Abstract
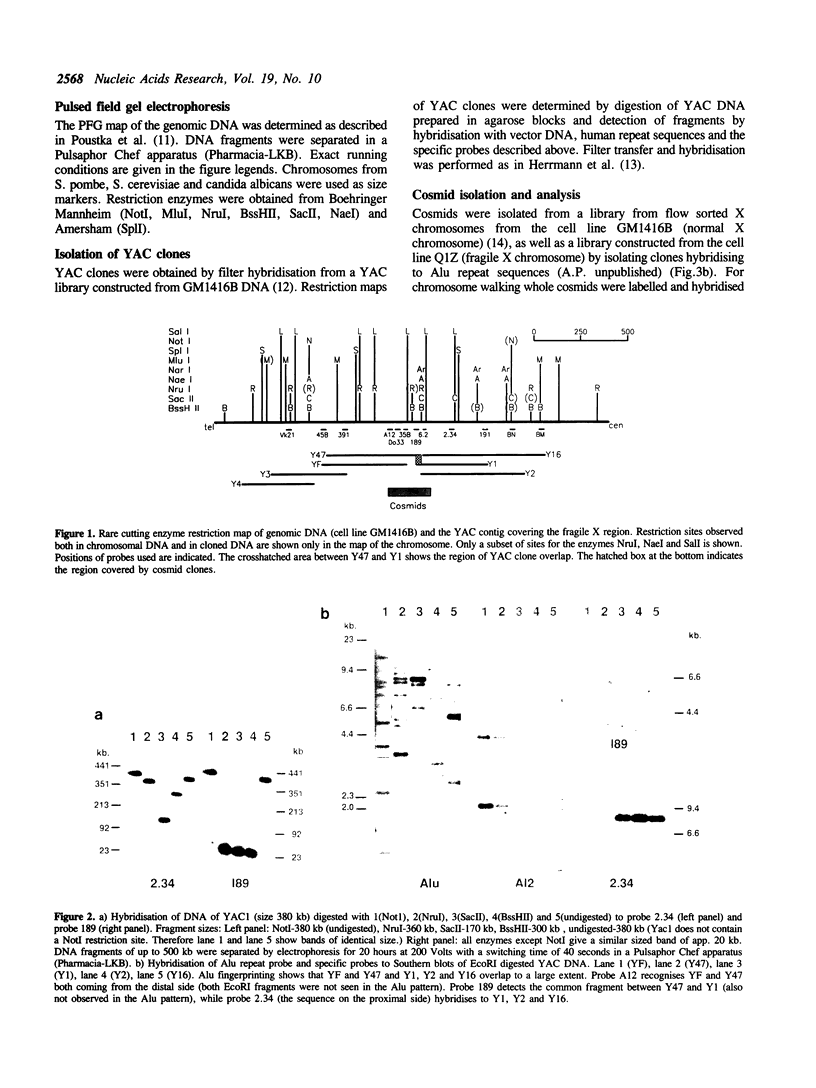
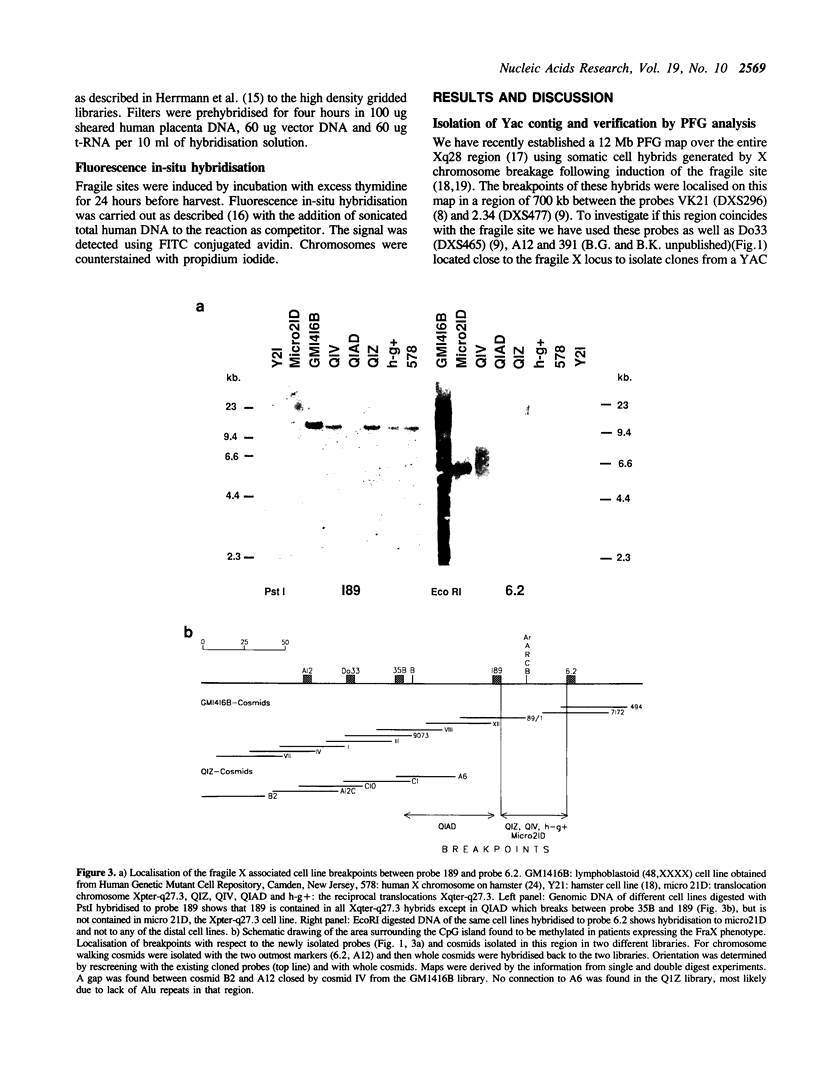
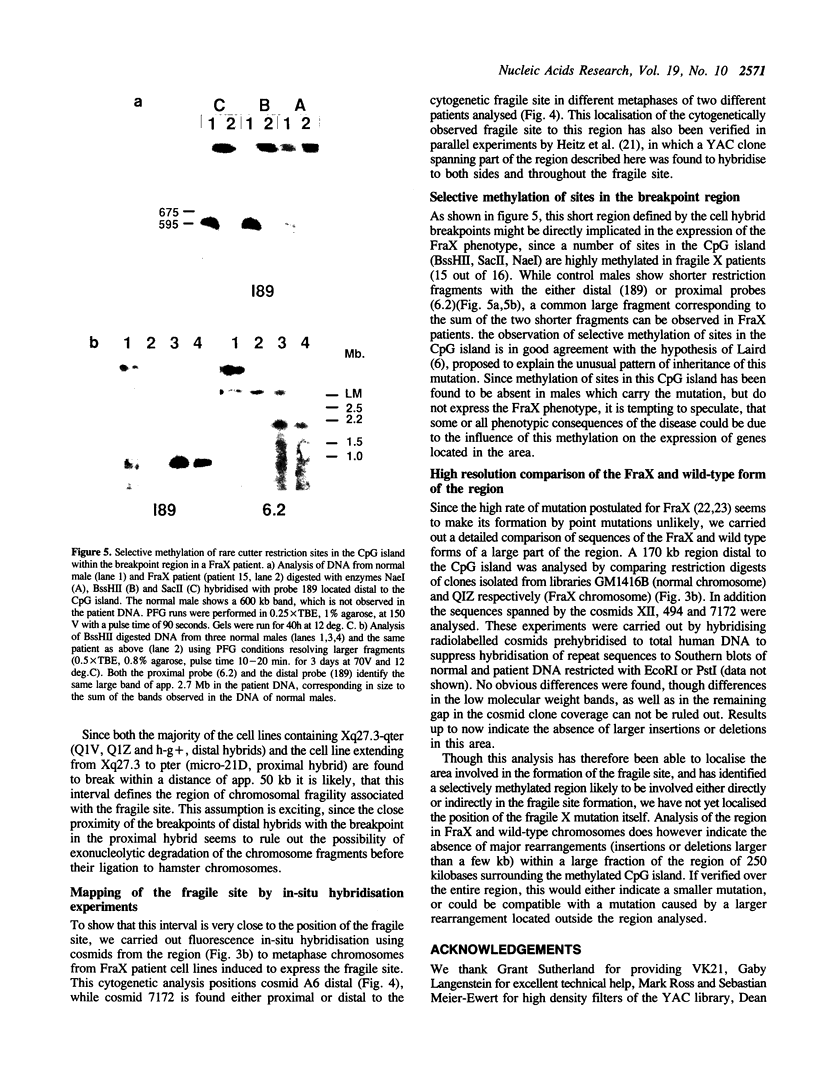
The fragile X syndrome (FraX), the most common inherited form of mental retardation, has been located to Xq27.3. As a step in the molecular analysis of this mutation, we have cloned a contiguous 1.8 Mb region containing the entire fragile X region in YAC and cosmid clones. The cloned area defines a region of 50 kb containing a CpG island, found to be selectively methylated in patients expressing the fragile X phenotype. In this 50kb area we have localised the breakpoints of four somatic cell hybrids selected to break at the position of the fragile site. Fluorescence in-situ hybridisation of cosmids flanking this area shows that the breakpoints, the CpG island and the fragile site coincide.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell M. V., Hirst M. C., Nakahori Y., MacKinnon R. N., Roche A., Flint T. J., Jacobs P. A., Tommerup N., Tranebjaerg L., Froster-Iskenius U. Physical mapping across the fragile X: hypermethylation and clinical expression of the fragile X syndrome. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):861–866. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90514-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards Y., Williams S., West L., Lipowicz S., Sheer D., Attwood J., Spurr N., Sarkar R., Saha N., Povey S. The polymorphic human DNA sequence D8S8 assigned to 8q13-21.1, close to the carbonic anhydrase gene cluster, by isotopic and nonisotopic in situ hybridization and by linkage analysis. Ann Hum Genet. 1990 May;54(Pt 2):131–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1990.tb00369.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitz D., Rousseau F., Devys D., Saccone S., Abderrahim H., Le Paslier D., Cohen D., Vincent A., Toniolo D., Della Valle G. Isolation of sequences that span the fragile X and identification of a fragile X-related CpG island. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1236–1239. doi: 10.1126/science.2006411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann B. G., Barlow D. P., Lehrach H. A large inverted duplication allows homologous recombination between chromosomes heterozygous for the proximal t complex inversion. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):813–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90078-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann B. G., Labeit S., Poustka A., King T. R., Lehrach H. Cloning of the T gene required in mesoderm formation in the mouse. Nature. 