Abstract
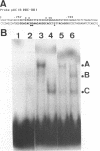
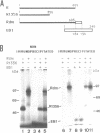
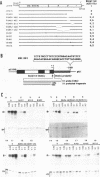
In cells latently infected with EBV, the switch from latency to a productive infection is linked to the expression of two transcriptional activators, the upstream element factor EB1 and the enhancer factor R. R activates by interacting directly with specific DNA sequences called RREs (R Responsive Elements). Each binding site covers about 18 bp, where R simultaneously contacts two core sequences separated by 5 to 7 bp (1). Here we show that R binds in vitro as a homodimer to an RRE, and that stable homodimers can also form in solution in the absence of DNA. By functional analysis of deletion and insertion mutants of R, we have localized the DNA binding region within the 280 N-terminal amino acids and the dimerization region within the 232 N-terminal amino acids. As no obvious homologies were detected with other known DNA binding or dimerization motifs, R could contain novel protein structures mediating these functions. The transcriptional activation domain has been located in the C-terminal half of the protein. This domain contains two regions with structures already identified in other transcription factors: one region is rich in proline, the other rich in acidic residues.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bodescot M., Perricaudet M. Epstein-Barr virus mRNAs produced by alternative splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):7103–7114. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.7103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buisson M., Manet E., Trescol-Biemont M. C., Gruffat H., Durand B., Sergeant A. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) early protein EB2 is a posttranscriptional activator expressed under the control of EBV transcription factors EB1 and R. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5276–5284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5276-5284.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch S. J., Sassone-Corsi P. Dimers, leucine zippers and DNA-binding domains. Trends Genet. 1990 Feb;6(2):36–40. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90071-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. N., Dong D. L., Hayward G. S., Hayward S. D. The Epstein-Barr virus Zta transactivator: a member of the bZIP family with unique DNA-binding specificity and a dimerization domain that lacks the characteristic heptad leucine zipper motif. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3358–3369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3358-3369.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevallier-Greco A., Gruffat H., Manet E., Calender A., Sergeant A. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DR enhancer contains two functionally different domains: domain A is constitutive and cell specific, domain B is transactivated by the EBV early protein R. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):615–623. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.615-623.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevallier-Greco A., Manet E., Chavrier P., Mosnier C., Daillie J., Sergeant A. Both Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded trans-acting factors, EB1 and EB2, are required to activate transcription from an EBV early promoter. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3243–3249. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04635.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Countryman J., Miller G. Activation of expression of latent Epstein-Barr herpesvirus after gene transfer with a small cloned subfragment of heterogeneous viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4085–4089. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox M. A., Leahy J., Hardwick J. M. An enhancer within the divergent promoter of Epstein-Barr virus responds synergistically to the R and Z transactivators. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):313–321. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.313-321.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. A detailed mutational analysis of Vmw110, a trans-acting transcriptional activator encoded by herpes simplex virus type 1. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2069–2076. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02472.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Rowe D. T., Rooney C. M., Kouzarides T. Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 trans-activator specifically binds to a consensus AP-1 site and is related to c-fos. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):127–132. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03356.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flemington E., Speck S. H. Autoregulation of Epstein-Barr virus putative lytic switch gene BZLF1. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1227–1232. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1227-1232.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruffat H., Manet E., Rigolet A., Sergeant A. The enhancer factor R of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is a sequence-specific DNA binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6835–6843. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruffat H., Moreno N., Sergeant A. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) ORI1yt enhancer is not B-cell specific and does not respond synergistically to the EBV transcription factors R and Z. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2810–2818. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2810-2818.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt W., Sugden B. Identification and characterization of oriLyt, a lytic origin of DNA replication of Epstein-Barr virus. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):427–433. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90028-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwick J. M., Lieberman P. M., Hayward S. D. A new Epstein-Barr virus transactivator, R, induces expression of a cytoplasmic early antigen. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2274–2284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2274-2284.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Fennewald S., Hummel M., Cole T., Kieff E. A membrane protein encoded by Epstein-Barr virus in latent growth-transforming infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7207–7211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Mahadevan S., Struhl K. Structural and functional characterization of the short acidic transcriptional activation region of yeast GCN4 protein. