Abstract
Background
Ethnobotanical studies are crucial in South-Eastern Europe for fostering local development and also for investigating the dynamics of Traditional Environmental Knowledge (TEK) related to plants in one of the most crucial European hotspots for biocultural diversity. The current medico-ethnobotanical survey was conducted in rural alpine communities in Kosovo. The aims of the study were twofold: 1) to document the state of TEK of medicinal plants in these communities; 2) to compare these findings with that of similar field studies previously conducted among local populations inhabiting the Montenegrin and Albanian side of the same Alpine range.
Methods
Field research was conducted in 36 villages on the Kosovar side of the Albanian Alps. Snowball sampling techniques were used to recruit 91 elderly informants (≥ 50 years-old) for participation in semi-structured interviews and structured surveys regarding the use of the local flora for medicinal and food purposes. Standard ethnobotanical methods were employed and prior informed consent was obtained for all study participants.
Results and Conclusion
The uses of 98 plants species belonging to 39 families were recorded; the most quoted botanical families were Rosaceae, Asteraceae, and Lamiaceae. Mainly decoctions and infusions were quoted as folk medicinal preparations and the most common uses referred to gastrointestinal and respiratory disorders, as well as illnesses of the uro-genital system. Among the most uncommon medicinal taxa quoted by the informants, Carduus nutans L., Echinops bannaticus Rochel ex Schrad., and Orlaya grandiflora Hoffm. may merit phytochemical and phytopharmacological investigations.
Comparison of the data with other ethnobotanical field studies recently conducted on the Albanian and Montenegrin sides of the same Alps has shown a remarkable link between the medical ethnobotany of Montenegrin and Kosovar side of the Albanian Alps. Moreover, folk uses of the most quoted wild medicinal taxa recorded in Kosovo often include those recorded both in Albania and in Montenegro, thus suggesting a hybrid character of the Kosovar local plant knowledge. This may be also explained with the fact that Montenegro and Kosovo, despite their differences in the ethnic composition, have shared a common history during the last Century.
Keywords: Albanian Alps, Ethnobotany, Traditional Medicine, Kosovo, Medicinal plants
Background
Ethnobotanical studies in South-Eastern Europe are seen as a crucial initial step for local rural development based on eco-tourism, small-scale trade of local medicinal plants, high-quality local foods, eco-museums, and community-based bio-conservation strategies [1].
However, this region is also considered very special for conducting studies having a human ecological focus, since it represents a unique hotspot of biological and cultural diversity in Europe, thus allowing cross-cultural comparisons of traditional environmental knowledge (TEK) concerning medicinal plants. In very recent years, the Western Balkans have been the focus of a remarkable number of ethnobotanical studies [2-9], mainly focused on mountainous communities [10-15].
In this study, we investigated the Kosovo side of the Albanian Alps (in Albanian known as Bjeshkët e Nemuna or Alpet Shqipëtare; in Serbo-Croatian known as Prokletije), which extends within a triangle among the Dinaric Mountains in the North-West, the Sharri (Šar) Mountains in the South-East and the Rhodope Mountains in the East and North-East. This covers a very pristine, and sometimes, remote area of ca. 3,500 km2, which is geo-politically divided among the sovereign states of Albania, Kosovo, and Montenegro.
About 1,000 km2 of these mountains belong to the Kosovo territory. The Albanian Alps system consists of 24 groups of mountains with 152 peaks higher than 2,000 m a.s.l. (the highest altitude in the Kosovo territory is reached by Maja e Gjeravicës at 2,460 m a.s.l.), with a large number of gorges, canyons, valleys, which make them among the most inaccessible [16], but also magnificent areas of the Balkans [17].
Due to the rich levels of biodiversity characteristic to this region, three national parks were established in the past in the Albanian Alps: one in Montenegro (Prokletije National Park) and two others in Albania (Theth and Valbona National Parks). A fourth national park in the area has been proposed to be located in Kosovo. Furthermore, Kosovo, Albania, and Montenegro are planning to join these parks and to create the cross-border Balkan Peace Park [18].
In general, Kosovo is characterised by a continental climate and in higher altitudes it is influenced by Alpine features [19]; for this reason, it has cold winters and hot summers, with an average temperature of 11.4°C. The Alpine area of Kosovo is characterised by total annual precipitation levels exceeding 2,000 mm. Specific geo-morphological, soil and climatic features provide an interesting richness and diversity of plant life in the Albanian Alps massif, with a flora belonging to three different bio-geographic zones: the Mediterranean, the Central-European and the Central-South European regions [17,20-22].
These unique features are reflected in the high plant biodiversity, which includes 1,609 taxa and ca. 150 vegetation units [23]. The most representative vegetation unites are: oriental hornbeam forest (Carpinetum orientalis scardicu), hop hornbeam mixed and with oriental hornbeam forest (Ostryo-Carpinion orientalis), thermophilous oak forests community (Quercus frainetto Ten., Quercetum frainetto-cerris scardicum, and Quercetum petraeae-cerris), chestnut forests (Castanetum sativae), beech forests (Fagetum montanum), and pine forests (Pinetum heldreichii typicum, Pinetum heldreichii thalictretum, Pinetum peucis, and Pinetum mughi typicum) [22,24].
People have withstood the extreme conditions of these areas for centuries - including very harsh winters. Until very recent decades, limitations in infrastructure and communication forced local residents to be self-sufficient in the provision of their healthcare. As a result, their primary pharmacopoeia consisted of local medicinal plants.
While recent studies on the Albanian and Montenegrin sides of the Albanian Alps have reported findings on TEK of wild medicinal and food plants [10,12,13,15], no ethnobotanical surveys have been conducted thus far in Kosovo, with the exception of a very recent work carried out by our research group in the Gollak area [9], and a review on folk botanical names in diverse Albanian-speaking areas in South-Eastern and Southern Europe [25].
The aims of this study were twofold: 1) to document the ethnobotanical knowledge related to the use of local medicinal plants in the Albanian Alps region of Kosovo; and 2) to compare the recorded data with the ethnobotanical studies recently conducted in the Albanian and Montenegrin sides of the same Albanian Alps. This was done with the overarching goal in mind of elucidating the role played by cultural/ethnic components in shaping use patterns of wild medicinal plants.
