Abstract
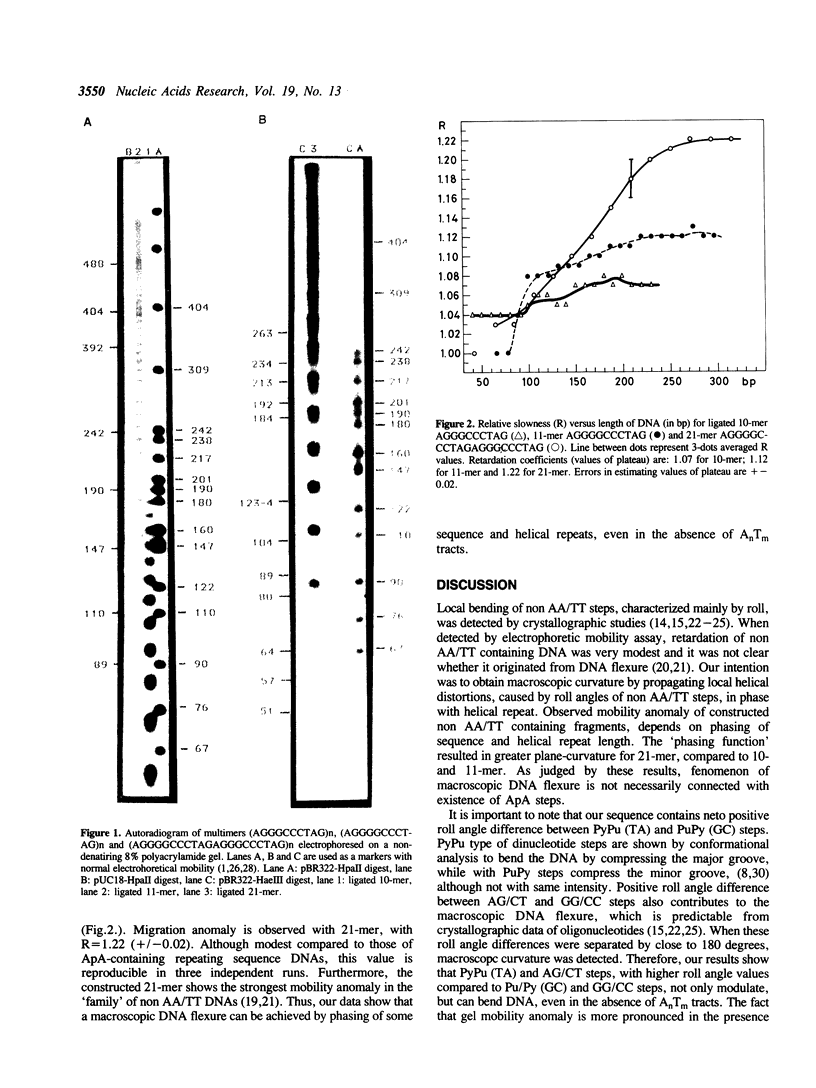
The evidence is accumulating that dinucleotide steps other than AA/TT affect DNA flexure of AnTm (m + n greater than = 4) containing fragments. However, it is not clear whether macroscopic DNA flexure without AA/TT steps might occur. In this paper we demonstrate the anomaly in electrophoretic mobility of non AA/TT repetitive DNA sequences which is a function of sequence phasing. Therefore, our results show that PyPu (TA) and AG/CT steps, angulary separated by close to 180 degrees from Pu/Py (GC) and GG/CC steps, bend DNA, even in the absence of AnTm tracts.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abagyan R. A., Mironov V. N., Chernov B. K., Chuprina V. P., Ulyanov A. V. Electrophoretic behavior of d(GGAAAAAAGG)n, d(CCAAAAAACC)n, and (CCAAAAAAGG)n and implications for a DNA bending model. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):989–992. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhoff A. M., Tullius T. D. Structural details of an adenine tract that does not cause DNA to bend. Nature. 1988 Feb 4;331(6155):455–457. doi: 10.1038/331455a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calladine C. R., Drew H. R., McCall M. J. The intrinsic curvature of DNA in solution. J Mol Biol. 1988 May 5;201(1):127–137. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90444-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calladine C. R., Drew H. R. Principles of sequence-dependent flexure of DNA. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 20;192(4):907–918. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90036-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuprina V. P., Fedoroff OYu, Reid B. R. New insights into the structure of An tracts and B'-B' bends in DNA. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 15;30(2):561–568. doi: 10.1021/bi00216a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark G. R., Brown D. G., Sanderson M. R., Chwalinski T., Neidle S., Veal J. M., Jones R. L., Wilson W. D., Zon G., Garman E. Crystal and solution structures of the oligonucleotide d(ATGCGCAT)2: a combined X-ray and NMR study. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 25;18(18):5521–5528. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.18.5521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Drew H. R. Structure of a B-DNA dodecamer. II. Influence of base sequence on helix structure. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 15;149(4):761–786. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90357-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diekmann S., McLaughlin L. W. DNA curvature in native and modified EcoRI recognition sites and possible influence upon the endonuclease cleavage reaction. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 20;202(4):823–834. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90561-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diekmann S. Sequence specificity of curved DNA. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 20;195(1-2):53–56. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80128-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fratini A. V., Kopka M. L., Drew H. R., Dickerson R. E. Reversible bending and helix geometry in a B-DNA dodecamer: CGCGAATTBrCGCG. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14686–14707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagerman P. J. Sequence dependence of the curvature of DNA: a test of the phasing hypothesis. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 3;24(25):7033–7037. doi: 10.1021/bi00346a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagerman P. J. Sequence-directed curvature of DNA. Nature. 