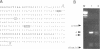Abstract
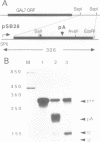
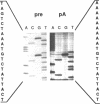
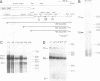
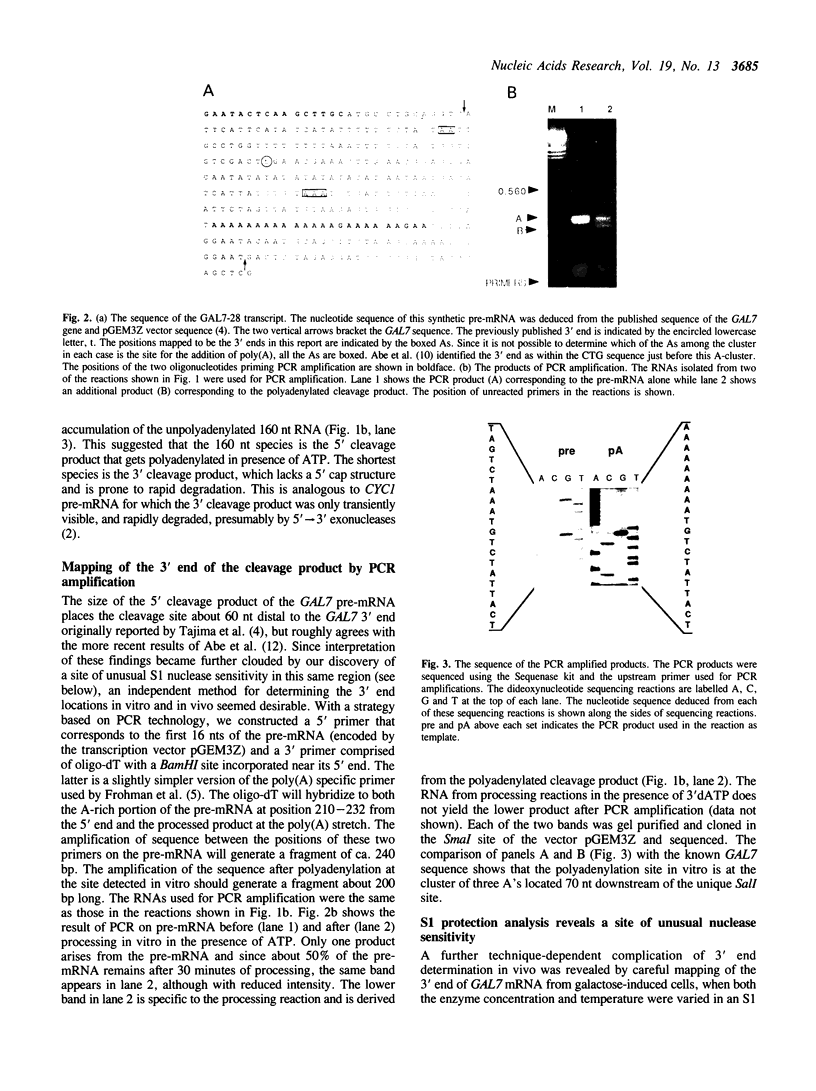
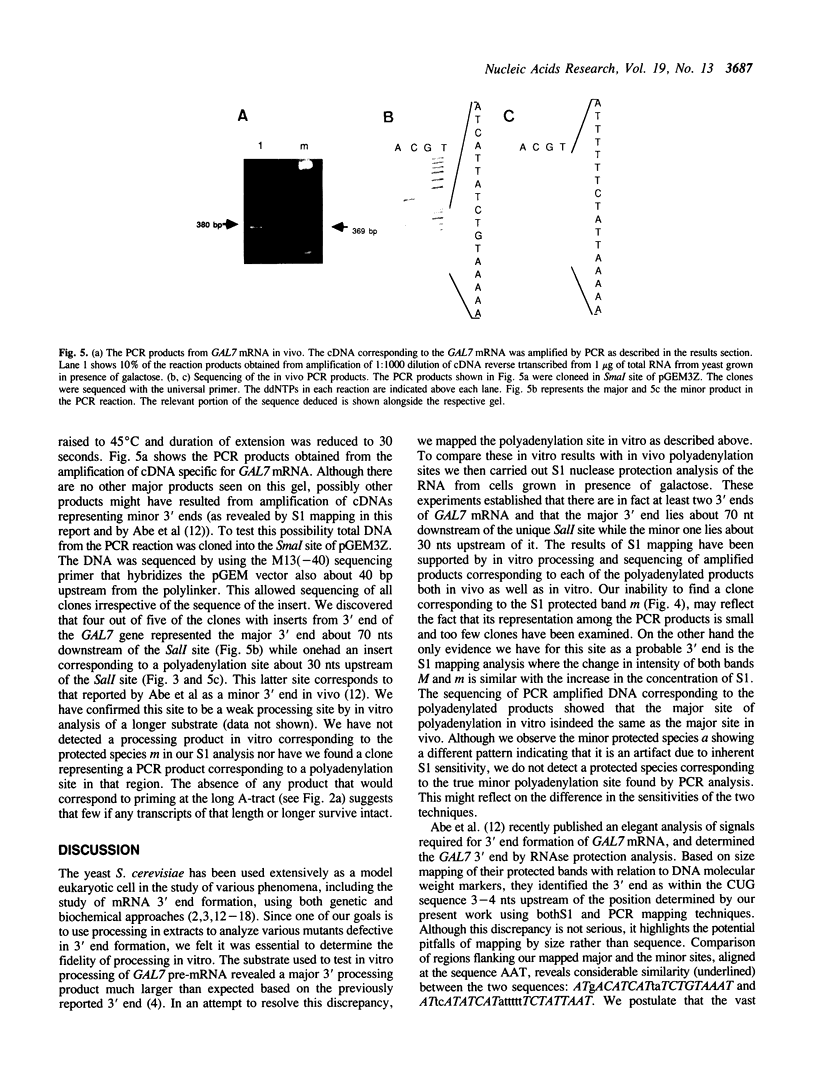
In general, synthetic RNA transcripts corresponding to the 3' ends of Saccharomyces cerevisiae genes appear to be accurately cleaved and polyadenylated in vitro under appropriate conditions in yeast cell extracts. Initially, however, the endpoints observed in vitro for the GAL7 gene failed to correlate adequately with those reported in vivo as derived from traditional S1 nuclease protection analyses. This led us to apply an independent method for analyzing mRNA 3' ends, using the polymerase chain reaction, with a first strand primer that incorporated a BamHI restriction site sequence near its 5' end, followed by (dT)17. This proved to be a sensitive and accurate means for determining precisely the major and minor polyadenylation sites of the GAL7 mRNA. Moreover, there was complete agreement between the sites identified with this technique when applied to cellular RNA and those generated in vitro by our 3' end mRNA processing reaction. This provides further support for the likelihood that processing in vitro faithfully reflects the endonucleolytic cleavage and polyadenylation events that occur within the living cell.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe A., Hiraoka Y., Fukasawa T. Signal sequence for generation of mRNA 3' end in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL7 gene. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3691–3697. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07581.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler J. S., Platt T. RNA processing generates the mature 3' end of yeast CYC1 messenger RNA in vitro. Science. 1988 Dec 2;242(4883):1270–1274. doi: 10.1126/science.2848317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler J. S., Sadhale P. P., Platt T. RNA processing in vitro produces mature 3' ends of a variety of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2599–2605. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Kelly J. D., Cohen E. H. Transcription terminates in yeast distal to a control sequence. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):607–614. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90441-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne B. I., Guarente L. Mutational analysis of a yeast transcriptional terminator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4097–4101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne B. I., Guarente L. Transcription by RNA polymerase II induces changes of DNA topology in yeast. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):766–772. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T. Transcription termination and the regulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:339–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruohola H., Baker S. M., Parker R., Platt T. Orientation-dependent function of a short CYC1 DNA fragment in directing mRNA 3' end formation in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5041–5045. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo P., Li W. Z., Hampsey D. M., Zaret K. S., Sherman F. Distinct cis-acting signals enhance 3' endpoint formation of CYC1 mRNA in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1991 Mar;10(3):563–571. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07983.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo P., Sherman F. Transcription terminates near the poly(A) site in the CYC1 gene of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8348–8352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B., Davis R. W. The poly(A) binding protein is required for poly(A) shortening and 60S ribosomal subunit-dependent translation initiation. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):857–867. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90938-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M., Sapolsky R. J., Davis R. W. Transcription interferes with elements important for chromosome maintenance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2184–2194. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St John T. P., Davis R. W. The organization and transcription of the galactose gene cluster of Saccharomyces. J Mol Biol. 1981 Oct 25;152(2):285–315. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90244-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tajima M., Nogi Y., Fukasawa T. Primary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL7 gene. Yeast. 1985 Sep;1(1):67–77. doi: 10.1002/yea.320010108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Sherman F. DNA sequence required for efficient transcription termination in yeast. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarkower D., Stephenson P., Sheets M., Wickens M. The AAUAAA sequence is required both for cleavage and for polyadenylation of simian virus 40 pre-mRNA in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2317–2323. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]