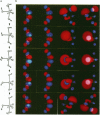
Abstract
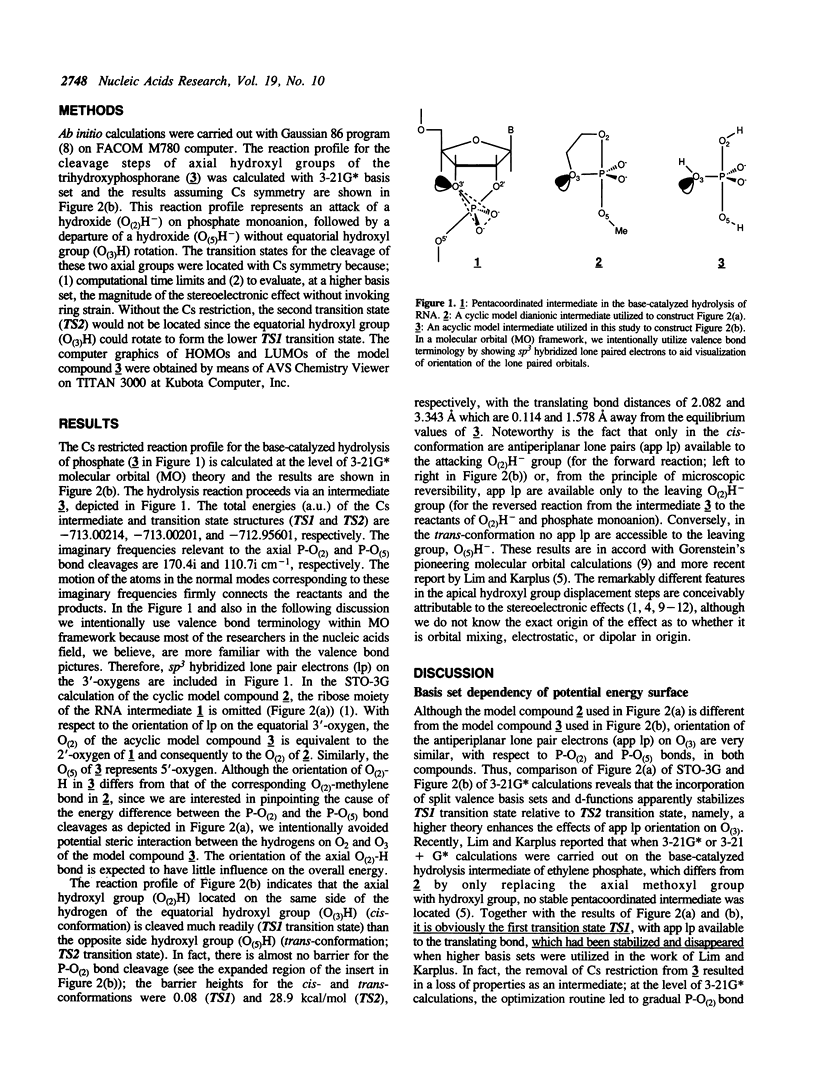
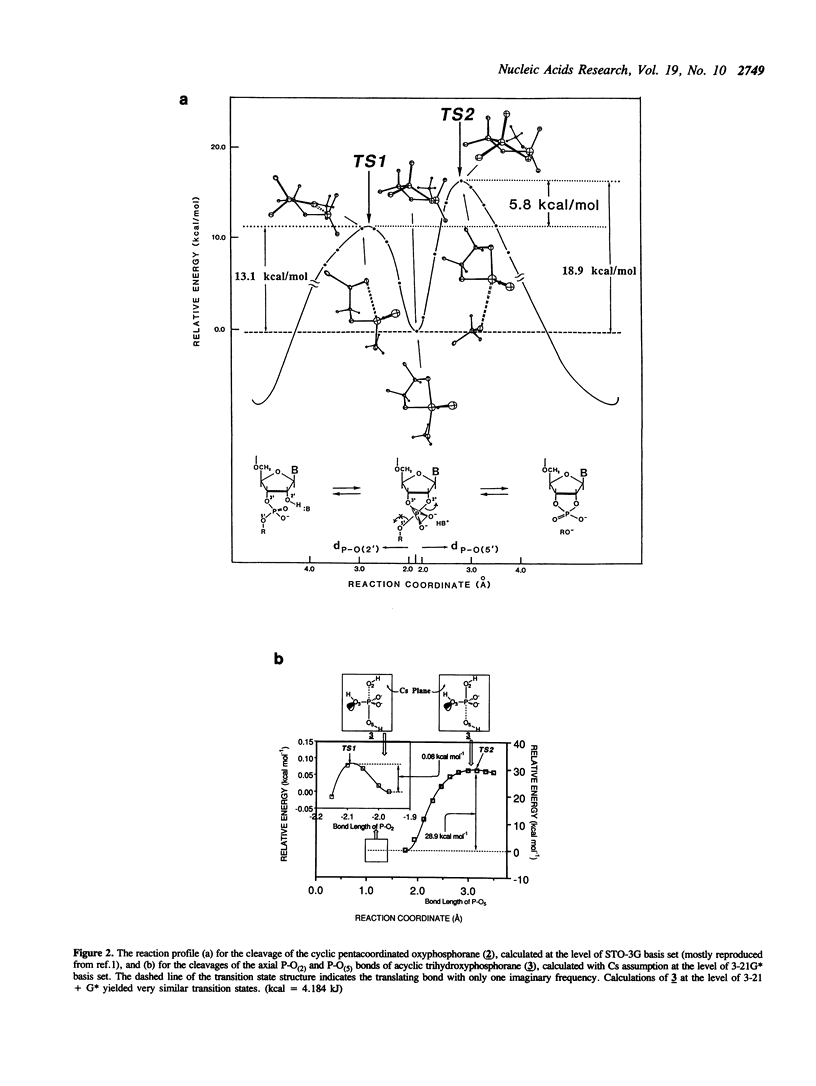
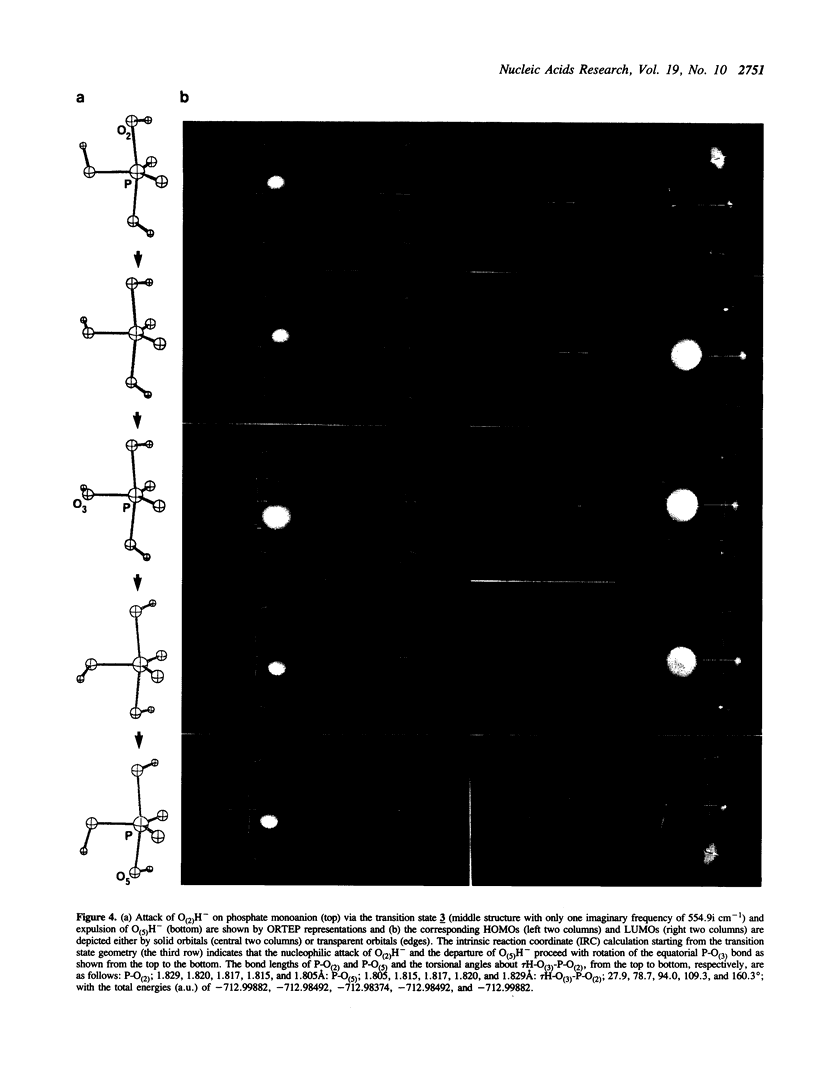
In order to examine the energetics in base-catalyzed hydrolysis of RNA, a tentative pentacoordinated intermediate (3) has been characterized by molecular orbital calculations. Ab initio studies at the level of 3-21G* indicate that, under the Cs symmetry restricted conditions, the P-O(2) bond possessing antiperiplanar (app) lone pair electrons (Ip) on the equatorial oxygen (O(3)) can be cleaved with almost no barrier (TS1 transition state; 0.08 kcal mol-1), from the pentacoordinated intermediate (3) of base-catalyzed hydrolysis of phosphate, compared to the P-O(5) bond (TS2 transition state; 28.9 kcal mol-1) which lacks app lp assistance from O(3). The dianionic intermediate, however, loses the TS1 transition state thus its property as an intermediate when the Cs restriction is removed. The analysis of the entire potential energy surface enables us to conclude that, in a related system examined by Lim and Karplus [1990) J. Am. Chem. Soc., 112, 5872-5873) for attack by OH- on ethylene phosphate monoanion, the TS1 transition state had also been lost and thus no intermediate had been found. These results further support our earlier conclusions (Taira et al. (1990) Protein Engineering, 3, 691-701) of rate limiting transition state possessing extended P-O(5') bond breaking character (the TS2 transition state) in the base-catalyzed hydrolysis of RNA. Finally, although the lack of 2',3' -migration of phosphate moieties in basic condition appears to be in accord with the short-lived intermediate, it really does not prove the absence of the intermediate. The detail will be discussed in the text.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Taira K., Uebayasi M., Maeda H., Furukawa K. Energetics of RNA cleavage: implications for the mechanism of action of ribozymes. Protein Eng. 1990 Aug;3(8):691–701. doi: 10.1093/protein/3.8.691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]