcAce1 (TcAP-AChE)
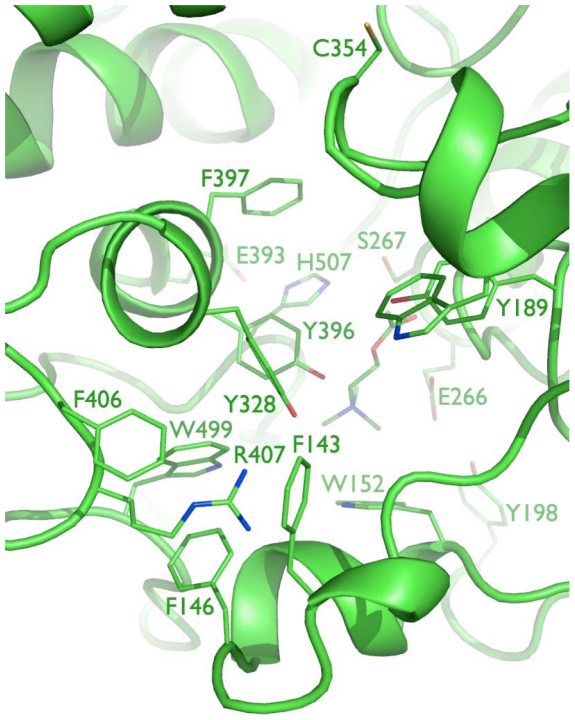
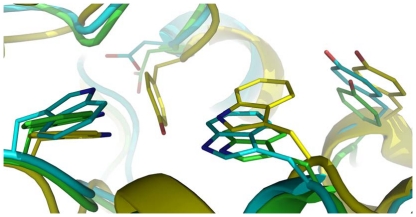
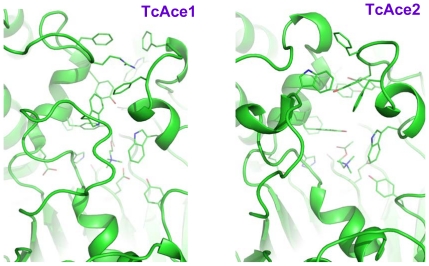
Eighteen 10-ns molecular dynamics simulations of the substrate-bound TcAce1 protein homology model derived from a human butyrylcholinesterase (hBChE) crystal structure (Protein Data Bank ID: 2J4C [42]) resulted in a time-averaged model with a distorted catalytic triad and partial unfold of the omega loop. This result indicates that the homology model is structurally unstable, presumably due to the low sequence identity of the omega loop between TcAce1 and hBChE that results in gaps in the omega loop. Another homology model was therefore built from a simulation-refined model of the African malaria mosquito (A. gambiae) AP-AChE (Protein Data Bank ID: 2AZG) [33] that has a higher sequence identity to TcAce1 (73%) than the identity between hBChE and TcAce1 (46%). Twenty-two 10-ns molecular dynamics simulations of this model liganded with its substrate yielded a time-averaged model without distortions in the catalytic triad and the omega loop. In this final model of TcAce1 (Fig. 5), C354 is exposed to solvent and accessible to covalent bonding at the opening of the active-site gorge [33]; R407 is enclosed by F143, F146, and F406 via cation-pi interactions; Y189, Y396, and Y400 adopt conformations that make the gorge relatively open; ACh adopts the fully extended conformation with its ammonium group forming a cation-pi interaction with the indole ring of W152 and its carbonyl oxygen atom anchored at the oxyanion hole comprising of G186, G187, and A268; E266 forms a hydrogen bond with Y198 at the bottom of the active-site gorge; E393, H507, and S267 form the catalytic triad. The TcAce1 active site is very similar to those of A. gambiae and S. graminum AP-AChEs [33], [34], and different from the human AChE active site in that Y449 in the human enzyme is replaced by Asp creating void space at the bottom of the TcAce1 active site (Fig. 6). In T. californica AChE, rotation of Y442, which corresponds to Y449 of human AChE, reportedly controls the opening of a 3.4-Å-wide channel that enables rapid clearance of substrate hydrolysis products [43]. In DmAChE, the counterpart of Y449 is also mutated to Asp; hence the crystal structure of DmAChE (Protein Data Bank ID: 1DX4 [41]) has a channel with a diameter of ∼5 Å that is formed by G79, W83, W472, L479, and D482 and connects the active-site gorge to solvent [44]. Because of the mutation Tyr of human to Asp of TcAce1, the final model of TcAce1 has a similar channel that is comprised of G148, W152, W499, M506, and D509. The TcAce1 channel is, however, partially blocked by M151 and P498.
Figure 5. Close-up view of the active site of TcAce1 with a perspective from the free cysteine at the opening of the active-site gorge down to ACh and the catalytic triad at the bottom of the gorge.
Figure 6. Comparison of the bottom of the active-site gorge in TcAce1 to those in human AChE and Anopheles gambiae AP-AChE.
Tyr449 in human AChE (yellow) is mutated to Asp509 in TcAce1 (green) and Asp441 in A. gambiae AChE (cyan).
TcAce2 (TcAO-AChE)
A homology study identified the crystal structure of DmAChE (PDB ID: 1DX4 [41]) as a template with a sequence identity of 60% and generated a homology model of TcAce2. This model has a protruded large loop conformation for residues 145–162, which is due to the omission of the corresponding loop (residues 103–136) in the 1DX4 crystal structure. An initial set of 21 10-ns molecular dynamics simulations of the TcAce2 homology model without residues 145–162 resulted in a time-average model with the catalytic triad distorted.
