Abstract
Objective
Previously, we found that oocyte specific homeobox (Obox) 4 plays significant role in completion of meiosis specifically at meiosis I-meiosis II (MI-MII) transition. The purpose of this study was to determine the mechanism of action of Obox4 in oocyte maturation by evaluating downstream signal networking.
Methods
The Obox4 dsRNA was prepared by in vitro transcription and microinjected into the cytoplasm of germinal vesicle oocytes followed by in vitro maturation in the presence or absence of 0.2 mM 3-isobutyl-1-metyl-xanthine. Total RNA was extracted from 200 oocytes of each group using a PicoPure RNA isolation kit then amplified two-rounds. The probe hybridization and data analysis were used by Affymetrix GeneChip® Mouse Genome 430 2.0 array and GenPlex 3.0 (ISTECH, Korea) software, respectively.
Results
Total 424 genes were up (n=80) and down (n=344) regulated after Obox4 RNA interference (RNAi). Genes mainly related to metabolic pathways and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway was changed. Among the protein kinase C (PKC) isoforms, PKC-alpha, beta, gamma were down-regulated and especially the MAPK signaling pathway PKC-gamma was dramatically decreased by Obox4 RNAi. In the cell cycle pathway, we evaluated the expression of genes involved in regulation of chromosome separation, and found that these genes were down-regulated. It may cause the aberrant chromosome segregation during MI-MII transition.
Conclusion
From the results of this study, it is concluded that Obox4 is important upstream regulator of the PKC and anaphase-promoting complex action for maintaining intact germinal vesicle.
Keywords: Oocyte Maturation; Obox4, Mouse; RNA Interference; Microarray Analysis
Introduction
Oocyte maturation refers to the process that prophase I arrested germinal vesicle (GV) drives the progression of meiosis to metaphase II (MII) to have the capacity for fertilization and embryo development [1]. Spontaneous oocyte maturation in vitro is suppressed when oocytes are cultured with high levels of cAMP maintained by the addition of cAMP analogues or phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitors, such as 3-isobutyl-1-metyl-xanthine (IBMX), in the culture medium [2,3]. Thus, a high cAMP level in the oocyte is crucial for an environment that maintains the meiotic arrest of oocytes in vitro [2-7]. Active form of cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA)-mediated cAMP action that inhibits the resumption of meiosis also prevents mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) activation [8-11]. Also, protein kinase C (PKC) has been reported to plays an important role in inducing MAPK, maturation promoting factor (MPF) activation and oocyte maturation [12-15]. However, the role of PKC system in vertebrate oocytes is still not fully identified.
Oocyte specific homeobox (Obox) family proteins may play an important role in follicle development and oogenesis, because their expression pattern is similar to that of growth differentiation factor-9 (GDF9) and bone morphogenetic protein-15 (BMP15), which are oocyte-specific and play important roles in follicle development and oogenesis [16]. In Obox6 knockout mice, expressions of the Obox1, 2, 3, and 5 genes were increased during early embryo development, suggesting that these family members compensated for the loss of Obox6 expression [17]. In addition, mice lacking the Obox6 gene undergo normal morphological development with normal fertile [17].
In contrast, we found that the expression of the other Obox members such as 1, 2, 3, 5, and 6 genes not affected in the Obox4 knocked down oocytes [18]. Obox4 plays significant role in completion of meiosis specifically at meiosis I-meiosis II (MI-MII) transition with normal spindle-chromosome formation. Interestingly, Obox4 RNA interference (RNAi) resulted in the MI-arrest regardless of the presence (77.7%) or absence (72.5%) of IBMX in the culture medium. Therefore, in that previous study, we concluded that Obox4 is a key factor in cAMP-dependent GV-arrest in oocytes [18].
