Abstract
In the Guillain-Barré syndrome subform acute motor axonal neuropathy (AMAN), Campylobacter jejuni enteritis triggers the production of anti-ganglioside Abs (AGAbs), leading to immune-mediated injury of distal motor nerves. An important question has been whether injury to the presynaptic neuron at the neuromuscular junction is a major factor in AMAN. Although disease modeling in mice exposed to AGAbs indicates that complement-mediated necrosis occurs extensively in the presynaptic axons, evidence in humans is more limited, in comparison to the extensive injury seen at nodes of Ranvier. We considered that rapid AGAb uptake at the motor nerve terminal membrane might attenuate complement-mediated injury. We found that PC12 rat neuronal cells rapidly internalized AGAb, which were trafficked to recycling endosomes and lysosomes. Consequently, complement-mediated cytotoxicity was attenuated. Importantly, we observed the same AGAb endocytosis and protection from cytotoxicity in live mouse nerve terminals. AGAb uptake was attenuated following membrane cholesterol depletion in vitro and ex vivo, indicating that this process may be dependent upon cholesterol-enriched microdomains. In contrast, we observed minimal AGAb uptake at nodes of Ranvier, and this structure thus remained vulnerable to complement-mediated injury. These results indicate that differential endocytic processing of AGAbs by different neuronal and glial membranes might be an important modulator of site-specific injury in acute AGAb-mediated Guillain-Barré syndrome subforms and their chronic counterparts.
Introduction
The Guillain-Barré syndromes (GBSs) are acute, immune-mediated neuropathies affecting the peripheral nervous system (PNS), usually triggered by preceding infectious events including Campylobacter jejuni enteritis. In the acute motor axonal neuropathy (AMAN) variant of GBS, the lipopolysaccharide of C. jejuni initiates the production of Abs against the gangliosides GM1 and GD1a via molecular mimicry (1). Human autopsy (2) and experimental animal (3–5) evidence suggests that anti-ganglioside Abs (AGAbs) bind to the axolemmal membrane at the node of Ranvier, where they fix complement, resulting in nodal dysfunction and, in severe cases, axonal degeneration.
Besides the node of Ranvier, the presynaptic motor nerve terminals at neuromuscular junctions (NMJs) are also targets for AGAbs (6–8). In ex vivo experiments using mouse diaphragm and triangularis sterni (TS) preparations, interaction between AGAbs derived from immunized mice or GBS patients and the presynaptic membrane of NMJs induces an α-latrotoxin–like effect on transmitter release due to uncontrolled calcium influx through complement pores. Consequently, motor nerve terminal electrophysiological function is blocked, accompanied by structural damage (8, 9). These animal data suggest that motor nerve terminal dysfunction might in part account for motor weakness in axonal forms of GBS. Considering that motor nerve terminals lie outside the blood-nerve barrier, are the target site for other Ab-mediated diseases such as Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome and myasthenia gravis, and express gangliosides (10), which act as receptors for toxins (11, 12), it seems highly plausible that presynaptic membranes are targeted for AGAb-mediated attack. Although the impairment of presynaptic NMJs is experimentally compelling, the clinical involvement of this phenomenon in GBS is less clear, except for some case studies of atypical clinical subforms (9).
In part this may be because of the limitations of electrophysiological methods in interrogating this site, especially when motor axons are concomitantly blocked by more proximal injury, for example at pre-terminal nodes of Ranvier. One other important confounding factor may be that AGAbs are very rapidly cleared from the presynaptic membrane by endocytotic pathways, including those involved in synaptic vesicle (SV) retrieval (13), whereas they may be retained on the extracellular face of the axolemmal membrane at other sites such as the node of Ranvier. At the former site, AGAbs would no longer be available for activating complement, whereas the node of Ranvier would remain vulnerable to attack. The possibility that AGAbs may be rapidly endocytosed at this site is supported by evidence of uptake at NMJs and retrograde transport of Abs against neuronal surface proteins (14, 15) and toxins that use gangliosides as receptors (16–19).
Here, we evaluated the impact of AGAb internalization on the pathology of AGAb-mediated injury, using a variety of cell- and tissue-based model systems. We selectively analyzed AGAb uptake in vitro in PC12 cells, and ex vivo and in vivo in mouse tissues, and show that internalization takes place at a physiological temperature via cholesterol-enriched microdomains and that internalized AGAbs either enter recycling endosomes (REs) or are degraded in lysosomes. Furthermore, we demonstrate that AGAb internalization greatly attenuates complement activation, thus preventing injury and consequently preserving nerve terminal function. These results indicate that AGAb internalization may be one mechanism by which NMJs could be relatively protected in AGAb-mediated GBS compared with other neural and non-neural sites.
Results
AGAbs are internalized by PC12 cells and dorsal root ganglion neurons and localize to distinct endocytic compartments.
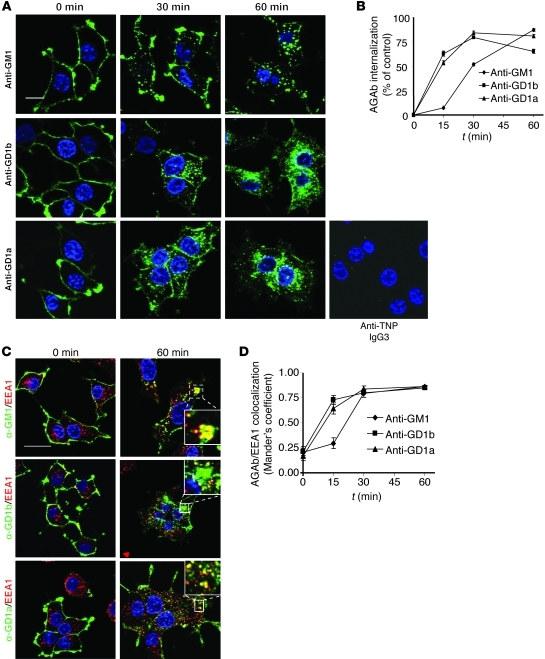
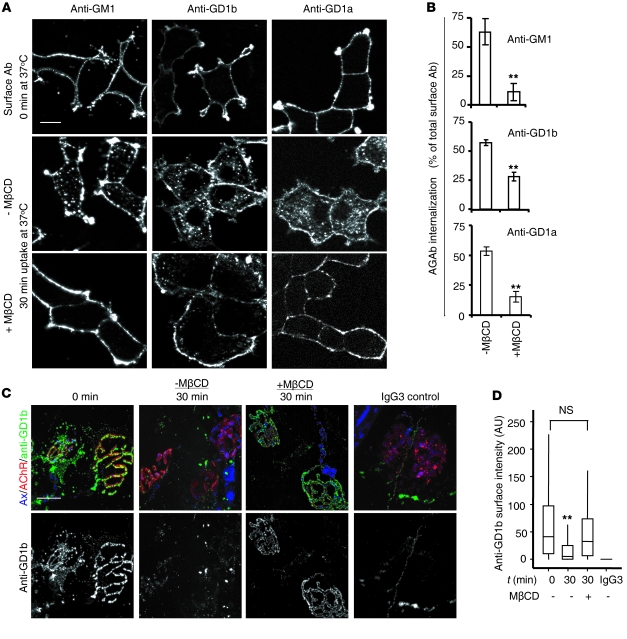
We first examined the kinetics and pathways of AGAb uptake and trafficking in neuronal cell culture models in vitro. Differentiated PC12 cells were surface labeled with 3 different AGAbs by incubation at 4°C. Control Ab conditions included either an anti-trinitrophenol (anti-TNP) IgG3 Ab (IgG3 control, as shown in Figure 1 and Supplemental Figure 6; supplemental material available online with this article; doi: 10.1172/JCI59110DS1), followed by fluorophore-labeled secondary Ab, or fluorophore-labeled secondary Ab alone (control, as shown in other figures). In all control experiments throughout the study, significant binding or uptake of irrelevant primary or secondary Ab was not observed. Subsequently cells were transferred to 37°C for defined time periods in order to initiate any AGAb endocytosis and intracellular trafficking. All three AGAbs bound to PC12 cell plasma membranes under steady-state conditions (4°C, t = 0 minutes) (Figure 1A). No binding was seen with negative control anti-TNP IgG3 (Figure 1A). Fifteen minutes after initiation of endocytosis by transfer to 37°C, approximately 50% of anti-GD1a and anti-GD1b was redistributed throughout the cytoplasm, displaying punctate staining suggesting vesicular localization, while the bulk of anti-GM1 Ab still remained close to or at the plasma membrane (Figure 1B). As the incubation at 37°C proceeded, the concentration of all three Abs increased in the cytoplasm (Figure 1, A and B). Concomitantly, the level of AGAbs associated with the plasma membrane was substantially diminished by 60 minutes incubation at 37°C. Endocytosed AGAbs colocalized with the early endosome (EE) compartment marker EEA1 (Figure 1, C and D), as defined by a Manders coefficient greater than 0.7. In primary dorsal root ganglion neurons (DRGNs) exposed to the AGAb reactive with GD1b (known to be highly expressed on DRGNs; ref. 20) and subjected to the same incubation conditions as PC12 cells, extensive uptake that associated with EEA1 was also observed (Supplemental Figure 1).
Figure 1. AGAbs are internalized by PC12 cells and transported to the EE compartment.
(A) PC12 cells labeled with AGAb on ice were incubated at 37°C for 15, 30, and 60 minutes. Surface-bound and internalized Ab was detected using secondary Ab and analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. No binding to PC12 cells was seen upon labeling with the anti-TNP IgG3 control Ab, followed by secondary Ab. Scale bar: 20 μM. (B) Surface and internalized Ab was quantitated using AxioVision software. At least 30 cells were examined per condition (n = 3). (C) PC12 cells were labeled as described above and further allowed to internalize Ab over different time periods. The cells were then permeabilized and further stained for EEs using anti-EEA1 Ab and appropriate secondary Ab. Scale bar: 20 μM. (D) Co-localization of AGAbs with EEs was determined using AxioVision software. Five to 10 dots per cell were assessed, at least 25 cells per condition were analyzed, and the average Manders coefficient was calculated. Plotted values are mean ± SEM (n = 3).