In the loop of residues 145–162, there are two histidine residues, four arginine residues, two lysine residues, one aspartate residue, and one glutamate residue. At the physiological pH of 7.4, this loop has a net charge of +4. To avoid a possible effect of the highly-charged loop on the catalytic triad distortion, a second set of 21 10-ns simulations of the TcAce2 homology model possessing residues 145–162 was performed. The triad was still distorted in an average conformation of all trajectories saved at 1.0-ps intervals during the last 1-ns period of all 21 simulations or in an average of each cluster of the trajectories generated by a cluster analysis. As to the loop conformation of residues 145–162, the cluster analysis showed that 24% of the trajectories had residues 145–162 folded in contact with surface residues such as R21, D148, D501, and D203.
A third set of 22 10-ns simulations of TcAce2 with residues 145–162 adopting the folded conformation was then carried out. The initial conformation of the third set of simulations was obtained from averaging all the trajectories of TcAce2 with the folded loop conformation of residues 145–162 followed by manual adjustment of the side-chain torsions to restore the hydrogen bond network of the catalytic triad. A cluster analysis of all the trajectories saved at 1.0-ps intervals during the last 1.0-ns period of all 22 simulations showed that residues 145–162 remain the folded conformation. However, the average of all the trajectories had a distorted catalytic triad. Visual inspection of all 22 simulations found that conformations of the first of the 22 simulations have a catalytic triad engaging in a hydrogen-bond network. The final model of TcAce2 was then obtained from averaging all trajectories saved at 1.0-ps intervals during the last 1.0 ns period of the first simulation.
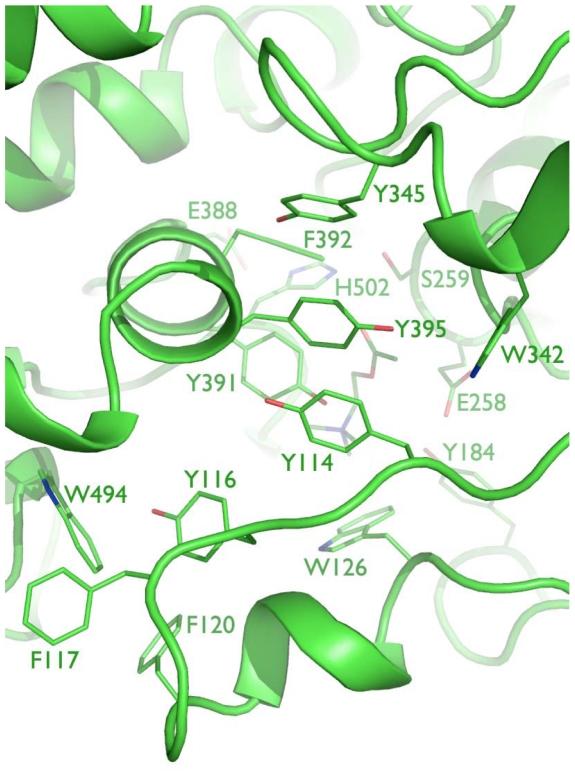
Although the homology model of TcAce2 was based on the DmAChE crystal structure, the active site of the simulation-refined TcAce2 model (Fig. 7) is very different from that of the DmAChE crystal structure. It is also different from those of human AChE and insect AP-AChEs (i.e., AChE1s). In the refined model of TcAce2 (Fig. 7), Y114, Y345, Y395, and W342 form an aromatic cluster that completely block the entrance of the active site; E388, H502, and S259 form a catalytic triad; ACh has a cation-pi interaction with W126, but it does not adopt the fully extended conformation, nor is its carbonyl oxygen atom located in the oxyanion hole. In contrast to the TcAce1 model with residues 146–154 and 493–509 that partially shield ACh from interacting with solvent, the TcAce2 model has its corresponding residues (120–128 and 488–504) adopt conformations that leave ACh to be exposed to solvent (Fig. 8).
Figure 7. Close-up view of the active site of TcAce2 with a perspective looking down to acetylcholine and the catalytic triad at the bottom of the gorge.
Figure 8. Comparison of loop conformations of residues 146–154 and 493–509 in TcAce1 with the corresponding ones of residues 120–128 and 488–504 in TcAce2.
TcAce gene expression profiles
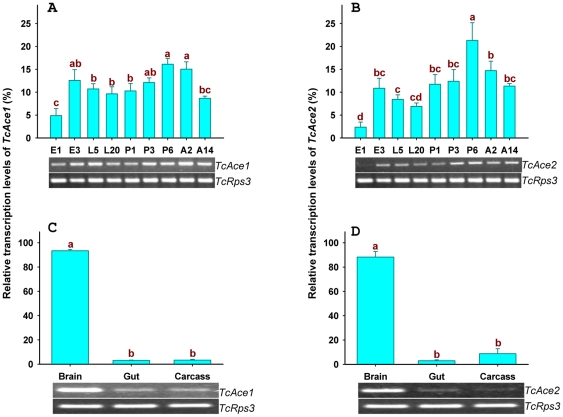
The transcript levels of TcAce1 and TcAce2 were evaluated by reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) and quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) in tissues of T. castaneum at different developmental stages (Fig. 9). Both TcAce genes were transcribed in all the stages examined, including 1-day (d) and 3-d eggs; 5-d and 20-d larvae; 1-d, 3-d and 6-d pupae; and 2-d and 14-d adults. The lowest expression levels of these genes were found in eggs, particularly for TcAce2 whose expression level was undetectable by RT-PCR in 1-d eggs (Fig. 9A and 9B). The expression patterns of TcAce1 and TcAce2 were very similar. In addition, the TcAce1 and TcAce2 genes also exhibited similar tissue-specific expression patterns (Fig. 9C and 9D). As expected, these genes were predominately expressed in the brain, although their expressions were also detected in the gut and carcass after the brain and ventral nerve cord were removed.
Figure 9. The two TcAce genes mRNA expression levels of developmental stages and different tissues were determined by RT-PCR as shown by gel pictures at the bottom of each panel and quantitative real-time PCR as shown by histograms.