Methods
Field study
Ethnobotanical field research was conducted in 36 villages belonging to the municipalities of Pejë and Deçan, located close to the Koprivnik and Strellc mountains, and which represent the central group of the Albanian Alps located in the western part of Kosovo (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
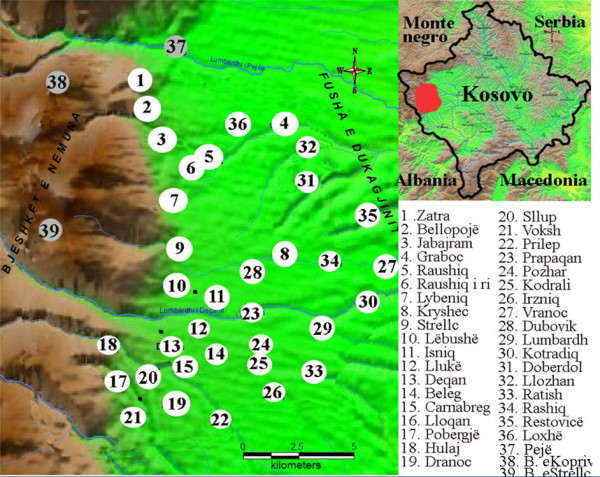
Study area in Kosovo.
The settlements and villages investigated are relatively small in terms of inhabitants (≤ 500 inhabitants per village). The native residents are ethnic Albanians, who speak Gheg varieties of the Albanian language. The exact population is currently unknown, as no population census has been conducted in Kosovo since 1981. Most recently, the area populations have been negatively affected by migration due to displacement and harsh economic conditions caused by the last Kosovo War (1998-1999).
Field studies were conducted from May to October 2010. TEK was recorded using semi-structured interviews and a questionnaire [26]. In particular, we sought the following information: respondent name and community of residence; local botanical names of useful plants; plant part(s) used; preparation/administration; local folk medicinal uses of plants.
Data were collected from 91 informants (67 male and 24 female) older than 50 years (50 to 79 years old). The respondents were mainly engaged in agricultural activities and typically inherited their ethnobotanical knowledge from their direct ancestors (parents, grandparents) via oral traditions. Study participants were selected using the snowball sampling method [2], and we particularly focused on local people who regularly use plants for medicinal purposes.
Prior informed consent was obtained conducting interviews and researchers adhered to the ethical guidelines of the International Society of Ethnobiology [27]. During the interviews, fresh plants were collected to create voucher specimens for the herbarium and the informants were followed into the field to show us the quoted species. Most plant species were collected while flowering.
Taxonomic identification was done using relevant standard botanical literature of the area [28-31]. Plant nomenclature largely follows the Flora Europaea [32], while plant family assignments follow the current Angiosperm Phylogeny Group guidelines [33]. Voucher specimens of the wild taxa were deposited at the Department of Biology (Herbarium code DE/10), University of Prishtina.
Data analysis
Despite the fact that it is always problematic to compare ethnobotanical data recorded from studies conducted using different field methods and at different times, we have attempted to compare the wild medicinal plant uses recorded in Albanian Alps in Kosovo with those recorded in previously conducted ethnobotanical studies on the Albanian and Montenegrin sides of the same alpine range [11-14]. The Jaccard similarity index among the considered studies has been calculated as in the recent comparative analysis of the circum-Mediterranean medical ethnobotany [34].
Results and Discussion
The Kosovar medico-ethnobotany of the Albanian Alps
The results of the field survey are presented in Table 1; plants are arranged in alphabetical order by genus. For each species, the botanical name and family, local names, English name, botanical status, preparation/administration and folk medical or food uses are reported.
Table 1.
Medicinal plant uses recorded on the Kosovar side of the Albanian Alps in the current study.
| Botanical taxon, botanical family and voucher specimen code | Folk name(s) quoted by respondents | English name | Status | Quotation frequency | Part(s) used | Administration | Treated disease(s) or folk medical uses(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abies alba Mill. (Pinaceae) 13/DE/10 | Bredhi i bardhë | European silver fir | W | + | Resin | Boiled in oil | Stomach pain Eczemas |
| Topically applied | Skin infections | ||||||
| Mixed and boiled with milk butter | Skin hematomas Skin infections |
||||||
| Achillea millefolium L. (Asteraceae) 03/DE/10 | Hajdukati | Yarrow | W | ++ | Areal parts | Infusion | Anti-diarrhoeal Stomach pain Anti-diabetic Eczema |
| Tincture topical used in wound | Antibacterial | ||||||
|
Aconitum divergens Pančić (Ranunculaceae) 04/DE/10 |
Pelini i egër (i zi) | W | ++ | Areal parts | Infusion | Stomach disorders Oral cavity antiseptic Anti-haemorrhoidal |
|
| Whole plant | Infusion | Anti-cholesterolemic | |||||
| Leaves | Squeezed and topically applied to the wound | Anti-bacterial Skin infections |
|||||
|
Adiantum capillus-veneris L. (Adiantaceae) 01/DE/10 |
Majdanozi i egër | Southern maidenhair fern | W | + | Areal parts | Decoction | Bronchitis Sour throat Expectorant |
| Aesculus hippocastanum L. (Sapindaceae) 06/DE/10 | Gështenja e egër | Horse chestnut | W | ++ | Leaves | Infusion | Expectorant Anti-rheumatic |
| Fruits | Decoction | Antitussive Anti-hypertensive |
|||||
| Tincture | Anti-rheumatic | ||||||
|
Agropyron repens (L.) P. Beauv. (Poaceae) 08/DE/10 |
Pirrovina | Couch grass | W | + | Roots | Decoction | Anti-rheumatic Anti-anaemic Stomach and hepatic disorders Lithontriptic |
| Infusion | Lithontriptic | ||||||
| Allium cepa L. (Amaryllidaceae) 11/DE/10 | Qepa | Onion | C | + | Leaves | Decoction | To treat influenza |
| Bulb | Extracted with cold mineral water | Anti-hypertensive | |||||
| Allium porrum L. (Amaryllidaceae) 09/DE/10 | Purrini | Garden leek | C | + | Leaves and stem | Eaten fresh | Anti-cholesterolemic |
| Allium sativum L. (Amaryllidaceae) 10/DE/10 | Hudhra | Garlic | C | + | Bulb Leaves |
Tincture | Improve blood circulation Anti-diabetic Antibacterial Anti-hypertensive |
| Decoction | Tooth ache | ||||||
|
Alnus glutinosa (L.) Gaertn. (Betulaceae) 05/DE/10 |
