Abstract
The nine possible single-base substitutions were produced at positions 913 to 915 of the 16S ribosomal RNA of Escherichia coli, a region known to be protected by streptomycin [Moazed, D. and Noller, H.F. (1987) Nature, 327, 389-394]. When the mutations were introduced into the expression vector pKK3535, only two of them (913A----G and 915A----G) permitted recovery of viable transformants. Ribosomes were isolated from the transformed bacteria and were assayed for their response to streptomycin in poly(U)- and MS2 RNA-directed assays. They were resistant to the stimulation of misreading and to the inhibition of protein synthesis by streptomycin, and this correlated with a decreased binding of the drug. These results therefore demonstrate that, in line with the footprinting studies of Moazed and Noller, mutations in the 915 region alter the interaction between the ribosome and streptomycin.
Full text
PDF
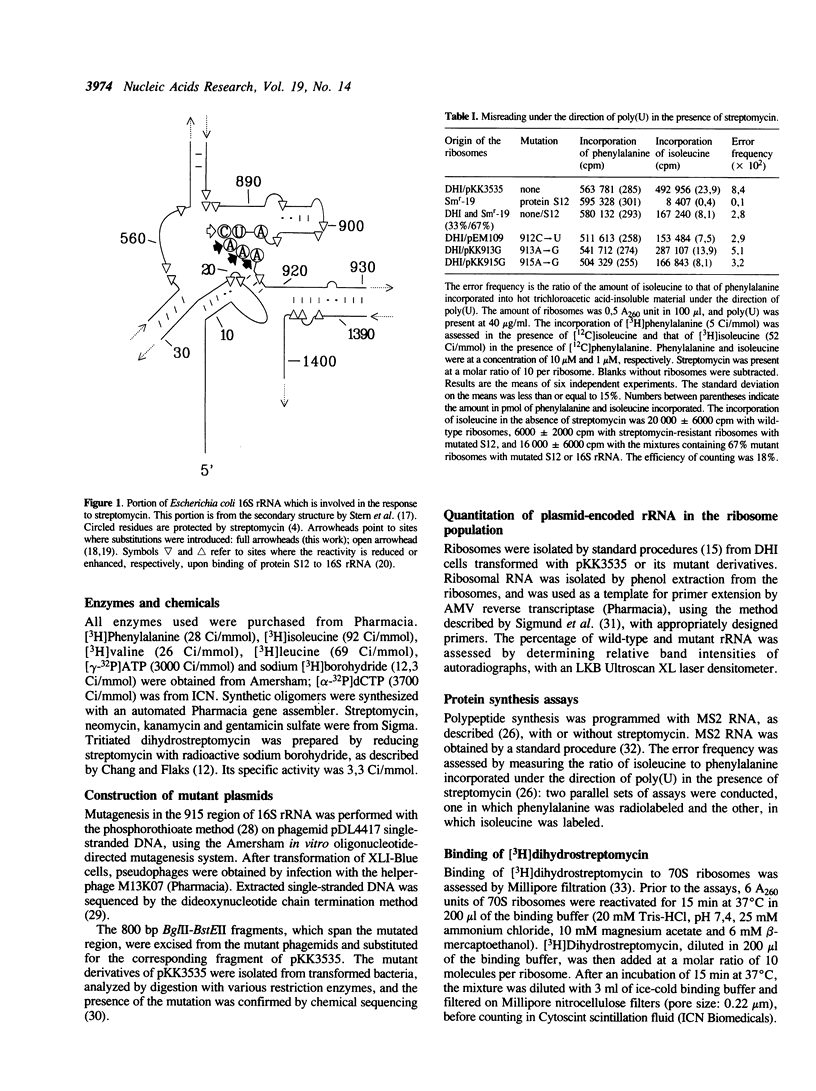


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen P. N., Noller H. F. Mutations in ribosomal proteins S4 and S12 influence the higher order structure of 16 S ribosomal RNA. J Mol Biol. 1989 Aug 5;208(3):457–468. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90509-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauclerk A. A., Cundliffe E. Sites of action of two ribosomal RNA methylases responsible for resistance to aminoglycosides. J Mol Biol. 1987 Feb 20;193(4):661–671. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90349-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birge E. A., Kurland C. G. Altered ribosomal protein in streptomycin-dependent Escherichia coli. Science. 1969 Dec 5;166(3910):1282–1284. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3910.1282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimacombe R., Atmadja J., Stiege W., Schüler D. A detailed model of the three-dimensional structure of Escherichia coli 16 S ribosomal RNA in situ in the 30 S subunit. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 5;199(1):115–136. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90383-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Ullrich A., Raker M. A., Gray A., Dull T. J., Gutell R. R., Noller H. F. Construction and fine mapping of recombinant plasmids containing the rrnB ribosomal RNA operon of E. coli. Plasmid. 1981 Jul;6(1):112–118. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böck A., Petzet A., Piepersberg W. Ribosomal ambiguity (ram) mutations facilitate diyhydrostreptomycin binding to ribosomes. FEBS Lett. 1979 Aug 15;104(2):317–321. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80842-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campuzano S., Cabañas M. J., Modolell J. The binding of non-cognate Tyr-tRNATyr to poly(uridylic acid)-programmed Escherichia coli ribosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct;100(1):133–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb02041.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F. N., Flaks J. G. Binding of dihydrostreptomycin to Escherichia coli ribosomes: characteristics and equilibrium of the reaction. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Oct;2(4):294–307. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.4.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cundliffe E. On the nature of antibiotic binding sites in ribosomes. Biochimie. 1987 Aug;69(8):863–869. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90213-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlberg A. E. The functional role of ribosomal RNA in protein synthesis. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):525–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90122-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Stasio E. A., Moazed D., Noller H. F., Dahlberg A. E. Mutations in 16S ribosomal RNA disrupt antibiotic--RNA interactions. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1213–1216. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03494.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckstein F., Gish G. Phosphorothioates in molecular biology. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Mar;14(3):97–100. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90130-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvin R. T., Biswas D. K., Gorini L. The effects of streptomycin or dihydrostreptomycin binding to 16S RNA or to 30S ribosomal subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):3814–3818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.3814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier A., Turmel M., Lemieux C. Mapping of chloroplast mutations conferring resistance to antibiotics in Chlamydomonas: evidence for a novel site of streptomycin resistance in the small subunit rRNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Oct;214(2):192–197. doi: 10.1007/BF00337710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman E., Hatfield G. W. Use of purified isoacceptor tRNAs for the study of codon-anticodon recognition in vitro with sequenced natural messenger RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1979;59:292–309. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)59092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourse R. L., Stark M. J., Dahlberg A. E. Site-directed mutagenesis of ribosomal RNA. Construction and characterization of deletion mutants. J Mol Biol. 1982 Aug 15;159(3):397–416. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90291-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gravel M., Leclerc D., Melançon P., Brakier-Gingras L. The conserved 900 stem/loop region in Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA is not required for protein synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 11;17(7):2723–2732. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.7.2723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gravel M., Melançon P., Brakier-Gingras L. Cross-linking of streptomycin to the 16S ribosomal RNA of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 22;26(19):6227–6232. doi: 10.1021/bi00393a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grisé-Miron L., Brakier-Gingras L. Effect of neomycin and protein S1 on the binding of streptomycin to the ribosome. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Apr;123(3):643–646. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06580.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. H., Burkhart B. D., Gillham N. W., Boynton J. E. Antibiotic resistance mutations in the chloroplast 16S and 23S rRNA genes of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: correlation of genetic and physical maps of the chloroplast genome. Genetics. 1989 Oct;123(2):281–292. doi: 10.1093/genetics/123.2.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelenc P. C., Kurland C. G. Multiple effects of kanamycin on translational accuracy. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;194(1-2):195–199. doi: 10.1007/BF00383516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lando D., Cousin M. A., Ojasoo T., Raymond J. P. Paromomycin and dihydrostreptomycin binding to Escherichia coli ribosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jul 15;66(3):597–606. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10587.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclerc D., Brakier-Gingras L. A conformational switch involving the 915 region of Escherichia coli 16 S ribosomal RNA. FEBS Lett. 1991 Feb 25;279(2):171–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80141-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclerc D., Brakier-Gingras L. Study of the function of Escherichia coli ribosomal RNA through site-directed mutagenesis. Biochem Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;68(1):169–179. doi: 10.1139/o90-023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li M., Tzagoloff A., Underbrink-Lyon K., Martin N. C. Identification of the paromomycin-resistance mutation in the 15 S rRNA gene of yeast mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5921–5928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melançon P., Boileau G., Brakier-Gingras L. Cross-linking of streptomycin to the 30S subunit of Escherichia coli with phenyldiglyoxal. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6697–6703. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melançon P., Leclerc D., Brakier-Gingras L. A deletion mutation at the 5' end of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):98–103. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90148-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melançon P., Lemieux C., Brakier-Gingras L. A mutation in the 530 loop of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA causes resistance to streptomycin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9631–9639. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Interaction of antibiotics with functional sites in 16S ribosomal RNA. Nature. 