We next assessed the trafficking pathways by which AGAbs were handled in PC12 cells. First we investigated whether the three AGAbs are internalized as predicted through the cholesterol- and glycosphingolipid-enriched membrane microdomains by evaluating the extent of co-localization with caveolin-1. We observed strong co-localization for anti-GM1 Ab with caveolin-1 at early time points (Manders coefficient, 0.7–0.9), while anti-GD1a and -GD1b Abs showed a partial co-localization throughout the incubation time (Manders coefficient, 0.3–0.7) (Supplemental Figure 2, A and B).
Late endosome (LE) and RE compartments were next assessed for involvement in Ab trafficking. Since LEs derive from EEs by maturation, we investigated whether AGAb cargoes are transported to LEs by probing with the LE marker Lamp1. Anti-GM1 and anti-GD1b Abs colocalized with Lamp1-positive vesicles 30 minutes after initiation of endocytosis, whereas anti-GD1a Ab colocalized by 60 minutes (Supplemental Figure 3, A and B). We next examined the trafficking of AGAbs to the REs using Rab11 as marker for the recycling compartment (Supplemental Figure 4, A and B). Anti-GM1 and -GD1b Abs colocalized with Rab11 after 30 minutes of internalization at 37°C, whereas significant co-localization of anti-GD1a Ab was not observed over this time course.
Having demonstrated that AGAbs are transported to LEs, we examined whether they were then delivered to lysosomes for degradation, using LysoTracker (LysoT) dye, which labels acidic vesicles (Supplemental Figure 4, C and D). Anti-GM1 and -GD1b Abs significantly associated with LysoT after 30 minutes of incubation at 37°C and with anti-GD1a Ab by 60 minutes.
Overall, these results demonstrate that AGAbs, but not the mouse anti-TNP IgG3 control Ab or the secondary Ab, are rapidly endocytosed by conventional trafficking pathways in PC12 cells, and either recycled or sorted to lysosomes for degradation.
AGAbs are rapidly internalized at NMJs but not at the node of Ranvier.
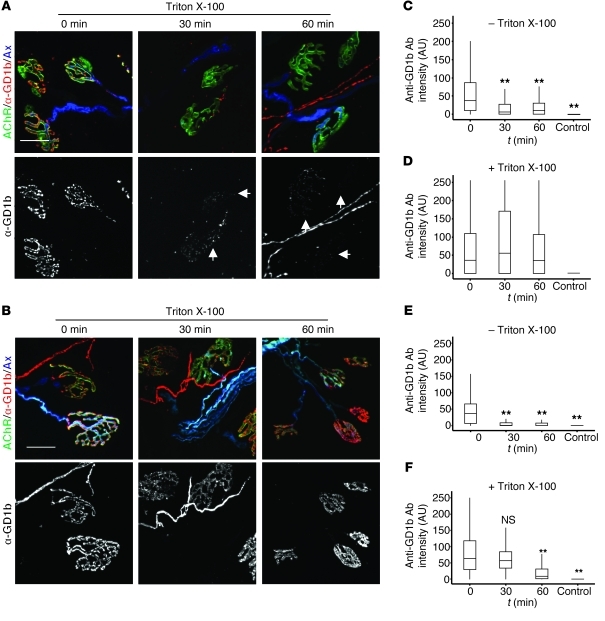
Having demonstrated that AGAbs are capable of being rapidly internalized into endosomal compartments in PC12 cells and primary DRGNs, we next assessed whether they are internalized at neuronal membranes as found in physiologically intact neural structures, namely the presynaptic motor nerve terminal and node of Ranvier. Experiments were conducted under conditions and time course similar to those in the PC12 and DRGN studies. We used TS nerve-muscle preparations from both WT and a-series ganglioside–overexpressing mice (GD3 synthase KO, GD3s–/–), both of which also expressed cytosolic cyan fluorescent protein (CFP) in their axons to facilitate axonal visualization (WT/CFP, GD3s–/–/CFP; see Methods). TS preparations were labeled at 4°C with anti-GD1a, -GD1b, or -GM1 Ab, and all three Abs were monitored for internalization at 37°C. Controls included anti-TNP IgG3 and secondary Ab (Supplemental Figure 6) or secondary Ab alone, neither of which labeled or was taken up at nerve terminal or nodes of Ranvier. We differentiated surface and internalized Abs by assessing permeabilized and non-permeabilized tissue using fluorescence microscopy. The signal intensity of all three AGAbs associated with the extracellular aspect of the presynaptic membrane (i.e., non-permeabilized tissue) significantly decreased over time (1 hour) when incubated at 37°C (Figure 2, A, C, and E; Supplemental Figure 5, A and B), suggesting that AGAbs were internalized. To confirm this, TS preparations were then permeabilized (to allow secondary Ab access for detection of AGAb) for assessment of internalized AGAbs and found to contain extensive deposits of intraterminal Ab. Quantification of anti-GD1b Ab levels in permeabilized NMJs showed equal total Ab amounts in tissues incubated for 30 and 60 minutes at 37°C, in comparison to 0 minutes, following Ab loading at 4°C (Figure 2, B and D). Quantitative data for anti-GM1 Ab were similar (Supplemental Figure 5, C and D). For anti-GD1a Ab, the level had significantly fallen after 60 minutes incubation at 37°C (Figure 2F), suggesting that anti-GD1a Ab may be cleared from the endplate region at a faster rate than anti-GM1 and anti-GD1b Abs.
Figure 2. Internalization of AGAb from presynaptic membranes at NMJs occurs rapidly at physiological temperature (37°C).
(A) TS muscle was labeled with anti-GD1b Ab on ice and subsequently incubated at 37°C for 30 and 60 minutes to allow endocytosis. Surface anti-GD1b Ab was detected with secondary Ab and analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. Arrowheads indicate the expected site of surface anti-GD1b Ab signal overlying the acetylcholine receptor (AChR) signal at the NMJ upon incubation at 37°C. (B) Following microscopic analysis, the same TS preparations were permeabilized (with Triton X-100), and the total internalized and surface anti-GD1b Ab was imaged using secondary Ab. (C and D) Fluorescence images for anti-GD1b Ab were quantitated using ImageJ software. (C) Anti-GD1b Ab was rapidly depleted from the cell surface over time. (D) Following permeabilization, no significant difference in total anti-GD1b Ab signal overlying the NMJ was observed, compared with surface Ab levels at t = 0. (E and F) For anti-GD1a Ab (images not shown) rapid clearance by internalization from the cell surface was also observed (E), and by 60 minutes, there was also a mild but significant overall reduction in total anti-GD1a Ab over the NMJ (F, 60-minute time point), suggesting clearance away from this site. At least 150 NMJs were analyzed per time point, and results are from 3 independent experiments per Ab. n = 3; **P < 0.005. Scale bars: 20 μM. Control tissues exposed to secondary Ab alone showed no significant binding or uptake (for anti-TNP IgG3 control data, see Figures 7 and 8).
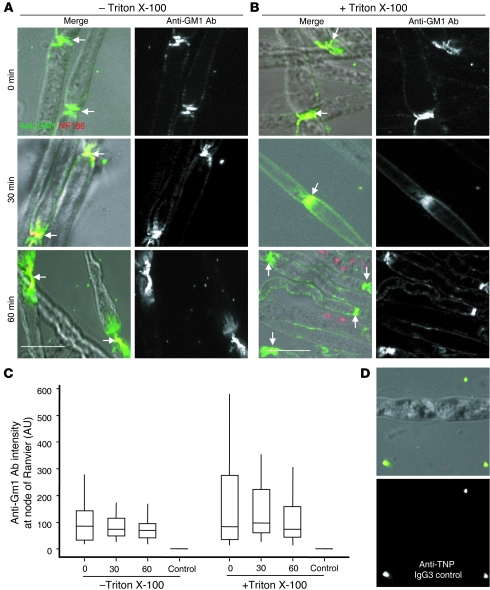
We next examined AGAb binding and uptake at the node of Ranvier. Teased, unfixed fibers were freshly isolated from sciatic nerve of GD3s–/– mice and exposed to anti-GM1 Ab at 4°C, then incubated at 37°C to initiate endocytosis (Figure 3, A–C). When Ab levels in non-permeabilized (Figure 3A) and permeabilized (Figure 3B) fibers were compared, it was evident that anti-GM1 was not internalized at the node of Ranvier or may have been internalized at a much reduced rate over a longer time course, compared with the presynaptic membrane.
Figure 3. Anti-GM1 is not internalized at the node of Ranvier.
(A and B) Teased sciatic nerve fibers from GD3s–/– mice labeled with anti-GM1 Ab at 4°C were further incubated at 37°C for 30–60 minutes to allow endocytosis, or studied immediately (t = 0 minutes). Anti-GM1 Ab was detected with secondary Ab in non-permeabilized tissue (A) and Triton X-100–permeabilized tissue (B) and analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. Scale bars: 20 μm. (C) Quantification of anti-GM1 Ab levels at the node of Ranvier of permeabilized and non-permeabilized tissues was conducted using ImageJ software. In tissue incubated solely at 4°C or for a further 30–60 minutes at 37°C, there was no significant difference in anti-GM1 Ab levels at the node of Ranvier in either permeabilized or non-permeabilized conditions, indicating that insignificant uptake of antibody had occurred. For quantitative data, control fibers were labeled with secondary Ab alone and showed no binding. (D) No binding to nodes of Ranvier is seen upon labeling with the anti-TNP IgG3 control Ab, followed by secondary Ab. Data are the mean of 2 independent experiment, and at least 75 nodes were assessed per condition.
Internalization of anti-GD1b and anti-GM1 Abs is not paralleled by internalization of GD1b and GM1 gangliosides.