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):635–640. doi: 10.1038/333635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalinot P., Kédinger C. Negative regulatory sequences in the EIa-inducible enhancer of the adenovirus-2 early EIIa promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2651–2669. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney S., Holley-Guthrie E., Mar E. C., Smith M. The Epstein-Barr virus BMLF1 promoter contains an enhancer element that is responsive to the BZLF1 and BRLF1 transactivators. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3878–3883. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3878-3883.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney S., Kamine J., Holley-Guthrie E., Mar E. C., Lin J. C., Markovitz D., Pagano J. The Epstein-Barr virus immediate-early gene product, BMLF1, acts in trans by a posttranscriptional mechanism which is reporter gene dependent. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3870–3877. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3870-3877.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laux G., Freese U. K., Bornkamm G. W. Structure and evolution of two related transcription units of Epstein-Barr virus carrying small tandem repeats. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):987–995. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.987-995.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laux G., Perricaudet M., Farrell P. J. A spliced Epstein-Barr virus gene expressed in immortalized lymphocytes is created by circularization of the linear viral genome. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):769–774. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02874.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Andrews N. C., Miller G., Steitz J. A. Two small RNAs encoded by Epstein-Barr virus and complexed with protein are precipitated by antibodies from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):805–809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin B. Commitment and activation at pol II promoters: a tail of protein-protein interactions. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1161–1164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90675-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman P. M., Berk A. J. In vitro transcriptional activation, dimerization, and DNA-binding specificity of the Epstein-Barr virus Zta protein. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2560–2568. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2560-2568.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Ptashne M. Deletion analysis of GAL4 defines two transcriptional activating segments. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):847–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manet E., Gruffat H., Trescol-Biemont M. C., Moreno N., Chambard P., Giot J. F., Sergeant A. Epstein-Barr virus bicistronic mRNAs generated by facultative splicing code for two transcriptional trans-activators. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1819–1826. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03576.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermod N., O'Neill E. A., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. The proline-rich transcriptional activator of CTF/NF-I is distinct from the replication and DNA binding domain. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):741–753. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90108-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Rabson M., Heston L. Epstein-Barr virus with heterogeneous DNA disrupts latency. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):174–182. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.174-182.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman C., Runswick M., Pollock R., Treisman R. Isolation and properties of cDNA clones encoding SRF, a transcription factor that binds to the c-fos serum response element. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):989–1003. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90244-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfitzner A. J., Strominger J. L., Speck S. H. Characterization of a cDNA clone corresponding to a transcript from the Epstein-Barr virus BamHI M fragment: evidence for overlapping mRNAs. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2943–2946. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2943-2946.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample J., Liebowitz D., Kieff E. Two related Epstein-Barr virus membrane proteins are encoded by separate genes. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):933–937. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.933-937.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seibl R., Motz M., Wolf H. Strain-specific transcription and translation of the BamHI Z area of Epstein-Barr Virus. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):902–909. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.902-909.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada K., Shimizu N., Sakuma S., Ono Y. trans activation of the latent Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) genome after transfection of the EBV DNA fragment. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1016–1022. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1016-1022.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor N., Countryman J., Rooney C., Katz D., Miller G. Expression of the BZLF1 latency-disrupting gene differs in standard and defective Epstein-Barr viruses. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1721–1728. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1721-1728.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urier G., Buisson M., Chambard P., Sergeant A. The Epstein-Barr virus early protein EB1 activates transcription from different responsive elements including AP-1 binding sites. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1447–1453. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03527.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H., O'Neill F. J., Freese U. K., Hecker E. Persisting oncogenic herpesvirus induced by the tumour promotor TPA. Nature. 1978 Mar 23;272(5651):373–375. doi: 10.1038/272373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]