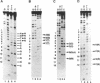Abstract
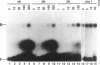
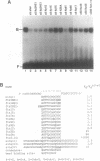
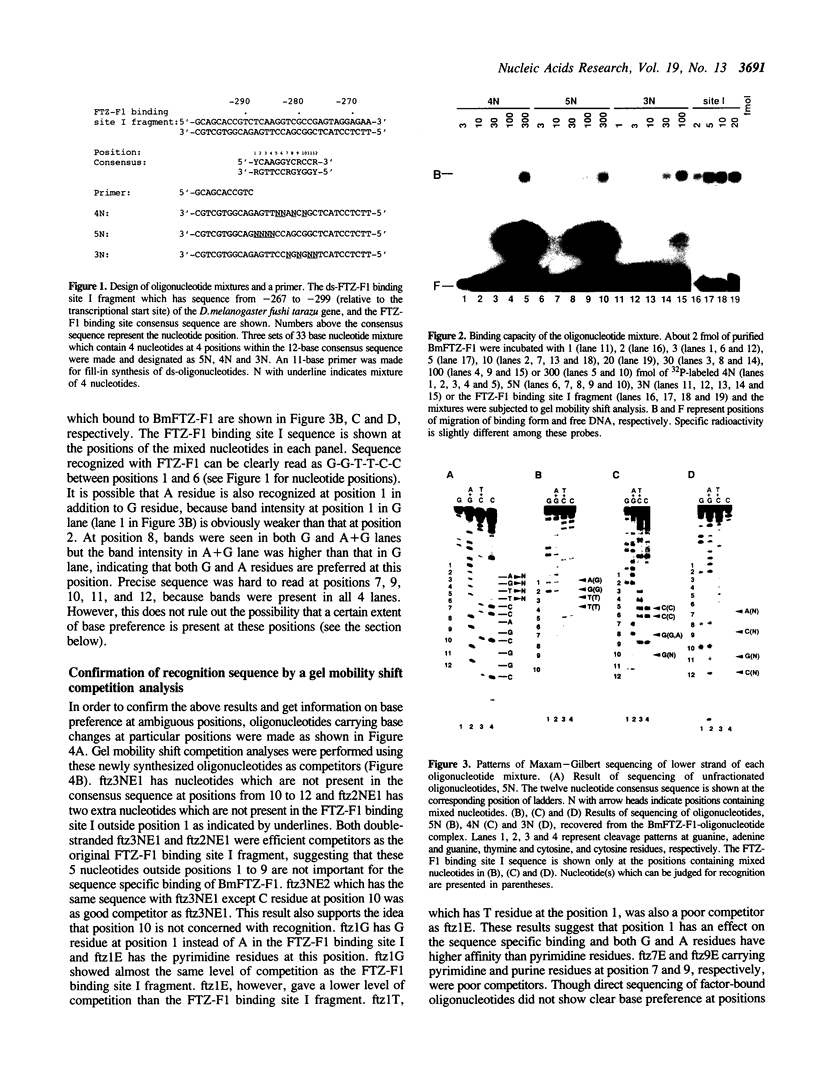
BmFTZ-F1 is a Bombyx mori homologue of FTZ-F1, a positive regulator of the fushi tarazu gene of Drosophila melanogaster. In order to determine the sequence recognized with this factor, we made three sets of oligonucleotide mixture which contain 4 possible nucleotides at different positions within the previously proposed 12-bp binding consensus sequence. Oligonucleotides which bound to purified BmFTZ-F1 were separated by a gel mobility shift procedure and a binding sequence was determined by direct sequencing through Maxam-Gilbert method. By this analysis, 7 positions showed clear sequence preference and 5 positions showed weak or no sequence preference. The importance of each nucleotide at each position was confirmed by a gel mobility shift competition analysis and results were presented as a quantitative difference in the binding affinity. From these analyses, we conclude that the best binding sequence of BmFTZ-F1 is 5'-PyCAAGGPyCPu-3'. This method may be useful for the determination of a binding sequence of other sequence specific DNA binding factor.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackwell T. K., Kretzner L., Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N., Weintraub H. Sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc protein. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1149–1151. doi: 10.1126/science.2251503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Weintraub H. Differences and similarities in DNA-binding preferences of MyoD and E2A protein complexes revealed by binding site selection. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1104–1110. doi: 10.1126/science.2174572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronostajski R. M. Site-specific DNA binding of nuclear factor I: effect of the spacer region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5545–5559. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. D., Travers A. A. Identification of the binding sites for potential regulatory proteins in the upstream enhancer element of the Drosophila fushi tarazu gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 23;16(24):11403–11416. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.24.11403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier D., Preiss A., Powell J. R. Regulation of the segmentation gene fushi tarazu has been functionally conserved in Drosophila. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3957–3966. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07616.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliphant A. R., Brandl C. J., Struhl K. Defining the sequence specificity of DNA-binding proteins by selecting binding sites from random-sequence oligonucleotides: analysis of yeast GCN4 protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2944–2949. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliphant A. R., Struhl K. Defining the consensus sequences of E.coli promoter elements by random selection. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7673–7683. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliphant A. R., Struhl K. The use of random-sequence oligonucleotides for determining consensus sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:568–582. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55037-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick L., Schier A., Affolter M., Schmidt-Glenewinkel T., Gehring W. J. Analysis of the ftz upstream element: germ layer-specific enhancers are independently autoregulated. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1224–1239. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serfling E. Autoregulation--a common property of eukaryotic transcription factors? Trends Genet. 1989 May;5(5):131–133. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Gilbert W. Contacts between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and an early promoter of phage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):122–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullius T. D., Dombroski B. A., Churchill M. E., Kam L. Hydroxyl radical footprinting: a high-resolution method for mapping protein-DNA contacts. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:537–558. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda H., Hirose S. Identification and purification of a Bombyx mori homologue of FTZ-F1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7229–7234. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda H., Sonoda S., Brown J. L., Scott M. P., Wu C. A sequence-specific DNA-binding protein that activates fushi tarazu segmentation gene expression. Genes Dev. 1990 Apr;4(4):624–635. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.4.624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. An exonuclease protection assay reveals heat-shock element and TATA box DNA-binding proteins in crude nuclear extracts. Nature. 1985 Sep 5;317(6032):84–87. doi: 10.1038/317084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]