Real-time PCR data were normalized to TcRps3 gene expression. E1, 1-d eggs; E3, 3-d eggs; L5, 5-d larvae; L20, 20-day larvae; P1, 1-d pupae; P3, 3-d pupae; P6, 6-d pupae; A2, 2-d adults; A14, 14-d adults. Gut (including midgut and hindgut), Carcass (not including head, gut and nerve system). Standard error bars were base on three replicates. One-Way ANOVA-Fisher's LSD was used in statistical analysis of quantitative real-time PCR data.
Discussion
Since the first insect AChE orthologous gene (i.e., the one later named Ace2 or AO-Ace) and the first insect AChE paralogous gene (i.e., the one later named Ace1 or AP-Ace) were reported in D. melanogaster in 1986 [9] and in S. graminum in 2002 [10], respectively, cDNAs encoding both Ace1 and Ace2 have been sequenced from each of at least 27 insect species. However, the gene models and the genomic organizations of Ace1 and Ace2 have not been well established in insects. In this study, we confirmed the two Ace gene (TcAce1 and TcAce2) models in T. castaneum by sequencing the coding regions of their cDNAs followed by comparative analyses of their cDNA and genomic sequences. The TcAce1 and TcAce2 genes are significantly different not only in the length of their genomic DNA (TcAce1 with 2,986 bp and TcAce2 with 32,243 bp) but also in the intron/exon organizations. Specifically, TcAce1 possesses only one intron whereas TcAce2 has five introns. Furthermore, TcAce1 is located on chromosome 5 (ChLG5), whereas TcAce2 is on chromosome 2 (ChLG2; Fig. 3). Apparently, the intron/exon organizations and the chromosomal locations of these genes in T. castaneum are different from their counterparts in other insect species [8], [14], [18], [23], [45].
Despite the significant differences in genomic structures and the chromosomal locations of TcAce1 and TcAce2, the deduced protein sequences of the two genes exhibit all the common features of an AChE sequence wise. These features include (1) a conserved active-site triad, including S267 in TcAce1 and S259 in TcAce2 (S200 in Torpedo), E393 in TcAce1 and E388 in TcAce2 (E327 in Torpedo), and H507 in TcAce1 and H502 in TcAce2 (H440 in Torpedo); (2) a choline binding site, W152 in TcAce1 and W126 in TcAce2 (W84 in Torpedo); (3) three pairs of cysteines putatively forming intramolecular disulfide bonding (C135∼C162, C321∼C334, and C469∼C591 in TcAce1; and C109∼C136, C313∼C328, and C464∼C580 in TcAce2); (4) a cysteine forming intermolecular disulfide bonding (C617 in TcAce1 and C600 in TcAce2); (5) 10 conserved aromatic amino acid residues out of 14 aromatic residues lining the catalytic gorge of AChE; and (6) the conserved sequence FGESAG, flanking S267 in TcAce1 and S259 in TcAce2 (Fig. 2).
Ethanolmine and glucosamine residues are characteristic of a C-terminal glycolipid anchor in most G2 AChE [46], [47]. Our analysis by using PredGPI predictor suggests that DmAChE and TcAce1 contain a GPI-anchor at the C-terminal. Although TcAce2 has higher sequence identity level with DmAChE than TcAce1, TcAce2 does not appear to contain a GPI-anchor at the C-terminal. Because the C-terminal Cys residue in AChE is reportedly for the intermolecular disulfide linkage [48], C617 in TcAce1 and C600 in TcAce2 are likely involved in the intermolecular disulfide linkage, although the corresponding Cys residue is missing in DmAChE [46]. We also analyzed the hydrophilic and hydrophobic of non-homologous amino acid residues of TcAce1 and TcAce2 and compared homologous sequences of TcAce1 and TcAce2 with mAChE and DmAChE at the C-terminal for possible formation of the four-helix bundle. Our analysis suggests that C-terminal sequences of both TcAce1 and TcAce2 may form the dimeric four-helix bundle.
According to comparisons of TcAce1 and TcAce2 with Ace proteins from other insect species, TcAce1 showed high sequence identities to the AChE1 (AP-AChE) proteins from Sitobion avenae (57%), A. gambiae (61%), Blattella germanica (70%), S. graminum (57%), and Helicoverpa assulta (64%; Table 2). Similarly, TcAce2 also showed high amino acid identities to the AChE2 (AO-AChE) proteins of S. avenae (57%), D. melanogaster (55%), A. gambiae (60%), B. germanica (68%), Leptinotarsa decemlineata (84%), and H. assulta (69%). Based on our analysis of deduced amino acid sequences from the two genes among respective insect species, the sequence identity levels within the paralogous (Ace1) or orthologous (Ace2) genes range from 48 to 96%, whereas the sequence identity levels between the Ace1 and Ace2 genes of the same insect species range only from 31 to 36% in all insect species examined (Table 2). These results support the hypothesis that the two Ace genes were originated from an old duplication before the diversification of insect species [32].
Furthermore, a phylogenetic tree, which was generated from the highly conserved regions of all insect and T. urticae AChE amino acid sequences available in GenBank and the corresponding one in T. californica using the neighbor-joining method, revealed two insect AChE clusters. TcAce1 was grouped into the insect Ace1 cluster and TcAce2 into the insect Ace2 cluster. The significant divergence between TcAce1 and TcAce2 suggests that these genes were evolved from their corresponding Ace gene lineages in insect species [49]. These results also suggest, for the first time, that the divergence of Ace1 and Ace2 might occur prior to insect speciation and that the Ace1 gene might be lost in D. melanogaster and other species in Cyclorrapha suborder of Diptera during the evolutionary process [14], [25], [32]. Thus, it is likely that both the Ace genes in insects may have different functions because these genes have evolved during the evolutionary histories of these insect species.