It is established that tetanus neurotoxin fragment (TeNT Hc) binds to GD1b ganglioside at the presynaptic membrane and is internalized through clathrin-coated pits, leaving behind its GD1b antigen. In contrast, cholera toxin B (CTB), which binds to GM1 in detergent-resistant membrane (DRM) microdomains, is endocytosed in complex with GM1 (16, 17). The predicted consequence of this would be a reduction in the amount of cell surface GM1 available for further ligand binding, but not of GD1b. In light of this, we assessed whether uptake of AGAbs affects the level of ganglioside epitope subsequently available for further AGAb binding at the presynaptic nerve terminal membrane. TS preparations from WT/CFP and GD3s–/–/CFP mice were exposed to unlabeled anti-GD1b and anti-GM1 Abs at 4°C, respectively (Supplemental Figure 6, A–D). TS preparations were then incubated at 37°C for 30 minutes to allow Ab endocytosis, which was monitored for completeness (30 minutes internalization). The remaining surface ganglioside available for further Ab binding was estimated by relabeling the tissue with anti-GD1b or anti-GM1 Abs (30 minutes RE). This relabeled Ab signal was insignificantly different from the original Ab signal obtained on first labeling the tissue (t = 0 minutes). Thus, no reduction in surface GD1b or GM1 immunoreactivity was observed in tissue subjected to prior AGAb uptake, compared with naive tissue. In contrast, preincubation with CTB, followed by surface probing with anti-GM1 Ab, resulted in a significant reduction (43%, P < 0.001) in surface GM1 (median, 82 AU) compared with control tissue not subjected to CTB pretreatment (median, 143 AU) (Supplemental Figure 6, E–G). These results indicate that internalization of anti-GD1b and anti-GM1 Abs is not paralleled by internalization of GD1b and GM1 gangliosides under these conditions.
AGAb uptake attenuates complement activation in PC12 cells.
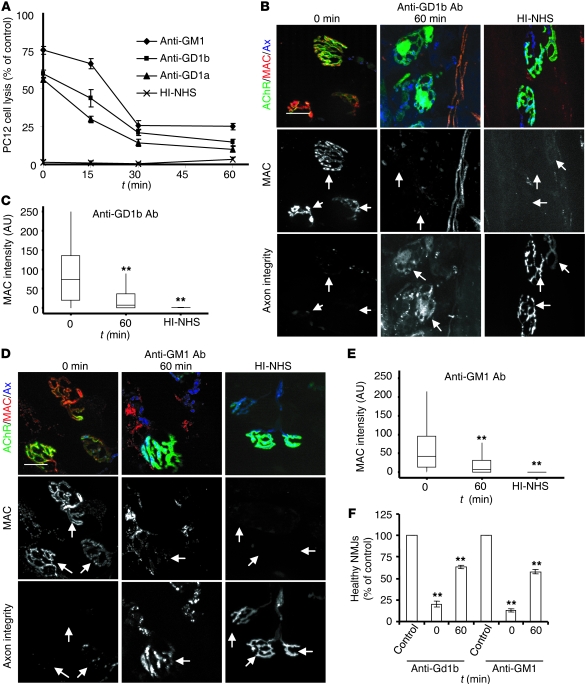
After demonstrating that AGAbs are internalized by PC12 cells, DRGNs, and the presynaptic nerve terminal, we next addressed the extent to which AGAb internalization affects the pathological cascade driven by complement activation. We first compared the amount of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release (as an index of complement-mediated cell lysis) from AGAb-opsonized PC12 cells upon incubation at 4°C and 37°C, prior to exposure to normal human serum (NHS) as a complement source. Complement-depleted NHS (heat inactivated [HI], negative control) and a cell lysis buffer (positive control, equating to 100% LDH release, 100% cell lysis) were used as comparators. At the initial state (transfer to 37°C, t = 0), anti-GM1, -GD1a, and -GD1b Ab–coated PC12 cells resulted in 75% (P < 0.001), 56% (P < 0.05), and 60% (P < 0.05) cell lysis, respectively (Figure 4A). After 15 minutes of incubation at 37°C and complement exposure, LDH release fell to 30% (P < 0.001) and 43% (P < 0.001), respectively, for anti-GD1a– and anti-GD1b–labeled PC12 cells. For anti-GM1–labeled PC12 cells, LDH release at 15 minutes was less marked, consistent with its slightly slower internalization (Figure 1B). By 30 minutes at 37°C with NHS exposure, all AGAb-labeled PC12 cells showed significant attenuation of LDH release. These results indicate that Ab internalization with concomitant clearance of cell surface Ab attenuates complement activation and subsequent cell membrane lysis.
Figure 4. AGAb uptake attenuates complement activation in vitro and ex vivo, and protects tissue from injury.
(A) PC12 cells labeled with AGAbs at 4°C were incubated at 37°C over time (15–60 minutes) to allow endocytosis or maintained at 4°C to retain all Ab on the surface. Cells were subsequently exposed to NHS for 60 minutes at 37°C. Control samples were exposed to the HI-NHS under the same conditions. Cell death (assessed using the CytoTox 96 kit) was greatly attenuated in samples incubated at 37°C for increasing time periods, compared with those maintained at 4°C. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3; P < 0.001 for 15-, 30-, and 60-minute time points, compared with samples incubated for 0 minutes). (B–F) TS from WT (B) and GD3s–/– (D) mice were labeled at 4°C with anti-GD1b and anti-GM1 Abs, respectively, then further incubated at 37°C for 60 minutes (or maintained at 4°C) before exposure to NHS. Control tissues were exposed to HI-NHS. MAC deposits at the endplates were detected with anti–C5b-9 Ab. MAC deposits at NMJs of TS incubated at 37°C for 60 minutes were greatly reduced compared with incubation maintained at 4°C. Arrows indicate expected positions of NMJs. Scale bars: 20 μm. (C and E) Quantitation of MAC was conducted using ImageJ software. At least 150 NMJs were investigated per condition. n = 3; **P < 0.005. (F) The NMJ was assessed for the loss of intraterminal cytosolic CFP overlying the acetylcholine receptor staining, and the percentage of NMJs that retained CFP (healthy NMJs) was calculated. An increase in the number of healthy NMJs in tissue incubated for 60 minutes at 37°C was observed. Control data were obtained with HI-NHS. Data are the mean from 3 independent experiments, and at least 150 NMJs were investigated per condition; **P = 0.003.
Complement activation is attenuated upon AGAb internalization at the presynaptic nerve terminal, whereas the node of Ranvier remains vulnerable.
We next examined whether AGAb uptake at the presynaptic nerve terminal attenuates complement activation and thereby protects NMJs against injury. First, TS nerve-muscle preparations from WT/CFP or GD3s–/–/CFP mice were incubated at 4°C with anti-GM1 or -GD1a/-GD1b Ab, respectively. AGAb-labeled TS preparations were then incubated at 37°C for 60 minutes before exposure to NHS. HI-NHS was used as a negative control. At time zero (i.e., prior to any incubation at 37°C), membrane attack complex (MAC) deposits were observed at the presynaptic nerve terminal of all tissues that had been preexposed to AGAb followed by NHS (Figure 4 and Supplemental Figure 7). Conversely, the levels of MAC at the presynaptic nerve terminal in AGAb-labeled tissue incubated at 37°C for 1 hour prior to the exposure to NHS were significantly reduced. Taken together, these data indicate that the attenuation of complement activation is due to AGAb clearance from the presynaptic nerve terminal membrane by endocytosis.
We next investigated the effect of AGAb uptake on complement activation at the node of Ranvier. Teased, unfixed fibers freshly isolated from sciatic nerve of GD3s–/– mice were exposed to anti-GM1 Ab at 4°C and then incubated for 1 hour at 37°C to facilitate endocytosis, before exposure to the NHS. As a control, HI-NHS was used (Supplemental Figure 8, A and B; arrows indicate the node of Ranvier). As expected, the level of MAC deposited at the node of Ranvier did not vary between tissues incubated for 0 and 60 minutes at 37°C. This result supports the previous finding showing an absence of significant anti-GM1 Ab uptake at the node of Ranvier.
Presynaptic nerve terminal membrane integrity and function are protected as a consequence of AGAb uptake.
To investigate whether the attenuation of MAC deposition at AGAb-labeled NMJs results in the preservation of the presynaptic membrane integrity, we assessed the number of AGAb-labeled terminal axons overlying endplates that retained their CFP fluorescence, comparing those incubated at 37°C for 0 and 60 minutes, followed by exposure to NHS. Previous studies have shown that leakage of CFP through MAC pores, and thus loss of fluorescence signal, is a reliable index of terminal axon integrity (21). AGAb-labeled TS preparations that had been immediately (0 minutes at 37°C) exposed to NHS showed a relative loss of endplate CFP compared with those allowed to internalize Ab for 60 minutes at 37°C (Figure 4, B and D, and Supplemental Figure 7A, lower panels; arrows indicate expected position of terminal axonal CFP). Quantitatively, 20% or fewer of endplates sensitized by any of the three AGAbs and then immediately exposed to NHS remained healthy, compared with more than 60% of those allowed to internalize Ab for 60 minutes at 37°C (Figure 4F and Supplemental Figure 7C).
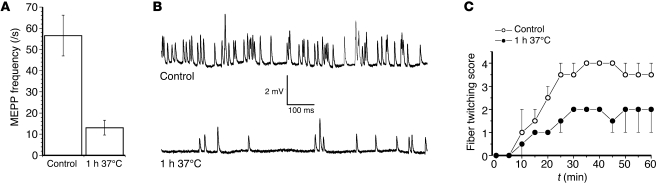
We next assessed the effects of uptake of AGAb on complement-mediated neurophysiological disruption of motor nerve terminal function using the nerve-muscle hemidiaphragm preparation, restricting these studies to anti-GM1 Ab in GD3s–/– mice (Figure 5). As shown in previous studies (9), aberrant calcium influx through MAC pores in the presynaptic membrane triggers massive uncontrolled exocytosis (manifested by an increase in miniature endplate potential [MEPP] frequency accompanied by spontaneous twitching of muscle fibers), followed by neuromuscular transmission block. At hemidiaphragm NMJs sensitized by anti-GM1 Ab, but prior to exposure with NHS, MEPP frequency was normal, at approximately 1.5/s, as expected (Figure 5, A and B) (22). When these preparations were immediately exposed to NHS, a large elevation in the MEPP frequency — to a level of 56.6 ± 9.6/s (n = 51 NMJs from 2 muscles) — occurred, as expected from earlier studies with this Ab (23). When anti-GM1 Ab–sensitized preparations were incubated for 1 hour at 37°C prior to exposure to NHS, the increase in MEPP frequency was significantly attenuated, by approximately 75% (13.1 ± 3.5/s; n = 46 NMJs; P < 0.001). Similarly, the muscle fiber twitch score was greatly attenuated by inclusion of a 1-hour period of Ab uptake at 37°C (Figure 5C). Thus, the membrane integrity as assessed by CFP intensity and electrophysiological function was largely preserved by allowing Ab uptake at the nerve terminal prior to complement exposure.
