Abstract
Previous work from our laboratory has established that cellular signaling processes of endogenous morphine are mediated by cognate G protein coupled receptor (GPCR) proteins, designated µ3 and µ4 opiate receptors. µ3 and µ4 opiate receptors are structurally unique “short” 6 transmembrane helical (TMH) domain GPCRs that are selectively responsive to endogenous morphine, not to families of endogenous opioid peptides, and are uniquely coupled to activation of constitutive nitric oxide synthase (cNOS). Based on high resolution predictive measures, it appears likely that domestic poultry express a µ opiate receptor mRNA encoding potentially two novel GPCRs with similar biochemical characteristics as described for µ3 and µ4 opiate receptors as well as traditional µ1 opioid receptors. The biological indications of these novel µ opiate receptors are discussed within the context of this short review.
Keywords: endogenous morphine, chicken µ opiate receptor, G protein coupled receptor, transmembrane helical domain
Introduction
Previous work from our laboratory has focused on the elucidation of biochemical, cellular, and molecular mechanisms underlying the regulatory roles of endogenously expressed, chemically authentic, morphine in animal cells and organ systems [1–9]. As a critical corollary, we have established that cellular signaling processes of endogenous morphine are mediated by cognate G protein coupled receptor (GPCR) proteins, designated µ3 and µ4 opiate receptors. µ3 and µ4 opiate receptors are structurally tailored to be selectively activated by morphine and morphine-related opiate alkaloids and not by related families of endogenous opioid peptides [10, 11] and are functionally coupled to activation of constitutive nitric oxide (NO) production and release [3, 6, 8, 9, 12–14].
The unique structural features of µ3 and µ4 opiate receptors are determined post-transcriptionally via selective splicing of the primary transcript of the µ1 opioid receptor (MOR) gene [1, 15–17]. Mature µ3 and µ4 opiate receptor-encoding mRNAs translate into receptor proteins lacking an amino acid sequence of approximately 90 amino acids that constitute the extracellular N-terminal and transmembrane helical (TMH)1 domains and part of the first intracellular loop of the µ1 receptor, but retain the empirically defined ligand binding pocket distributed across conserved TMH2, TMH3, and TMH7 domains of the µ1 sequence. In effect, µ3 and µ4 opiate receptors are “short” 6TMH domain GPCRs that are selectively responsive to endogenous morphine.
Predictive measures indicate a novel “short” µ opiate receptor in domestic chicken
Our compelling demonstration of novel “short” 6 TMH domain µ opiate receptors stimulated an exhaustive search of existing databases to determine whether additional 6TMH domain u opiate receptors were expressed in various animal species [17]. The National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) database yielded a predicted chicken µ opioid receptor mRNA sequence that provided putative evidence supporting the existence of a novel “short” µ opiate receptor in the domestic chicken. Interestingly, the 5’ end of predicted mRNA sequence was observed to contain three potential ATG start codons (Figure 1). Consensus sequence analysis of probable translation initiation site (TIS) was performed as according to Kozak sequence guidelines, as previously described [18–23]. Accordingly, predicted nucleotide sequences utilizing the first and the third initiation codons as likely TIS candidates were translated into two probable protein sequences of 327 and 300 amino acids, respectively, using the Translation Web Tool provided by EXPASY.
Figure 1.