Using a reported simulation-refined model of A. gambiae AP-AChE [33] and a crystal structure of DmAChE [41] with high sequence identities to TcAce1 (73%) and TcAce2 (60%), respectively, and the same multiple molecular dynamics simulation method to model and refine TcAce1 and TcAce2, we obtained models of TcAce1 and TcAce2 both which are in complex with acetylcholine. The TcAce1 model has an active site that is almost identical to those of A. gambiae and S. graminum AP-AChEs, and it has C354 at the opening of the active-site gorge just like the insect-specific C286 of A. gambiae and C289 of S. graminum that are susceptible to sulfhydryl agents [33], [34]. The TcAce2 model has an active site with an entrance comprised of G122, W126, W494, M501, and D504. This entrance corresponds to the small opening at the bottom of the active-site gorge of DmAChE [44] or T. californica AChE when Y442 moves away from W84 [43]. In the TcAce2 model, the region that corresponds to the entrance of TcAce1 is completely blocked by Y114, Y345, Y395, and W342. Of the four aromatic residues, Y395 and W342 correspond to Y334 and W279 of T. californica AChE, respectively, and belong to the 14 conserved aromatic residues that line the active-site gorge of T. californica AChE [50]. In other words, the entrance of the active-site gorge of TcAce2 appears to be reversed relative to that of TcAce1. Unlike ACh in the TcAce1 model, ACh does not adopt the fully extended conformation and its carbonyl oxygen atom is not placed in the oxyanion hole in the TcAce2 model.
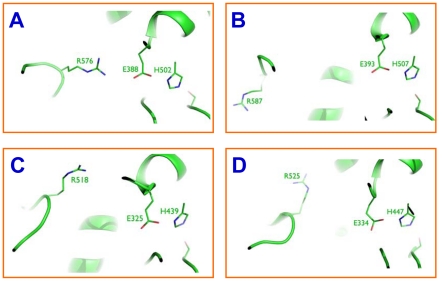
In addition, R576 in the TcAce2 model is close to E388 (the separation between the side-chain N atom of R576 and the side-chain O atom of E388 is 3.9 Å), a composite residue of the catalytic triad, in contrast to the corresponding arginine residue that is away from the catalytic glutamate residue in TcAce1, A. gambiae AP-AChE and human AChE (Fig. 10). Analysis of all the trajectories of the third set of simulations of TcAce2 showed that 95% of the trajectories has a hydrogen bond between R576 and E388, accompanied by hydrogen bonds between H502 and E505 and between S259 and E258, leading to disruption of the catalytic triad. These computational observations suggest that TcAce1 is a robust ACh hydrolase and susceptible to sulfhydryl agents and that TcAce2 is not a catalytically efficient ACh hydrolase, although further study is needed to comprehensively elucidate physiological functions of Ace1 and Ace2 genes. In view of these computational results, it is logical to investigate whether TcAce2 functions more as a cholinesterase-like adhesion molecule (CLAM) [51], [52] than TcAce1. However, our sequence analysis using ClustalW 2.0.12 shows that TcAce1 has a slightly higher sequence homology to D. melanogaster gliotactin, which is one of the three D. melanogaster CLAMs, than TcAce2 (Table 3); both TcAce1 and TcAce2 have dipole moments that are comparable to those of other AChEs (Table 4). The orientations of the dipole moments of TcAce1 and TcAce2 are almost the same. The two dipole moments are approximately along the beta strand that corresponds to Strand 5 of the T. californica AChE crystal structure [53] and nearly identical to those of other AChEs but orthogonal to that of Galactomyces geotrichum lipase [52], [54]. These sequence and dipole moment analyses do not support the hypothesis that TcAce2 functions as a CLAM.
Figure 10. Separation of Arg from the catalytic triad in TcAce2 (A), TcAce1 (B), Anopheles gambiae AP-AChE (C), and human AChE (D).
Table 3. Percentages of amino acid sequence identity of TcAce1 and TcAce2 to cholinesterase-like lipase and adhesion proteins.
| AChE | GcNeutralLipase | DmNeuroligin | DmNeurotactin | DmGliotactin |
| Torpedo californica AChE | 23 | 19 | 17 | 25 |
| TcAChE1 | 19 | 21 | 17 | 27 |
| TcAChE2 | 20 | 20 | 18 | 25 |
Table 4. The electrostatic characteristics of TcAce1, TcAce2, and other proteins.
| PDB ID (Species) | Total atoms | Total residues | Net charge of N terminal deletion (e) | Net charge of C terminal deletion (e) | Net charge of deletion between N and C termini (e) | Net charge of the structure or model (e) | Dipole moment (Debye) | Dipole moment per atom (Debye) |
| TcAce1 (Tribolium castaneum, AP) | 4201 | 529 | −5 | 0 | 0 | −3 | 1490 | 0.35 |
| TcAce2 (Tribolium castaneum, AO) | 4353 | 545 | −1 | +1 | 0 | −19 | 1163 | 0.27 |
| 1QO9 (Drosophila melanogaster, AO) | 4273 | 540 | 0 | −2 | +1 | −18 | 669 | 0.16 |
| 2AZG (Anopheles gambiae, AP) | 4243 | 536 | 0 | −1 | 0 | −8 | 1718 | 0.40 |
| 2HCP (Schizaphis graminum, AP) | 4302 | 540 | −7 | +2 | 0 | −8 | 1312 | 0.30 |
| 2ACE (Torpedo californica) | 4143 | 527 | −2 | −1 | −1 | −8 | 1819 | 0.44 |
| 1J06 (Mus musculus) | 4177 | 535 | +2 | −2 | 0 | −9 | 867 | 0.21 |
| 2X8B (Homo sapiens) | 4179 | 536 | 0 | −2 | 0 | −10 | 1384 | 0.33 |
| 1THG (Galactomyces geotrichum, lipase) | 4287 | 543 | +1 | 0 | 0 | −15 | 814 | 0.19 |
Materials and Methods
Insect culture
The Georgia-1 (GA-1) strain of T. castaneum was reared on whole-wheat flour containing 5% (by weight) of brewers' yeast at 30°C and 65% relative humidity under standard conditions in the laboratory of Kansas State University (Manhattan, Kansas, United States of America) based on the method of Haliscak and Beeman [55].