Figure 5. Incubation of anti-GM1 Ab pretreated GD3s–/– NMJs in Ringer’s solution for 1 hour at 37°C before addition of NHS attenuates complement-mediated pathophysiological effects.
(A) NMJs incubated for 1 hour at 37°C in Ringer’s medium (to facilitate Ab endocytosis) exhibited a lower increase in MEPP frequency following the addition of NHS as a complement source, compared with positive pathological controls pretreated with anti-GM1 Ab, then directly exposed to NHS (i.e., without an Ab endocytosis step). (B) Typical examples of MEPP recordings under pathological control conditions in comparison with 1 hour of Ab uptake prior to exposure to NHS. One-second trace. (C) The lower MEPP frequency in the 1-hour 37°C Ringer’s medium–incubated muscles was accompanied by less intense muscle fiber twitching.
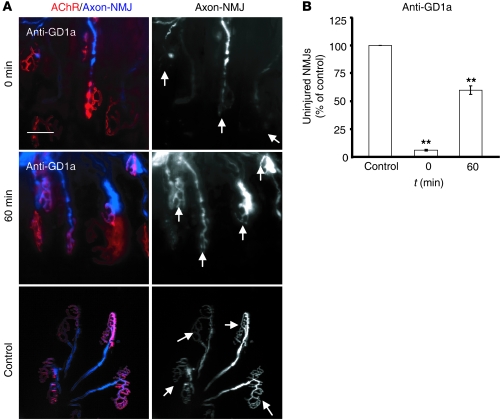
Anti-GD1a uptake protects the presynaptic nerve terminal from the complement-mediated injury in vivo.
Having demonstrated that AGAb uptake in vitro and ex vivo attenuates complement activation and preserves presynaptic nerve terminal integrity, we sought to determine whether the same finding could be observed in vivo. This study was restricted to anti-GD1a Ab applied to WT mice constitutively expressing CFP in their axons (WT/CFP mice). Following the topical application of anti-GD1a Ab together with NHS to sternomastoid muscles of mice under general anesthesia, only 7% (Figure 6B) of the nerve terminals maintained a healthy state (as determined by the retention of CFP fluorescence in terminal axons) (Figure 6A, top row; arrows indicate the complete disappearance of terminal CFP at 0 minutes) compared with control (100% healthy) (Figure 6A, bottom row; arrows indicate healthy endplates). When anti-GD1a Ab was topically applied for 30 minutes, followed by 60 minutes of incubation with Ringer’s before topical application of NHS, a significant attenuation of injury resulted as manifested by the retention of CFP in terminal axons (Figure 6A, middle row; arrows), with 60% of NMJs maintaining their healthy state (Figure 6B; P < 0.001).
Figure 6. Anti-GD1a Ab uptake protects NMJs from injury in vivo.
(A) Sternomastoid muscles from live anesthetized mice were labeled with anti-GD1a together with NHS (0 minutes) or anti-GD1a alone for 30 minutes, followed by 60 minutes with Ringer’s before exposure to NHS. Control mice received Ringer’s alone. NMJs were visually assessed for the loss of CFP overlying the acetylcholine receptor staining, and the percentage of NMJs that retained the CFP (healthy NMJs) was calculated. There is an increase in healthy NMJs in tissue incubated at 37°C. NMJs incubated in Ringer’s for 60 minutes (to allow Ab uptake) before exposure to NHS are protected from injury. Scale bar: 50 μm. (B) Quantitative analysis of NMJ integrity showing significant preservation of the endplate structure (arrows in A) in tissues subjected to a gap of 60 minutes incubation with Ringer’s prior to exposure to NHS. n = 3; **P < 0.001.
AGAb uptake is regulated by membrane cholesterol in vitro and ex vivo.
Finally, we considered whether biochemical perturbation of AGAb uptake might affect the pathophysiological outcome and addressed this by manipulating membrane cholesterol. We treated differentiated PC12 cells and TS preparations with methyl-β cyclodextrin (MβCD), a cholesterol-depleting agent. First, PC12 cells were incubated for 30 minutes at 37°C with 5 mM MβCD diluted in serum-free DMEM. Control cells were untreated. After incubation, cells were rinsed with cold serum-free DMEM and labeled with 10 μg/ml AGAbs for 1 hour. After labeling, cells were reincubated at 37°C for 30 minutes to initiate endocytosis, and surface and internalized Abs were then assessed. Pretreatment of PC12 cells with 5 mM MβCD significantly inhibited the uptake of all three Abs by 30%–50% (P < 0.001) (Figure 7, A and B).
Figure 7. Cholesterol is required for AGAb uptake in vitro and ex vivo.
(A) MβCD-treated and untreated PC12 cells were labeled with AGAbs at 4°C and incubated for 30 minutes at 37°C to allow endocytosis. AGAbs were detected using secondary Ab and analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. Scale bar: 20 μm. (B) Levels of surface and internalized AGAb were estimated using the quantification module of AxioVision software, and the percentage of internalized AGAb was calculated. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3; **P < 0.001). (C) MβCD-treated and untreated TS preparations were labeled with anti-GD1b at 4°C and incubated at 37°C for 30 minutes to allow endocytosis. No Ab binding or uptake was observed in parallel preparations receiving anti-TNP IgG3 control Ab. Anti-GD1b was detected using FITC-labeled secondary Ab, and NMJs were detected using Alexa Fluor 555 α-BTx. Scale bar: 20 μm. (D) Surface anti-GD1b Ab overlying the AChR was estimated using ImageJ software. While incubation at 37°C for 30 minutes resulted in significant Ab endocytosis compared with 0 minutes (**P < 0.01), this was completely attenuated in the presence of MβCD, with no significant difference observed compared with TS maintained at 4°C. At least 150 NMJs were analyzed per condition in 2 independent experiments.
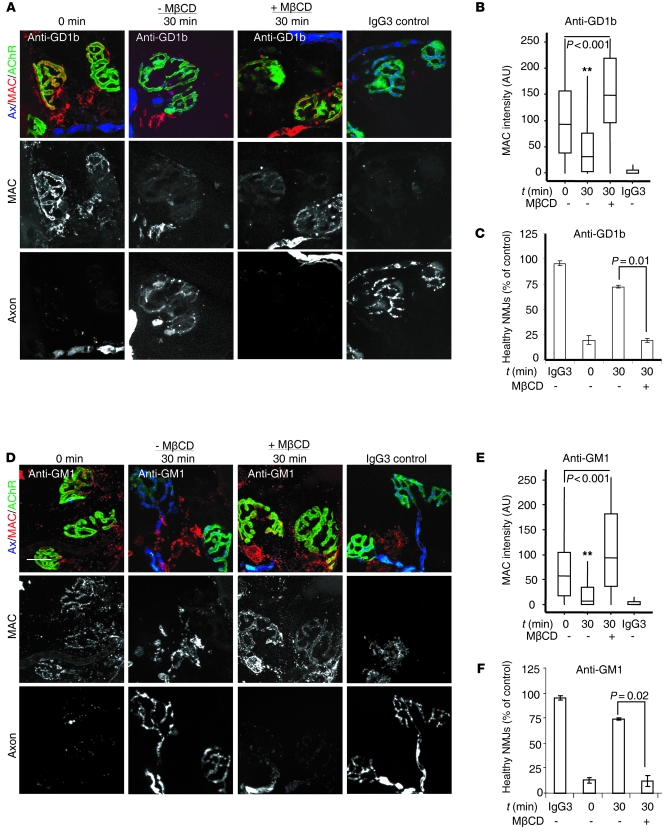
To investigate the dependence on cholesterol of Ab endocytosis at the presynaptic motor nerve terminal, we investigated whether MβCD would affect uptake of AGAbs in TS preparations, restricting these studies to anti-GD1b and -GM1 Abs. First, we showed that preincubation of WT TS preparations with 5 mM MβCD almost completely inhibited the uptake of anti-GD1b Ab (100 μg/ml, incubated for 2 hours at 4°C) at the presynaptic motor nerve terminal (Figure 7, C and D). No tissue binding of the mouse IgG3 negative control Ab was observed. We then sought to determine whether the inhibition of Ab uptake at this site increased the membrane vulnerability to complement. TS preparations from WT and GD3s–/– mice were preincubated with 5 mM MβCD and then labeled at 4°C for 2 hours with anti-GD1b and anti-GM1 Abs, respectively. TS tissues were further incubated at 37°C before exposure to NHS as source of complement. There was a substantial increase in MAC deposit at the presynaptic nerve terminal of tissues pretreated with MβCD, compared with MβCD-untreated tissue (Figure 8, A, B, D, and E). In addition, the increase in MAC deposition at NMJs of MβCD-treated TS was accompanied by the loss of nerve terminal integrity as assessed by loss of axonal CFP fluorescence, while a substantial preservation of endplate integrity was observed in MβCD-untreated tissue (30 minutes, control) (Figure 8, C and F). These results indicate that cholesterol-enriched membrane microdomains regulate the uptake of AGAbs both in vitro and ex vivo.
Figure 8. MβCD treatment of TS preparations increases AGAb-dependent MAC deposition and tissue injury at NMJs by attenuating Ab uptake.
