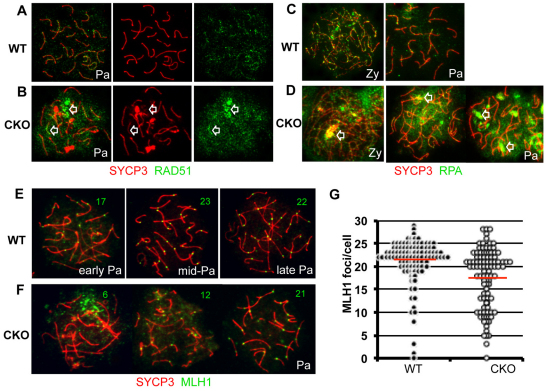
Fig. 5.
Ectopic accumulation of DNA repair factors in Brg1CKO spermatocytes. (A-D) Distribution of repair proteins RAD51 (green; A,B) and RPA (green; C,D) in wild-type (A,C) and Brg1CKO (B,D) spermatocytes. SYCP3 (red) was used in nuclear spreads to identify spermatocytes in the zygotene or pachytene stages. Arrowheads in B and D depict abnormal repair foci of Brg1CKO. (E,F) Crossover formation in pachytene spermatocytes. MLH1-containing recombination nodules (green) on the synaptic axes (red) in wild-type (E) and mutant spermatocytes (F) are shown in nuclei spreads prepared from 15 dpp testis. Numbers in representative images (E,F) indicate the number of MLH1 foci per nucleus. (G) Beeswarm plot of MLH1 foci in each control (black circle, n=110) and Brg1CKO (open circle, n=108) spermatocyte. The red line is the average number of MLH1 foci in each genotype (21.1 in wild type versus 17.3 in Brg1CKO; P=2.3x10–6); statistical significance was determined by t-test. Pa, pachynema; Zy, zygonema.