1990 Feb 15;343(6259):617–622. doi: 10.1038/343617a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird C. D., Lamb M. M., Thorne J. L. Two progenitor cells for human oogonia inferred from pedigree data and the X-inactivation imprinting model of the fragile-X syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Apr;46(4):696–719. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird C. D. Proposed mechanism of inheritance and expression of the human fragile-X syndrome of mental retardation. Genetics. 1987 Nov;117(3):587–599. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.3.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussbaum R. L., Ledbetter D. H. Fragile X syndrome: a unique mutation in man. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:109–145. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.000545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlino E., Paonessa G., Ciliberto G. Alu sequences transcription in X. laevis oocytes: nuclear-cytoplasmic partitioning and evidence for 3' end processing reactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8359–8377. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poustka A. M., Lehrach H., Williamson R., Bates G. A long-range restriction map encompassing the cystic fibrosis locus and its closely linked genetic markers. Genomics. 1988 May;2(4):337–345. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90023-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley J., Butler R., Ogilvie D., Finniear R., Jenner D., Powell S., Anand R., Smith J. C., Markham A. F. A novel, rapid method for the isolation of terminal sequences from yeast artificial chromosome (YAC) clones. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):2887–2890. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.2887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman S. L., Jacobs P. A., Morton N. E., Froster-Iskenius U., Howard-Peebles P. N., Nielsen K. B., Partington M. W., Sutherland G. R., Turner G., Watson M. Further segregation analysis of the fragile X syndrome with special reference to transmitting males. Hum Genet. 1985;69(4):289–299. doi: 10.1007/BF00291644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman S. L., Morton N. E., Jacobs P. A., Turner G. The marker (X) syndrome: a cytogenetic and genetic analysis. Ann Hum Genet. 