Total RNA isolation and reverse transcription
Total RNA was isolated from T. castaneum samples using TRIzol reagent following the recommended procedure by Invitrogen (Carlsbad, California, United States of America). The RNA was treated with DNase I (Fermentas, Glen Burnie, Maryland, United States of America) according to the manufacturer's instruction and the first-strand cDNA template was synthesized from 3.0 µg of total RNA by using First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Fermentas) with oligo (dT)18 as the primer.
Subcloning and sequencing of cDNA
To obtain the cDNAs corresponding to the entire protein coding regions of TcAce1 and TcAce2, we designed specific primers based on TcAce gene predictions and their genomic organization (Table 1). The PCR products of each reaction were subjected to electrophoresis on 1% agarose gel containing ethidium bromide. The PCR bands were excised and purified using QIAEX II Agarose Gel Extraction Kit (Qiagen, Valencia, California, United States of America). The purified fragment was subcloned into a pGEM-T Easy Vector (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer's instruction. The ligation DNA mixtures were used to transform bacterial cells by using Z-Competent E. coli Transformation Kit and Buffer Set™ (Zymo Research Corporation, Irvine, California, United States of America). Plasmids were isolated from the bacterial cells and used for DNA sequencing (KSU DNA Sequencing and Genotyping Facility, Manhattan, Kansas, United States of America). Signal P software was used to predict signal peptide [56].
Phylogenetic analysis of AChEs
ClustalW software (www.ebi.ac.uk/clustalw/) [57], was used to perform multiple sequence alignments prior to phylogenetic analysis. Phylogenetic analysis was done using MEGA 4.0 [58] for construction a neighbor-joining tree to examine the evolutionary relationships among T. californica, T. urticae and 43 insect species. To evaluate the branch strength of the phylogenetic tree, a bootstrap analysis of 1000 replications was performed.
AChE model prediction
Model preparation
The starting conformations of TcAce1 and TcAce2 used in the multiple molecular dynamics simulations were generated by the SWISSMODEL homology program using a computer model (Protein Data Bank ID: 2AZG [33]) and a crystal structure (Protein Data Bank ID: 1DX4 [41]) as templates, respectively. ACh was manually docked into the active site of TcAce1 or TcAce2 according to the bound ACh conformation in the crystal structure of T. californica AChE (Protein Data Bank ID: 2ACE [59]). All His, Glu, Asp, Arg, and Lys residues of the ACh-bound TcAce1 or TcAce2 were treated as HIP, GLU, ASP, ARG, and LYS, respectively. The topology and coordinate files were generated by the PREP, LINK, EDIT, and PARM modules of the AMBER 5.0 program [60]. The complex was refined by energy minimization using the SANDER module of the AMBER 5.0 program with a dielectric constant of 1.0 and 500 cycles of steepest-descent minimization followed by 10,000 cycles of conjugate-gradient minimization. The energy-minimized ACh complex with TcAce1 or TcAce2 was solvated with 5,897 or 6,744 TIP3P water molecules [61], leading to a system of 20,703 or 23,244 atoms, respectively. The water molecules were obtained from solvating the complex using a pre-equilibrated box of 216,000 TIP3P molecules, whose hydrogen atom charge was set to 0.4170, where any water molecule was removed if it had an oxygen atom closer than 2.2 Å to any solute atom or a hydrogen atom closer than 2.0 Å to any solute atom, or if it was located further than 10.0 Å along the x-, y-, or z-axis from any solute atom.
Multiple molecular dynamics simulations
The solvated protein complex was energy-minimized for 100 cycles of steepest-descent minimization followed by 100 cycles of conjugate-gradient minimization to remove close van der Waals contacts in the system, then heated from 0 to 300 K at a rate of 10 K/ps under constant temperature and volume, and finally simulated independently with a unique seed number for initial velocities at 300 K under constant temperature and pressure using the PMEMD module of the AMBER 8.0 program [62] with the AMBER force field (ff99SB) [63], [64]. All simulations used (1) a dielectric constant of 1.0, (2) the Berendsen coupling algorithm [65], (3) a periodic boundary condition at a constant temperature of 300 K and a constant pressure of 1 atm with isotropic molecule-based scaling, (4) the Particle Mesh Ewald method to calculate long-range electrostatic interactions [66], (5) a time step of 1.0 fs, (6) the SHAKE-bond-length constraints applied to all the bonds involving the H atom, (7) saving the image closest to the middle of the “primary box” to the restart and trajectory files, (8) formatted restart file, and (9) default values of all other inputs of the PMEMD module. All simulations were performed on a cluster of Apple Mac Pros with 80 Intel Xeon cores (3.0 GHz) and a cluster of Apple Xserves with 590 G5 processors (2.2/2.3 GHz).
Simulation analysis
Average structures were obtained by using the CARNAL module of AMBER 5.0. Cluster analyses were performed by using the PTRAJ module [67] of AMBER 10.
Dipole moment calculations
All dipole moment calculations were performed using the Protein Dipole Moments Server (http://bioinfo.weizmann.ac.il/dipol/indexj.html) [68]. Protein structures with minimal deletions were used and ligands and structural water molecules were removed before the dipole moment calculations.
