Abstract
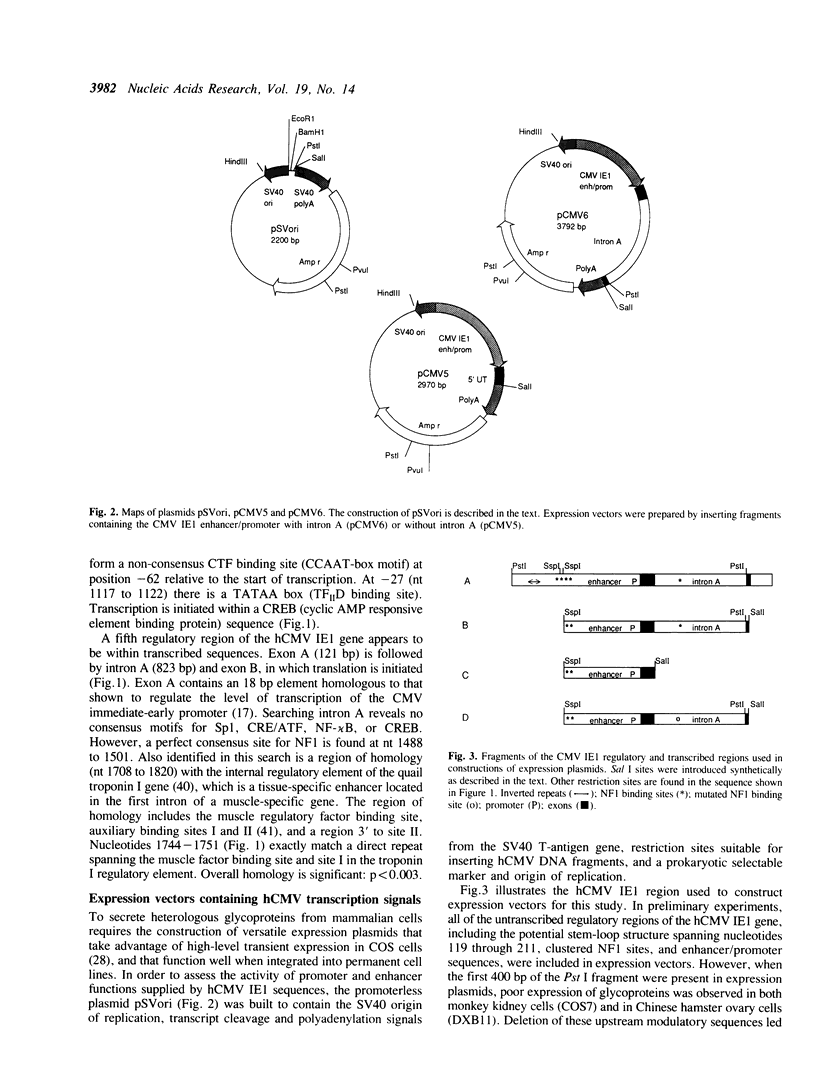
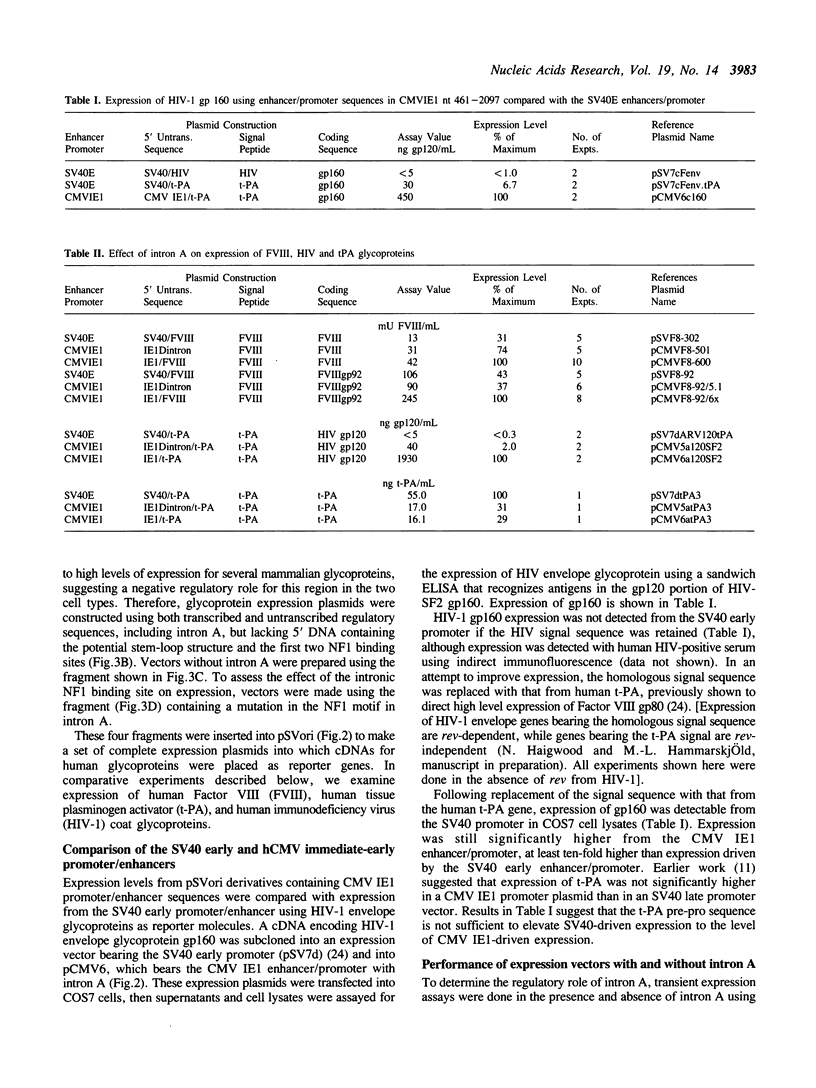
A 2.4 kb fragment of hCMV (Towne strain), containing the 5' end of the major immediate-early gene, has been cloned, sequenced, and used to construct a series of mammalian cell expression plasmids. The effects of regulatory regions present on this fragment were assessed using human glycoproteins as reporter molecules. We compared secreted levels of Factor VIII, t-PA, and HIV-1 envelope glycoproteins in cells transfected with plasmids in which intron A of the immediate-early gene was present or absent. Secretion of several glycoproteins was significantly higher when cells were transfected with intron A-containing plasmids. Mutation of three basepairs in the strong nuclear factor 1 (NF1) binding site in intron A led to reduced transient expression levels, but not to the level observed in the absence of intron A. Reduced expression from NF1 mutant plasmids was roughly correlated with reduced binding in vitro of NF1 proteins to a synthetic oligonucleotide containing the mutation. The evidence indicates that sequences in intron A positively regulate expression from the hCMV immediate-early enhancer/promoter in transformed monkey kidney cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akrigg A., Wilkinson G. W., Oram J. D. The structure of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Virus Res. 1985 Mar;2(2):107–121. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(85)90242-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson S., Davis D. L., Dahlbäck H., Jörnvall H., Russell D. W. Cloning, structure, and expression of the mitochondrial cytochrome P-450 sterol 26-hydroxylase, a bile acid biosynthetic enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8222–8229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayer D. E., Dynan W. S. A downstream-element-binding factor facilitates assembly of a functional preinitiation complex at the simian virus 40 major late promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3635–3645. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Weber F., Jahn G., Dorsch-Häsler K., Fleckenstein B., Schaffner W. A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):521–530. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Berg P. Comparison of intron-dependent and intron-independent gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4395–4405. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. L., Pachl C., Quiroga M., Rosenberg S., Haigwood N., Nordfang O., Ezban M. The functional domains of coagulation factor VIII:C. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12574–12578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S., Perry R. P. Importance of introns for expression of mouse ribosomal protein gene rpL32. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2075–2082. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockett M. I., Bebbington C. R., Yarranton G. T. High level expression of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases in Chinese hamster ovary cells using glutamine synthetase gene amplification. Biotechnology (N Y) 1990 Jul;8(7):662–667. doi: 10.1038/nbt0790-662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denome R. M., Cole C. N. Patterns of polyadenylation site selection in gene constructs containing multiple polyadenylation signals. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4829–4839. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D. L., Wood W. I., Eaton D., Hass P. E., Hollingshead P., Wion K., Mather J., Lawn R. M., Vehar G. A., Gorman C. Construction and characterization of an active factor VIII variant lacking the central one-third of the molecule. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 30;25(26):8343–8347. doi: 10.1021/bi00374a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foecking M. K., Hofstetter H. Powerful and versatile enhancer-promoter unit for mammalian expression vectors. Gene. 1986;45(1):101–105. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90137-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghazal P., Lubon H., Fleckenstein B., Hennighausen L. Binding of transcription factors and creation of a large nucleoprotein complex on the human cytomegalovirus enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3658–3662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghazal P., Nelson J. A. Enhancement of RNA polymerase II initiation complexes by a novel DNA control domain downstream from the cap site of the cytomegalovirus major immediate-early promoter. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2299–2307. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2299-2307.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghogawala Z., Choi E., Daly K. R., Blanco L. R., Griffith I. J., Glimcher L. H. An intronic 10-base-pair deletion in a class II A beta gene affects RNA processing. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4402–4408. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Rigby P. W., Lane D. P. Negative regulation of viral enhancers in undifferentiated embryonic stem cells. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):519–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90109-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyal N., Knox J., Gronostajski R. M. Analysis of multiple forms of nuclear factor I in human and murine cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1041–1048. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronostajski R. M. Analysis of nuclear factor I binding to DNA using degenerate oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):9117–9132. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.9117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigwood N. L., Mullenbach G. T., Moore G. K., DesJardin L. E., Tabrizi A., Brown-Shimer S. L., Stauss H., Stöhr H. A., Pâques E. P. Variants of human tissue-type plasminogen activator substituted at the protease cleavage site and glycosylation sites, and truncated at the N- and C-termini. Protein Eng. 1989 Aug;2(8):611–620. doi: 10.1093/protein/2.8.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer D. H., Leder P. Splicing and the formation of stable RNA. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1299–1302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90240-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennighausen L., Fleckenstein B. Nuclear factor 1 interacts with five DNA elements in the promoter region of the human cytomegalovirus major immediate early gene. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1367–1371. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04368.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M. T., Gorman C. M. Intervening sequences increase efficiency of RNA 3' processing and accumulation of cytoplasmic RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):937–947. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imler J. L., Lemaire C., Wasylyk C., Wasylyk B. Negative regulation contributes to tissue specificity of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2558–2567. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox J. J., Rebstein P. J., Manoukian A., Gronostajski R. M. In vivo stimulation of a chimeric promoter by binding sites for nuclear factor I. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):2946–2951. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.2946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H., Yutzey K. E., Konieczny S. F. Muscle-specific expression of the troponin I gene requires interactions between helix-loop-helix muscle regulatory factors and ubiquitous transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):267–280. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubon H., Ghazal P., Hennighausen L., Reynolds-Kohler C., Lockshin C., Nelson J. Cell-specific activity of the modulator region in the human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1342–1345. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthman H., Magnusson G. High efficiency polyoma DNA transfection of chloroquine treated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1295–1308. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour S. L., Grodzicker T., Tjian R. Downstream sequences affect transcription initiation from the adenovirus major late promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2684–2694. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. A., Reynolds-Kohler C., Smith B. A. Negative and positive regulation by a short segment in the 5'-flanking region of the human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4125–4129. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordfang O., Ezban M., Dinesen B. Reactivity of factor VIII inhibitors in a micro ELISA for factor VIII: CAg and in solid phase immunoisolation of VIII: CAg. Thromb Haemost. 1985 Jun 24;53(3):346–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordfang O., Ezban M., Nilsson P., Knudsen J. B. Radioimmunoassay for quantitative measurement of factor VIII-heavy chain. Br J Haematol. 1988 Mar;68(3):307–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1988.tb04207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasleau F., Tocci M. J., Leung F., Kopchick J. J. Growth hormone gene expression in eukaryotic cells directed by the Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat or cytomegalovirus immediate-early promoter. Gene. 1985;38(1-3):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90221-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rio D. C., Clark S. G., Tjian R. A mammalian host-vector system that regulates expression and amplification of transfected genes by temperature induction. Science. 1985 Jan 4;227(4682):23–28. doi: 10.1126/science.2981116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rio D. C., Tjian R. SV40 T antigen binding site mutations that affect autoregulation. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1227–1240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90305-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rippe R. A., Lorenzen S. I., Brenner D. A., Breindl M. Regulatory elements in the 5'-flanking region and the first intron contribute to transcriptional control of the mouse alpha 1 type I collagen gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2224–2227. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt E. V., Christoph G., Zeller R., Leder P. The cytomegalovirus enhancer: a pan-active control element in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4406–4411. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sevarino K. A., Felix R., Banks C. M., Low M. J., Montminy M. R., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. Cell-specific processing of preprosomatostatin in cultured neuroendocrine cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):4987–4993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompayrac L. M., Danna K. J. Efficient infection of monkey cells with DNA of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7575–7578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Thomsen D. R., Stinski M. F. Structural analysis of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):190–199. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.190-199.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen D. R., Stenberg R. M., Goins W. F., Stinski M. F. Promoter-regulatory region of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):659–663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yutzey K. E., Kline R. L., Konieczny S. F. An internal regulatory element controls troponin I gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1397–1405. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang F., Denome R. M., Cole C. N. Fine-structure analysis of the processing and polyadenylation region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase gene by using linker scanning, internal deletion, and insertion mutations. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4611–4623. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]