Verri | Black alder | W | + | Cortex | Decoction, used to wash whole body | Anti-rheumatic |
| Leaves | Extracted with cold water | Disinfectant on wounds | |||||
| Althaea officinalis L. (Malvaceae) 07/DE/10 | Mëllaga e bardhë | Marshmallow | W | ++ | Roots | Extracted with cold water | Expectorant |
| Decoction | To treat lung disorders Oral cavity antiseptic Expectorant |
||||||
| Arctium lappa L. (Asteraceae) 12/DE/10 | Bullushtra | Greater burdock | W | + | Areal parts | Decoction | Gastrointestinal disorders Bronchitis Lithontriptic |
| Leaves | Boiled in milk (used externally | Skin inflammation and ulcers | |||||
|
Aristolochia clematitis L. (Aristolochiaceae) 14/DE/10 |
Fiku i egër | Birthwort | W | + | Fruits | Decoction | Anti-haemorrhoidal Eczemas |
| Areal parts | Decoction | Infected wounds Ulcers |
|||||
| Artemisia absinthium L. (Asteraceae) 02/DE/10 | Pelini i butë | Wormwood | W | + | Areal parts | Infusion | Stomach disorders Anti-diabetic |
|
Beta vulgaris L. (Amaranthaceae) 17/DE/10 |
Sveklla | Common beet | C | + | Roots | Decoction | Anti-anaemic |
| Betula verrucosa Ehrh. (Betulaceae) 16/DE/10 | Mështekna | Silver birch | W | + | Cortex | Decoction | Kidney infections |
| Leaves | Decoction | Lithontriptic | |||||
| Brassica oleracea L. (Brassicaceae) 18/DE/10 | Lakra | Cabbage | C | + | Leaves | Fermented leaves topically applied | Anti-bacterial |
| Bryonia alba L. (Cucurbitaceae) 15/DE/10 | Stërkungulli | White bryony | W | + | Roots | Extracted with sunflower oil, apply topically in pain place | Anti-rheumatic |
| Calendula officinalis L. (Asteraceae) 28/DE/10 | Lulduhani | Pot marigold | C | + | Flowers | Extracted with cold milk | Kidney disorders Hepatitis Stomach ulcers |
| Capsella bursa-pastoris (L.) Medik. (Brassicaceae) 29/DE/10 | Shtrapër | Shepherd's-purse | W | + | Whole plant | Infusion | Fever Eczemas |
| Capsicum annuum L. (Solanaceae) 32/DE/10 | Speci djegës | Pepper | C | + | Fruits | Eaten fresh fruits | Anti-rheumatic Appetizing Lung disorders |
| Carduus nutans L. (Asteraceae) 27/DE/10 | Gjemb gomari | Musk thistle | W | + | Inflorescences | Extracted with cold water for ten days and then used as tea | Eczemas |
| Castanea sativa Mill. (Fagaceae) 20/DE/10 | Gështenja e butë | Sweet chestnut | W/C | + | Fruits | Decoction | Headache |
| Fruits | Decoction external applied | Anti-haemorrhoidal | |||||
| Centaurea cyanus L. (Asteraceae) 30/DE/10 | Kokoçeli | Cornflower | W | + | Flowers | Decoction | Eye infections |
| Centaurium erythraea Rafin. (Gentianaceae) 21/De/10 | Kiçica | Common centaury | W | ++ | Areal parts | Extracted with cold water | Stomach disorders Urinary system infections |
| Decoction | Anti-haemorrhoid Anti-diabetic Lithontriptic Fever |
||||||
| Stem | Decoction | Lithontriptic | |||||
| Cichorium intybus L. (Asteraceae) 22/DE/10 | Çikorja | Common chicory | W | + | Stem | Infusion | Anti-diarrhoeal |
| Roots | Decoction | Bronchitis Urinary system infections Anti-haemorrhoid |
|||||
| Chelidonium majus L. (Papaveraceae) 31/DE/10 | Tamblaqoku | Tetterwort | W | + | Areal parts | Infusion | Bronchitis Lithontriptic Stomach ulcers |
| Citrullus vulgaris Schrad. (Cucurbitaceae) 33/DE/10 | Shalqiri | Watermelon | C | + | Fruit juice | Fruit juice applied into the ear | Ear-ache |
| Seeds | Eaten dried seeds of watermelon, apple, melon | To prevent prostate cancer | |||||
| Citrus limon (L.) Burm. f. (Rutaceae) 35/DE/10 | Limoni | Lemon | C | + | Fruits | Lemon juice mixed with honey | Anti-tussive Respiratory infections |
| Cornus mas L. (Cornaceae) 24/DE/10 | Thana | Dogwood | W | ++ | Fruits | Decoction | Anti diabetic |
| Tincture | Stomach disorders Anti-rheumatic |
||||||
| Consumed | Eaten raw | ||||||
| Decoction | Anti-anaemic | ||||||
| Corylus avellana L. (Betulaceae) 25/DE/10 | Lajthia | Hazel | W | + | Leaves | Decoction | Anti-diabetic |
| Crataegus monogyna Jacq. (Rosaceae) 19/DE/10 | Murrizi | Oneseed | W | ++ | Areal parts | Infusion | Heart rhythm regulator Anti-hypertensive |
| Fruits | Decoction | Anti-hypertensive | |||||
| Flowers | Decoction | Anti-hypertensive Insomnia |
|||||
| Cucumis melo L. (Cucurbitaceae) 36/DE/10 | Pjepri | Melon | C | + | Seeds | Eaten dried seeds of watermelon, apple, melon | To prevent the prostate cancer |
| Cucurbita pepo L. (Cucurbitaceae) 26/DE/10 | Kungulli | Pumpkin | C | + | Seeds | Eaten | Anti-helminthic To prevent prostate cancer |
| Cydonia oblonga Mill. (Rosaceae) 23/DE/10 | Ftoni | Quince | C | + | Leaves | Infusion | Respiratory inflammations |
| Seeds | Decoction | Appetizing | |||||
| Cynodon dactylon (L.).Pers. (Poaceae) 34/DE/10 | Bar magari | Bermuda grass | W | + | Roots | Decoction | Anti-haemorrhoidal |
| Daucus carota L. (Apiaceae) 37/DE/10 | Karota | Carrot | C | + | Storage root | Boiled and eaten | Stomach infections |
| Digitalis grandiflora Mill. (Plantaginaceae) 38/DE/10 | Naprastak | Big-flowered foxglove | W | + | Whole plant | Infusion | Hart disorders |
| Echinops bannaticus Rochel ex Schrad. (Asteraceae) 40/DE/10 | Gjembardha | W | + | Roots | Decoction | Lithontriptic | |
| Equisetum arvense L. (Equisetaceae) 39/DE/10 | Këputja e arave | Horsetail | W | + | Stem and Leaves | Infusion | Lithontriptic Urinary system infections |
| Euphorbia cyparissias L. (Euphorbiaceae) 41/DE/10 | Bima e lythave | Cypress spurge | W | + | Stem | Fresh leaves topically applied | Warts |
| Foeniculum vulgare Mill. (Apiaceae) 43/DE/10 | Kopra e egër | Fennel | W | + | Flowers | Decoction | Constipation |
| Fragaria vesca L. (Rosaceae) 42/DE/10 | Dredhëza e egër | Strawberry | W | + | Leaves | Infusion | Neuro-relaxant |
| Gentiana asclepiadea L. (Gentianaceae) 45/DE/10 | Utrobica | W | + | Roots | Tincture | Anti-rheumatic Stomach ulcers Hepatitis |
