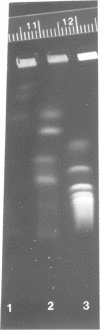
Abstract
Previous estimates of the size of the Giardia lamblia genome have ranged from 30 to 80 million base pairs (Mb), based on DNA renaturation kinetics. This is much larger than the sum of the sizes of the 4 to 5 chromosomal DNAs seen in typical pulsed field gel electrophoretic analyses. One possible explanation is that each visible chromosomal DNA consists of several unresolved DNA species. To examine this we have performed quantitative densitometry of ethidium stained chromosomal DNAs and Notl genomic digests. We have also examined the distribution of rDNA on Notl genomic fragments. All of our results suggests that the true genome size is 10.6 to 11.9 Mb. It is conceivable that the previous larger estimates may be distorted by impurities in the DNA preparations used.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam R. D., Nash T. E., Wellems T. E. The Giardia lamblia trophozoite contains sets of closely related chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 25;16(10):4555–4567. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.10.4555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertram M. A., Meyer E. A., Lile J. D., Morse S. A. A comparison of isozymes of five axenic Giardia isolates. J Parasitol. 1983 Oct;69(5):793–801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingham A. K., Meyer E. A. Giardia excystation can be induced in vitro in acidic solutions. Nature. 1979 Jan 25;277(5694):301–302. doi: 10.1038/277301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boothroyd J. C., Wang A., Campbell D. A., Wang C. C. An unusually compact ribosomal DNA repeat in the protozoan Giardia lamblia. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):4065–4084. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.4065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis T. H., Cleary W. G., Burcham K. W., Bowen B. A. Ramped field inversion gel electrophoresis: a cautionary note. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5489–5489. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan J. B., Chikashige Y., Smith C. L., Niwa O., Yanagida M., Cantor C. R. Construction of a Not I restriction map of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 11;17(7):2801–2818. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.7.2801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healey A., Mitchell R., Upcroft J. A., Boreham P. F., Upcroft P. Complete nucleotide sequence of the ribosomal RNA tandem repeat unit from Giardia intestinalis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):4006–4006. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.4006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korman S. H., Le Blancq S. M., Spira D. T., el On J., Reifen R. M., Deckelbaum R. J. Giardia lamblia: identification of different strains from man. Z Parasitenkd. 1986;72(2):173–180. doi: 10.1007/BF00931144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew M. K., Smith C. L., Cantor C. R. High-resolution separation and accurate size determination in pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of DNA. 2. Effect of pulse time and electric field strength and implications for models of the separation process. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 27;27(26):9210–9216. doi: 10.1021/bi00426a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. L., Wang A. L., Wang C. C. Identification of Giardia lamblia isolates susceptible and resistant to infection by the double-stranded RNA virus. Exp Parasitol. 1988 Jun;66(1):118–123. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(88)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., McCutchan T., Keister D., Dame J. B., Conrad J. D., Gillin F. D. Restriction-endonuclease analysis of DNA from 15 Giardia isolates obtained from humans and animals. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jul;152(1):64–73. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Econome J. G., Schutt A., Klco S., Cantor C. R. A physical map of the Escherichia coli K12 genome. Science. 1987 Jun 12;236(4807):1448–1453. doi: 10.1126/science.3296194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Matsumoto T., Niwa O., Klco S., Fan J. B., Yanagida M., Cantor C. R. An electrophoretic karyotype for Schizosaccharomyces pombe by pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4481–4489. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogin M. L., Gunderson J. H., Elwood H. J., Alonso R. A., Peattie D. A. Phylogenetic meaning of the kingdom concept: an unusual ribosomal RNA from Giardia lamblia. Science. 1989 Jan 6;243(4887):75–77. doi: 10.1126/science.2911720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turmel C., Brassard E., Slater G. W., Noolandi J. Molecular detrapping and band narrowing with high frequency modulation of pulsed field electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):569–575. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulanovsky L., Drouin G., Gilbert W. DNA trapping electrophoresis. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):190–192. doi: 10.1038/343190a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Resolution of DNA molecules greater than 5 megabases by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7865–7876. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]