The present study was conducted to determine the molecular mechanism of Obox4 function. We did Obox4 RNAi at GV stage, cultured oocytes 4 hours for knockdown of Obox4, and did microarray analysis. We found the multiple signaling pathways regulated by Obox4 RNAi during oocyte maturation. Among those multiple pathways, the current study was focused on cell cycle and MAPK pathway because we previously found that Obox4 plays a role in spindle- chromosome configuration during MI-MII transition.
Methods
1. Animals
ICR mice were obtained from Koatech (Pyeongtaek, Korea) and maintained at the animal facility of the CHA Stem Cell Institute of CHA University to obtain oocytes. All procedures described within were reviewed and approved by the University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC), and were performed in accordance with the Guiding Principles for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
2. RNAi for Obox4
Production of Obox4 double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) and RNAi by microinjection was performed as described previously [18]. We prepared dsRNA for Obox4 (240 bp) using the MEGAscript RNAi Kit (Ambion, Austin, TX, USA). GV oocytes were microinjected with Obox4 dsRNA in M2 medium containing 0.2 mM IBMX. Obox4 dsRNA-injected oocytes were cultured in M16 medium containing 0.2 mM IBMX for 4 hours in 5% CO2 at 37℃. Control oocytes cultured in M16 medium containing 0.2 mM IBMX for 4 hours in 5% CO2 at 37℃.
3. Microarray analysis
Due to the small amounts of initial total RNA from 200 oocytes, the process required an amplifying two-cycle target labeling assay step to obtain sufficient amounts of labeled cRNA target for analysis with microarrays. Total RNA was used to synthesize double-stranded cDNA with the MEGAscript kit (Ambion) with an oligo (dT) primer containing a T7 RNA polymerase promoter. The labeled cRNA was hybridized to the Affymetrix GeneChip Mouse Genome 430 2.0 array (Affyme70trix, Santa Clara, CA, USA), which covers transcripts and variants from 34,000 well characterized mouse genes. Probe sets on this array are derived from sequences from GenBank and dbEST. The chips were analyzed by using a GeneChip array scanner 3000 7 G (Affymetrix) and GenPlex 3.0 (ISTECH, Goyang, Korea) software.
4. mRNA isolation and real-time RT-PCR
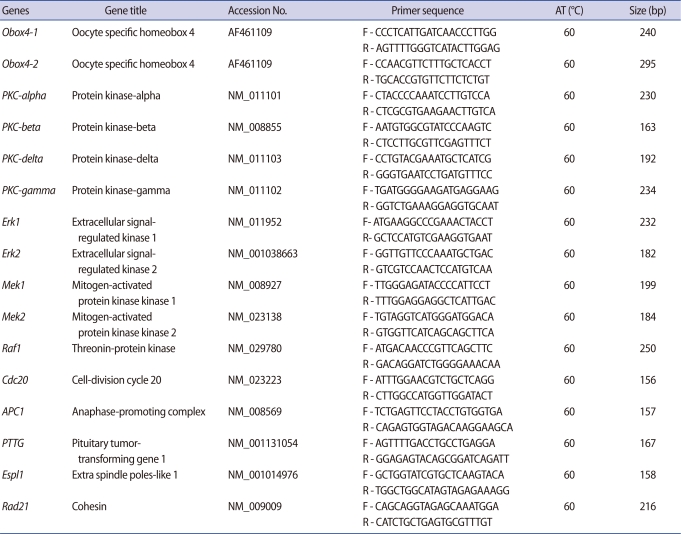
Messenger RNA was isolated from oocytes using the Dynabeads mRNA DIRECT kit (Invitrogen Dynal AS, Oslo, Norway), according to the manufacturer's instructions. Complementary DNA (cDNA) was synthesized from mRNA using oligo (dT) primer, according to the Super Script Preamplification System protocol (Gibco-BRL, Grand Island, NY, USA). Quantitative real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis was performed using the iCycler (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). The iQ™ SYBR Green Supermix PCR reagents (Bio-Rad) were used for monitoring amplification and results were evaluated with the iCycler iQ real-time detection system software. Quantitation of gene amplification was performed by determining the cycle threshold (CT), based on the fluorescence detected within the geometric region of the semi-log amplification plot. Expression of each mRNA species was normalized to that of H1foo mRNA. Relative quantitation of target gene expression was evaluated using the comparative CT method and experiments were repeated at least three times. Real-time PCR reaction conditions and primer sequences for the encoding genes are listed in Table 1.