Full length untranslated mRNA species from novel chicken opioid receptor has the potential for three different start sites, the first will produce a protein species equivalent to 37 kDa, and the last will produce a protein species equivalent to 34 kDa
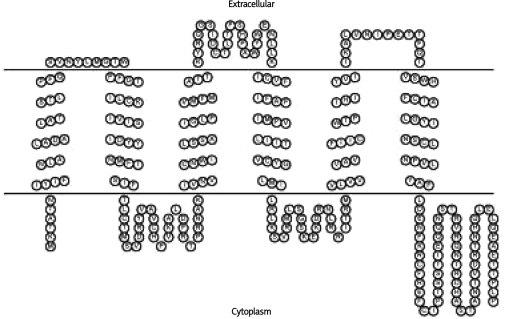
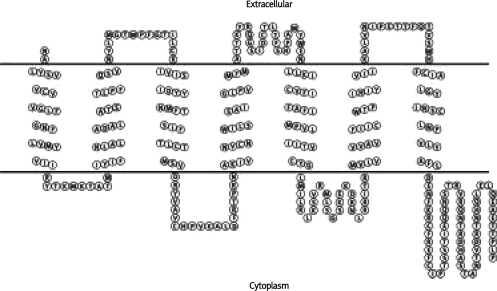
Conformational analysis of the smaller 300 amino acid µ opiate receptor protein species, performed by computer program TMHMM, indicated a 6TMH domain GPCR with an identical membrane topology to native µ3 and µ4 opiate receptors (Figure 2A) [16, 17]. Interestingly, computational analysis of the larger 327 amino acid µ opiate receptor protein species indicated a novel 7TMH domain GPCR lacking a typical extracellular domain containing consensus N-linked glycosylation sites (Figure 2B). In both cases, predictive measures indicate that the domestic chicken expresses one or two novel “short” GPCRs with similar biochemical characteristics as previously described for µ3 and µ4 opiate receptors as well as traditional MOR's.
Figure 2A.
Graphic representation of the predicted 300 amino acid receptor species based on the previously shown TMHMM predictions and determinations. Image was provided by the Sequence Analysis and Consulting Service using TOPO2 [52] software funded by the University of California, San Francisco, USA
Figure 2B.
Graphic representation of the predicted 327 amino acid receptor species based on TMHMM determinations. Image was provided by the Sequence Analysis and Consulting Service using TOPO2 [52] software funded by the University of California, San Francisco, USA
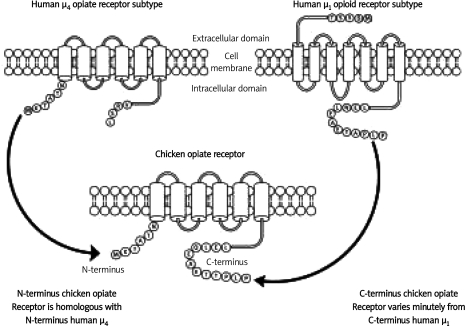
Finally, BLAST (Basic Local Alignment Search Tool)-mediated comparative amino acid sequence analysis yielded an N-terminal sequence homology of 96% for an alignment containing amino acid residues 1-290 of the predicted 300 amino acid chicken µ opiate receptor in comparison to amino acid residues 1-290 of the 292 amino acid µ4 opiate receptor [16, 17]. BLAST analysis also yielded a C-terminal sequence homology of 96% for an alignment containing amino acid residues 1-300 of the predicted 300 amino acid chicken µ opiate receptor in comparison to amino acid residues 101 to 400 of the 400 amino acid µ1 opiate receptor. Thus, the 300 amino acid 6 TMH domain chicken µ opiate receptor may be operationally defined as an N-terminally truncated “short” homolog of the µ1 opioid receptor (Figure 3). Due to the novel 6 TMH domain configuration and sequence identity to µ3 and µ4 opiate receptors at its N-terminus, we predict that the 300 amino acid chicken µ opiate receptor functions as a “hybrid” signaling GPCR with selective preference for morphine and related morphinan alkaloids with the exclusion of endogenous opioid peptides [10, 11]. Similar criteria relating to ligand selectivity will most certainly apply to the predicted novel “short” 7TMH domain 327 amino acid chicken µ opiate receptor due to the genetic deletion of the glycosylated extracellular N-terminal domain.