MβCD-treated and untreated TS preparations from WT (A–C) and GD3s–/– (D–F) mice were labeled at 4°C with anti-GD1b and anti-GM1 Abs, respectively. Ab-labeled TS was either directly exposed to NHS (0 minutes) at 37°C or further incubated for 30 minutes at 37°C (to allow Ab internalization) and then exposed to NHS (30 minutes). MAC deposits at NMJs were detected with anti–C5b-9 and TRITC-labeled secondary Ab. NMJs were identified using α-BTx-488 that binds AchR. Representative fluorescence images are shown. Scale bar: 20 μm. (B and E) Quantitative analysis of MAC deposits at NMJs of MβCD-treated and untreated TS from confocal images using ImageJ software. Incubation of Ab-labeled TS for 30 minutes at 37°C (t = 30 minutes) in comparison to immediate exposure to NHS (t = 0 minutes) resulted in greatly reduced MAC deposition for both Abs; **P < 0.0001. Pretreatment with MβCD attenuated both anti-GD1b and -GM1 Ab uptake, and as a consequence, MAC deposition was enhanced, even to levels greater than those seen with immediate exposure to NHS (t = 0 minutes); P < 0.001 for both Abs. (C and F) NMJ integrity was assessed by counting α-BTx–positive NMJs that retained cytosolic CFP (healthy NMJs). A decrease in the number of healthy NMJs in tissues pretreated with MβCD was observed. P = 0.01 for anti-GD1b Ab; P = 0.02 for anti-GM1 Ab. At least 150 NMJs were analyzed per condition in 3 independent experiments. Control studies using anti-TNP Ab (IgG3) were conducted, and no effects were induced. Data are expressed as median values and interquartile ranges.
Discussion
The current study was undertaken to investigate whether the presynaptic motor nerve terminal at NMJs might be protected from AGAb-directed, complement-mediated injury due to rapid Ab clearance by vesicular endocytosis. In contrast, other sites also containing abundant membrane gangliosides — including the nodal axolemmal membrane, where endosomal trafficking pathways are less active — may be especially vulnerable to complement-mediated injury due to their inability to rapidly clear Ab by this mechanism. Although substantial experimental evidence supports a role for NMJ disruption in GBS pathology (12, 24, 25), clinical electrophysiological evidence to support the view that the NMJ is either the earliest or the primary target is modest (9, 26–28). Here we demonstrate that at a physiological temperature, AGAbs were rapidly internalized by presynaptic motor nerve terminal membranes. As a consequence, uptake of AGAbs was accompanied by substantial attenuation of complement activation, both in vitro and ex vivo. In parallel, the pathophysiological effects mediated by AGAbs and complement at the presynaptic nerve terminal were also attenuated. In contrast, AGAb was not endocytosed at the node of Ranvier, and consequently complement activation over this time course under the same conditions was unaffected. These data suggest that a critical factor in determining membrane vulnerability to complement-mediated attack in human GBS and related disorders may be the rate of clearance of AGAb from the membrane by endocytosis, and that this might differ widely in different membrane regions of the PNS. Put another way, neural membranes unable to rapidly clear surface-bound Abs by endocytosis may be especially vulnerable to AGAb-mediated, complement-dependent injury in GBS.
Ab uptake by different mechanisms is well recognized in microbial evasion of host defense, including complement-mediated lysis in trypanosomes (29). Autoantibodies against membrane self antigens, including gangliosides, become endocytosed and undergo various intracellular trafficking fates (30, 31). In some cases, Ab endocytosis accompanied by accelerated internalization of ligand may affect function (32). To elucidate the entry routes and sorting pathways of AGAbs, including the effects of depleting membrane cholesterol, we examined PC12 cells as a readily tractable system and also conducted live tissue studies (33). Cholesterol is a major component of caveolae and lipid rafts, two structurally distinct membrane microdomains (34), and the disruption of cholesterol content has been shown to displace proteins, thereby altering their functional performance (35, 36). In our studies, AGAbs associated with caveolae and their uptake was attenuated following cholesterol depletion, both in vitro and ex vivo, indicating that cholesterol is an essential stabilizer of the membrane domains involved in AGAb uptake, although the precise mechanism by which cholesterol exerts its effect in this system remains unknown. Involvement of clathrin-mediated endocytosis of AGAbs is equally likely, as cholera and tetanus toxins that bind to GM1 and GD1b, respectively, are internalized by sequential mechanisms that implicate both caveolae and clathrin-mediated endocytosis (17, 37). Whether AGAb uptake exclusively occurs within caveolae or clathrin microdomains remains unknown, although it is likely that both occur. Unlike cholera toxin, but similarly to tetanus toxin (17), AGAbs appeared to dissociate from ganglioside upon entry, leaving the ganglioside on the plasma membrane. Alternatively, intracellular gangliosides may very rapidly recycle back to cell surface, where further binding and uptake of Ab might take place.
In PC12 cells, AGAbs were rapidly sorted to EEs, the common convergence point from the plasma membrane, and then transported to both the RE compartment and the acidic compartment for lysosomal degradation. If recycled Ab became available in the extracellular environment to re-bind antigen, the recycling pathway may be a route whereby AGAb pathogenic capability is regulated. Equally, under certain disease or experimental conditions, saturation of the recycling pathway might result in excess Ab being directed to the acidic compartment for degradation.
Retention of AGAbs on the presynaptic motor nerve terminal membranes rapidly decayed at a physiological temperature (37°C), similar to the rate seen in PC12 cells. Following endocytosis, the total amount of AGAb contained within the endplate region (either intracellularly or extracellularly) was unchanged over the short time frame studied (apart from a slight fall in anti-GD1a Ab), indicating that AGAb was retained locally in the synaptic region. Once they are internalized at the synapse, the trafficking route of AGAbs is unknown; however, evidence from many studies indicates the presence of multiple endosomal trafficking pathways at motor nerve terminals, the molecular apparatus involved in neurotransmitter uptake and recycling being particularly well studied. Endosomal sorting pathways for structural components of synaptic membranes including channels and receptors are also present in separate domains lateral to the active zones and thus distinct from the neuroexocytotic machinery, although it is likely that there is some overlap between these pathways (38). Thus, nerve terminals contain the two small GTPases Rab5 and Rab4, which in non-neuronal cells regulate transport to and from the EE, respectively (39, 40), and also appear to be implicated in the SV recycling/formation processes. Rab5-positive endosomes are implicated in the differential sorting of amyloid precursor protein and SV components, which are internalized at nerve terminals and directed to the retrograde transport route and the recycling SV pool, respectively (41). The localization of different gangliosides within these membrane domains that would act as entry points for AGAbs is unknown, but may be widespread. At nodes of Ranvier in mature myelinated axons, data about endosomal trafficking pathways are sparse. Sorting capability must exist, especially during the formation of specialized domains integral to nodal organization that take place during development and repair (42); however, in the mature steady state, endosomal cycling of nodal axolemmal membrane components may be relatively modest in comparison to synaptic membranes. Our data on the lack of AGAb uptake at the node of Ranvier would support this view.
Abs against neuronal proteins and bacterial toxins that use gangliosides as receptors are retrogradely transported to the neuronal cell body following internalization at the motor nerve terminal (15, 18, 43, 44). Extrapolating these findings to AGAbs, we would expect all three endocytosed AGAbs to also be retrogradely transported to the neuronal cell body, where they may be destined for lysosomal degradation, as seen in PC12 cells. Whether they may also be recycled back to the synaptic membrane through local endosomal circuits is not known.
An important feature of the AGAbs used in this study is that they fix complement upon binding to the membrane ganglioside (8, 45, 46). In this study and previous mouse models of acute axonal neuropathy and Fisher syndrome, nerve terminal injury is dependent upon MAC pore formation and is attenuated by terminal complement inhibitors (5, 47–49). Once any MAC-mediated membrane injury has occurred, thereby allowing uncontrolled calcium influx and calpain activation (50), the ability of the endosomal machinery to actively endocytose additional AGAb will be severely compromised, and the pathological cascade would thus accelerate. In our studies, nerve terminals were pulsed with a high concentration of AGAb at a single time point, whereas in human disease, chronic exposure to smaller amounts of Ab over longer time frames occurs; thus, further consideration of the kinetics and saturation dynamics would need to be introduced to this model to predict the implications of these effects in humans.
Based on these data, we conclude that uptake of AGAbs at NMJs maintains nerve terminal integrity by attenuating complement activation, in contrast to the axolemmal membrane at the node of Ranvier. These effects could vary substantially between different neural and glial membranes. Such internalization events are very likely to modify the development of the clinical and pathological phenotypes observed in human AGAb-mediated disease in complex ways, modified by local factors including Ab access, dose, binding affinity, complement fixing properties, and complement regulation. It is clear that a highly dynamic environment exists at target membranes for AGAbs that needs to be considered when modeling such disorders.
Methods
Animals.
Adult male and female C57BL/6 mice and GD3s–/– mice were used (51). WT C57BL/6 mice express a normal repertoire of gangliosides, including the major “a” and “b” series gangliosides in their nerve terminals. GD3s–/– mice are unable to synthesize b-series gangliosides (e.g., GD3, GD1b, GT1b) and consequently overexpress a-series gangliosides (e.g., GM1, GD1a); thus, they are more vulnerable to the pathological effects of anti-GM1 and anti-GD1a Abs than WT mice, as a greater abundance of target is present (8). In the current studies, the use of GD3s–/– mice was restricted to experiments with anti-GM1 Ab. WT mice were used for studies on anti-GD1b and anti-GD1a Abs. To facilitate visualization of nerve terminal and pre-terminal axons, mice expressing the cytosolic CFP in axons [B6.Cg/TgN (Thy1-CFP)] (52) were used. Using these mice, we have shown that CFP leaks out through MAC pores in the axolemmal membrane, and thus the loss of intracytosolic CFP indirectly indicates a breaching of the axolemmal membrane integrity. These mice crossed with GD3s–/– mice are herein referred to as GD3s–/–/CFP, and the WT counterpart as WT/CFP.
Abs and reagents.