Table 1.
Oligonucleotide primers, sequences, annealing temperatures (AT), and expected sizes of the real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) products
F and R in the primer codes indicate forward and reverse.
The Obox4-1 primers were used for RT-PCR and synthesis of dsRNA.
The Obox4-2 primers were used to confirm the knockdown of Obox4 after RNAi treatment.
Results
To define and compare control and Obox4-deficient oocytes transcriptomes, gene expressions of control and Obox4 RNAi treated oocytes were analyzed with the Affymetrix Mouse Genome 430 2.0 arrays and GenPlex 3.0 (ISTECH) software. The Affymetrix 430 2.0 mouse microarray was used because it is the most comprehensive array system that allows expression inquiry for over 34,000 well substantiated mouse genes.
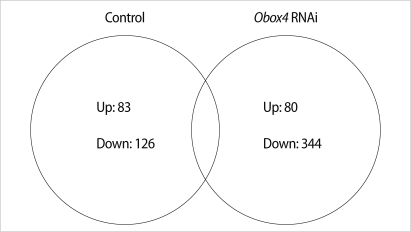
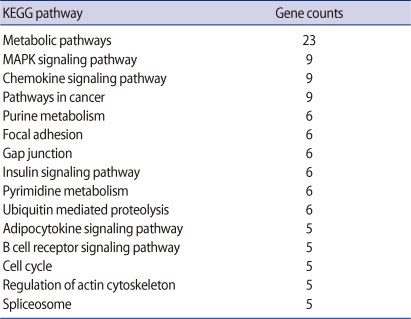
A total of 424 genes were significantly changed at least 2-fold in Obox4 deficient oocytes. This analysis revealed that 80 genes were up-regulated and 344 genes were down-regulated by Obox4 RNAi (Figure 1). Top 15 functional Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways changed after Obox4 RNAi were summarized in Table 2. Among 424 genes, 306 genes were not included for this pathway analysis since functions of these genes are still unknown. Many genes were changed in the pathways related with metabolism, MAPK, and chemokine signaling.
Figure 1.
Venn diagram showing the number of transcripts up- and down-regulated more than 2-fold in comparisons between control and oocyte specific homeobox (Obox) 4 RNA interference, RNAi treated oocytes. Control group; germinal vesicles (GVs) cultured for 0 hour vs. GVs cultured for 4 hours in 3-isobutyl-1-metyl-xanthine (IBMX) supplemented medium (non-injected), Obox4 RNAi group; GVs cultured for 0 hour vs. GVs cultured for 4 hours in IBMX supplemented medium (Obox4 dsRNA-injected).
Table 2.
Top 15 functional groups of genes differentially expressed in oocyte specific homeobox 4 RNAi oocytes
KEGG, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase.
