Abstract
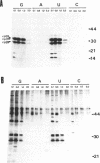
Many ribonucleoproteins (RNPs) are involved in the regulation of gene expression at the post-transcriptional level. We previously isolated three nuclear-encoded RNPs from tobacco chloroplasts. Here we report their binding specificities for various nucleic acids. The three RNPs synthesized in vitro were subjected to binding assays using ssDNA, dsDNA and four ribonucleotide homopolymers. The affinities for ribonucleotide homopolymers are higher than those for ssDNA and dsDNA, suggesting that they bind preferentially to RNA in vivo. All three RNPs show high specificities for poly(G) and poly(U) in the presence of 1.2-1.8 M NaCl, providing additional evidence for the similarity to HeLa hnRNP proteins. Possible involvement of these RNPs in the post-transcriptional regulation of chloroplast gene expression is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bandziulis R. J., Swanson M. S., Dreyfuss G. RNA-binding proteins as developmental regulators. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):431–437. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buvoli M., Cobianchi F., Biamonti G., Riva S. Recombinant hnRNP protein A1 and its N-terminal domain show preferential affinity for oligodeoxynucleotides homologous to intron/exon acceptor sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6595–6600. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Philipson L., Mattaj I. W. Ribonucleoprotein particles in cellular processes. J Cell Biol. 1988 May;106(5):1419–1425. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.5.1419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G. Structure and function of nuclear and cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein particles. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:459–498. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Swanson M. S., Piñol-Roma S. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles and the pathway of mRNA formation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Mar;13(3):86–91. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90046-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallie D. R., Sleat D. E., Watts J. W., Turner P. C., Wilson T. M. The 5'-leader sequence of tobacco mosaic virus RNA enhances the expression of foreign gene transcripts in vitro and in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 24;15(8):3257–3273. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.8.3257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamble P. E., Mullet J. E. Blue light regulates the accumulation of two psbD-psbC transcripts in barley chloroplasts. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):2785–2794. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08424.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruissem W. Chloroplast gene expression: how plants turn their plastids on. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):161–170. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90889-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemsley A., Arnheim N., Toney M. D., Cortopassi G., Galas D. J. A simple method for site-directed mutagenesis using the polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 25;17(16):6545–6551. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.16.6545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Sharp P. A. Electrophoretic separation of complexes involved in the splicing of precursors to mRNAs. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):845–855. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90066-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchka M. R., Goldschmidt-Clermont M., van Dillewijn J., Rochaix J. D. Mutation at the Chlamydomonas nuclear NAC2 locus specifically affects stability of the chloroplast psbD transcript encoding polypeptide D2 of PS II. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):869–876. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90939-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. Q., Sugiura M. Three distinct ribonucleoproteins from tobacco chloroplasts: each contains a unique amino terminal acidic domain and two ribonucleoprotein consensus motifs. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3059–3066. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07502.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W. A binding consensus: RNA-protein interactions in splicing, snRNPs, and sex. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90164-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill B. M., Stone K. L., Cobianchi F., Wilson S. H., Williams K. R. Phenylalanines that are conserved among several RNA-binding proteins form part of a nucleic acid-binding pocket in the A1 heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3307–3313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel B., Zinder N. D. In vitro binding of the bacteriophage f1 gene V protein to the gene II RNA-operator and its DNA analog. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7333–7344. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickelsen J., Link G. Interaction of a 3' RNA region of the mustard trnK gene with chloroplast proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):9637–9648. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.9637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. D. Contrasting modes and tempos of genome evolution in land plant organelles. Trends Genet. 1990 Apr;6(4):115–120. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90125-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandolfo M., Valentini O., Biamonti G., Rossi P., Riva S. Large-scale purification of hnRNP proteins from HeLa cells by affinity chromatography on ssDNA-cellulose. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jan 2;162(1):213–220. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10563.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piñol-Roma S., Choi Y. D., Matunis M. J., Dreyfuss G. Immunopurification of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles reveals an assortment of RNA-binding proteins. Genes Dev. 1988 Feb;2(2):215–227. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.2.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sexton T. B., Christopher D. A., Mullet J. E. Light-induced switch in barley psbD-psbC promoter utilization: a novel mechanism regulating chloroplast gene expression. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4485–4494. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07899.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozaki K., Ohme M., Tanaka M., Wakasugi T., Hayashida N., Matsubayashi T., Zaita N., Chunwongse J., Obokata J., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. The complete nucleotide sequence of the tobacco chloroplast genome: its gene organization and expression. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2043–2049. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04464.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. B., Gruissem W. Control of plastid gene expression: 3' inverted repeats act as mRNA processing and stabilizing elements, but do not terminate transcription. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1145–1157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90600-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. B., Jones H., Gruissem W. Function of plastid mRNA 3' inverted repeats. RNA stabilization and gene-specific protein binding. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18742–18750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura M. The chloroplast chromosomes in land plants. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:51–70. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.000411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson M. S., Dreyfuss G. Classification and purification of proteins of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles by RNA-binding specificities. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2237–2241. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]