Analysis of expression of TcAce1 and TcAce2 by RT-PCR and qPCR
The expression patterns of both TcAce1 and TcAce2 genes were analyzed at various developmental stages including embryos (1 day and 3 days eggs), early larvae (5 days larvae), late larvae (20 days larvae), early pupae (1 day pupae), middle pupae (3 days larvae), late pupae (6 days pupae), early adults (2 days adults) and two weeks old adults. To analyze tissue specific expression, we collected samples from the following dissected late pupa tissues (pooled from thirty late pupae): brain, gut (midgut and hind gut) and carcass (the whole body excluding brain, ganglia and gut). For all the samples, 3.0 µg of total RNA were treated with DNase I (Fermentas) to remove any genomic DNA contaminations, and then used as templates for the first strand cDNA synthesis. The cDNAs prepared from total RNA were used as templates for amplification and detection of specific TcAce sequences. The gene-specific primers were designed by using the Beacon Designer 2.0 software (Premier Biosoft International, Palo Alto, California, United States of America) and are shown in Table 1. For reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR), cDNA fragments of each TcAce were amplified using the PCR conditions as follows: 94°C for 1.5 min followed by 30 cycles (26 cycles for TcRps3 gene) of 94°C 30 s, 55°C 30 s and 72°C 45 s. A final extension at 72°C for 5 min was added at the end of the PCR. The relative mRNA expression of each TcAce was assessed by qRT-PCR using SYBR-Green in the Bio-Rad iCycler iQ™ multi-coclor real-time PCR detection system (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA) based on the method of Giulietti et al. [69]. All the experiments were performed in triplicate and normalized to the mRNA level of ribosomal protein S3 (Rps3) as a reference gene for each sample [70]. The relative mRNA expression levels were calculated according to the 2−ΔΔCt method [71].
Statistical analysis
The data from the qPCR analysis were subjected to ANOVA followed by Fisher's least significant difference (LSD) multiple comparisons to separate the means among the treatments by using ProStat software (Poly Software International, Pearl River, New York, United States of America).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Ming-Shun Chen for his helpful comments on an earlier draft of this manuscript. The computational studies were supported in part by the University of Minnesota Supercomputing Institute. Mention of trade names or commercial products in this publication is solely for the purpose of providing specific information and does not imply recommendation or endorsement by Kansas State University or the Mayo Clinic. This paper is contribution No. 11-210-J from the Kansas Agricultural Experiment Station. The T. castaneum voucher specimens (voucher No. 159) are located in the Kansas State University Museum of Entomological and Prairie Arthropod Research, Manhattan, Kansas, United States of America.
Footnotes
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Funding: This study was supported by the Kansas Agricultural Experiment Station and the Arthropod Genomics Center funded by K-State Targeted Excellence program at Kansas State University to KYZ, China Scholarship Council to YL, and the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA/NIFA 2009-05236) to YPP. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Taylor P, Radic Z. The cholinesterases: from genes to proteins. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1994;34:281–320. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.34.040194.001433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Soderlund DM, Bloomquist JR. Roush RT, Tabashnik BE, editors. Molecular mechanism of insecticide resistance, Pesticide resistance in Arthropods. 1990. pp. 58–96. Chapman and Hall, New York.
- 3.Zhu KY, Brindley WA. Enzymological and inhibitory properties of acetylcholinesterase purified from Lygus hesperus Knight (Hemiptera: Miridae). Insect. Biochem Mol Biol. 1992;22:245–251. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Fournier D, Mutero A. Modification of acetylcholinesterase as a mechanism of resistance to insecticides. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1994;108C:19–31. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zhu KY, Clark JM. Cloning and sequencing of a cDNA encoding acetylcholinesterase in Colorado potato beetle, Leptinotarsa decemlineata (Say). Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 1995;25:1129–1138. doi: 10.1016/0965-1748(95)00055-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zhu KY, Lee SH, Clark JM. A point mutation of acetylcholinesterase associated with azinphosmethyl resistance and reduced fitness in Colorado potato beetle. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 1996;55:100–108. doi: 10.1006/pest.1996.0039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Guedes RNC, Zhu KY, Kambhampati S, Dover BA. An altered acetylcholinesterase conferring negative cross-insensitivity to different insecticidal inhibitors in organophosphate resistant lesser grain borer, Rhyzopertha dominica. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 1997;58:55–62. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kono Y, Tomita T. Amino acid substitutions conferring insecticide insensitivity in Ace-paralogous acetylcholinesterase. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2006;85:123–132. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hall LMC, Spierer P. The Ace locus of Drosophila melanogaster: structural gene for acetylcholinesterase with an unusual 5′ leader. Embo J. 1986;5:2949–2954. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04591.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gao J-R, Kambhampati S, Zhu KY. Molecular cloning and characterization of a greenbug (Schizaphis graminum) cDNA encoding acetylcholinesterase possibly evolved from a duplicate gene lineage. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2002;32:765–775. doi: 10.1016/s0965-1748(01)00159-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Myers EW, Sutton GG, Delcher AL, Dew IM, Fasulo DP, et al. A whole-genome assembly of Drosophila. Science. 2000;5461:2196–2204. doi: 10.1126/science.287.5461.2196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Pang Y-P, Brimijoin S, Ragsdale DW, Zhu KY, Suranyi R. Novel and viable acetylcholinesterase target site for developing effective and environmentally safe insecticides. Curr Drug Targets. 2011 doi: 10.2174/138945012799499703. (in press) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chen MH, Han ZJ. Cloning and sequence analysis of 2 different acetylcholinesterase genes in Rhopalosiphum padi and Sitobion avenae. Genome. 2006;49:239–243. doi: 10.1139/g05-104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Weill M, Fort P, Berthomieu A, Dubois MP, Pasteur N, et al. A novel acetylcholinesterase gene in mosquitoes codes for the insecticide target and is non-homologous to the ace gene in Drosophila. Proc R Soc Lond Ser B. 2002;269:2007–2016. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2002.2122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Nardi F, Barazzuoli B, Ciolfi S, Carapelli A, Dallai R, et al. Acetylcholinesterase genes in the basal Hexapod Orchesella villosa. Insect Mol Biol. 2009;18:45–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2583.2008.00848.