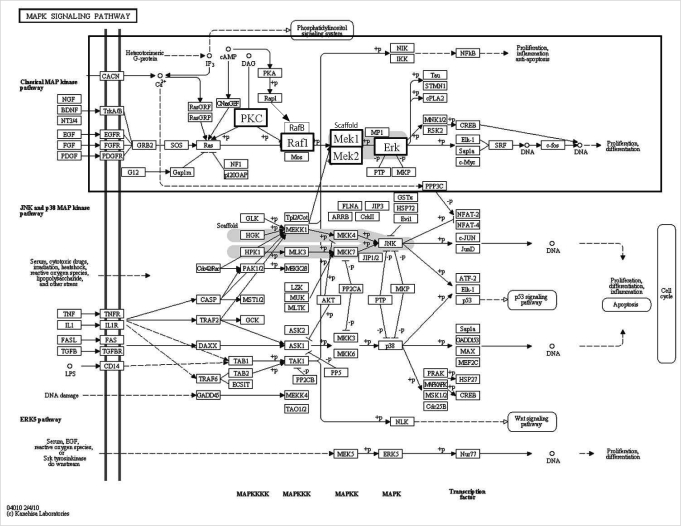
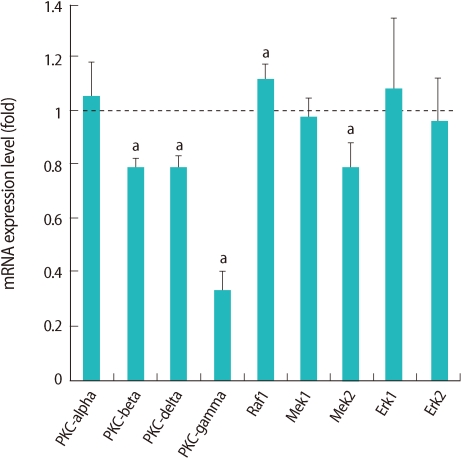
Selected genes in the MAPK signaling pathway are presented in the box with bold characters (Figure 2) and we confirmed their expression by real-time RT-PCR (Figure 3). Four genes (PKC-beta, PKC-delta, PKC-gamma, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 2 [MEK2]) were down-regulated and only Threonin-protein kinase (Raf1) was up-regulated (Figure 3).
Figure 2.
Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway displaying transcripts in mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway. Selected genes are presented with bold characters in a small box and their expression was confirmed by real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction as summarized in Figure 3 [34]. PKC, protein kinase; Raf1, threonin-protein kinase; MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; Erk, extracellular signal-regulated kinase.
Figure 3.
Relative expression of genes related to mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in germinal vesicle (GV) oocytes after oocyte specific homeobox 4 RNA interference. Expression of mRNA was confirmed by real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analysis. The expression levels were calculated cycle threshold values, and then mRNA expression ratio was determined relative to that of control GV oocytes. Experiments were repeated least three times, and data was expressed as mean±SE. PKC, protein kinase; Raf1, threonin-protein kinase; MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; Erk, extracellular signal-regulated kinase. aStatistical significance at p<0.05.
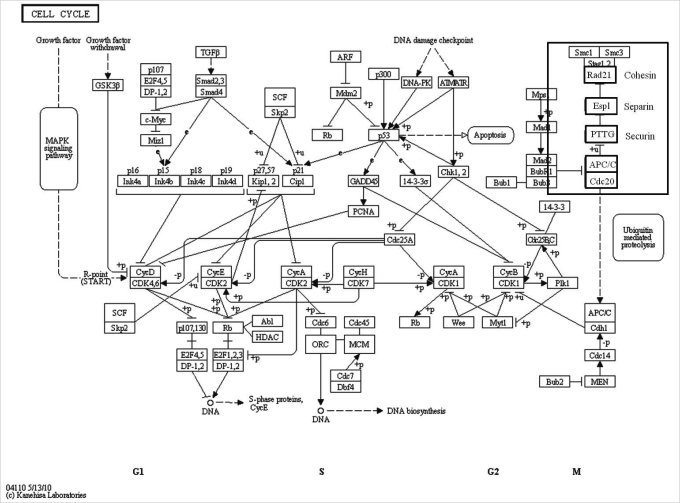
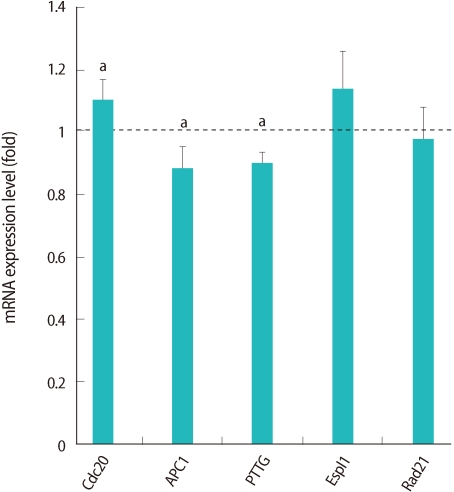
Selected 5 genes in the cell cycle pathway are presented in bold type (Figure 4) and we confirmed their expression by real-time RT-PCR (Figure 5). These genes are related to spindle and chromosome configuration during oocyte maturation, and we selected it based on our previous findings that Obox4 may be involved in the chromosome segregation [18]. Two genes (APC1, PTTG) were down-regulated, while Cdc20 was up-regulated (Figure 5).
