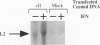Abstract
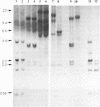
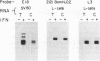
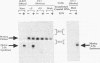
The cloning of cDNAs encoding murine 2-5A synthetase has identified three related transcripts, represented by a previously described cDNA clone, L3 and two novel cDNAs, L1 and L2. L1 contains an open reading frame coding for a protein that shows 70% conservation at the amino acid level when compared to the protein predicted to be encoded by L3. L2 recognizes an IFN-induced transcript 600-bp larger than the L3 transcript. These three cDNAs map to a cosmid, cII, containing two murine 2-5A synthetase genes, ME12 and ME5/ME8, situated in a head-to-tail orientation separated by approximately 8 kb. Southern analyses of ME12 and ME5/ME8 using L3, L1-specific and L2-specific probes indicate that these genes have a similar organization. cII was transiently and stably transfected into CV-1 cells. When treated with interferon, the transfected cells produced mature, murine 2-5A synthetase transcripts identified using L3 and L2-specific probes. Thus all transcripts present in IFN-treated mouse cells which are recognized by the available murine 2-5A synthetase cDNA probes map to an approximately 40 kb region of the mouse genome containing two 2-5A synthetase genes.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benech P., Merlin G., Revel M., Chebath J. 3' end structure of the human (2'-5') oligo A synthetase gene: prediction of two distinct proteins with cell type-specific expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1267–1281. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benech P., Mory Y., Revel M., Chebath J. Structure of two forms of the interferon-induced (2'-5') oligo A synthetase of human cells based on cDNAs and gene sequences. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2249–2256. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03922.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chebath J., Benech P., Hovanessian A., Galabru J., Revel M. Four different forms of interferon-induced 2',5'-oligo(A) synthetase identified by immunoblotting in human cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3852–3857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coccia E. M., Romeo G., Nissim A., Marziali G., Albertini R., Affabris E., Battistini A., Fiorucci G., Orsatti R., Rossi G. B. A full-length murine 2-5A synthetase cDNA transfected in NIH-3T3 cells impairs EMCV but not VSV replication. Virology. 1990 Nov;179(1):228–233. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90292-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B., Peretz D., Vaiman D., Benech P., Chebath J. Enhancer-like interferon responsive sequences of the human and murine (2'-5') oligoadenylate synthetase gene promoters. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1411–1419. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02958.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty J. P., Samanta H., Farrell P. J., Lengyel P. Interferon, double-stranded RNA, and RNA degradation. Isolation of homogeneous pppA(2'p5'A)n-1 synthetase from Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):3813–3816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Howard B. H., Reeves R. Expression of recombinant plasmids in mammalian cells is enhanced by sodium butyrate. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 11;11(21):7631–7648. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.21.7631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovanessian A. G., Laurent A. G., Chebath J., Galabru J., Robert N., Svab J. Identification of 69-kd and 100-kd forms of 2-5A synthetase in interferon-treated human cells by specific monoclonal antibodies. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1273–1280. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02364.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovanessian A. G., Svab J., Marié I., Robert N., Chamaret S., Laurent A. G. Characterization of 69- and 100-kDa forms of 2-5A-synthetase from interferon-treated human cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4945–4949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichii Y., Fukunaga R., Shiojiri S., Sokawa Y. Mouse 2-5A synthetase cDNA: nucleotide sequence and comparison to human 2-5A synthetase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 22;14(24):10117–10117. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.24.10117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilson D. H., Torrence P. F., Vilcek J. Two molecular weight forms of human 2',5'-oligoadenylate synthetase have different activation requirements. J Interferon Res. 1986 Feb;6(1):5–12. doi: 10.1089/jir.1986.6.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr I. M., Brown R. E. pppA2'p5'A2'p5'A: an inhibitor of protein synthesis synthesized with an enzyme fraction from interferon-treated cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):256–260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., Langer J. A., Zoon K. C., Samuel C. E. Interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:727–777. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poustka A., Rackwitz H. R., Frischauf A. M., Hohn B., Lehrach H. Selective isolation of cosmid clones by homologous recombination in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4129–4133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quan F., Korneluk R. G., Tropak M. B., Gravel R. A. Isolation and characterization of the human catalase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5321–5335. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revel M., Kimchi A., Friedman M., Wolf D., Merlin G., Panet A., Rapoport S., Lapidot Y. Cell-regulatory functions of interferon induced enzymes: antimitogenic effect of (2'-5')oligo-A, growth-related variations in (2'-5')oligo-A synthetase, and isolation of its mRNA. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1981;41:452–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutherford M. N., Hannigan G. E., Williams B. R. Interferon-induced binding of nuclear factors to promoter elements of the 2-5A synthetase gene. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):751–759. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02872.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samanta H., Dougherty J. P., Lengyel P. Synthesis of (2'-5')(A)n from ATP. Characteristics of the reaction catalyzed by (2'-5')(A)n synthetase purified from mouse Ehrlich ascites tumor cells treated with interferon. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9807–9813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders M. E., Gewert D. R., Tugwell M. E., McMahon M., Williams B. R. Human 2-5A synthetase: characterization of a novel cDNA and corresponding gene structure. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1761–1768. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03848.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A., Chernajovsky Y., Shulman L., Federman P., Berissi H., Revel M. An interferon-induced phosphodiesterase degrading (2'-5') oligoisoadenylate and the C-C-A terminus of tRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4788–4792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu N., Sokawa Y., Sokawa J. Immunological cross-reactivity between large and small (2'-5')oligoadenylate synthetases from pig cells. J Biochem. 1984 Jun;95(6):1827–1830. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Fernandez J. M., Sorge J. A., Huse W. D. Lambda ZAP: a bacteriophage lambda expression vector with in vivo excision properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7583–7600. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Laurent G., Yoshie O., Floyd-Smith G., Samanta H., Sehgal P. B., Lengyel P. Interferon action: two (2'-5')(A)n synthetases specified by distinct mRNAs in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells treated with interferon. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):95–102. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90338-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathelet M., Moutschen S., Cravador A., DeWit L., Defilippi P., Huez G., Content J. Full-length sequence and expression of the 42 kDa 2-5A synthetase induced by human interferon. FEBS Lett. 1986 Feb 3;196(1):113–120. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80224-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. A., Swyryd E. A., Stark G. R. An improved method for purifying 2',5'-oligoadenylate synthetases. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):1363–1370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. R., Kerr I. M., Gilbert C. S., White C. N., Ball L. A. Synthesis and breakdown of pppA2'p5'A2'p5'A and transient inhibiton of protein synthesis in extracts from interferon-treated and control cells. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Dec;92(2):455–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12767.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. R., Saunders M. E., Willard H. F. Interferon-regulated human 2-5A synthetase gene maps to chromosome 12. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1986 Jul;12(4):403–408. doi: 10.1007/BF01570735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang K., Samanta H., Dougherty J., Jayaram B., Broeze R., Lengyel P. Interferons, double-stranded RNA, and RNA degradation. Isolation and characterization of homogeneous human (2'-5')(a)n synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9324–9328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]