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kim JI, Jung CS, Koh YH, Lee SH. Molecular, biochemical and histochemical characterization of two acetylcholinesterase cDNAs from the German cockroach Blattella germanica. Insect Mol Biol. 2006;15:513–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2583.2006.00666.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Alon M, Alon F, Nauen R, Morin S. Organophosphates resistance in the B-biotype of Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) is associated with a point mutation in an ace1-type acetylcholinesterase and overexpression of carboxylesterase. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2008;38:940–949. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2008.07.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Seino A, Kazuma T, Tan AJ, Tanaka H, Kono Y, et al. Analysis of two acetylcholinesterase genes in Bombyx mori. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2007;88:92–101. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lee SW, Kasai S, Komagata O, Kobayashi M, Agui N, et al. Molecular characterization of two acetylcholinesterase cDNAs in Pediculus human lice. J Med Entomol. 2007;44:72–79. doi: 10.1603/0022-2585(2007)44[72:mcotac]2.0.co;2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Cassanelli S, Reyes M, Rault M, Manicardi CG, Sauphanor B. Acetylcholinesterase mutation in an insecticide-resistant population of the codling moth Cydia pomonella (L.). Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2006;36:642–653. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2006.05.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lee DW, Kim SS, Shin SW, Kim WT, Boo KS. Molecular characterization of two acetylcholinesterase genes from the oriental tobacco budworm, Helicoverpa assulta (Guenée). Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1760:125–133. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2005.10.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Li F, Han ZJ. Two different genes encoding acetylcholinesterase existing in cotton aphid (Aphis gossypii). Genome. 2002;45:1134–1141. doi: 10.1139/g02-085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Nabeshima T, Mori A, Kozaki T, Iwata Y, Hidoh O, et al. An amino acid substitution attributable to insecticide-insensitivity of acetylcholinesterase in a Japanese encephalitis vector mosquito, Culex tritaeniorhynchus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;313:794–801. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2003.11.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Nabeshima T, Kozaki T, Tomita T, Kono Y. An amino acid substitution on the second acetylcholinesterase in the pirimicarb-resistant strains of the peach potato aphid, Myzus persicae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;307:15–22. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(03)01101-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Huchard E, Martinez M, Alout H, Douzery EJ, Lutfalla G, et al. Acetylcholinesterase genes within the Diptera: Takeover and loss in true flies. Proc R Soc Lond Ser B. 2006;273:2595–2604. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2006.3621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ni X-Y, Tomita T, Kasai S, Kono Y. cDNA and deduced protein sequence of acetylcholinesterase from the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). Appl Entomol Zool (Jpn) 2003;38:49–56. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Baek JH, Kim JI, Lee DW, Chung BK, Miyata T, et al. Identification and characterization of ace1-type acetylcholinesterase likely associated with organophosphate resistance in Plutella xylostella. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2005;81:164–175. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lee DW, Choi JY, Kim WT, Je YH, Song JT, et al. Mutations of acetylcholinesterase 1 contribute to prothiofos-resistance in Plutella xylostella (L.). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;353:591–597. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.12.088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Jiang X, Qu M, Denholm I, Fang J, Jiang W, et al. Mutation in acetylcholinesterase1 associated with triazophos resistance in rice stem borer, Chilo suppressalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;378:269–272. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.11.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Mori A, Lobo NF, de Bruyn B, Severson DW. Molecular cloning and characterization of the complete acetylcholinesterase gene (Ace1) from the mosquito Aedes aegypti with implications for comparative genome analysis. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2007;37:667–674. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2007.03.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kozaki T, Kimmelblatt BA, Hamm RL, Scott JG. Comparison of two acetylcholinesterase gene cDNAs of the lesser mealworm, Alphitobius diaperinus, in insecticide susceptible and resistant strains. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2008;67:130–138. doi: 10.1002/arch.20229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Chen HJ, Liao Z, Liu XM, Li GQ, Li F, et al. Ace2, rather than Ace1, is the major acetylcholinesterase in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Insect Sci. 2009;16:297–303. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Pang Y-P. Novel acetylcholinesterase target site for malaria mosquito control. PLoS ONE. 2006;1:e58. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Pang Y-P. Species marker for developing novel and safe pesticides. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007;17:197–199. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2006.09.073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Pang Y-P, Singh SK, Gao Y, Lassiter TL, Mishra RK, et al. Selective and irreversible inhibitors of aphid acetylcholinesterases: steps toward human-safe insecticides. PLoS ONE. 2009;4:e4349. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Pang Y-P, Ekström F, Polsinelli GA, Gao Y, Rana S, et al. Selective and irreversible inhibitors of mosquito acetylcholinesterases for controlling malaria and other mosquito-borne diseases. PLoS ONE. 2009;4:e6851. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lang GJ, Zhang XH, Zhang MY, Zhang CX. Comparison of catalytic properties and inhibition kinetics of two acetylcholinesterases from a lepidopteran insect. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2010;98:175–182. [Google Scholar]