Figure 4.
Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway display transcripts in cell cycle pathway. Selected genes are presented in bold characters in a small box and their expression was confirmed by real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Rad21 encodes cohesin, esp1 encodes separin, and PTTG encodes securin [35]. Cdc20, cell-division cycle 20; APC1, anaphase-promoting complex; PTTG, pituitary tumor-transforming gene 1; Espl, extra spindle poles-like; Rad21, cohesin.
Figure 5.
Relative expression of genes related to cell cycle pathway in germinal vesicle (GV) oocytes after oocyte specific homeobox 4 RNAi. Expression of mRNA was confirmed by real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analysis. The expression levels were calculated cycle threshold values, and then mRNA expression ratio was determined relative to that of control GV oocytes. Experiments were repeated least three times, and data was expressed as mean±SE. Cdc20, cell-division cycle 20; APC1, anaphase- promoting complex; PTTG, pituitary tumor-transforming gene 1; Espl, extra spindle poles-like; Rad21, cohesin. aStatistical significance at p<0.05.
Discussion
MAPK plays crucial roles in maturation of oocytes in all animals [19]. Activation of MAPKs requires the dual-specific kinase MEK (MAPKK), which phosphorylates MAPK on critical threonine and tyrosine residues [20-22]. MAPK super-family can be divided in to three major subgroups: extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK), c-jun-N-terminal kinase, and p38 as depicted in Figure 2 [23]. The first characterized subfamily of MAP kinase, Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway [24]. Raf proteins have been shown to phosphorylate and activate MAP kinase kinases (MAPKKs) called MEKs (MAPK or ERK kinases) which in turn phosphorylate and activate ERKs (Raf→MAPKK→MEK cascade) [25,26]. This cascade is inhibited by PKA [5].
We observed that PKC affected by Obox4 RNAi among the MAPK signaling pathway in microarray analysis. The PKC is another major kinase for oocyte maturation in MAPK signaling pathway [27-30]. It has been identified that PKC superfamily has at least 12 isoforms [31]. We focused on the expression of conventional (alpha, beta, gamma) and novel (delta) PKC. These isoforms have been reported in human or mouse oocytes [27-30]. Especially, among 4 isoforms of PKC, 3 isoforms were down-regulated and the expression of PKC-gamma was dramatically decreased after Obox4 RNAi. PKC activity suppressed by PKC antagonists have been shown to induce germinal vesicle breakdown (GVBD) in denuded mouse oocytes in a medium contained hypoxanthine [30]. The authors demonstrated that the meiotic inhibitors such as hypoxanthine might activate PKC in the oocytes [30].
The function of each PKC isoform in oocytes is still largely unknown. Relationship between PKC and Obox4 in regulation of GVBD requires further study. The APC complex is composed of at least 11 APC components and APC1 is the largest of these subunits. The APC/C-CDC20 is known to be suppressed in the metaphase arrest by the spindle assembly checkpoint [32]. CDC20 accumulates during the GV stage but does not activate APC until the resumption of GVBD, because the phosphorylation of APC subunits by the MPF is required for the binding of CDC20 to APC [33]. The APC/C-CDC20 mediated degradation of securin and the degradation of securin activate separase [32]. Separase then cleaves the cohesion, allowing chromosome segregation [32].