|
| Gentiana lutea L. (Gentianaceae) 44/DE/10 | Sanëza | W | ++ | Roots | Tincture | Improve the blood circulation Bronchitis Stomach disorders Anti-hypertensive Anti-asthmatic Anti rheumatic Anti-diabetic |
|
| Galium verum L. (Rubiaceae) 46/DE/10 | Ngjitësi i vërtetë | Yellow bedstraw | W | + | Flowers | Infusion | Urinary system infections |
| Helleborus odorus Waldst. et. Kit. (Ranunculaceae) 49/DE/10 | Shpendra | Fragrant hellebore | W | + | Fruits | Applied in tooth | Tooth-ache |
| Humulus lupulus L. (Cannabaceae) 48/DE/10 | Sumbullari | Common hop | W | + | Fruits | Infusion | Kidney inflammations Neuro-relaxant |
| Areal parts | Decoction | Insomnia Menstrual cycle regulator |
|||||
| Hypericum perforatum L. (Hypericaceae) 47/DE/10 | Kantarioni | St. John's wort | W | +++ | Flowers | Decoction | Stomach pain |
| Whole plant | Decoction | Respiratory disorders | |||||
| Areal parts | Extracted with olive oil | Stomach pain Skin infections To treat skin after sunburn or thermal burn Anti-tussive Anti haemorrhoidal Respiratory infections Anti-cholesterolemic Eczemas |
|||||
| Iris sp. (Iridaceae) 50/DE/10 | Lule purriri | W | + | Leaves | Squeezed and topically applied to the ear | Ear ache | |
| Juglans regia L. (Juglandaceae) 52/DE/10 | Arra | Common walnut | W/C | +++ | Roots | Extracted for one month with sunflower oil and then liquid mixed with honey. | Lung inflammations Anti asthmatic Bronchitis |
| Fruits | Decoction | Anti-tussive | |||||
| Honey (1 kg) mixed with fruits (1 kg) extracted for one month | Lung inflammations Anti-asthmatic Anti-anaemic |
||||||
| Extracted with cold water. | Anti-cholesterolemic | ||||||
| Tincture | Stomach disorders | ||||||
| Leaves | Infusion | Anti-haemorrhoid al | |||||
| Juniperus communis L. (Cupressaceae) 51/DE/10 | Gllia | Juniper | W | ++ | Fruits | Decoction | Back pains |
| Extracted for 10 days in cold water mixed with lemons | Kidney inflammations Anti rheumatic |
||||||
| Decoction | Respiratory inflammations | ||||||
| Decoction | Stomach disorders | ||||||
| Lagenaria siceraria (Molina) Standl. (Cucurbitaceae) 53/DE/10 | Pocerka | Bottle gourd | C | + | Fruits | Fruits opened and filled with water and then water used to flush the nose | Sinusitis |
| Linaria peloponnesiaca Boiss. et. Heldr. (Plantaginaceae) 57/DE/10 | Lanilist | W | + | Seeds | Decoction | Constipation | |
| Linaria vulgaris Mill. (Plantaginaceae) 56/DE/10 | Gjineshtra | Common toadflax | W | + | Areal parts | Decoction | Urinary system inflammations |
|
Linum hirsutum L. (Linaceae) 54/DE/10 |
Liri | W | + | Seeds | Decoction | Anti-haemorrhoidal Urinary system inflammations |
|
| Leaves | Infusion | Headache Respiratory inflammations |
|||||
| Lycopersicon esculentum Mill. (Solanaceae) 55/DE10 | Domatja | Tomato | C | + | Fruits | Beaked fruits mixed with sugar topically applied in wound | Wound infections |
| Malus dasyphylla Borkh. (Rosaceae) 60/DE/10 | Molla sherbete | Apple | W | + | Fruits | Squeezed and topically applied to the ear | Earache |
| Malus sylvestris Mill. (Rosaceae) 61/DE10 | Molla e pyllit Molla e egër |
European wild apple | W | ++ | Areal parts | Infusion | Anti-tussive Expectorant |
| Fruits | Extracted with cold water then fruit juice mixed sugar | Anti-hypertensive Anti-cholesterolemic |
|||||
| Fruits | Decoction | Anti-diabetic | |||||
| Leaves | Applied topically in wound | Wound infections | |||||
| Matricaria recutita L. (Asteraceae) 59/DE/10 | Kamomili | Chamomile | W | ++ | Areal parts | Infusion | Stomachache Oral cavity inflammations Gingivitis Urinary system infections |
| Flowers Flowers |
Infusion | Oral inflammations Urinary system infections |
|||||
| Decoction | Constipation | ||||||
| Areal parts | Infusion | Drunk as a tea | |||||
| Melissa officinalis L. (Lamiaceae) 58/DE/10 | Bari i bletës | Lemon balm | W | + | Areal parts | Infusion | For treating abdominal pains during pregnancy |
| Areal parts | Decoction | Neuro-relaxant | |||||
| Mentha longifolia (L.) Huds. (Lamiaceae) 63/DE/10 | Menta | Horse mint | W | + | Areal parts | Infusion | Neuro-relaxant Anti-diarrhoeal Anti-hypertensive |
| Morus nigra L. (Moraceae) 64/DE/10 | Mani i zi | Black mulberry | W | + | Leaves | Decoction | Anti diabetic |
|
Origanum vulgare L. 65/DE/10 (Lamiaceae) |
Qaji i bjeshkës | Oregano | W | + | Areal parts Areal parts |
Infusion | Respiratory inflammations, flu |
| Decoction | Anti-tussive Digestive |
||||||
| Orlaya grandiflora (L.) Hoffm. (Apiaceae) 66/DE/10 | Torilis | White lace flower | W | + | Areal parts | Decoction | Constipation |
| Petroselinum crispum (Mill.) Fuss (Apiaceae) 70/DE/10 | Majdanozi | Parsley | C | + | Leaves | Boiled with garlic and carrot | Stomach infections |
| Decoction together with lemon | Anti-cholesterolemic | ||||||
| Pinus sylvestris L. (Pinaceae) 69/DE/10 | Çetina | Scots pine | W | ++ | Cones | 40 cones mixed with honey (1 kg) eaten after one month | Bronchitis |
| Decoction | Anti-tussive Anti-asthmatic Bronchitis |
||||||
|
Phaseolus vulgaris L. (Fabaceae) 77/DE/10 |
Fasulja | Common bean | C | + | Seeds | 2-3 soup spoons in the morning | Anti-acid |
| Plantago lanceolata L. (Plantaginaceae) 73/DE/10 | Dejzi heshtor | Narrowleaf plantain | W | ++ | Leaves | Fresh leaves applied topically in wound | Wound infections |
| Plantago major L. (Plantaginaceae) 67/DE/10 | Dejzi gjethegjerë | Common plantain | W | ++ | Leaves | Infusion | Back pains |
| Eaten squeezed juice mixed with honey | Bronchitis Anti haemorrhoid Stomach-ache |
||||||
| Applied topically in wound | Wound infections | ||||||
| Polygonum bistorta L. (Polygonaceae) 75/DE/10 | Reni | Meadow bistort | W | + | Roots | Macerated roots (200-300 g) mixed honey (1 kg) | Respiratory infections Expectorant |
