Abstract
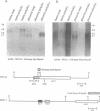
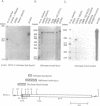
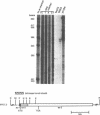
We have characterized the expression of MYCL2, an intronless X-linked gene related to MYCL1. RNase protection analysis of a panel of human normal and tumor tissues has revealed that MYCL2 is expressed almost exclusively in human adult normal testis; much lower levels of transcript were detected in one human lung adenocarcinoma. No MYCL2 transcript was found in human testis RNA obtained from second trimester fetuses. This observation suggests a germ cell rather than somatic cell origin of the transcript and possible developmental regulation of MYCL2. Northern blot analysis of poly(A)+ RNA from adult human normal testis with an antisense riboprobe revealed a transcript of approximately 4.8-kb, which is in agreement with the size predicted from the MYCL2 nucleotide sequence. Antisense transcripts were found spanning regions of MYCL2 corresponding to all three exons of MYCL1. No sizable open reading frame was seen for the MYCL2 antisense transcripts suggesting that they may represent either regulatory sequences or an intron of a gene encoded by the complementary strand. RNase protection assays and the 5' RACE protocol (Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends) were used to address the localization of the transcription start site of the MYCL2 sense transcript and different putative promoters and transcription regulatory elements have been identified.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashworth A., Skene B., Swift S., Lovell-Badge R. Zfa is an expressed retroposon derived from an alternative transcript of the Zfx gene. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1529–1534. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08271.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battey J., Moulding C., Taub R., Murphy W., Stewart T., Potter H., Lenoir G., Leder P. The human c-myc oncogene: structural consequences of translocation into the IgH locus in Burkitt lymphoma. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):779–787. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90534-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. L., Groudine M. A block to elongation is largely responsible for decreased transcription of c-myc in differentiated HL60 cells. Nature. 1986 Jun 12;321(6071):702–706. doi: 10.1038/321702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Kretzner L., Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N., Weintraub H. Sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc protein. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1149–1151. doi: 10.1126/science.2251503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. R., Kadonaga J. T., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):47–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3529394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collum R. G., Alt F. W. Are myc proteins transcription factors? Cancer Cells. 1990 Mar;2(3):69–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouse G. F., Leys E. J., McEwan R. N., Frayne E. G., Kellems R. E. Analysis of the mouse dhfr promoter region: existence of a divergently transcribed gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1847–1858. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl H. H., Brown R. M., Hutchison W. M., Maragos C., Brown G. K. A testis-specific form of the human pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 alpha subunit is coded for by an intronless gene on chromosome 4. Genomics. 1990 Oct;8(2):225–232. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90275-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePinho R. A., Hatton K. S., Tesfaye A., Yancopoulos G. D., Alt F. W. The human myc gene family: structure and activity of L-myc and an L-myc pseudogene. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1311–1326. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePinho R. A., Legouy E., Feldman L. B., Kohl N. E., Yancopoulos G. D., Alt F. W. Structure and expression of the murine N-myc gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1827–1831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePinho R., Mitsock L., Hatton K., Ferrier P., Zimmerman K., Legouy E., Tesfaye A., Collum R., Yancopoulos G., Nisen P. Myc family of cellular oncogenes. J Cell Biochem. 1987 Apr;33(4):257–266. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240330404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Sazer S., Tjian R., Schimke R. T. Transcription factor Sp1 recognizes a DNA sequence in the mouse dihydrofolate reductase promoter. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):246–248. doi: 10.1038/319246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Isolation of transcription factors that discriminate between different promoters recognized by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):669–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson R. P. Post-meiotic gene expression. Trends Genet. 1990 Aug;6(8):264–269. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90209-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnham P. J., Schimke R. T. In vitro transcription and delimitation of promoter elements of the murine dihydrofolate reductase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2392–2401. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fourel G., Trepo C., Bougueleret L., Henglein B., Ponzetto A., Tiollais P., Buendia M. A. Frequent activation of N-myc genes by hepadnavirus insertion in woodchuck liver tumours. Nature. 