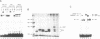Abstract
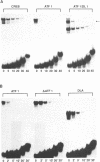
The promoter motif CGTCA binds multiple cellular factors that mediate a variety of inducible events, including positive responses to raised cellular levels of cAMP and to the Adenovirus E1a protein. To date, at least ten mammalian cDNA clones have been isolated that encode distinct proteins capable of binding to this motif. However, in most cases the precise stimuli that may regulate these different factors have yet to be determined. We have previously shown that the abundant Hela protein ATF-43 forms a complex in vivo with the cyclic AMP response element binding protein (CREB). In this report we definitively show that ATF-43 is the product of the two published cDNA clones, ATF1 and TREB 36. We confirm that ATF1 efficiently heterodimerises with CREB and demonstrate that even though ATF1 and CREB homodimers, as well as the ATF1/CREB heterodimer efficiently bind to the CGTCA motif, the resulting DNA-protein complexes have significantly different stabilities. A region outside the DNA binding domain of ATF1 contributes to the instability of its interaction with DNA. We further show that despite ATF1's homology to CREB, it responds poorly to activation by protein kinase A. In light of our finding that in Hela cells the majority of CREB protein is heterodimerised with ATF1, we speculate on the functional significance of such heterodimers.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebersold R. H., Leavitt J., Saavedra R. A., Hood L. E., Kent S. B. Internal amino acid sequence analysis of proteins separated by one- or two-dimensional gel electrophoresis after in situ protease digestion on nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):6970–6974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.6970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrisani O., Dixon J. E. Identification and purification of a novel 120-kDa protein that recognizes the cAMP-responsive element. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3212–3218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benbrook D. M., Jones N. C. Heterodimer formation between CREB and JUN proteins. Oncogene. 1990 Mar;5(3):295–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz L. A., Gilman M. Z. Two distinct forms of active transcription factor CREB (cAMP response element binding protein). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5258–5262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredow S., Sürig D., Müller J., Kleinert H., Benecke B. J. Activating-transcription-factor (ATF) regulates human 7S L RNA transcription by RNA polymerase III in vivo and in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6779–6784. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R., Angel P., Karin M. Jun-B differs in its biological properties from, and is a negative regulator of, c-Jun. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):979–986. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90754-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortes P., Buckbinder L., Leza M. A., Rak N., Hearing P., Merino A., Reinberg D. EivF, a factor required for transcription of the adenovirus EIV promoter, binds to an element involved in EIa-dependent activation and cAMP induction. Genes Dev. 1988 Aug;2(8):975–990. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.8.975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwarki V. J., Montminy M., Verma I. M. Both the basic region and the 'leucine zipper' domain of the cyclic AMP response element binding (CREB) protein are essential for transcriptional activation. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):225–232. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08099.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes N. S., Borrelli E., Sassone-Corsi P. CREM gene: use of alternative DNA-binding domains generates multiple antagonists of cAMP-induced transcription. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):739–749. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90503-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa J., Toita M., Yoshida M. A unique enhancer element for the trans activator (p40tax) of human T-cell leukemia virus type I that is distinct from cyclic AMP- and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-responsive elements. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3234–3239. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3234-3239.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaire M., Chatton B., Kedinger C. Isolation and characterization of two novel, closely related ATF cDNA clones from HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 25;18(12):3467–3473. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.12.3467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Menzel P., Leonard J., Fischer W. H., Montminy M. R. Characterization of motifs which are critical for activity of the cyclic AMP-responsive transcription factor CREB. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1306–1312. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Montminy M. R. Cyclic AMP stimulates somatostatin gene transcription by phosphorylation of CREB at serine 133. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):675–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Yamamoto K. K., Fischer W. H., Karr D., Menzel P., Biggs W., 3rd, Vale W. W., Montminy M. R. A cluster of phosphorylation sites on the cyclic AMP-regulated nuclear factor CREB predicted by its sequence. Nature. 1989 Feb 23;337(6209):749–752. doi: 10.1038/337749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T. W., Liu F., Allegretto E. A., Karin M., Green M. R. A family of immunologically related transcription factors that includes multiple forms of ATF and AP-1. Genes Dev. 1988 Oct;2(10):1216–1226. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.10.1216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T. W., Liu F., Coukos W. J., Green M. R. Transcription factor ATF cDNA clones: an extensive family of leucine zipper proteins able to selectively form DNA-binding heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2083–2090. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T., Curran T. Cross-family dimerization of transcription factors Fos/Jun and ATF/CREB alters DNA binding specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3720–3724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy S., Shenk T. Adenoviral control regions activated by E1A and the cAMP response element bind to the same factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4171–4175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeffler J. P., Meyer T. E., Yun Y., Jameson J. L., Habener J. F. Cyclic AMP-responsive DNA-binding protein: structure based on a cloned placental cDNA. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1430–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.2974179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. G., Shu M. D. Epstein-Barr virus small RNA (EBER) genes: unique transcription units that combine RNA polymerase II and III promoter elements. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):825–834. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90797-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu J. C., Laz T., Mohn K. L., Taub R. Identification of LRF-1, a leucine-zipper protein that is rapidly and highly induced in regenerating liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3511–3515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst H. C., Jones N. C. Identification of factors that interact with the E1A-inducible adenovirus E3 promoter. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1132–1146. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst H. C., Masson N., Jones N. C., Lee K. A. The cellular transcription factor CREB corresponds to activating transcription factor 47 (ATF-47) and forms complexes with a group of polypeptides related to ATF-43. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6192–6203. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivashkiv L. B., Liou H. C., Kara C. J., Lamph W. W., Verma I. M., Glimcher L. H. mXBP/CRE-BP2 and c-Jun form a complex which binds to the cyclic AMP, but not to the 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate, response element. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1609–1621. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalinot P., Wintzerith M., Gaire M., Hauss C., Egly J. M., Kédinger C. Purification and functional characterization of a cellular transcription factor that binds to an enhancer element within the adenovirus early EIIa promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2484–2488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanei-Ishii C., Ishii S. Dual enhancer activities of the cyclic-AMP responsive element with cell type and promoter specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 25;17(4):1521–1536. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.4.1521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kara C. J., Liou H. C., Ivashkiv L. B., Glimcher L. H. A cDNA for a human cyclic AMP response element-binding protein which is distinct from CREB and expressed preferentially in brain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1347–1357. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzarides T., Ziff E. The role of the leucine zipper in the fos-jun interaction. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):646–651. doi: 10.1038/336646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Q., Yun Y. D., Hoeffler J. P., Habener J. F. Cyclic-AMP-responsive transcriptional activation of CREB-327 involves interdependent phosphorylated subdomains. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4455–4465. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07896.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Lee K. A., Fink J. S., Goodman R. H., Green M. R. Distinguishable promoter elements are involved in transcriptional activation by E1a and cyclic AMP. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4390–4397. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Green M. R. A cellular transcription factor E4F1 interacts with an E1a-inducible enhancer and mediates constitutive enhancer function in vitro. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1345–1353. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02374.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Hai T. Y., SivaRaman L., Thimmappaya B., Hurst H. C., Jones N. C., Green M. R. A cellular protein, activating transcription factor, activates transcription of multiple E1A-inducible adenovirus early promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8355–8359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leza M. A., Hearing P. Cellular transcription factor binds to adenovirus early region promoters and to a cyclic AMP response element. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):3003–3013. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.3003-3013.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Green M. R. Interaction of a common cellular transcription factor, ATF, with regulatory elements in both E1a- and cyclic AMP-inducible promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3396–3400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liou H. C., Boothby M. R., Finn P. W., Davidon R., Nabavi N., Zeleznik-Le N. J., Ting J. P., Glimcher L. H. A new member of the leucine zipper class of proteins that binds to the HLA DR alpha promoter. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1581–1584. doi: 10.1126/science.2321018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F., Green M. R. A specific member of the ATF transcription factor family can mediate transcription activation by the adenovirus E1a protein. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1217–1224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90686-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macgregor P. F., Abate C., Curran T. Direct cloning of leucine zipper proteins: Jun binds cooperatively to the CRE with CRE-BP1. Oncogene. 1990 Apr;5(4):451–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maekawa T., Matsuda S., Fujisawa J., Yoshida M., Ishii S. Cyclic AMP response element-binding protein, CRE-BP1, mediates the E1A-induced but not the Tax-induced trans-activation. Oncogene. 