| Populus nigra L. (Salicaceae) 72/DE10 | Plepi i zi | Black poplar | W | + | Cortex | Decoction | Urinary system inflammations |
| Leaves | Decoction | Tuberculosis Bronchitis Anti-diabetic |
|||||
| Prunus avium (L.) L. (Rosaceae)71/DE/10 | Bojlia | Wild cherry | C | + | Fruits | Infusion | Anti- diabetic Anti-hypertensive Respiratory inflammations |
| Prunus domestica L. (Rosaceae) 68/DE/10 | Kumbulla | Plum | C | + | Fruits | Decoction | Constipation |
| Prunus spinosa L. (Rosaceae) 74/DE/10 | Kulumria | Blackthorn | W | + | Fruits | Decoction | Anti-hypertensive Anti-asthmatic |
| Eaten fresh fruits | Consumption | ||||||
| Pteridium aquilinum Kuhn. (Dennstaedtiaceae) 76/DE/10 | Fieri | Bracken | W | + | Leaves | Decoction | Anti-bacterial Diuretic |
| Pyrus pyraster (L.) Du Roi (Rosaceae) 78/DE/10 | Dardha e egër | Wild pear | W | + | Fruits | Tincture | Anti-hypertensive Anti-cholesterolemic |
| Robinia pseudoacacia L. (Fabaceae) 82/DE/10 | Bagreni | Black locust | W | + | Flowers | Decoction | Respiratory inflammations |
| Rosa canina L. (Rosaceae) 80/DE/10 | Kaça | Dog rose | W | + | Fruits | Infusion | Drunk as a tea |
| Fruits | Decoction | Influenza Increase immunity |
|||||
| Rubus fruticosus L. (Rosaceae) 79/DE/10 | Mani | Blackberry | W | ++ | Leaves | Fresh leaves applied topically in wound | Skin infection |
| Leaves and fruits | Decoction | Tuberculosis Influenza Increase immunity |
|||||
| Fruits | Eaten fresh fruits Jam |
Consumption | |||||
| Rubus idaeus L. (Rosaceae) 80/DE/10 | Mjedra | Raspberry | W | + | Leaves | Decoction | Sore throat Influenza Increase immunity |
| Sambucus ebulus L. (Adoxaceae) 83/DE/10 | Kinla | Dwarf elderberry | W | ++ | Areal parts | Topically in applied in pain place | Anti rheumatic |
| Fruits | Tincture | Menstrual pains Regulation of menstrual cycle | |||||
| Flowers | Tincture | Urinary inflammations | |||||
| Sambucus nigra L. (Adoxaceae) 85/DE/10 | Shtogu | Elderberry | W | +++ | Stem cortex | Extracted with sunflower oil | To treat sunburns |
| Boiled with butter milk | To treat thermal burns | ||||||
| Flowers | Infusion mixed with lemon and sugar | Anti asthmatic Bronchitis |
|||||
| Infusion | Antitussive | ||||||
| Fruits | Drunk fruit juice | Anti-anaemic | |||||
| Areal parts | Decoction | Anti-allergic | |||||
| Salix purpurea L. (Salicaceae) 86/DE/10 | Shelgu | Purple willow | W | + | Leaves | Applied topically in breast | Anti-fever |
| Salvia officinalis L. (Lamiaceae) 88/DE/10 | Sherbela | Garden sage | C | + | Leaves | Decoction | Sedative Antipyretic |
| Sempervivum tectorum L. (Crassulaceae) 87/DE/10 | Bar veshi | Houseleek | W | + | Leaves | Decoction after cooled applied in ear | Ear ache |
| Solanum tuberosum L. (Solanaceae) 84/DE/10 | Patatja | Potato | C | + | Tuber | Cut in several pieces and placed in front of the head | Head-ache |
| Taraxacum officinale F.H. Wigg. (Asteraceae) 96/DE/10 | Lule dielli | Dandelion | W | + | Flowers | Decoction mixed with lemon fruits. | Bronchitis |
| Teucrium chamaedrys L. (Lamiaceae) 94/DE/10 | Arrsi i vogël | Wall germander | W | + | Areal parts | Infusion | Anti-haemorrhoidal |
| Whole parts | Infusion | Anti diabetic | |||||
| Thymus spp. (Lamiaceae) 93/DE/10 | Shpirti i nënës | Wild thyme | W | ++ | Areal parts | Decoction | Respiratory inflammations Expectorant |
| Whole plant | Infusion | Bronchitis Anti-tussive Expectorant |
|||||
| Areal parts | Infusion | Lung inflammations Expectorant |
|||||
| Tilia platyphyllos Scop. (Malvaceae) 95/DE/10 | Blini | Largeleaf linden | W | + | Flowers | Decoction | Sore throat Lung inflammations |
| Trifolium pratense L. (Fabaceae) 92/DE/10 | Tërfoja e kuqe | Red clover | W/C | + | Leaves | Squeezed leaves juice | Stomach disorders |
| Trifolium repens L. (Fabaceae) 91/DE/10 | Tërfili i bardhë | White clover | W | + | Flowers | Decoction | Anti-diarrhoeal |
| Triticum vulgare L. (Poaceae) 89/DE/10 | Gruri Karajpeli |
Wheat | C | + | Seeds | Boiled seeds with water and added sugar | Constipation Anti-haemorrhoid |
| Flowers | Decoction | Kidney disorders Anti rheumatic Neuro-relaxant |
|||||
| Urtica dioica L. (Urticaceae) 97/DE/10 | Hithi | Common nettle | W | ++ | Leaves | Eaten fresh | Anti anaemic |
| Leaves and stem | Tincture | Improve blood circulation | |||||
| Roots and Leaves | Decoction | Alopecia | |||||
| Roots | Decoction | Anti-haemorrhoidal | |||||
| Vaccinium myrtillus L. (Ericaceae) 98/DE/10 | Boronica | Bilberry | W | + | Areal parts | Infusion | Anti-diabetic |
| Fruits and Leaves | Decoction | Neuro-relaxant Urinary inflammations Lung inflammations Stomach disorders Anti-hypertensive |
|||||
| Fruits | Eaten fresh | Consumed | |||||
| Veratrum album L. (Melanthiaceae) 99/DE/10 | Shtara | White hellebore | W | + | Leaves | Decoction | Anti-lice |
| Roots | Decoction | Head ache | |||||
| Leaves | Extracted with sunflower oil | Eczemas Haemorrhoids |
|||||
| Zea mays L. (Poaceae) 100/DE/10 | Misri | Corn | W | + | Silks | Infusion | Anti-diabetic |
+ quoted by less than 5% of the participants; ++ quoted by more than 5% and less than 30% of the participants; +++ quoted by more than 30% of the participants
We found that 98 species (belonging to 39 families) are employed in the traditional medicine of the area. These includes three fern species, three gymnosperms and 92 angiosperms (84 dicotyledonous and 8 monocotyledons); 74 taxa are wild. Of these species, Achillea millefolium L., Cornus mas L., Hypericum perforatum L., Juglans regia L., Juniperus communis L., Malus sylvestris Mill., Plantago major L., Sambucus nigra L. were cited more then 30% of the informants. From 98 species presented in Table 1, 23 species are also included in the official Pharmacopoeia of Europe [35].