1990 Sep 20;347(6290):294–298. doi: 10.1038/347294a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentz R., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Abate C., Curran T. Parallel association of Fos and Jun leucine zippers juxtaposes DNA binding domains. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1695–1699. doi: 10.1126/science.2494702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Multiple specific contacts between a mammalian transcription factor and its cognate promoters. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):409–413. doi: 10.1038/312409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto M., Koji T., Mizuno K., Tamaru M., Koikeda S., Nakane P. K., Mori N., Masamune Y., Nakanishi Y. Transcription switch of two phosphoglycerate kinase genes during spermatogenesis as determined with mouse testis sections in situ. Exp Cell Res. 1990 Feb;186(2):273–278. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(90)90306-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. J., Pines O., Inouye M. The role of antisense RNA in gene regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:569–597. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht N. B. Regulation of 'haploid expressed genes' in male germ cells. J Reprod Fertil. 1990 Mar;88(2):679–693. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0880679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Keene M. A., Fechtel K., Fristrom J. W. Gene within a gene: nested Drosophila genes encode unrelated proteins on opposite DNA strands. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):33–42. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90482-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izant J. G., Weintraub H. Inhibition of thymidine kinase gene expression by anti-sense RNA: a molecular approach to genetic analysis. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1007–1015. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90050-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye F., Battey J., Nau M., Brooks B., Seifter E., De Greve J., Birrer M., Sausville E., Minna J. Structure and expression of the human L-myc gene reveal a complex pattern of alternative mRNA processing. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):186–195. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. K., Wold B. J. Stable reduction of thymidine kinase activity in cells expressing high levels of anti-sense RNA. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):129–138. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindy M. S., McCormack J. E., Buckler A. J., Levine R. A., Sonenshein G. E. Independent regulation of transcription of the two strands of the c-myc gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2857–2862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl N. E., Legouy E., DePinho R. A., Nisen P. D., Smith R. K., Gee C. E., Alt F. W. Human N-myc is closely related in organization and nucleotide sequence to c-myc. Nature. 1986 Jan 2;319(6048):73–77. doi: 10.1038/319073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koji T., Izumi S., Tanno M., Moriuchi T., Nakane P. K. Localization in situ of c-myc mRNA and c-myc protein in adult mouse testis. Histochem J. 1988 Oct;20(10):551–557. doi: 10.1007/BF01002609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystal G. W., Armstrong B. C., Battey J. F. N-myc mRNA forms an RNA-RNA duplex with endogenous antisense transcripts. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4180–4191. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystal G., Birrer M., Way J., Nau M., Sausville E., Thompson C., Minna J., Battey J. Multiple mechanisms for transcriptional regulation of the myc gene family in small-cell lung cancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3373–3381. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The DNA binding domain of the rat liver nuclear protein C/EBP is bipartite. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1681–1688. doi: 10.1126/science.2494700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazar M. A., Hodin R. A., Darling D. S., Chin W. W. A novel member of the thyroid/steroid hormone receptor family is encoded by the opposite strand of the rat c-erbA alpha transcriptional unit. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1128–1136. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAlpine P. J., Shows T. B., Boucheix C., Stranc L. C., Berent T. G., Pakstis A. J., Douté R. C. Report of the nomenclature committee and the 1989 catalog of mapped genes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):13–66. doi: 10.1159/000132780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarrey J. R., Thomas K. Human testis-specific PGK gene lacks introns and possesses characteristics of a processed gene. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):501–505. doi: 10.1038/326501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGarry T. J., Lindquist S. Inhibition of heat shock protein synthesis by heat-inducible antisense RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):399–403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrogan M., Simonsen C. C., Smouse D. T., Farnham P. J., Schimke R. T. Heterogeneity at the 5' termini of mouse dihydrofolate reductase mRNAs. Evidence for multiple promoter regions. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2307–2314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. W., Konecki D. S., Brennand J., Caskey C. T. Structure, expression, and mutation of the hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2147–2151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Carothers A. M., Han J. H., Harding J. D., Kas E., Venolia L., Chasin L. A. Multiple transcription start sites, DNase I-hypersensitive sites, and an opposite-strand exon in the 5' region of the CHO dhfr gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):425–440. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Chou M. Y., Inouye M. A unique mechanism regulating gene expression: translational inhibition by a complementary RNA transcript (micRNA). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1966–1970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton C. C., Nussenzweig M. C., Sousa R., Sorenson G. D., Pettengill O. S., Shows T. B. Mapping and characterization of an X-linked processed gene related to MYCL1. Genomics. 1989 Apr;4(3):367–375. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90344-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutter G. L., Wolgemuth D. J. Distinct developmental patterns of c-mos protooncogene expression in female and male mouse germ cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5301–5305. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nepveu A., Marcu K. B. Intragenic pausing and anti-sense transcription within the murine c-myc locus. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2859–2865. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04580.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliva R., Dixon G. H. Chicken protamine genes are intronless. The complete genomic sequence and organization of the two loci. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12472–12481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne T. F., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. 5' end of HMG CoA reductase gene contains sequences responsible for cholesterol-mediated inhibition of transcription. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):203–212. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponzetto C., Wolgemuth D. J. Haploid expression of a unique c-abl transcript in the mouse male germ line. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1791–1794. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Propst F., Rosenberg M. P., Iyer A., Kaul K., Vande Woude G. F. c-mos proto-oncogene RNA transcripts in mouse tissues: structural features, developmental regulation, and localization in specific cell types. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1629–1637. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransone L. J., Visvader J., Sassone-Corsi P., Verma I. M. Fos-Jun interaction: mutational analysis of the leucine zipper domain of both proteins. Genes Dev. 1989 Jun;3(6):770–781. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.6.770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saksela K., Mäkelä T. P., Alitalo K. Oncogene expression in small-cell lung cancer cell lines and a testicular germ-cell tumor: activation of the N-myc gene and decreased RB mRNA. Int J Cancer. 1989 Jul 15;44(1):182–185. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910440132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackleford G. M., Varmus H. E. Expression of the proto-oncogene int-1 is restricted to postmeiotic male germ cells and the neural tube of mid-gestational embryos. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90665-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikora K., Evan G., Stewart J., Watson J. V. Detection of the c-myc oncogene product in testicular cancer. Br J Cancer. 1985 Aug;52(2):171–176. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1985.174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer C. A., Gietz R. D., Hodgetts R. B. Overlapping transcription units in the dopa decarboxylase region of Drosophila. Nature. 1986 Jul 17;322(6076):279–281. doi: 10.1038/322279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton L. W., Bishop J. M. Alternative processing of RNA transcribed from NMYC. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4266–4272. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart T. A., Bellvé A. R., Leder P. Transcription and promoter usage of the myc gene in normal somatic and spermatogenic cells. Science. 1984 Nov 9;226(4675):707–710. doi: 10.1126/science.6494906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama A., Kume A., Nemoto K., Lee S. Y., Asami Y., Nemoto F., Nishimura S., Kuchino Y. Isolation and characterization of s-myc, a member of the rat myc gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9144–9148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swick A. G., Blake M. C., Kahn J. W., Azizkhan J. C. Functional analysis of GC element binding and transcription in the hamster dihydrofolate reductase gene promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9291–9304. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R., Tjian R. Leucine repeats and an adjacent DNA binding domain mediate the formation of functional cFos-cJun heterodimers. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1689–1694. doi: 10.1126/science.2494701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T., Fried M. A mouse locus at which transcription from both DNA strands produces mRNAs complementary at their 3' ends. Nature. 1986 Jul 17;322(6076):275–279. doi: 10.1038/322275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfes H., Kogawa K., Millette C. F., Cooper G. M. Specific expression of nuclear proto-oncogenes before entry into meiotic prophase of spermatogenesis. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):740–743. doi: 10.1126/science.2475907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman K., Alt F. W. Expression and function of myc family genes. Crit Rev Oncog. 1990;2(1):75–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]