1986 May 22;321(6068):449–450. doi: 10.1038/321449a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katahira M., Sugeta H., Kyogoku Y. A new model for the bending of DNAs containing the oligo(dA) tracts based on NMR observations. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):613–618. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Crothers D. M. Calibration of DNA curvature and a unified description of sequence-directed bending. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1763–1767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. DNA bending at adenine . thymine tracts. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):501–506. doi: 10.1038/320501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marini J. C., Levene S. D., Crothers D. M., Englund P. T. Bent helical structure in kinetoplast DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7664–7668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall M., Brown T., Kennard O. The crystal structure of d(G-G-G-G-C-C-C-C). A model for poly(dG).poly(dC). J Mol Biol. 1985 Jun 5;183(3):385–396. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamara P. T., Bolshoy A., Trifonov E. N., Harrington R. E. Sequence-dependent kinks induced in curved DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1990 Dec;8(3):529–538. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1990.10507827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milton D. L., Casper M. L., Gesteland R. F. Saturation mutagenesis of a DNA region of bend. Base steps other than ApA influence the bend. J Mol Biol. 1990 May 5;213(1):135–140. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80126-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milton D. L., Casper M. L., Wills N. M., Gesteland R. F. Guanine tracts enhance sequence directed DNA bends. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):817–820. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muzard G., Théveny B., Révet B. Electron microscopy mapping of pBR322 DNA curvature. Comparison with theoretical models. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1289–1298. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08238.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson H. C., Finch J. T., Luisi B. F., Klug A. The structure of an oligo(dA).oligo(dT) tract and its biological implications. Nature. 1987 Nov 19;330(6145):221–226. doi: 10.1038/330221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shliakhtenko L. S., Liubchenko Iu L., Chernov B. K., Zhurkin V. B. Vliianie temperatury i ionnoi sily na élektroforeticheskuiu podvizhnost' sinteticheskikh fragmentov DNK. Mol Biol (Mosk) 1990 Jan-Feb;24(1):79–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A. Why bend DNA? Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):177–180. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90729-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trifonov E. N. Curved DNA. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1985;19(2):89–106. doi: 10.3109/10409238509082540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulanovsky L. E., Trifonov E. N. Estimation of wedge components in curved DNA. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):720–722. doi: 10.1038/326720a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulanovsky L., Bodner M., Trifonov E. N., Choder M. Curved DNA: design, synthesis, and circularization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):862–866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon C., Privé G. G., Goodsell D. S., Dickerson R. E. Structure of an alternating-B DNA helix and its relationship to A-tract DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6332–6336. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]