The predominantly quoted botanical families were Rosaceae (12%), Asteraceae (10%), and Lamiaceae (5%). These same three "top" families were found to be also predominant among the wild medicinal taxa used in the folk medicine of the Alps in Montenegro, Albania, and in the Gollak region in Kosovo [9,11-14].
The most frequently quoted manner of preparation of medicinal plants was represented by decoctions (51%) and infusions (26%). The most frequently cited medicinal uses referred to gastrointestinal (26%), respiratory (19%) troubles, and illnesses affecting the urogenital system (12%). The first two categories were also the most frequently quoted in the ethnobotanical studies conducted on the Montenegrin and Albanian sides [11-14].
Most uncommon medicinal plants
Upon analysis of the bio-pharmacological literature on the quoted medicinal species available on PubMed, we found that it could be worthwhile to further investigate the following reports:
1. The internal use of cold water macerates of the inflorescences of Carduus nutans L. in the treatment of eczema (this taxon is scarcely known in the phytochemical and pharmacological literature). In 2000 a Turkish research group pointed out the hepatoprotective effects of extracts from this plant [36];
2. The internal use of decoction of the roots of Echinops bannaticus Rochel ex Schrad. for kidney stones (despite a few studies on other species of the genus Echinops, this Balkan species is largely under-investigated); and
3. The internal use of decoctions of aerial parts of Orlaya grandiflora Hoffm. for its laxative effects (the plant is completely unknown in the phytopharmacological literature).
Comparison with the Albanian and Montenegrin Alpine ethnobotanical literature
Table 2 and Figure 2 show the sites and field studies that have been compared with the data gathered in the Kosovar Alps.
Table 2.
Summary of the field ethnobotanical studies considered in the cross-cultural data analysis.
| Area and country | Study participants | Year(s) when the field studies were conducted | Number of study participants | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Albanian Alps (Kosovo) | Albanians | 2010 | 91 | Current study |
| Prokletije mountains (Montenegro) | Bosniaks and Serbs | 2006 and 2007 | 75 | [15] |
| Northern Albanian Alps (Albania) |
Albanians | 2004, 2005, and 2007 | 62 | [11-14] |
Figure 2.
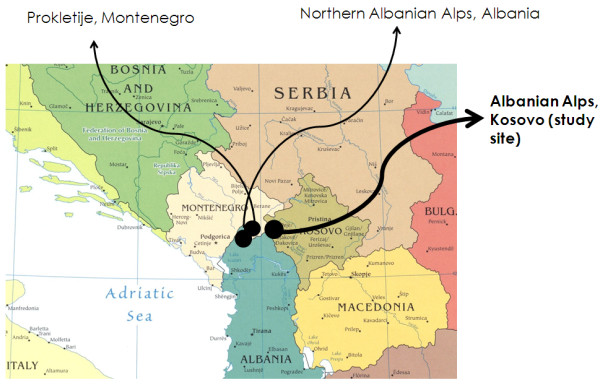
Location of the study area in Kosovo and of the sites where previous ethnobotanical works have been conducted in Albania and Montenegro [11-14] .
Figure 3 and Table 3 illustrate the similarity between the wild medicinal plants used and recorded in the current study and those recorded in the Montenegrin and Albanian sides of the same Albanian Alps.
Figure 3.
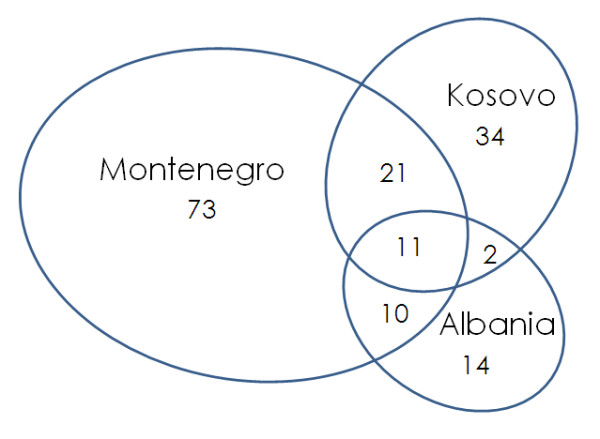
Representation of the commonalities among the wild medicinal species quoted on the Kosovar, Montenegrin, and Albanian sides of the Albanian Alps [data from the current study and [11-14]].
Table 3.
Jaccard similarity index of the wild medicinal plants used in the Kosovar, Albanian, and Montenegrin Alps.
| Group I | Group 2 | Species used in both groups | Species used in one group only (Group 1/Group 2) |
Jaccard Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Albanians in Albania | Albanians in Kosovo | 13 | 24/45 | 15.9 |
| Albanians in Albania | Serbs and Bosniaks in Montenegro | 21 | 16/94 | 16.0 |
| Serbs and Bosniaks in Montenegro | Albanians in Kosovo | 32 | 83/36 | 21.2 |
The link between the medical ethnobotany of the Montenegrin and Kosovar sides of the Alps - despite the different ethnicity/language of the local populations - appears stronger than the link between the ethnobotany of these two locations and the ethnobotany Albania.