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of the predicted amino acid sequence of the 300 amino acid 6 TMH domain µ chicken opiate receptor in comparison to the 6 TMH domain µ4 opiate receptor and the traditional 7 TMH domain µ1 opioid receptor. The 300 amino acid 6 TMH domain chicken µ opiate receptor may be operationally defined as an N-terminally truncated “short” homolog of the µ1 opioid receptor. The novel 6 TMH domain configuration and sequence identity to µ3 and µ4 opiate receptors at its N-terminus suggest that the chicken µ opiate receptor functions as a “hybrid” signaling GPCR with selective preference for morphine and related morphinan alkaloids with the exclusion of endogenous opioid peptides. Illustration was designed using ChemBioOffice 2008, Cambridgesoft, Cambridge Massachusetts, USA
Biological indications of a novel “short” µ opiate receptor in domestic chicken
Based on guidelines established by Kozak et al. [22, 23] it appears that mature chicken µ opiate receptor-encoding mRNA contains two probable TISs with the potential for translation of two distinct 300 and 327 amino acid µ opiate receptor proteins. Prior literature indicates that many mRNAs are capable of producing functionally distinct proteins using different in frame start codons within the same mature fully spliced mRNA [20, 24]. Furthermore, the effects of upstream start codons can vary with cell type during differentiation [25–28]. Accordingly, mature chicken µ opiate receptor-encoding mRNA may be similarly translated into one or two functional receptor proteins that are sorted or expressed according to tissue or cell type. Morphine and other chemically related opiate alkaloids represent classical and reliable analgesic principles for management of severe pain associated with disease [5, 8, 9, 12, 14, 29–43]. Paradoxical morphine-mediated hyperalgesia in the presence of typical morphine-mediated respiratory depression has been observed in the domestic chicken [44–46]. It is a reasonable, therefore, to speculate that these markedly different physiological responses to administered morphine may be due differential expression of the 300 vs. the 327 amino acid µ opiate receptor in spinal cord and brain stem loci.
Conclusions
The presence of this biologically unique, functional “short” membrane bound receptor protein in the chicken not only reinforces the primacy of said receptor but in doing that it also gives us view into a window of learning and understanding the history of evolution. The chicken is evolutionarily placed to bridge the gap between mammals and non-amniote vertebrates, and is therefore the best studied representative of all avian species, thus providing a valuable resource for understanding comparative genomics [47]. Interestingly, inspection of the chicken MOR gene indicated a very streamlined nucleotide sequence. The link between genome size and metabolic rate was first made in 1970 by Henryk Szarski [48–50]. Birds have the smallest genome when compared to other vertebrates including humans [51]. Avian species require a high metabolic rate to carry out basic physiological functions. The metabolic advantage of a smaller, relatively streamlined genome within all cells allows cells not only to be smaller but operationally expands cellular surface area to volume ratios. Smaller genomes do not necessarily mean fewer genes, but rather a more succinct use of space on the chromosomes. In effect, smaller cells are more energy efficient that larger ones, resulting in an increased metabolic advantage. These complementary data may also contribute to understanding the physiological role of nucleated red blood cells in birds [16, 17]. It is possible that avian species due to their relatively streamlined genome and smaller size do not require expulsion of the nucleus from the red blood cells before its entry into the blood stream. In effect, the high surface to volume ratio of nucleated red cells in avian species facilitates markedly efficient gas exchange with surrounding tissues. Future studies to elucidate the physiological role of novel µ opiate receptors in these same metabolic processes are highly necessitated by our initial findings.