1984 Jan;48(Pt 1):21–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1984.tb00830.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R. Heritable fragile sites on human chromosomes I. Factors affecting expression in lymphocyte culture. Am J Hum Genet. 1979 Mar;31(2):125–135. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suthers G. K., Callen D. F., Hyland V. J., Kozman H. M., Baker E., Eyre H., Harper P. S., Roberts S. H., Hors-Cayla M. C., Davies K. E. A new DNA marker tightly linked to the fragile X locus (FRAXA). Science. 1989 Dec 8;246(4935):1298–1300. doi: 10.1126/science.2573953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sved J. A., Laird C. D. Population genetic consequences of the fragile-X syndrome, based on the X-inactivation imprinting model. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Mar;46(3):443–451. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., Heitz D., Petit C., Kretz C., Oberlé I., Mandel J. L. Abnormal pattern detected in fragile-X patients by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Nature. 1991 Feb 14;349(6310):624–626. doi: 10.1038/349624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren S. T., Knight S. J., Peters J. F., Stayton C. L., Consalez G. G., Zhang F. P. Isolation of the human chromosomal band Xq28 within somatic cell hybrids by fragile X site breakage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3856–3860. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren S. T., Zhang F., Licameli G. R., Peters J. F. The fragile X site in somatic cell hybrids: an approach for molecular cloning of fragile sites. Science. 1987 Jul 24;237(4813):420–423. doi: 10.1126/science.3603029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieacker P., Davies K. E., Cooke H. J., Pearson P. L., Williamson R., Bhattacharya S., Zimmer J., Ropers H. H. Toward a complete linkage map of the human X chromosome: regional assignment of 16 cloned single-copy DNA sequences employing a panel of somatic cell hybrids. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):265–276. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard H. F., Smith K. D., Sutherland J. Isolation and characterization of a major tandem repeat family from the human X chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 11;11(7):2017–2033. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.7.2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]