This apparent paradox could be explained in a number of ways:
1. Different sampling techniques may have been adopted during the field survey in the three locations or the socio-economic background of the interviewees could have been different. For example, on the Albanian side of the Alps, the previous ethnobotanical studies selected local informants from very remote areas, which remained quite isolated during Communist times and with very limited access to urban environments and culture. It could be especially worthwhile to further assess the influence of the popular phytotherapeutical literature on folk medicine in Montenegro and Kosovo, since during the Yugoslavian time this kind of popularised knowledge was said to be "en-vogue". For example, this is very evident in the Montenegrin data, where a number of possible "modern" uses of local medicinal plants (i.e. Hypericum perforatum used as an anti-depressive) were recorded.
2. The study sites chosen in Kosovo and Montenegro are on average located at lower elevations than the sites selected in Northern Albania, thus resulting in a partially different ecological setting and availability of certain species in the environments.
3. Both the Montenegrin and Kosovar side of the Albanian Alps have had a common history for the most part of the 20th Century, since belonging to the same country (former Yugoslavia). This may have "homogenised" eventual pre-existing differences in plant perceptions/uses between the Albanian and Slav communities. Moreover, a few South-Slav communities (i.e. Bosniaks [2-4,7,8]) could be surely considered much more "herbophilic" than the Albanian ones, and this may have influenced the folk medicine of the Kosovar population to a certain degree during the last century, who have always lived in contacts with the Slavs.
4. The Montenegrin study included self-declaring Serbian and Bosniak communities. However, a large part of the Bosniak community living in the Gusinje area is represented also by "bosniakised" Albanians, whose Catholic tribes settled on this side of the Albanian Alps and converted to Islam a couple of centuries ago [37]. This could mean that the ethnobotanical data of Montenegro and Kosovo may actually refer to the same core of Muslim Albanians.
Despite the commonalities found on the quoted medicinal plants, Table 4 shows the different uses of the wild taxa, which have been most quoted in all three sides of the Alps.
Table 4.
Comparison of the most quoted folk medicinal uses of wild taxa in the current study and in ethnobotanical studies previously conducted in Albania and Montenegro [11-14] (Same or similar uses are underlined
| Botanical taxon | Used part(s) | Pathologies treated in the folk medicine of the Kosovar Alps | Pathologies treated in the folk medicine of the Montenegrin Alps [15] | Pathologies treated in the folk medicine of Albanian Alps [11-14] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Centaurium erythraea Rafn. | Aerial parts | Stomach-disorders Diabetes Fever Kidney stones and UTIs |
Stomach disorders and loss of appetite Diabetes |
Fever |
| Cornus mas L. | Fruits | Stomach disorders Diabetes Rheumatisms Anaemia |
Dhiarroea | Intestinal troubles |
| Gentiana spp. | Roots |
Blood circulation- related diseases (including hypertension) Bronchitis and asthma Stomach disorders Rheumatisms |
Stomach-ache | Cardiovascular diseases |
| Hypericum spp. | Flowering aerial parts | Stomach disorders Bronchitis and asthma Hypertension Skin infections, sunburns, and eczemas Haemorrhoids Anti-cholesterolemic |
Gastritis Anxiety and depression Skin inflammations and burns |
Stomach and digestive disorders Anxiety Respiratory diseases Fever UTIs |
| Origanum vulgare L. | Aerial parts | Respiratory diseases Digestion UTIs |
Respiratory diseases Digestive |
Respiratory diseases Digestive Diuretic |
| Plantago spp. | Aerial parts |
Stomach-ache Respiratory diseases Wounds Haemorrhoids Back-pains |
Respiratory diseases Mouth and skin inflammations Fever Haemorrhoids |
Abdominal pains Wounds Diuretic |
| Urtica dioica L. | Roots | Haemorrhoids Alopecia |
Haemorrhoids Fever Arthritis Anaemia Alopecia UTIs |
Rheumatisms Alopecia Genital problems |
UTIs: Urinary Tract Infections
From Table 4 it is interesting to underline that the folk uses of the wild medicinal taxa recorded in Kosovo often include both the uses recorded in Albania and those in Montenegro. It would then appear that the medico-ethnobotany of Kosovo - because of its history in the last century and the exposure to the South-Slavic ethnobotanical traditions - has possibly incorporated both Albanian and Slavic plant uses.
Conclusions
Medicinal plants still play a crucial role in the sphere of human health in the Albanian Alps, not only in the Montenegrin and Albanian territory, but also on the Kosovar side. Oftentimes, these mountainous communities have limited or non-existent access to Western biomedical modalities, and are instead self-reliant on their TEK. The local flora is thus incredibly important to provide the first health care within the households of the Albanian Alps.
Moreover, the biodiversity richness and unique bio-cultural heritage of the local people here is something to be highly valued. Steps towards this end are evident in the formation of protected parks for biodiversity conservation - but further efforts in conservation of the human TEK diversity and cultural heritage are necessary as well. TEK-dependent activities such as sustainable gathering of wild medicinal taxa, their small-scale trade, and production of local high quality plant-based foods and dairy products can all contribute to the growing eco-tourism initiatives. Thus, TEK is a critical component to success in the future economic development and biocultural conservation efforts of the region.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
BM and AH conceived the study, and participated in its design and coordination. AH and HA carried out the field study; EH and FK verified the identification of the plant taxa; AH, AP, and CLQ performed the data analysis and drafted the discussion. CLQ edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Contributor Information
Behxhet Mustafa, Email: behxhetm@yahoo.com.
Avni Hajdari, Email: avhajdari@hotmail.com.
Feriz Krasniqi, Email: fkrasniqi@hotmail.com.
Esat Hoxha, Email: esathoxha@yahoo.com.
Hatixhe Ademi, Email: hademi@hotmail.com.
Cassandra L Quave, Email: cassy.quave@gmail.com.
Andrea Pieroni, Email: a.pieroni@unisg.it.
Acknowledgements
Special thanks are due to all the inhabitants of the Kosovar Alps who participated in this study.