1987 Jun 4;327(6121):389–394. doi: 10.1038/327389a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Transfer RNA shields specific nucleotides in 16S ribosomal RNA from attack by chemical probes. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):985–994. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90813-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montandon P. E., Nicolas P., Schürmann P., Stutz E. Streptomycin-resistance of Euglena gracilis chloroplasts: identification of a point mutation in the 16S rRNA gene in an invariant position. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4299–4310. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montandon P. E., Wagner R., Stutz E. E. coli ribosomes with a C912 to U base change in the 16S rRNA are streptomycin resistant. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3705–3708. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04703.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neefs J. M., Van de Peer Y., Hendriks L., De Wachter R. Compilation of small ribosomal subunit RNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18 (Suppl):2237–2317. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.suppl.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakes M. I., Kahan L., Lake J. A. DNA-hybridization electron microscopy tertiary structure of 16 S rRNA. J Mol Biol. 1990 Feb 20;211(4):907–918. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90083-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki M., Mizushima S., Nomura M. Identification and functional characterization of the protein controlled by the streptomycin-resistant locus in E. coli. Nature. 1969 Apr 26;222(5191):333–339. doi: 10.1038/222333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruusala T., Kurland C. G. Streptomycin preferentially perturbs ribosomal proofreading. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;198(2):100–104. doi: 10.1007/BF00328707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiner G., Nierhaus K. H. Protein involved in the binding of dihydrostreptomycin to ribosomes of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 25;81(1):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90248-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen Z. H., Fox T. D. Substitution of an invariant nucleotide at the base of the highly conserved '530-loop' of 15S rRNA causes suppression of yeast mitochondrial ochre mutations. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4535–4539. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigmund C. D., Ettayebi M., Borden A., Morgan E. A. Antibiotic resistance mutations in ribosomal RNA genes of Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1988;164:673–690. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)64077-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smailov S. K., Gavrilova L. P. Effect of streptomycin on the stoichiometry of GTP hydrolysis in a poly(U)-dependent cell-free translation system. FEBS Lett. 1985 Nov 11;192(1):165–169. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80065-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern S., Powers T., Changchien L. M., Noller H. F. Interaction of ribosomal proteins S5, S6, S11, S12, S18 and S21 with 16 S rRNA. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jun 20;201(4):683–695. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90467-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern S., Weiser B., Noller H. F. Model for the three-dimensional folding of 16 S ribosomal RNA. J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 20;204(2):447–481. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90588-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Cundliffe E., Dahlberg A. E. Site-directed mutagenesis of Escherichia coli 23 S ribosomal RNA at position 1067 within the GTP hydrolysis centre. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 20;203(2):457–465. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. C., Dix D. B., Gerson R. B., Karim A. M. Effect of Mg2+ concentration, polyamines, streptomycin, and mutations in ribosomal proteins on the accuracy of the two-step selection of aminoacyl-tRNAs in protein biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6676–6681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace B. J., Davis B. D. Cyclic blockade of initiation sites by streptomycin-damaged ribosomes in Escherichia coli: an explanation for dominance of sensitivity. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 5;75(2):377–390. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