We suggest that up-regulation of Cdc20 (Figure 5) may be involved in inducing the meiotic resumption in the Obox4-deficient oocytes in the IBMX medium. In addition, deficiency of spindle formation and aberrant chromosome configuration may be affected by abnormal expression of PTTG, of which protein product is securin.
Taken together, we suggest that Obox4 is important upstream regulator of the PKC and APC action for maintaining intact GV. Further elucidation of the molecular mechanism of the Obox4 would lead us to understand how to maintain the GV arrest.
Footnotes
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (20100022600) and by Priority Research Centers Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2009-0093821).
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
References
- 1.Barnes FL, Sirard MA. Oocyte maturation. Semin Reprod Med. 2000;18:123–131. doi: 10.1055/s-2000-12551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cho WK, Stern S, Biggers JD. Inhibitory effect of dibutyryl cAMP on mouse oocyte maturation in vitro. J Exp Zool. 1974;187:383–386. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401870307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Conti M. Specificity of the cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate signal in granulosa cell function. Biol Reprod. 2002;67:1653–1661. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.102.004952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Conti M, Andersen CB, Richard F, Mehats C, Chun SY, Horner K, et al. Role of cyclic nucleotide signaling in oocyte maturation. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2002;187:153–159. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(01)00686-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Eppig JJ. The participation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) in the regulation of meiotic maturation of oocytes in the laboratory mouse. J Reprod Fertil Suppl. 1989;38:3–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Maller JL, Krebs EG. Progesterone-stimulated meiotic cell division in Xenopus oocytes. Induction by regulatory subunit and inhibition by catalytic subunit of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1977;252:1712–1718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Mehlmann LM, Jones TL, Jaffe LA. Meiotic arrest in the mouse follicle maintained by a Gs protein in the oocyte. Science. 2002;297:1343–1345. doi: 10.1126/science.1073978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bornslaeger EA, Mattei P, Schultz RM. Involvement of cAMP-dependent protein kinase and protein phosphorylation in regulation of mouse oocyte maturation. Dev Biol. 1986;114:453–462. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90209-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Duckworth BC, Weaver JS, Ruderman JV. G2 arrest in Xenopus oocytes depends on phosphorylation of cdc25 by protein kinase A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99:16794–16799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.222661299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Han SJ, Conti M. New pathways from PKA to the Cdc2/cyclin B complex in oocytes: Wee1B as a potential PKA substrate. Cell Cycle. 2006;5:227–231. doi: 10.4161/cc.5.3.2395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lazar S, Galiani D, Dekel N. cAMP-Dependent PKA negatively regulates polyadenylation of c-mos mRNA in rat oocytes. Mol Endocrinol. 2002;16:331–341. doi: 10.1210/mend.16.2.0767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bornslaeger EA, Poueymirou WT, Mattei P, Schultz RM. Effects of protein kinase C activators on germinal vesicle breakdown and polar body emission of mouse oocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1986;165:507–517. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90603-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Stith BJ, Maller JL. Induction of meiotic maturation in Xenopus oocytes by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate. Exp Cell Res. 1987;169:514–523. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90211-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bement WM, Capco DG. Intracellular signals trigger ultrastructural events characteristic of meiotic maturation in oocytes of Xenopus laevis. Cell Tissue Res. 1989;255:183–191. doi: 10.1007/BF00229080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Smith LD. The induction of oocyte maturation: transmembrane signaling events and regulation of the cell cycle. Development. 1989;107:685–699. doi: 10.1242/dev.107.4.685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Rajkovic A, Yan C, Yan W, Klysik M, Matzuk MM. Obox, a family of homeobox genes preferentially expressed in germ cells. Genomics. 