Mouse monoclonal AGAbs (anti-GM1, anti-GD1a, and anti-GD1b) were all IgG3 subclass and generated as described previously (53). In all ex vivo tissue studies, Abs were used at a concentration of 100 μg/ml in order to ensure an ample quantity of Ab was distributed through the various membrane and intracellular compartments for visualization purposes. The mouse IgG3 mAb, clone MG3-35 raised against TNP, was used as an isotype control (BioLegend).
Rabbit anti-EEA1 and anti-Rab11 were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc.; rabbit anti-Lamp1 from Abcam; rabbit anti–caveolin-1 and anti–neurofilament-M (anti–NF-M) from BD Biosciences; and mouse anti–C5b-9 from Dako. Anti-neurofascin Ab (clone A12/18.1, mouse IgG2a) was a gift from P. Brophy (Centre for Neuroregeneration, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, United Kingdom). FITC-labeled goat anti-mouse IgG3, TRITC-labeled goat anti-mouse IgG2a, and TRITC-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG were from SouthernBiotech. CTB, poly-l-lysine, and methyl-β-cyclodextrin were from Sigma-Aldrich. DMEM, FCS, horse serum (HS), penicillin/streptomycin, Alexa Fluor 488–labeled α-bungarotoxin (α-BTx-488, used to identify NMJs), and LysoT DND-99 were from Invitrogen. The CytoTox 96 kit was from Promega. The NHS used in this study was collected from a single donor and stored in aliquots at –80°C.
Cells.
PC12 cells, differentiated in DMEM-containing nerve growth factor (NGF, Sigma-Aldrich) for 4 days as previously described (54), were used for in vitro AGAb internalization assays. DRGNs from P15 embryonic rat were isolated and cultured as described (55). Neurons were identified by staining for NF using anti–NF-M Ab.
Microscopic image acquisition.
For PC12 cells, 30–50 cells were randomly selected and imaged using a Zeiss AxioImager Z1 equipped with an Apotome attachment and a ×63 objective. All images were acquired as Z-stack of 0.5-μm thickness with identical acquisition parameters. In each experiment, detection thresholds were first established and all data subsequently collected using these settings. Vesicular staining in cytoplasmic areas were imaged, and any staining that appeared to overlap with nuclei (as seen with the anti-Rab11 Ab) was excluded. Co-localization of fluorescence signals in either of two channels was determined using the co-localization module of the AxioVision software. Two signals were considered as strongly colocalizing if the Manders coefficient was equal to or greater than 0.7 (56, 57). For quantitative assessment of Ab and complement levels in all ex vivo TS preparations, images were collected using confocal microscopy (Zeiss LMS 5 Pascal) under constant acquisition settings and quantified using ImageJ software ( http://rsbweb.nih.gov/ij/) as previously described (23). For illustrations, all images were collected using a Zeiss AxioImager equipped with an Apotome and AxioVision software. For sciatic nerve teased fiber studies, Ab and complement deposits at 30–50 nodes of Ranvier per condition were imaged and quantified in 3 independent experiments using the AxioImager Z1 equipped with an Apotome attachment as above for PC12 cells and as previously described (5).
In vitro Ab-mediated complement-dependent cytotoxic assay.
Differentiated PC12 cells (1500) seeded onto poly-l-lysine–coated 96-well plates were labeled with anti-GM1, anti-GD1b, or anti-GD1a (10 μg/ml in DMEM plus 1% BSA) for 1 hour. Cells were rinsed twice with serum-free DMEM and incubated at 37°C for 15, 30, and 60 minutes in the same medium. Following incubation, cells were rinsed once with PBS and exposed to 50 μl of 40% NHS for 60 minutes at 37°C alongside 40% heat-inactivated NHS, lysis buffer (positive control), and Ab-untreated cells (background control). Plates were then centrifuged at room temperature (RT) for 4 minutes at 250 g, and the supernatant was transferred to 96-well ELISA plates. The cytotoxicity assay and cell death estimation were performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
TS preparation and Ab internalization assay.
TS samples from adult mice were freshly dissected in Ringer’s solution (119 mM NaCl, 4.5 mM KCl, 2 mM CaCl2, 1 mM MgSO4, 1 mM NaH2PO4, 23 mM NaHCO3, 11 mM glucose, pH 7.4, pre-gassed with 95% O2/5% CO2) as described previously (5). TS preparations from WT/CFP mice were incubated with anti-GD1a or anti-GD1b Ab (100 μg/ml in Ringer’s) for 2 hours at 4°C. For anti-GM1 Ab, TS preparations from GD3s–/–/CFP mice were used. In control tissue, either Ab was omitted or mouse IgG3 mAb control was used. After AGAb binding, tissues were rinsed with Ringer’s and incubated at 37°C in Ringer’s for 30 and 60 minutes, followed sequentially by 4% PFA (20 minutes), 0.1 M glycine (10 minutes), 5% normal goat serum (NGS) (15 minutes), goat anti-mouse IgG3–TRITC (1:300) and α-BTx-488 (1:500) diluted in PBS (2 hours), all at RT. Finally, tissues were rinsed in PBS mounted in Citifluor and imaged. To subsequently visualize internalized Ab, tissues were removed from the microscopic slides, washed in water, incubated for 30 minutes in 0.5% Triton X-100, and blocked with 5% NGS at RT. Internalized AGAb was then visualized by reincubating tissue with goat anti-mouse IgG3–TRITC (1:300) and α-BTx-488 (1:500) for 4 hours at RT. Tissues were washed, remounted, and reimaged. AGAb deposits at nerve terminals (identified by α-BTx staining) were quantified as described above (23, 24).
For experiments on AGAb uptake at the node of Ranvier, 5 mm of sciatic nerve was dissected from GD3s–/– mice and rapidly teased into individual fibers on microscopic slides in Ringer’s solution. Teased fibers were incubated with anti-GM1 Ab (100 μg/ml in Ringer’s) at 4°C for 60 minutes, rinsed, and incubated at 37°C in Ringer’s for 30 and 60 minutes. After incubation, the tissues were further rinsed, incubated in 4% PFA (20 minutes) and then 5% NGS (30 minutes), both at RT. In parallel, tissues treated as above were permeabilized with 0.5% Triton X-100 to detect any internalized Ab. Nodes of Ranvier were identified using anti-neurofascin Ab (1:100, overnight at 4°C). Tissues were then rinsed and incubated with goat anti-mouse IgG3–FITC and goat anti-mouse IgG2a–TRITC and quantified.
AGAb-mediated complement activation and injury.
To investigate the effect of AGAb uptake on complement activation at the presynaptic nerve terminal, we first labeled TS preparations with anti-GM1, anti-GD1b, and anti-GD1a Abs (100 μg/ml) at 4°C for 2 hours. TS preparations were then either immediately exposed to 40% NHS for 60 minutes, or first incubated at 37°C for 60 minutes in Ringer’s solution (to allow endocytosis to occur) and then exposed to 40% NHS for 60 minutes. TS preparations were then rinsed and blocked with 5% NGS, then incubated with mouse anti–human C5b-9 (1:50) and α-BTx-488 (1:500) in Ringer’s solution overnight. Tissue was then sequentially rinsed, fixed for 20 minutes at RT with 4% PFA, incubated at RT for 3 hours with TRITC-labeled goat anti-mouse IgG2a (1:300) and α-BTx (1:500) in PBS, washed, mounted, and imaged. MAC deposits at NMJs were estimated as above. The integrity of the presynaptic membrane was monitored by assessing the CFP intensity (present or absent), and the percentage of healthy NMJs was calculated.
To investigate the effect of Ab uptake on complement activation at the node of Ranvier, sciatic nerves from GD3s–/– mice were teased and labeled with anti-GM1 Ab as described above. Teased fibers were then either directly exposed to 40% NHS or further incubated at 37°C for 60 minutes in Ringer’s solution (to allow endocytosis), followed by 60 minutes incubation at RT in 40% NHS. Teased fibers were then rinsed, incubated at RT for 20 minutes in 4% PFA, blocked with 5% NGS for 30 minutes at RT, exposed to mouse anti–human C5b-9 (1:50) overnight at 4°C, washed in PBS and incubated with goat anti-mouse IgG2a–FITC (1:300), and imaged for quantification
NMJ electrophysiology and fiber twitch observation.
To investigate whether AGAb uptake limits complement-dependent pathophysiology at the NMJ, we performed micro-electrode electrophysiology (22). Muscle fiber twitching (grade 0–4), which results from uncontrolled acetylcholine release caused by AGAb/complement-mediated presynaptic damage, was also scored (58). Hemidiaphragms from GD3s–/– mice were exposed to anti-GM1 mAb (100 μg/ml) at 32°C for 2 hours, followed by 30 minutes at 4°C and 10 minutes at RT. NHS (33%) was added at RT to one of the hemidiaphragms directly thereafter and to the contralateral hemidiaphragm after a further 1-hour incubation period in Ringer’s medium at 37°C. After 1 hour in the presence of NHS, MEPPs (the postsynaptic responses to uniquantal acetylcholine release) were measured at multiple NMJs in each preparation. Concomitantly, the intensity of muscle fiber twitching was scored every 5 minutes.
AGAb-mediated injury of the nerve terminal in vital imaging studies.
To investigate the effect of AGAb uptake at NMJs on complement activation in living mice, the sternomastoid muscles of adult WT/CFP mice under general anesthesia were exposed and anti-GD1a Ab (200 μg/ml plus BTx-555, diluted 1:500, in Ringer’s solution) was topically applied, together with 40% NHS (0-minute time point). In a second group, anti-GD1a Ab alone was applied for 30 minutes, followed by 60 minutes incubation in Ringer’s (to allow Ab uptake), then 30 minutes with 40% NHS (60-minute time point). Control animals received either Ringer’s or heat-inactivated NHS. Mice were then sacrificed, and the sternomastoid muscles were fixed in situ with 4% PFA for 1 hour, rinsed with PBS, and imaged as a whole mount preparation. A total of 12 mice were studied in 3 independent experiments. NMJs of the extracted sternomastoid muscles were assessed quantitatively for loss of CFP overlying the α-BTx signal with a Zeiss AxioImager and AxioVision software.