References
- Pardo de Santayana M, Pieroni A, Puri R. Ethnbotany in the New Europe. People, Health and Wild Plant Resources. New York/Oxford: Berghahn Books; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Redzic S. Wild edible plants and their traditional use in the human nutrition in Bosnia-Herzegovina. Ecol Food Nutr. 2006;45:189–232. doi: 10.1080/03670240600648963. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Redžić S. The ecological aspect of ethnobotany and ethnopharmacology of population in Bosnia and Herzegovina. Coll Anthrop. 2007;31:869–890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Šaric-Kundalić B, Dobeš C, Klatte-Asselmeyer V, Saukel J. Ethnobotanical study on medicinal use of wild and cultivated plants in middle, south and west Bosnia and Herzegovina. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010;131:33–55. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2010.05.061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redžić S. Use of wild and semi-wild edible plants in nutrition and survival of people in 1430 days of siege of Sarajevo during the war in Bosnia and Herzegovina (1992-1995) Coll Anthrop. pp. 551–570. [PubMed]
- Redzic S. Wild mushrooms and lichens used as human food for survival in war conditions; Podrinje - Zepa Region (Bosnia and Herzegovina, W. Balkan) Hum Ecol Rev. 2010;17:175–187. [Google Scholar]
- Redzic S. Wild medicinal plants and their usage in traditional human therapy (Southern Bosnia and Herzegovina, W. Balkan) J Med Plants Res. 2010;4:1003–1027. [Google Scholar]
- Šaric-Kundalić B, Dobeš C, Klatte-Asselmeyer V, Saukel J. Ethnobotanical survey of traditionally used plants in human therapy of east, north and north-east Bosnia and Herzegovina. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011;133:1051–1076. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2010.11.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa B, Hajdari A, Pajazita Q, Syla B, Quave CL, Pieroni A. An ethnobotanical survey of the Gollak region, Kosovo. Genet Resour Crop Evol. in press DOI: 10.1007/s10722-011-9715-4.
- Jarić Z, Popović Z, Mačukanović-Jocić M, Djurdjević L, Mijatović M, Karadžić B, Mitrović M, Pavlović P. An ethnobotanical study on the usage of wild medicinal herbs from Kopaonik Mountain (Central Serbia) J Ethnopharmacol. 2007;111:160–175. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2006.11.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieroni A, Dibra B, Grishaj G, Grishaj I, Maçai SG. Traditional phytotherapy of the Albanians of Lepushe, Northern Albanians Alps. Fitoterapia. 2005;76:379–399. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2005.03.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieroni A. Local plant resources in the ethnobotany of Theth, a village in the Northern Albanian Alps. Genet Resour Crop Evol. 2008;55:1197–1214. doi: 10.1007/s10722-008-9320-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Pieroni A. In: Ethnobotany in the New Europe. People, Health and Wild Plant Resources. Pardo de Santayana M, Pieroni A, Puri R, editor. New York/Oxford: Berhahn Books; 2010. People and plants in Lëpushë. Traditional medicine, local foods, and post-communism in a North Albanian village; pp. 16–50. [Google Scholar]
- Menković N, Šavikin K, Tasić S, Zdunić G, Stešević D, Milosavljević S, Vincek D. Ethnobotanical study on traditional uses of wild medicinal plants in Prokletije Mountains (Montenegro) J Ethnopharmacol. 2011;133:97–107. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2010.09.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Šaric-Kundalić B, Fritz E, Dobeš C, Saukel J. Traditional medicine in the pristine village of Prokoško Lake on Vranica Mountain, Bosnia and Herzegovina. Scientia Pharm. 2010;78:275–290. doi: 10.3797/scipharm.1003-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrović J. Zagađivanje kraških voda u Metohiji. Priroda Kosova. 1985;6:53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa B. Basic characteristic of flora and vegetation of Kosovo and danger of their disappearance. Albanian Journal of Natural and Technical Sciences. 1998;5:115–121. [Google Scholar]
- Balkans Peace Park Project. http://balkanspeacepark.org/
- Çavolli R. Gjeografia regjionale e Kosovës. Prishtina: Enti i Teksteve dhe i Mjeteve Mësimore i Kosovës; 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Krasniqi F. Promene u flori i vegetacije Kosova poslednjih decenija i mere njihove zashtite. Makedonska Akademija na Naukite i Umetnostite. 1982;III:59–67. [Google Scholar]
- Krasniqi F. Veçoritë e florës dhe të vegjetacionit të Kosovës dhe problemi i mbrojtjes së tyre. ASHAK. 1998;6:51–66. [Google Scholar]
- Rexhepi F Vegjetacioni i Kosovës 1994Prishtina: FSHMN, Universiteti i Prishtinë; 22070296 [Google Scholar]
- Amidžić L. Visokoplaninska flora i vegetacija. U: Nacionalni Park "Prokletije" - Nucne i strucne, osnove za zastitu planinskog masiva Prokletija. Belgrade: Arhiv Zavoda za zaštitu prirode Srbije; 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Krasniqi F. Shumska Vegetavija Brdskoc Regiona Kosova. Studime nr. 27. Prishtina: Bashkësia e Instutucioneve Shkencore të Kosovës; 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Sejdiu S. Fjalorth etnobotanik i shqipes. Prishtina: Rilindja; 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Russell Bernard H. Research Methods in Anthropology. Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches. Walnut Creek, USA: Altamira Press; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- The International Society of Ethnobiology Code of Ethics. http://ethnobiology.net/code-of-ethics/
- Paparisto K Vangjeli J Ruci B Mullaj A Qosja X Flora e Shqipërisë 20001-4Tirana: ASHASH. Instituti i Kërkimeve Biologjike; 20623768 [Google Scholar]
- Jordanov D. Flora NR Bulgaria I-VII. Sofia: BANU; 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Pajazitaj Q Përcaktuesi i bimëve Pteridofite dhe Spermatofite 2004Prishtina: Universiteti i Prishtinës; 22292155 [Google Scholar]
- Demiri M. Flora ekskursioniste e Shqipërisë. Tirana: Libri Shkollor; 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Tutin T, Heywood V, Burges N, Valentine D, Walters S, Webb D. Flora Europaea. Cambridge, UK: University Press; 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Angiosperm Phylogeny Website. http://www.mobot.org/MOBOT/research/APweb/
- González-Tejero MR, Casares-Porcel M, Sánchez-Rojas CP, Ramiro-Gutiérrez JM, Molero-Mesa Pieroni A, Giusti ME, Censorii C, de Pasquale C, Della A, Paraskeva-Hadijchambi D, Hadjichambis A, Houmani Z, El-Demerdash M, El-Zayat M, Hmamouchi M, El-Johrig S. Medicinal plants in the Mediterranean area: Synthesis of the results of the project Rubia. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008;116:341–357. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2007.11.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- European Pharmacopoeia. 6. Brussels: Council of Europe; 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Aktay G, Deliorman D, Ergun E, Ergun F, Yeşilada E, Cevik C. Hepatoprotective effects of Turkish folk remedies on experimental liver injury. J Ethnopharmacol. 2000;73:121–129. doi: 10.1016/S0378-8741(00)00286-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxhaku F, Kaser K. Die Stammesgesellschaften Nordalbaniens. Berichte und Forschungen österreichischer Konsuln und Gelehrter (1861-1917) Vienna: Böhlau Verlag; 1996. [Google Scholar]