- 38.von Heijne G. Sequence Analysis in Molecular Biology. Academic Press San Diego; 1987. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Bourne Y, Grassi J, Bougis PE, Marchot P. Conformational flexibility of the acetylcholinesterase tetramer suggested by X-ray crystallography. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:30370–30376. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.43.30370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Bourne Y, Taylor P, Bougis PE, Marchot P. Crystal structure of mouse acetylcholinesterase: A peripheral site-occluding loop in a tetrameric assembly. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:2963–2970. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.5.2963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Harel M, Kryger G, Rosenberry TL, Mallender WD, Lewis T, et al. Three-dimensional structures of Drosophila melanogaster acetylcholinesterase and of its complexes with two potent inhibitors. Protein Sci. 2000;9:1063–1072. doi: 10.1110/ps.9.6.1063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Nicolet Y, Lockridge O, Masson P, Fontecilla-Camps JC, Nachon F. Crystal structure of human butyrylcholinesterase and of its complexes with substrate and products. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:41141–41147. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M210241200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Sanson B, Colletier JP, Xu Y, Therese Lang P, Jiang H, et al. Backdoor opening mechanism in acetylcholinesterase based on X-ray crystallography and MD simulations. Protein Sci. 2011;20:1114–1118. doi: 10.1002/pro.661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Nachon F, Stojan J, Fournier D. Insights into substrate and product traffic in the Drosophila melanogaster acetylcholinesterase active site gorge by enlarging a back channel. FEBS J. 2008;275:2659–2664. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06413.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Mori A, Tomita T, Hidoh O, Kono Y, Severson DW. Comparative linkage map development and identification of an autosomal locus for insensitive acetylcholinesterase-mediated insecticide resistance in Culex tritaeniorhynchus. Insect Mol Biol. 2001;10:197–203. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2583.2001.00255.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Gnagey AL, Forte M, Rosenberry TL. Isolation and characterization of acetylcholinesterase from Drosophila. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:13290–13298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Haas R, Marshall TL, Rosenberry TL. Drosophila acetylcholinesterase: demonstration of a glycoinositol phospholipid anchor and an endogenous proteolytic cleavage. Biochemistry. 1988;27:6453–6457. doi: 10.1021/bi00417a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.MacPhee-Quigley K, Vedvick TS, Taylor P, Taylor SS. Profile of the disulfide bonds in acetylcholinesterase. J Biol Chem. 1986;261:13565–13570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Page RDM, Holmes EC. Molecular Evolution: A Phylogenetic Approach. Blackwell Science, Oxford, UK; 1998. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Xu Y, Colletier JP, Weik M, Jiang H, Moult J, et al. Flexibility of aromatic residues in the active-site gorge of acetylcholinesterase: X-ray versus molecular dynamics. Biophys J. 2008;95:2500–2511. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.108.129601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Auld VJ, Fetter RD, Broadie K, Goodman CS. Gliotactin, a novel transmembrane protein on peripheral glia, is required to form the blood-nerve barrier in Drosophila. Cell. 1995;81:757–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90537-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Botti SA, Felder CE, Sussman JL, Silman I. Electrotactins: a class of adhesion proteins with conserved electrostatic and structural motifs. Protein Eng. 1998;11:415–420. doi: 10.1093/protein/11.6.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Raves ML, Harel M, Pang Y-P, Silman I, Kozikowski AP, et al. Structure of acetylcholinesterase complexed with the nootropic alkaloid (-)-huperzine A. Nature Struct Biol. 1997;4:57–63. doi: 10.1038/nsb0197-57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Schrag JD, Cygler M. 1·8 Å refined structure of the lipase from Geotrichum candidum. J Mol Biol. 1993;230:575–591. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Haliscak JP, Beeman RW. Status of malathion resistance in genera of beetles infesting farm-stored corn, wheat, and oats in the United States. J Econ Entomol. 1983;76:717–722. [Google Scholar]
- 56.Bendtsen JD, Nielsen H, von Heijne G, Brunak S. Improved prediction of signal 459 peptides: SignalP 3.0. J Mol Biol. 2004;340:783–795. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.05.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, et al. ClustalW and ClustalX version 2.0. Bioinformatics. 2007;23:2947–2948. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S. Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2007;24:1596–1599. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msm092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Sanson B, Nachon F, Colletier JP, Froment MT, Toker L, et al. Crystallographic snapshots of nonaged and aged conjugates of soman with acetylcholinesterase, and of a ternary complex of the aged conjugate with pralidoxime (dagger). J Med Chem. 2009;52:7593–7603. doi: 10.1021/jm900433t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Pearlman DA, Case DA, Caldwell JW, Ross WS, Cheatham TE, III, et al. AMBER, a package of computer programs for applying molecular mechanics, normal mode analysis, molecular dynamics and free energy calculations to simulate the structural and energetic properties of molecules. Comput Phys Commun. 1995;91:1–41. [Google Scholar]
- 61.Jorgensen WL, Chandreskhar J, Madura JD, Impey RW, Klein ML. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J Chem Phys. 1982;79:926–935. [Google Scholar]
- 62.Case DA, Cheatham TE, III, Darden T, Gohlke H, Luo R, et al. The Amber biomolecular simulation programs. J Comput Chem. 2005;26:1668–1688. doi: 10.1002/jcc.20290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Hornak V, Abel R, Okur A, Strockbine B, Roitberg A, et al. Comparison of multiple Amber force fields and development of improved protein backbone parameters. Proteins. 2006;65:712–725. doi: 10.1002/prot.21123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Wickstrom L, Okur A, Simmerling C. Evaluating the performance of the ff99SB force field based on NMR scalar coupling data. Biophys J. 2009;97:853–856. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2009.04.063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Berendsen HJC, Postma JPM, van Gunsteren WF, Di Nola A, Haak JR. Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J Chem Phys. 1984;81:3684–3690. [Google Scholar]
- 66.Darden TA, York DM, Pedersen LG. Particle mesh Ewald: an N log(N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J Chem Phys. 1993;98:10089–10092. [Google Scholar]
- 67.Shao J, Tanner SW, Thompson N, Cheatham TE., III Clustering molecular dynamics trajectories: 1. Characterizing the performance of different clustering algorithms. J Chem Theory Comput. 2007;3:2312–2334. doi: 10.1021/ct700119m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Felder CE, Prilusky J, Silman I, Sussman JL. A server and database for dipole moments of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35:W512–521. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Giulietti A, Overbergh L, Valckx D, Decallonne B, Bouillon R, et al. An overview of real-time quantitative PCR: Applications to quantify cytokine gene expression. Methods. 2001;25:386–401. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Li HR, Oppert B, Higgins RA, Huang FN, Buschman LL, et al. Characterization of cDNAs encoding three trypsin-like proteinases and quantitative analysis of mRNA in Bt-resistant and -susceptible strains of Ostrinia nubilalis. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2005;35:847–860. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2005.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Togawa T, Dunn WA, Emmons AC, Nagao J, Willis JH. Developmental expression patterns of cuticular protein genes with the R&R Consensus from Anopheles gambiae. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2008;38:508–519. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2007.12.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]