Abstract
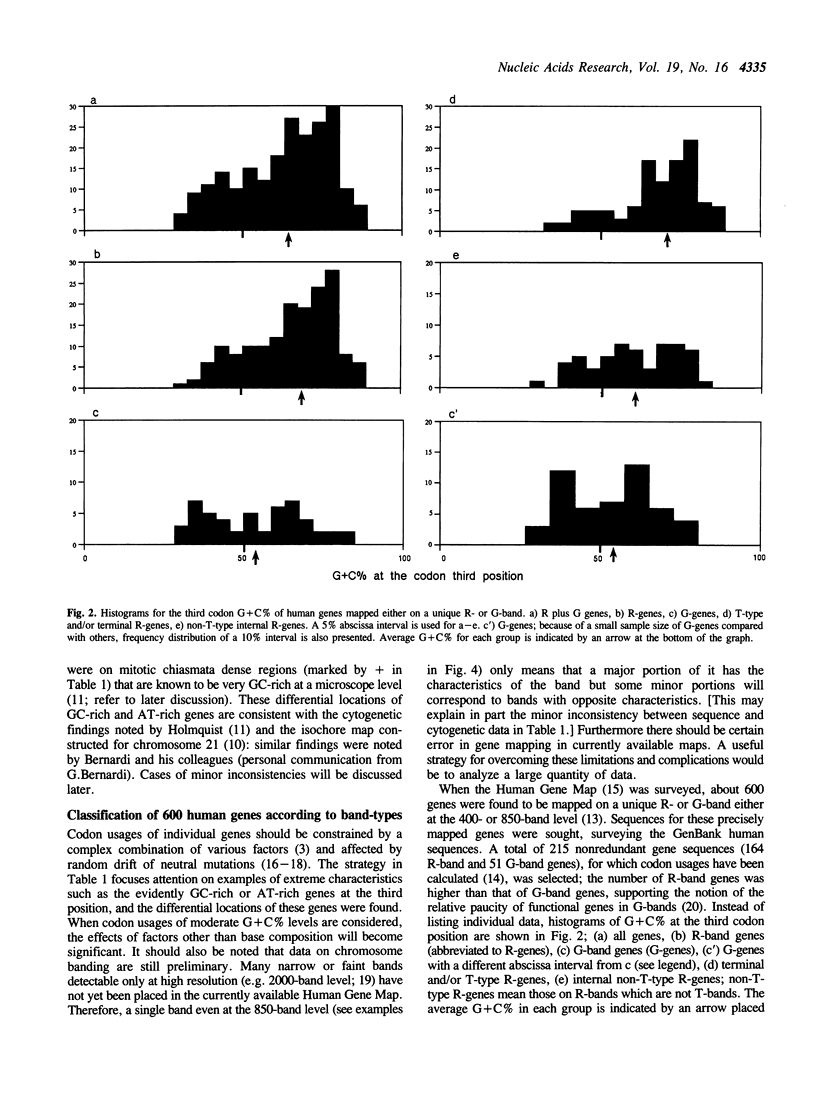
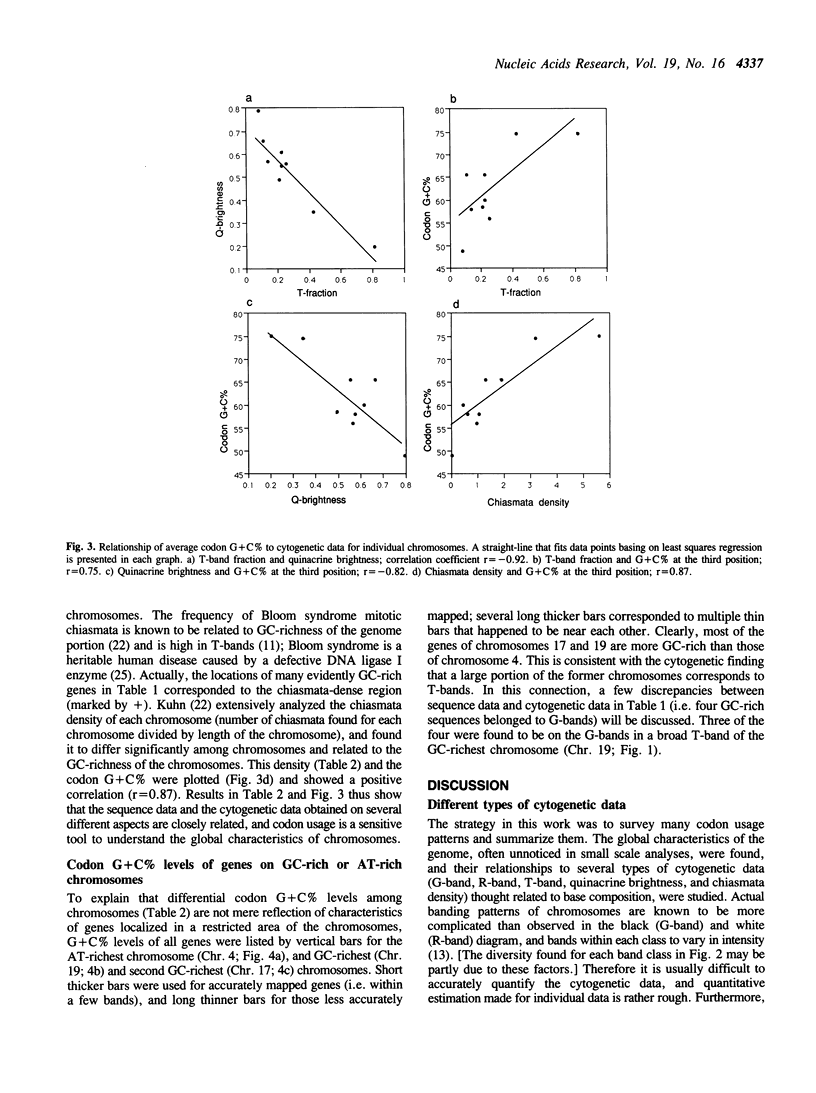
The sequences of the human genome compiled in DNA databases are now about 10 megabase pairs (Mb), and thus the size of the sequences is several times the average size of chromosome bands at high resolution. By surveying this large quantity of data, it may be possible to clarify the global characteristics of the human genome, that is, correlation of gene sequence data (kb-level) to cytogenetic data (Mb-level). By extensively searching the GenBank database, we calculated codon usages in about 2000 human sequences. The highest G + C percentage at the third codon position was 97%, and that of about 250 sequences was 80% or more. The lowest G + C% was 27%, and that in about 150 sequences was 40% or less. A major portion of the GC-rich genes was found to be on special subsets of R-bands (T-bands and/or terminal R-bands). AT-rich genes, however, were mainly on G-bands or non-T-type internal R-bands. Average G + C% at the third position for individual chromosomes differed among chromosomes, and were related to T-band density, quinacrine dullness, and mitotic chiasmata density in the respective chromosomes.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambros P. F., Sumner A. T. Correlation of pachytene chromomeres and metaphase bands of human chromosomes, and distinctive properties of telomeric regions. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1987;44(4):223–228. doi: 10.1159/000132375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aota S., Ikemura T. Diversity in G + C content at the third position of codons in vertebrate genes and its cause. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6345–6355. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi G., Olofsson B., Filipski J., Zerial M., Salinas J., Cuny G., Meunier-Rotival M., Rodier F. The mosaic genome of warm-blooded vertebrates. Science. 1985 May 24;228(4702):953–958. doi: 10.1126/science.4001930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi G. The isochore organization of the human genome. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:637–661. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.003225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulmer M. A statistical analysis of nucleotide sequences of introns and exons in human genes. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 Jul;4(4):395–405. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comings D. E. Mechanisms of chromosome banding and implications for chromosome structure. Annu Rev Genet. 1978;12:25–46. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.12.120178.000325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer T., Cremer C., Baumann H., Luedtke E. K., Sperling K., Teuber V., Zorn C. Rabl's model of the interphase chromosome arrangement tested in Chinese hamster cells by premature chromosome condensation and laser-UV-microbeam experiments. Hum Genet. 1982;60(1):46–56. doi: 10.1007/BF00281263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutrillaux B. Chromosomal evolution in primates: tentative phylogeny from Microcebus murinus (Prosimian) to man. Hum Genet. 1979 May 10;48(3):251–314. doi: 10.1007/BF00272830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filipski J., Salinas J., Rodier F. Two distinct compositional classes of vertebrate gene-bearing DNA stretches, their structures and possible evolutionary origin. DNA. 1987 Apr;6(2):109–118. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner K., Aissani B., Bernardi G. A compositional map of human chromosome 21. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1853–1858. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08310.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbomel P. From gene to chromosome: organization levels defined by the interplay of transcription and replication in vertebrates. New Biol. 1990 Nov;2(11):937–945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmquist G. P. Evolution of chromosome bands: molecular ecology of noncoding DNA. J Mol Evol. 1989 Jun;28(6):469–486. doi: 10.1007/BF02602928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T., Aota S. Global variation in G+C content along vertebrate genome DNA. Possible correlation with chromosome band structures. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 5;203(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90086-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Codon usage and tRNA content in unicellular and multicellular organisms. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Jan;2(1):13–34. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T., Wada K., Aota S. Giant G+C% mosaic structures of the human genome found by arrangement of GenBank human DNA sequences according to genetic positions. Genomics. 1990 Oct;8(2):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90273-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn E. M. Localization by Q-banding of mitotic chiasmata in cases of Bloom's syndrome. Chromosoma. 1976 Aug 4;57(1):1–11. doi: 10.1007/BF00292945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouchiroud D., Fichant G., Bernardi G. Compositional compartmentalization and gene composition in the genome of vertebrates. J Mol Evol. 1987;26(3):198–204. doi: 10.1007/BF02099852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satchwell S. C., Drew H. R., Travers A. A. Sequence periodicities in chicken nucleosome core DNA. J Mol Biol. 1986 Oct 20;191(4):659–675. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90452-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer J. R., Hozier J. C. High resolution of mouse chromosomes: banding conservation between man and mouse. Science. 1986 Jun 27;232(4758):1632–1635. doi: 10.1126/science.3715469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M., Li W. H. An evolutionary perspective on synonymous codon usage in unicellular organisms. J Mol Evol. 1986;24(1-2):28–38. doi: 10.1007/BF02099948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sueoka N. Directional mutation pressure and neutral molecular evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2653–2657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada K., Wada Y., Doi H., Ishibashi F., Gojobori T., Ikemura T. Codon usage tabulated from the GenBank genetic sequence data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19 (Suppl):1981–1986. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.suppl.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis A. E., Weksberg R., Tomlinson S., Lindahl T. Structural alterations of DNA ligase I in Bloom syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8016–8020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe K. H., Sharp P. M., Li W. H. Mutation rates differ among regions of the mammalian genome. Nature. 1989 Jan 19;337(6204):283–285. doi: 10.1038/337283a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunis J. J. Mid-prophase human chromosomes. The attainment of 2000 bands. Hum Genet. 1981;56(3):293–298. doi: 10.1007/BF00274682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