Cholesterol sequestration.
To evaluate the effect of membrane cholesterol removal on the uptake of AGAb in vitro, PC12 cells were pretreated with 5 mM of MβCD for 30 minutes at 37°C (34, 35). MβCD-treated and untreated cells were incubated at 4°C for 1 hour with AGAbs (10 μg/ml). Upon labeling, the cells were rinsed with cold PBS and incubated at 37°C for 30 minutes in PBS to allow Ab uptake. PC12 cells were then fixed (4% PFA for 15 minutes at RT), permeabilized (0.1% Triton X-100 for 5 minutes at RT), blocked (5% NGS for 30 minutes at RT), and incubated for 1 hour at RT with FITC-labeled goat anti-mouse IgG3 (1:300). Surface and internalized AGAb was quantified in 30–50 randomly selected cells. Images within the same experiment were acquired as Z-stack of 0.5-μm thickness with identical acquisition parameters. For each visual field, cells in the same focal plane were manually selected following either the cell contour (total AGAbs) or the intracellular contour (internalized AGAbs). A maximum of 4 Z-stacks were analyzed per cell and the results expressed as percentage of total surface AGAbs.
To evaluate the effect of membrane cholesterol depletion on the uptake of AGAb at live nerve terminals, we pretreated mouse ex vivo TS preparations with 5 mM MβCD (or PBS as control) at 37°C for 30 minutes. Preparations were then labeled with anti-GD1b (100 μg/ml) or mouse IgG3 isotype control (100 μg/ml) at 4°C for 2 hours. TS preparations were rinsed with cold Ringer’s solution and incubated at 37°C in Ringer’s for 30 minutes, further rinsed at 4°C with Ringer’s, and incubated in 5% NGS for 30 minutes. Surface anti-GD1b was detected by incubation of the TS preparations with TRITC-labeled IgG3 (1:300) containing FITC-labeled α-BTx (1:50). TS preparations were rinsed with Ringer’s and incubated in 4% PFA for 20 minutes at RT, rinsed with PBS, mounted, imaged, and quantified. To evaluate the effect of MβCD treatment on MAC deposition at the nerve terminal, TS preparations from WT and GD3s–/– mice pretreated with 5 mM MβCD (or PBS as control) for 30 minutes at 37°C were labeled with anti-GD1b (100 μg/ml) and anti-GM1 (100 μg/ml) for 2 hours at 4°C, respectively, rinsed with Ringer’s, then incubated at 37°C in Ringer’s for 30 minutes. Other TS control preparations were incubated in parallel with mouse IgG3 isotype control (100 μg/ml). TS preparations were then rinsed with Ringer’s and exposed to 40% NHS for 60 minutes at RT, then fixed for 30 minutes by incubation with 4% PFA and blocked for 30 minutes with 5% NGS. MAC deposits at NMJs were detected using mouse anti–human C5b-9 (1:50) and α-BTx-488 (1:500), followed by secondary Ab, then imaged and quantified for complement levels and NMJ integrity as described above.
Surface ganglioside depletion studies.
To investigate whether AGAb uptake depletes ganglioside epitopes from the surface of presynaptic nerve terminals, TS preparations from WT and GD3s–/– mice were labeled for 2 hours at 4°C with anti-GD1b and anti-GM1 Abs (100 μg/ml), respectively. TS preparations were then sequentially rinsed, incubated at 37°C for 30 minutes (to allow endocytosis), rinsed with Ringer’s at 4°C, and further incubated with anti-GD1b and anti-GM1 Abs for an additional 2 hours at 4°C to determine the level of remaining surface ganglioside. These data were compared with control TS preparations labeled with 100 μg/ml anti-GD1b and anti-GM1 Abs or 100 μg/ml mouse IgG3 (isotype control) not subjected to the Ab uptake step.
In comparative studies using CTB, which is known to internalize in complex with GM1, TS preparations were first incubated with CTB for 2 hours at 4°C, then at 37°C for 30 minutes (to allow endocytosis). Residual surface GM1 ganglioside was then quantified using anti-GM1 (100 μg/ml) Ab as above and compared with control (i.e., preparations not subjected to pretreatment with CTB).
In vitro endocytosis.
To assess endocytosis, 20,000 undifferentiated PC12 cells were seeded onto poly-l-lysine–coated (10 μg/ml) coverslips (13 mm) and cultured for 4 days at 37°C in DMEM supplemented with 4.5 g/l glucose, 5% (v/v) HS, 5% (v/v) FCS, 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 μg/ml streptomycin, and 100 ng/ml NGF. Thereafter, the cells were chilled on ice for 10 minutes and further incubated with anti-GM1, -GD1a, and -GD1b (10 μg/ml) for 60 minutes. Cells were rinsed with cold PBS and incubated in pre-warmed serum-free DMEM for 15, 30, and 60 minutes at 37°C, followed by 15 minutes incubation in 4% PFA and 5 minutes in 0.1% Triton X-100 at RT. The permeabilized PC12 cells were further incubated with 5% NGS at RT and the internalized cargoes visualized using FITC-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG3 (1:300 in PBS).
To follow the bulk of internalized AGAbs, PC12 cells were treated as described above. Following permeabilization, cells were incubated at 4°C overnight with rabbit anti-EEA1 (1:100), rabbit anti-Lamp1 (1 μg/ml), rabbit anti-Rab11 (1:100), and rabbit anti–caveolin-1 (1:100). The next day, cells were rinsed twice and incubated for 1 hour at RT with FITC-labeled goat anti-mouse IgG3 (1:300) and TRITC-labeled goat anti–rabbit IgG (1:300). Cells were washed and mounted using VECTASHIELD (Vector Laboratories) mounting medium containing DAPI for imaging of AGAb internalization.
To label acidic vesicles, PC12 cells were preincubated at 37°C for 1 hour with 75 nM LysoT DND-99 diluted in serum-free DMEM before AGAb labeling. The cells were then further treated and analyzed as described above. To investigate the uptake of anti-GD1b Ab by DRGNs, purified neurons were labeled with anti-GD1b Ab and the Ab allowed to internalize for 15, 30, and 60 minutes at 37°C. The cells were treated and analyzed as described above.
Statistics.
For PC12 cells, data from quantification and co-localization analyses were collected from images obtained from 2 independent coverslips per condition in 3 independent experiments. Data are expressed as mean values ± SEM. Statistical significance was determined by 1-tailed t test using Minitab software. For tissue preparations in which nonparametric data were obtained, all data are expressed as median values and interquartile ranges and were analyzed by the Mann-Whitney U test using Minitab software. All quantitative fluorescence data are expressed as fluorescence intensity units (AU) and represent the results of data acquisition from a minimum of 120 NMJs per condition and per time point, analyzed in 3 independent experiments. P values less than 0.05 were considered significant.
Study approval.
All animals experiments were carried out under UK Home Office Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act 1986, license number PPL 60/3842, and the University of Glasgow Ethical Review Process (ERP) committee. Study approval and written informed consent were received for the donor of the NHS used in the study by the West of Scotland Research Ethics Service.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful to Gwyn Gould, University of Glasgow, and Giampietro Schiavo of the Cancer Research UK London Research Institute for critical suggestions and review of the manuscript.
Footnotes
Conflict of interest: The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Citation for this article: J Clin Invest. 2012;122(3):1037–1051. doi:10.1172/JCI59110.