2002;79:711–717. doi: 10.1006/geno.2002.6759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Cheng WC, Hsieh-Li HM, Yeh YJ, Li H. Mice lacking the Obox6 homeobox gene undergo normal early embryonic development and are fertile. Dev Dyn. 2007;236:2636–2642. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.21261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lee HS, Kim EY, Kim KH, Moon J, Park KS, Kim KS, et al. Obox4 critically regulates cAMP-dependent meiotic arrest and MI-MII transition in oocytes. FASEB J. 2010;24:2314–2324. doi: 10.1096/fj.09-147314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Abrieu A, Dorée M, Fisher D. The interplay between cyclin-B-Cdc2 kinase (MPF) and MAP kinase during maturation of oocytes. J Cell Sci. 2001;114:257–267. doi: 10.1242/jcs.114.2.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Fan HY, Sun QY. Involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade during oocyte maturation and fertilization in mammals. Biol Reprod. 2004;70:535–547. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.103.022830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sun QY, Wu GM, Lai L, Bonk A, Cabot R, Park KW, et al. Regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylation, microtubule organization, chromatin behavior, and cell cycle progression by protein phosphatases during pig oocyte maturation and fertilization in vitro. Biol Reprod. 2002;66:580–588. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod66.3.580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Liang CG, Su YQ, Fan HY, Schatten H, Sun QY. Mechanisms regulating oocyte meiotic resumption: roles of mitogen-activated protein kinase. Mol Endocrinol. 2007;21:2037–2055. doi: 10.1210/me.2006-0408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Davis RJ. MAPKs: new JNK expands the group. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994;19:470–473. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Schmitt A, Nebreda AR. Signalling pathways in oocyte meiotic maturation. J Cell Sci. 2002;115:2457–2459. doi: 10.1242/jcs.115.12.2457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Howe LR, Leevers SJ, Gómez N, Nakielny S, Cohen P, Marshall CJ. Activation of the MAP kinase pathway by the protein kinase raf. Cell. 1992;71:335–342. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90361-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kyriakis JM, App H, Zhang XF, Banerjee P, Brautigan DL, Rapp UR, et al. Raf-1 activates MAP kinase-kinase. Nature. 1992;358:417–421. doi: 10.1038/358417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Gangeswaran R, Jones KT. Unique protein kinase C profile in mouse oocytes: lack of calcium-dependent conventional isoforms suggested by rtPCR and Western blotting. FEBS Lett. 1997;412:309–312. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(97)00782-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Luria A, Tennenbaum T, Sun QY, Rubinstein S, Breitbart H. Differential localization of conventional protein kinase C isoforms during mouse oocyte development. Biol Reprod. 2000;62:1564–1570. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod62.6.1564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Pauken CM, Capco DG. The expression and stage-specific localization of protein kinase C isotypes during mouse preimplantation development. Dev Biol. 2000;223:411–421. doi: 10.1006/dbio.2000.9763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Downs SM, Cottom J, Hunzicker-Dunn M. Protein kinase C and meiotic regulation in isolated mouse oocytes. Mol Reprod Dev. 2001;58:101–115. doi: 10.1002/1098-2795(200101)58:1<101::AID-MRD13>3.0.CO;2-J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Mellor H, Parker PJ. The extended protein kinase C superfamily. Biochem J. 1998;332:281–292. doi: 10.1042/bj3320281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Yu H. Regulation of APC-Cdc20 by the spindle checkpoint. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2002;14:706–714. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(02)00382-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Rudner AD, Murray AW. Phosphorylation by Cdc28 activates the Cdc20-dependent activity of the anaphase-promoting complex. J Cell Biol. 2000;149:1377–1390. doi: 10.1083/jcb.149.7.1377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.KEGG. Kyoto (JP): Kanehisa Laboratories; 2010. [cited 2011 May 31]. MAPK signaling pathway-reference pathway [Internet] Available from: http://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/highlight_pathway?scale=1.0&map=map04010. [Google Scholar]
- 35.KEGG. Kyoto (JP): Kanehisa Laboratories; 2010. [cited 2011 May 31]. Cell cycle-reference pathway [Internet] Available from: http://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/highlight_pathway?scale=1.0&map=map04110. [Google Scholar]