Abstract
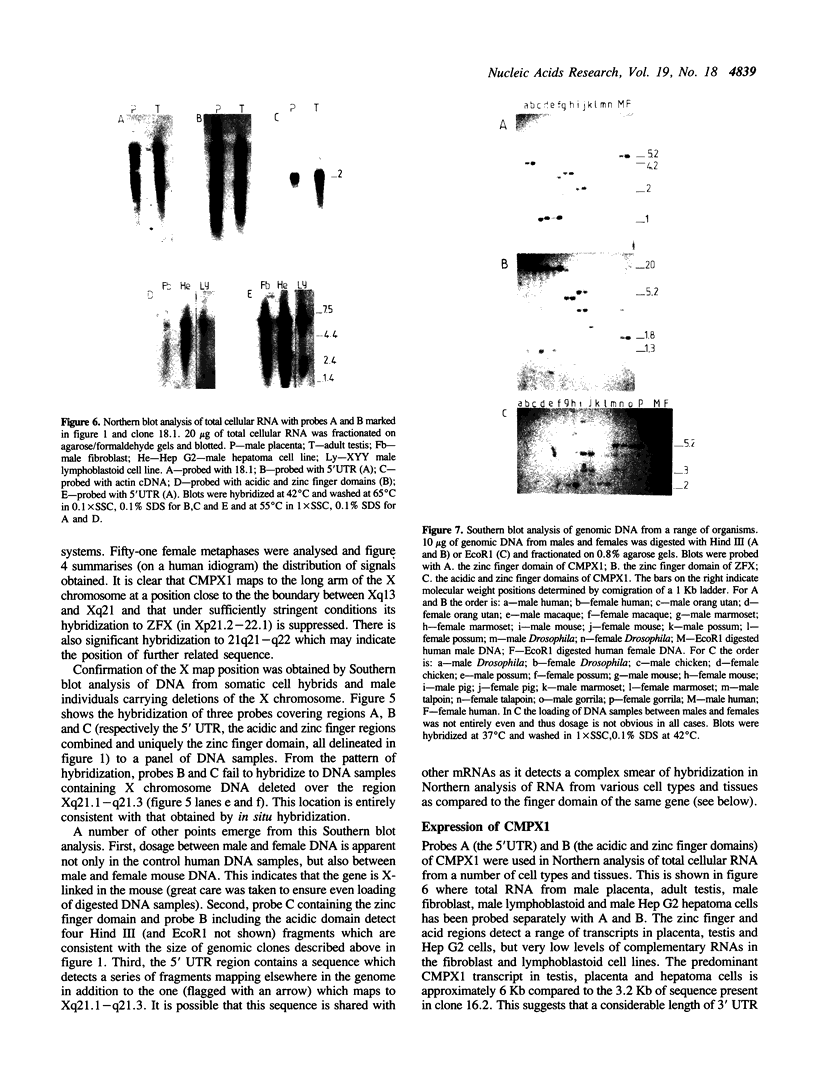
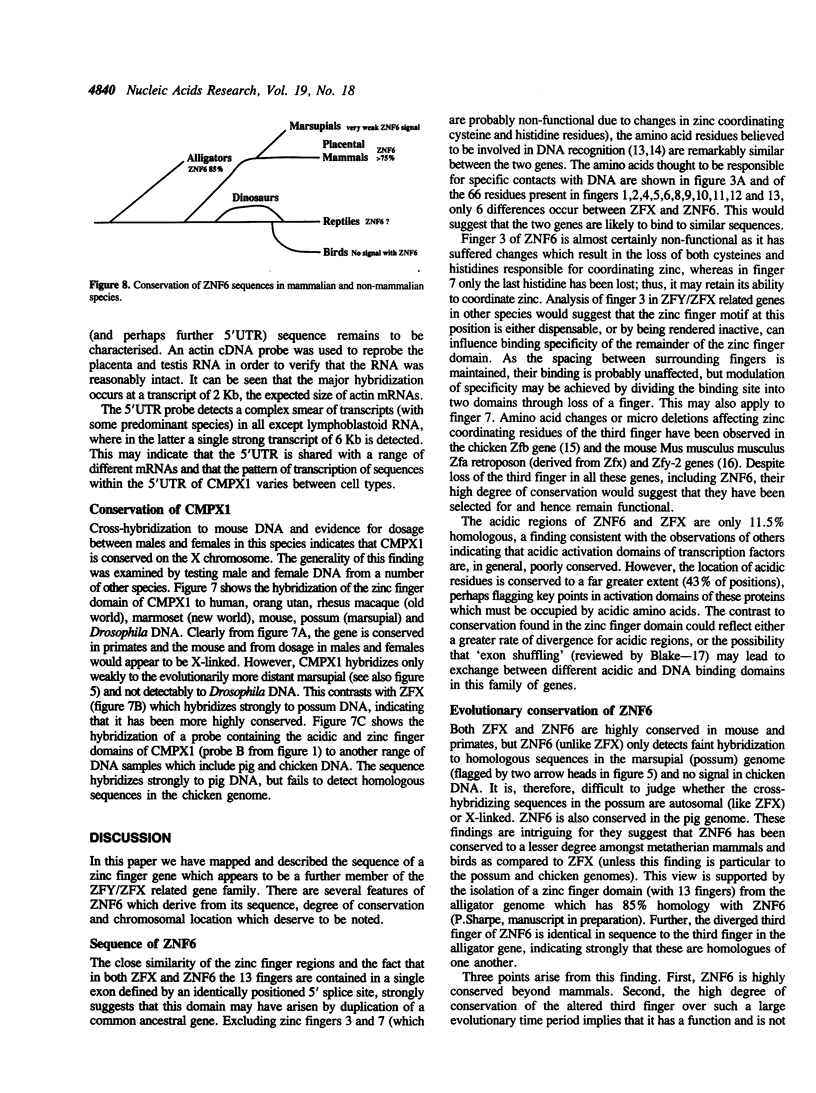
We describe a new zinc finger gene sequence (CMPX1 or HGM symbol ZNF6; isolated by cross-hybridization of ZFY to clones in a testis cDNA library) which possesses a zinc finger domain closely related to the transcriptional activator gene ZFX. The putative acidic activation domain is only 11.5% homologous with ZFX, whereas the putative DNA binding domain shares 75% homology and shows the same organisation composed of a basic two fingered repeat unit. ZNF6 has an unusually large 5' untranslated region (UTR) of 1.2 Kb which contains 26 potential ATG initiation codons, only one of which is associated with a long open reading frame. Southern and Northern blot analysis has shown that this 5' UTR is shared with many other sequences in the genome and transcribed associated with a large range of mRNA species. In situ hybridisation, analysis of somatic cell hybrids and male individuals carrying deleted X chromosomes have mapped the gene to Xq21.1-q21.3. The gene is highly conserved amongst the primates, in the mouse and can be detected weakly in the genome of a metatherian mammal (possum). Dosage in male and female mice indicates that it is also X-linked in this species. Possible origins of ZFX, ZFY and CMPX1 from a common ancestral gene are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Affara N. A., Chambers D., O'Brien J., Habeebu S. S., Kalaitsidaki M., Bishop C. E., Ferguson-Smith M. A. Evidence for distinguishable transcripts of the putative testis determining gene (ZFY) and mapping of homologous cDNA sequences to chromosomes X,Y and 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 25;17(8):2987–2999. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.8.2987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Affara N. A., Florentin L., Morrison N., Kwok K., Mitchell M., Cook A., Jamieson D., Glasgow L., Meredith L., Boyd E. Regional assignment of Y-linked DNA probes by deletion mapping and their homology with X-chromosome and autosomal sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5353–5373. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amar L. C., Dandolo L., Hanauer A., Cook A. R., Arnaud D., Mandel J. L., Avner P. Conservation and reorganization of loci on the mammalian X chromosome: a molecular framework for the identification of homologous subchromosomal regions in man and mouse. Genomics. 1988 Apr;2(3):220–230. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashworth A., Skene B., Swift S., Lovell-Badge R. Zfa is an expressed retroposon derived from an alternative transcript of the Zfx gene. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1529–1534. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08271.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Proposed structure for the zinc-binding domains from transcription factor IIIA and related proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):99–102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake C. Exons--present from the beginning? Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):535–537. doi: 10.1038/306535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiLella A. G., Page D. C., Smith R. G. A bird zinc-finger protein closely related to ZFY. New Biol. 1990 Jan;2(1):49–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher E. M., Beer-Romero P., Brown L. G., Ridley A., McNeil J. A., Lawrence J. B., Willard H. F., Bieber F. R., Page D. C. Homologous ribosomal protein genes on the human X and Y chromosomes: escape from X inactivation and possible implications for Turner syndrome. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1205–1218. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90416-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopman P., Ashworth A., Lovell-Badge R. The ZFY gene family in humans and mice. Trends Genet. 1991 Apr;7(4):132–136. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90458-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau Y. F., Chan K. M. The putative testis-determining factor and related genes are expressed as discrete-sized transcripts in adult gonadal and somatic tissues. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Dec;45(6):942–952. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. C., Simonsen C. C., Levinson A. D. Initiation of translation at internal AUG codons in mammalian cells. Nature. 1984 May 3;309(5963):82–85. doi: 10.1038/309082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mardon G., Luoh S. W., Simpson E. M., Gill G., Brown L. G., Page D. C. Mouse Zfx protein is similar to Zfy-2: each contains an acidic activating domain and 13 zinc fingers. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):681–688. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell M., Simon D., Affara N., Ferguson-Smith M., Avner P., Bishop C. Localization of murine X and autosomal sequences homologous to the human Y located testis-determining region. Genetics. 1989 Apr;121(4):803–809. doi: 10.1093/genetics/121.4.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. P., Hinnebusch A. G. Multiple upstream AUG codons mediate translational control of GCN4. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):201–207. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90384-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardelli J., Gibson T. J., Vesque C., Charnay P. Base sequence discrimination by zinc-finger DNA-binding domains. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):175–178. doi: 10.1038/349175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North M., Sargent C., O'Brien J., Taylor K., Wolfe J., Affara N. A., Ferguson-Smith M. A. Comparison of ZFY and ZFX gene structure and analysis of alternative 3' untranslated regions of ZFY. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 25;19(10):2579–2586. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.10.2579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page D. C., Mosher R., Simpson E. M., Fisher E. M., Mardon G., Pollack J., McGillivray B., de la Chapelle A., Brown L. G. The sex-determining region of the human Y chromosome encodes a finger protein. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1091–1104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90595-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer M. S., Sinclair A. H., Berta P., Ellis N. A., Goodfellow P. N., Abbas N. E., Fellous M. Genetic evidence that ZFY is not the testis-determining factor. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):937–939. doi: 10.1038/342937a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider-Gädicke A., Beer-Romero P., Brown L. G., Mardon G., Luoh S. W., Page D. C. Putative transcription activator with alternative isoforms encoded by human ZFX gene. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):708–711. doi: 10.1038/342708a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider-Gädicke A., Beer-Romero P., Brown L. G., Nussbaum R., Page D. C. ZFX has a gene structure similar to ZFY, the putative human sex determinant, and escapes X inactivation. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1247–1258. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90061-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]