References
- 1.Willison HJ, Yuki N. Peripheral neuropathies and anti-glycolipid antibodies. Brain. 2002;125(pt 12):2591–2625. doi: 10.1093/brain/awf272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hafer Macko C, et al. Acute motor axonal neuropathy: an antibody-mediated attack on axolemma. Ann Neurol. 1996;40(4):635–644. doi: 10.1002/ana.410400414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Paparounas K, O’Hanlon GM, O’Leary CP, Rowan EG, Willison HJ. Anti-ganglioside antibodies can bind peripheral nerve nodes of Ranvier and activate the complement cascade without inducing acute conduction block in vitro. Brain. 1999;122(pt 5):807–816. doi: 10.1093/brain/122.5.807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Susuki K, et al. Anti-GM1 antibodies cause complement-mediated disruption of sodium channel clusters in peripheral motor nerve fibers. J Neurosci. 2007;27(15):3956–3967. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4401-06.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.McGonigal R, et al. Anti-GD1a antibodies activate complement and calpain to injure distal motor nodes of Ranvier in mice. Brain. 2010;133(pt 7):1944–1960. doi: 10.1093/brain/awq119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Goodyear CS, et al. Monoclonal antibodies raised against Guillain-Barré syndrome-associated Campylobacter jejuni lipopolysaccharides react with neuronal gangliosides and paralyze muscle-nerve preparations. . J Clin Invest. 1999;104(6):697–708. doi: 10.1172/JCI6837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Buchwald B, et al. Anti-ganglioside antibodies alter presynaptic release and calcium influx. Neurobiol Dis. 2007;28(1):113–121. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2007.07.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Goodfellow JA, et al. Overexpression of GD1a ganglioside sensitizes motor nerve terminals to anti-GD1a antibody-mediated injury in a model of acute motor axonal neuropathy. J Neurosci. 2005;25(7):1620–1628. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4279-04.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Plomp JJ, Willison HJ. Pathophysiological actions of neuropathy-related anti-ganglioside antibodies at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 2009;587(pt 16):3979–3999. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.171702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Martin PT. Glycobiology of the neuromuscular junction. J Neurocytol. 2003;32(5–8):915–929. doi: 10.1023/B:NEUR.0000020632.41508.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Halpern JL, Loftus A. Characterization of the receptor-binding domain of tetanus toxin. J Biol Chem. 1993;268(15):11188–11192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bullens RWM, et al. Complex gangliosides at the neuromuscular junction are membrane receptors for autoantibodies and botulinum neurotoxin but redundant for normal synaptic function. J Neurosci. 2002;22(16):6876–6884. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-16-06876.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Perissinotti PP, Tropper BG, Uchitel OD. L-type calcium channels are involved in fast endocytosis at the mouse neuromuscular junction. Eur J Neurosci. 2008;27(6):1333–1344. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06113.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ritchie TC, Fabian RH, Choate JVA, Coulter JD. Axonal transport of monoclonal antibodies. J Neurosci. 1986;6(4):1177–1184. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-04-01177.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Fabian RH. Uptake of normal immunoglobulins by motor neurons in the rat — a study using radioiodinated Igg. Drug Dev Res. 1988;15(2–3):189–194. doi: 10.1002/ddr.430150211. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chinnapen DJ, Chinnapen H, Saslowsky D, Lencer WI. Rafting with cholera toxin: endocytosis and trafficking from plasma membrane to ER. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2007;266(2):129–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00545.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Deinhardt K, Berninghausen O, Willison HJ, Hopkins CR, Schiavo G. Tetanus toxin is internalized by a sequential clathrin-dependent mechanism initiated within lipid microdomains and independent of epsin 1. J Cell Biol. 2006;174(3):459–471. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200508170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Spooner RA, Smith DC, Easton AJ, Roberts LM, Lord JM. Retrograde transport pathways utilised by viruses and protein toxins. Virol J. 2006;3:26. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-3-26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Stenmark P, Dupuy J, Imamura A, Kiso M, Stevens RC. Crystal structure of botulinum neurotoxin type a in complex with the cell surface co-receptor GT1b — insight into the toxin-neuron interaction. PLoS Pathog. 2008;4(8):e1000129. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kusunoki S, Chiba A, Tai T, Kanazawa I. Localization of GM1 and GD1b antigens in the human peripheral nervous system. Muscle Nerve. 1993;16(7):752–756. doi: 10.1002/mus.880160710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Willison HJ. The immunobiology of Guillain-Barre syndromes. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2005;10(2):94–112. doi: 10.1111/j.1085-9489.2005.0010202.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zitman FMP, et al. Neuromuscular synaptic function in mice lacking major subsets of gangliosides. Neuroscience. 2008;156(4):885–897. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.08.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Greenshields KN, et al. The neuropathic potential of anti-GM1 autoantibodies is regulated by the local glycolipid environment in mice. J Clin Invest. 2009;119(3):595–610. doi: 10.1172/JCI37338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.O’Hanlon GM, et al. Anti-GQ1b ganglioside antibodies mediate complement-dependent destruction of the motor nerve terminal. Brain. 2001;124(pt 5):893–906. doi: 10.1093/brain/124.5.893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.O’Hanlon GM, Bullens RWM, Plomp JJ, Willison HJ. Complex gangliosides as autoantibody targets at the neuromuscular junction in Miller Fisher syndrome: a current perspective. Neurochem Res. 2002;27(7–8):697–709. doi: 10.1023/A:1020284302718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ho TW, et al. Motor nerve terminal degeneration provides a potential mechanism for rapid recovery in acute motor axonal neuropathy after Campylobacter infection. Neurology. 1997;48(3):717–724. doi: 10.1212/wnl.48.3.717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kuwabara S, et al. Neuromuscular transmission is not impaired in axonal Guillain-Barre syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2011;82(10):1174–1177. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.2010.210708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kuwabara S, et al. Anti–GQ1b antibody does not affect neuromuscular transmission in human limb muscle. J Neuroimmunol. 2007;189(1–2):158–162. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2007.07.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Engstler M, et al. Hydrodynamic flow-mediated protein sorting on the cell surface of trypanosomes. Cell. 2007;131(3):505–515. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.08.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Iglesias-Bartolome R, Crespo PM, Gomez GA, Daniotti JL. The antibody to GD3 ganglioside, R24, is rapidly endocytosed and recycled to the plasma membrane via the endocytic recycling compartment. Inhibitory effect of brefeldin A and monensin. FEBS J. 2006;273(8):1744–1758. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2006.05194.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Iglesias-Bartolome R, Trenchi A, Comin R, Moyano AL, Nores GA, Daniotti JL. Differential endocytic trafficking of neuropathy-associated antibodies to GM1 ganglioside and cholera toxin in epithelial and neural cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1788(12):2526–2540. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2009.09.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Appel SH, Anwyl R, McAdams MW, Elias S. Accelerated degradation of acetylcholine receptor from cultured rat myotubes with myasthenia gravis sera and globulins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977;74(5):2130–2134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Clift-O’Grady L, Linstedt AD, Lowe AW, Grote E, Kelly RB. Biogenesis of synaptic vesicle-like structures in a pheochromocytoma cell line PC-12. J Cell Biol. 1990;110(5):1693–1703. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.5.1693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Yao Y, Hong S, Zhou H, Yuan T, Zeng R, Liao K. The differential protein and lipid compositions of noncaveolar lipid microdomains and caveolae. Cell Res. 2009;19(4):497–506. doi: 10.1038/cr.2009.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Rodal SK, Skretting G, Garred O, Vilhardt F, van Deurs B, Sandvig K. Extraction of cholesterol with methyl-beta-cyclodextrin perturbs formation of clathrin-coated endocytic vesicles. Mol Biol Cell. 1999;10(4):961–974. doi: 10.1091/mbc.10.4.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Subtil A, Gaidarov I, Kobylarz K, Lampson MA, Keen JH, Mcgraw TE. Acute cholesterol depletion inhibits clathrin-coated pit budding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96(12):6775–6780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.12.6775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Torgersen ML, Skretting G, van Deurs B, Sandvig K. Internalization of cholera toxin by different endocytic mechanisms. J Cell Sci. 2001;114(pt 20):3737–3747. doi: 10.1242/jcs.114.20.3737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Roux S, et al. Internalization of a GFP-tetanus toxin C-terminal fragment fusion protein at mature mouse neuromuscular junctions. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2005;30(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2005.05.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Bucci C, et al. The small Gtpase Rab5 functions as a regulatory factor in the early endocytic pathway. Cell. 1992;70(5):715–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90306-W. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.van der Sluijs P, Hull M, Webster P, Male P, Goud B, Mellman I. The small GTP-binding protein rab4 controls an early sorting event on the endocytic pathway. Cell. 1992;70(5):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90307-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Deinhardt K, et al. Rab5 and Rab7 control endocytic sorting along the axonal retrograde transport pathway. Neuron. 2006;52(2):293–305. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.08.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Leterrier C, Brachet A, Dargent B, Vacher H. Determinants of voltage-gated sodium channel clustering in neurons. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011;22(2):171–177. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2010.09.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Deinhardt K, Reversi A, Berninghausen O, Hopkins CR, Schiavo G. Neurotrophins redirect p75(NTR) from a clathrin-independent to a clathrin-dependent endocytic pathway coupled to axonal transport. Traffic. 2007;8(12):1736–1749. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2007.00645.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Geny B, Popoff MR. Bacterial protein toxins and lipids: pore formation or toxin entry into cells. Biol Cell. 2006;98(11):667–678. doi: 10.1042/BC20050082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Halstead SK, et al. Anti-disialoside antibodies kill perisynaptic Schwann cells and damage motor nerve terminals via membrane attack complex in a murine model of neuropathy. Brain. 2004;127(pt 9):2109–2123. doi: 10.1093/brain/awh231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Willison HJ, Plomp JJ. Anti-ganglioside antibodies and the presynaptic motor nerve terminal. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008;1132:114–123. doi: 10.1196/annals.1405.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Halstead SK, Humphreys PD, Zitman FMP, Hamer J, Plomp JJ, Willison HJ. C5 inhibitor rEV576 protects against neural injury in an in vitro mouse model of Miller Fisher syndrome. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2008;13(3):228–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1529-8027.2008.00181.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Halstead SK, et al. Eculizumab prevents anti-ganglioside antibody-mediated neuropathy in a murine model. Brain. 2008;131(pt 5):1197–1208. doi: 10.1093/brain/awm316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Halstead SK, Humphreys PD, Goodfellow JA, Wagner ER, Smith RAG, Willison HJ. Complement inhibition abrogates nerve terminal injury in Miller Fisher syndrome. Ann Neurol. 2005;58(2):203–210. doi: 10.1002/ana.20546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.O’Hanlon GM, et al. Calpain inhibitors protect against axonal degeneration in a model of anti-ganglioside antibody-mediated motor nerve terminal injury. Brain. 2003;126(pt 11):2497–2509. doi: 10.1093/brain/awg254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Okada M, et al. b-series Ganglioside deficiency exhibits no definite changes in the neurogenesis and the sensitivity to fas-mediated apoptosis but impairs regeneration of the lesioned hypoglossal nerve. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(3):1633–1636. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C100395200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Feng G, et al. Imaging neuronal subsets in transgenic mice expressing multiple spectral variants of GFP. Neuron. 2000;28(1):41–51. doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)00084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Boffey J, et al. Characterisation of the immunoglobulin variable region gene usage encoding the murine anti–ganglio side antibody repertoire. . J Neuroimmunol. 2005;165(1–2):92–103. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2005.04.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Townson KH, Speak AO, Greenshields KN, Goodyear CS, Willison HJ, Platt FM. Glycosphingolipid depletion in PC12 cells using iminosugars protects neuronal membranes from anti-ganglioside antibody mediated injury. J Neuroimmunol. 2008;203(1):33–38. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2008.06.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Päiväläinen S, et al. Myelination in mouse dorsal root ganglion/Schwann cell cocultures. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2008;37(3):568–578. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2007.12.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Manders EMM, Verbeek FJ, Aten JA. Measurement of colocalization of objects in dual-color confocal images. J Microscopy. 1993;169(3):375–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1993.tb03313.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Zinchuk V, Grossenbacher-Zinchuk O. Recent advances in quantitative colocalization analysis: focus on neuroscience. Prog Histochem Cytochem. 2009;44(3):125–172. doi: 10.1016/j.proghi.2009.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Jacobs BC, Bullens RWM, O’Hanlon GM, Ang CW, Willison HJ, Plomp JJ. Detection and prevalence of alpha-Latrotoxin-like effects of serum from patients with Guillain-Barre syndrome. Muscle Nerve. 2002;25(4):549–558. doi: 10.1002/mus.10060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.