1991 Apr;6(4):627–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maekawa T., Sakura H., Kanei-Ishii C., Sudo T., Yoshimura T., Fujisawa J., Yoshida M., Ishii S. Leucine zipper structure of the protein CRE-BP1 binding to the cyclic AMP response element in brain. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2023–2028. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03610.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P. L., Clegg C. H., Correll L. A., McKnight G. S. Regulation of transcription by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4887–4891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merino A., Buckbinder L., Mermelstein F. H., Reinberg D. Phosphorylation of cellular proteins regulates their binding to the cAMP response element. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):21266–21276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montagne J., Béraud C., Crenon I., Lombard-Platet G., Gazzolo L., Sergeant A., Jalinot P. Tax1 induction of the HTLV-I 21 bp enhancer requires cooperation between two cellular DNA-binding proteins. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):957–964. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08194.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Bilezikjian L. M. Binding of a nuclear protein to the cyclic-AMP response element of the somatostatin gene. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):175–178. doi: 10.1038/328175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Sevarino K. A., Wagner J. A., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. Identification of a cyclic-AMP-responsive element within the rat somatostatin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6682–6686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura M., Niki M., Ohtani K., Sugamura K. Differential activation of the 21-base-pair enhancer element of human T-cell leukemia virus type I by its own trans-activator and cyclic AMP. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):5207–5221. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.5207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholas J., Nevins J. R. Distinct DNA targets for trans-activation by HTLV-1 tax and adenovirus E1A. Virology. 1991 May;182(1):156–167. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90659-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman C., Runswick M., Pollock R., Treisman R. Isolation and properties of cDNA clones encoding SRF, a transcription factor that binds to the c-fos serum response element. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):989–1003. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90244-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyborg J. K., Dynan W. S. Interaction of cellular proteins with the human T-cell leukemia virus type I transcriptional control region. Purification of cellular proteins that bind the 21-base pair repeat elements. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8230–8236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono S. J., Liou H. C., Davidon R., Strominger J. L., Glimcher L. H. Human X-box-binding protein 1 is required for the transcription of a subset of human class II major histocompatibility genes and forms a heterodimer with c-fos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4309–4312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poteat H. T., Chen F. Y., Kadison P., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. Protein kinase A-dependent binding of a nuclear factor to the 21-base-pair repeat of the human T-cell leukemia virus type I long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1264–1270. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1264-1270.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raychaudhuri P., Rooney R., Nevins J. R. Identification of an E1A-inducible cellular factor that interacts with regulatory sequences within the adenovirus E4 promoter. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4073–4081. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02753.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roesler W. J., Vandenbark G. R., Hanson R. W. Cyclic AMP and the induction of eukaryotic gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9063–9066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney R. J., Raychaudhuri P., Nevins J. R. E4F and ATF, two transcription factors that recognize the same site, can be distinguished both physically and functionally: a role for E4F in E1A trans activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5138–5149. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P. Cyclic AMP induction of early adenovirus promoters involves sequences required for E1A trans-activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7192–7196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan T. H., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Purification and characterization of multiple nuclear factors that bind to the TAX-inducible enhancer within the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1733–1745. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., Sigler P. B., McKnight S. L. Scissors-grip model for DNA recognition by a family of leucine zipper proteins. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):911–916. doi: 10.1126/science.2683088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada T., Watanabe H., Usuda Y., Handa H. Different biological activities of the hetero- and homodimers formed by the 47- and 43-kilodalton proteins of transcription factor ATF/E4TF3. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):557–564. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.557-564.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura T., Fujisawa J., Yoshida M. Multiple cDNA clones encoding nuclear proteins that bind to the tax-dependent enhancer of HTLV-1: all contain a leucine zipper structure and basic amino acid domain. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2537–2542. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07434.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]