References
- 1.Kream RM, Stefano GB. De novo biosynthesis of morphine in animal cells: an evidence-based model. Med Sci Monit. 2006;12:RA207–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Stefano GB, Goumon Y, Casares F, et al. Endogenous morphine. Trends Neurosci. 2000;9:436–42. doi: 10.1016/s0166-2236(00)01611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Fricchione G, Zhu W, Cadet P, et al. Identification of endogenous morphine and a mu3-like opiate alkaloid receptor in human brain tissue taken from a patient with intractable complex partial epilepsy. Med Sci Monit. 2008;14:CS45–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kream RM, Stefano GB. Homeopathic ethanol. Med Sci Monit. 2008;14:SC11–3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Stefano GB, Stefano JM, Esch T. Anticipatory stress response: a significant commonality in stress, relaxation, pleasure and love responses. Med Sci Monit. 2008;14:RA17–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Atmanene C, Laux A, Glattard E, et al. Characterization of human and bovine phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein (PEBP/RKIP) interactions with morphine and morphine-glucuronides determined by noncovalent mass spectrometry. Med Sci Monit. 2009;15:BR178–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kream RM, Stefano GB. Endogenous morphine and nitric oxide coupled regulation of mitochondrial processes. Med Sci Monit. 2009;15:RA263–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Stefano GB, Esch T, Kream RM. Xenobiotic perturbation of endogenous morphine signaling: paradoxical opiate hyperalgesia. Med Sci Monit. 2009;15:RA107–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Stefano GB, Kream RM, Esch T. Revisiting tolerance from the endogenous morphine perspective. Med Sci Monit. 2009;15:RA189–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cadet P, Mantione KJ, Zhu W, Kream RM, Sheehan M, Stefano GB. A functionally coupled mu3-like opiate receptor/nitric oxide regulatory pathway in human multi-lineage progenitor cells. J Immunol. 2007;179:5839–44. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.9.5839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cadet P, Mantione KJ, Stefano GB. Molecular identification and functional expression of mu3, a novel alternatively spliced variant of the human mu opiate receptor gene. J Immunol. 2003;170:5118–23. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.10.5118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Pflueger A, Abramowitz D, Calvin AD. Role of oxidative stress in contrast-induced acute kidney injury in diabetes mellitus. Med Sci Monit. 2009;15:RA125–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.De GC V, Bianchi M, Pascale V, et al. Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA): an endogenous inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase and a novel cardiovascular risk molecule. Med Sci Monit. 2009;15:RA91–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Tanii H, Higashi T, Nishimura F, Higuchi Y, Saijoh K. Effects of cruciferous allyl nitrile on phase 2 antioxidant and detoxification enzymes. Med Sci Monit. 2008;14:BR189–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kream RM, Sheehan M, Cadet P, et al. Persistence of evolutionary memory: primordial six-transmembrane helical domain mu opiate receptors selectively linked to endogenous morphine signaling. Med Sci Monit. 2007;13:SC5–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sheehan M. Opiate processes in poultry. Arch Med Sci. 2009;5:626–36. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sheehan M, Kream RM, Mantione KJ, Stefano GB. Prediction of a novel “short” u opiate receptor in domestic chicken; Activitas Nervosa Superior Rediviva 2010; in press. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Cavener DR, Ray SC. Eukaryotic start and stop translation sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991;19:3185–92. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.12.3185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kochetov AV. AUG codons at the beginning of protein coding sequences are frequent in eukaryotic mRNAs with a suboptimal start codon context. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:837–40. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kochetov AV. Alternative translation start sites and hidden coding potential of eukaryotic mRNAs. Bioessays. 2008;30:683–91. doi: 10.1002/bies.20771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kozak M. Pushing the limits of the scanning mechanism for initiation of translation. Gene. 2002;299:1–34. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1119(02)01056-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kozak M. Regulation of translation via mRNA structure in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Gene. 2005;361:13–37. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2005.06.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kozak M. A second look at cellular mRNA sequences said to function as internal ribosome entry sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33:6593–602. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gray NK, Wickens M. Control of translation initiation in animals. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1998;14:399–458. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.14.1.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Descombes P, Schibler U. A liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein, LAP, and a transcriptional inhibitory protein, LIP, are translated from the same mRNA. Cell. 1991;67:569–79. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90531-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Imataka H, Nakayama K, Yasumoto K, Mizuno A, Fujii-Kuriyama Y, Hayami M. Cell-specific translational control of transcription factor BTEB expression. The role of an upstream AUG in the 5'-untranslated region. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:20668–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lin FT, MacDougald OA, Diehl AM, Lane MD. A 30-kDa alternative translation product of the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha message: transcriptional activator lacking antimitotic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993;90:9606–10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zimmer A, Zimmer AM, Reynolds K. Tissue specific expression of the retinoic acid receptor-beta 2: regulation by short open reading frames in the 5'-noncoding region. J Cell Biol. 1994;127:1111–9. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.4.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Merlin MD. London: Associated University Press; 1984. On the trail of ancient opium poppy. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Stefano GB, Fricchione GL, Goumon Y, Esch T. Pain, immunity, opiate and opioid compounds and health. Med Sci Monit. 2005;11:MS47–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Neri C, Ghelardini C, Sotak B, et al. Dopamine is necessary to endogenous morphine formation in mammalian brain in vivo. J Neurochem. 2008;106:2337–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05572.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Stefano GB, Cadet P, Kream RM, Zhu W. The presence of endogenous morphine signaling in animals. Neurochem Res. 2008;33:1933–9. doi: 10.1007/s11064-008-9674-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Stefano GB, Kream RM, Mantione KJ, et al. Endogenous morphine/nitric oxide-coupled regulation of cellular physiology and gene expression: implications for cancer biology. Semin Cancer Biol. 2008;18:199–210. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2007.12.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Stefano GB, Kream R. Endogenous opiates, opioids, and immune function: evolutionary brokerage of defensive behaviors. Semin Cancer Biol. 2008;18:190–8. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2007.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Stefano GB, Kream RM. Dopamine, morphine, and nitric oxide: an evolutionary signaling triad. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2010;16:e124–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2009.00114.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Stefano GB, Kream RM. Endocannabinoid signaling transcends pain. Arch Med Sci. 2009;5:602–12. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Zhu W, Stefano GB. Comparative aspects of endogenous morphine synthesis and signaling in animals. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009;1163:330–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2008.03623.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Casares FM, Mantione KJ, Kream RM, Stefano GB. Neurotransmitter gene microarray analysis in human white blood cells and human stem cells following morphine exposure. Activitas Nervosa Superior Rediviva. 2010;51:153–8. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Esch T, Stefano GB. The neurobiology of stress management. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2010;31:30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Mantione KJ, Zhu W, Kream RM, Esch T, Stefano GB. Regulation of the transcription of the catechol-O-methyltransferase gene by morphine and epinephrine; Activitas Nervosa Superior Rediviva 2010; in press. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Wozniak B, Musialkiewicz D, Wozniak A, et al. Lack of changes in the concentration of thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances (TBARS) and in the activities of erythrocyte antioxidant enzymes in alcohol-dependent patients after detoxification. Med Sci Monit. 2008;14:CR32–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Yokusoglu M, Sag C, Cincik M, et al. Perindopril, atenolol, and amlodipine prevent aortic ultrastructural changes in rats exposed to ethanol. Med Sci Monit. 2008;14:BR96–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Naha N, Lee HY, Naser MI, Park TJ, Kim SH, Kim MO. Ethanol inhibited apoptosis-related RNA binding protein, Napor-3 gene expression in the prenatal rat brain. Med Sci Monit. 2009;15:BR6–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Hughes RA, Bowes M, Sufka KJ. Morphine hyperalgesic effects on developmental changes in thermal nociception and respiration in domestic fowl (Gallus gallus) Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2009;42:535–9. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(92)90151-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hughes RA, Sufka KJ. Morphine hyperalgesic effects on the formalin test in domestic fowl (Gallus gallus) Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1991;38:247–51. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(91)90273-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Sufka KJ, Hughes RA, Giordano J. Effects of selective opiate antagonists on morphine-induced hyperalgesia in domestic fowl. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1991;38:49–55. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(91)90588-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Trans-NIH Gallus Initiative. 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Szarski H. Changes in the amount of DNA in cell nuclei during vertebrate evolution. Nature. 1970;226:651–2. doi: 10.1038/226651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Szarski H. Cell size and nuclear DNA content in vertebrates. Int Rev Cytol. 1976;44:93–111. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61648-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Szarski H. Cell size and the concept of wasteful and frugal evolutionary strategies. J Theor Biol. 1983;105:201–9. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(83)80002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Gregory TR. A bird's-eye view of the C-value enigma: genome size, cell size, and metabolic rate in the class aves. Evolution. 2002;56:121–30. doi: 10.1111/j.0014-3820.2002.tb00854.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.John SJ. TOPO2, Transmembrane protein display software; 2010. [Google Scholar]