Abstract
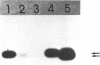
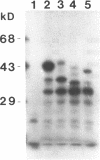
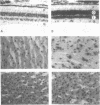
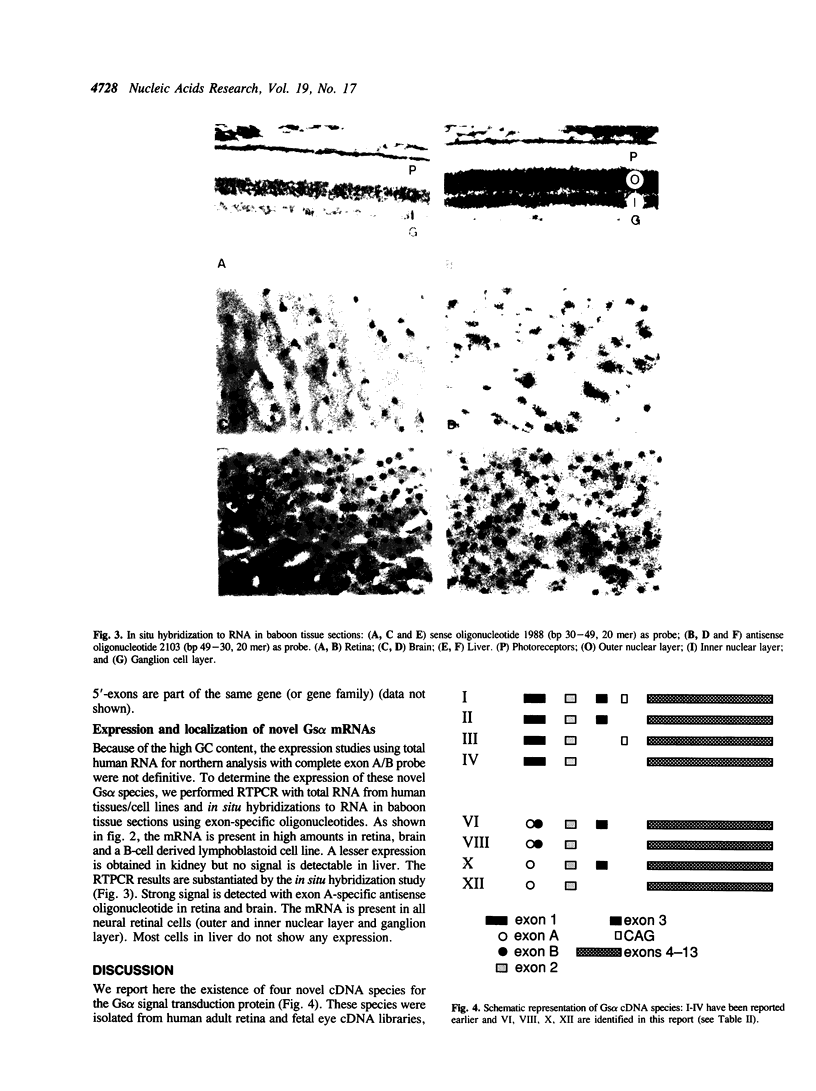
The Gs alpha guanine nucleotide-binding signal transduction protein is part of a heterotrimeric complex that is involved in the stimulation of adenylate cyclase upon activation of membrane receptors. We report the characterization of 16 Gs alpha cDNA clones isolated from the human adult retina and fetal eye libraries. Molecular heterogeneity in the 5'-region defines four novel Gs alpha cDNA species which are generated either by alternate splicing or by using alternative promoter. The novel exons upstream of exon 2 interrupt the highly conserved 'region A' in the Gs alpha polypeptide. Non-AUG codons in the novel 5'-exon can initiate translation of these Gs alpha species in vitro. Reverse transcription of total RNA coupled with polymerase chain reaction (RTPCR) using specific primers and in situ hybridization to mRNA in baboon tissue sections with a specific oligonucleotide probe show a high level of expression of these species in retina and brain but not in liver. Differential expression of alternatively spliced Gs alpha species suggests novel signal transducing pathways.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agarwal N., Hsieh C. L., Sills D., Swaroop M., Desai B., Francke U., Swaroop A. Sequence analysis, expression and chromosomal localization of a gene, isolated from a subtracted human retina cDNA library, that encodes an insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP2). Exp Eye Res. 1991 May;52(5):549–561. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(91)90056-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer L., Abramowitz J., Brown A. M. Receptor-effector coupling by G proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 7;1031(2):163–224. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(90)90007-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray P., Carter A., Simons C., Guo V., Puckett C., Kamholz J., Spiegel A., Nirenberg M. Human cDNA clones for four species of G alpha s signal transduction protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8893–8897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelly J., Hamard G., Koulakoff A., Kaplan J. C., Kahn A., Berwald-Netter Y. Dystrophin gene transcribed from different promoters in neuronal and glial cells. Nature. 1990 Mar 1;344(6261):64–65. doi: 10.1038/344064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. L., Hunsaker W. R. Improved hybridization assays employing tailed oligonucleotide probes: a direct comparison with 5'-end-labeled oligonucleotide probes and nick-translated plasmid probes. Anal Biochem. 1985 Dec;151(2):211–224. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feener C. A., Koenig M., Kunkel L. M. Alternative splicing of human dystrophin mRNA generates isoforms at the carboxy terminus. Nature. 1989 Apr 6;338(6215):509–511. doi: 10.1038/338509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florkiewicz R. Z., Sommer A. Human basic fibroblast growth factor gene encodes four polypeptides: three initiate translation from non-AUG codons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):3978–3981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.3978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziano M. P., Gilman A. G. Synthesis in Escherichia coli of GTPase-deficient mutants of Gs alpha. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15475–15482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook S. R., Kim S. H. Molecular model of the G protein alpha subunit based on the crystal structure of the HRAS protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1751–1755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa Y., Bianchi C., Nadal-Ginard B., Homcy C. J. Alternative promoter and 5' exon generate a novel Gs alpha mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8458–8462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. T., Reed R. R. Golf: an olfactory neuron specific-G protein involved in odorant signal transduction. Science. 1989 May 19;244(4906):790–795. doi: 10.1126/science.2499043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Journot L., Pantaloni C., Bockaert J., Audigier Y. Deletion within the amino-terminal region of Gs alpha impairs its ability to interact with beta gamma subunits and to activate adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9009–9015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozasa T., Itoh H., Tsukamoto T., Kaziro Y. Isolation and characterization of the human Gs alpha gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2081–2085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lochrie M. A., Simon M. I. G protein multiplicity in eukaryotic signal transduction systems. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 12;27(14):4957–4965. doi: 10.1021/bi00414a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma H., Yanofsky M. F., Meyerowitz E. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of GPA1, a G protein alpha subunit gene from Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3821–3825. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters S. B., Miller R. T., Chi M. H., Chang F. H., Beiderman B., Lopez N. G., Bourne H. R. Mutations in the GTP-binding site of GS alpha alter stimulation of adenylyl cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15467–15474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattera R., Codina J., Crozat A., Kidd V., Woo S. L., Birnbaumer L. Identification by molecular cloning of two forms of the alpha-subunit of the human liver stimulatory (GS) regulatory component of adenylyl cyclase. FEBS Lett. 1986 Sep 29;206(1):36–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81336-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattera R., Graziano M. P., Yatani A., Zhou Z., Graf R., Codina J., Birnbaumer L., Gilman A. G., Brown A. M. Splice variants of the alpha subunit of the G protein Gs activate both adenylyl cyclase and calcium channels. Science. 1989 Feb 10;243(4892):804–807. doi: 10.1126/science.2536957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navon S. E., Fung B. K. Characterization of transducin from bovine retinal rod outer segments. Participation of the amino-terminal region of T alpha in subunit interaction. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15746–15751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Clapham D. E. Roles of G protein subunits in transmembrane signalling. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):129–134. doi: 10.1038/333129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Pulsifer L., Wolf L. G. The amino terminus of G protein alpha subunits is required for interaction with beta gamma. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8996–8970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olate J., Mattera R., Codina J., Birnbaumer L. Reticulocyte lysates synthesize an active alpha subunit of the stimulatory G protein Gs. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10394–10400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pupillo M., Kumagai A., Pitt G. S., Firtel R. A., Devreotes P. N. Multiple alpha subunits of guanine nucleotide-binding proteins in Dictyostelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4892–4896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raport C. J., Dere B., Hurley J. B. Characterization of the mouse rod transducin alpha subunit gene. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7122–7128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robishaw J. D., Smigel M. D., Gilman A. G. Molecular basis for two forms of the G protein that stimulates adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9587–9590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saris C. J., Domen J., Berns A. The pim-1 oncogene encodes two related protein-serine/threonine kinases by alternative initiation at AUG and CUG. EMBO J. 1991 Mar;10(3):655–664. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07994.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathmann M., Simon M. I. G protein diversity: a distinct class of alpha subunits is present in vertebrates and invertebrates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9113–9117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathmann M., Wilkie T. M., Simon M. I. Diversity of the G-protein family: sequences from five additional alpha subunits in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7407–7409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L., Bourne H. R. G proteins: a family of signal transducers. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:391–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaroop A., Hogan B. L., Francke U. Molecular analysis of the cDNA for human SPARC/osteonectin/BM-40: sequence, expression, and localization of the gene to chromosome 5q31-q33. Genomics. 1988 Jan;2(1):37–47. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90107-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaroop A., Weissman S. M. Charon BS(+) and (-), versatile lambda phage vectors for constructing directional cDNA libraries and their efficient transfer to plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 12;16(17):8739–8739. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.17.8739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaroop A., Xu J. Z., Agarwal N., Weissman S. M. A simple and efficient cDNA library subtraction procedure: isolation of human retina-specific cDNA clones. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19(8):1954–1954. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.8.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woon C. W., Heasley L., Osawa S., Johnson G. L. Mutation of glycine 49 to valine in the alpha subunit of GS results in the constitutive elevation of cyclic AMP synthesis. Biochemistry. 1989 May 30;28(11):4547–4551. doi: 10.1021/bi00437a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]