Abstract
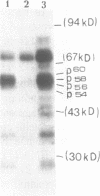
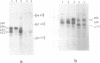
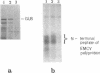
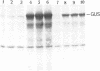
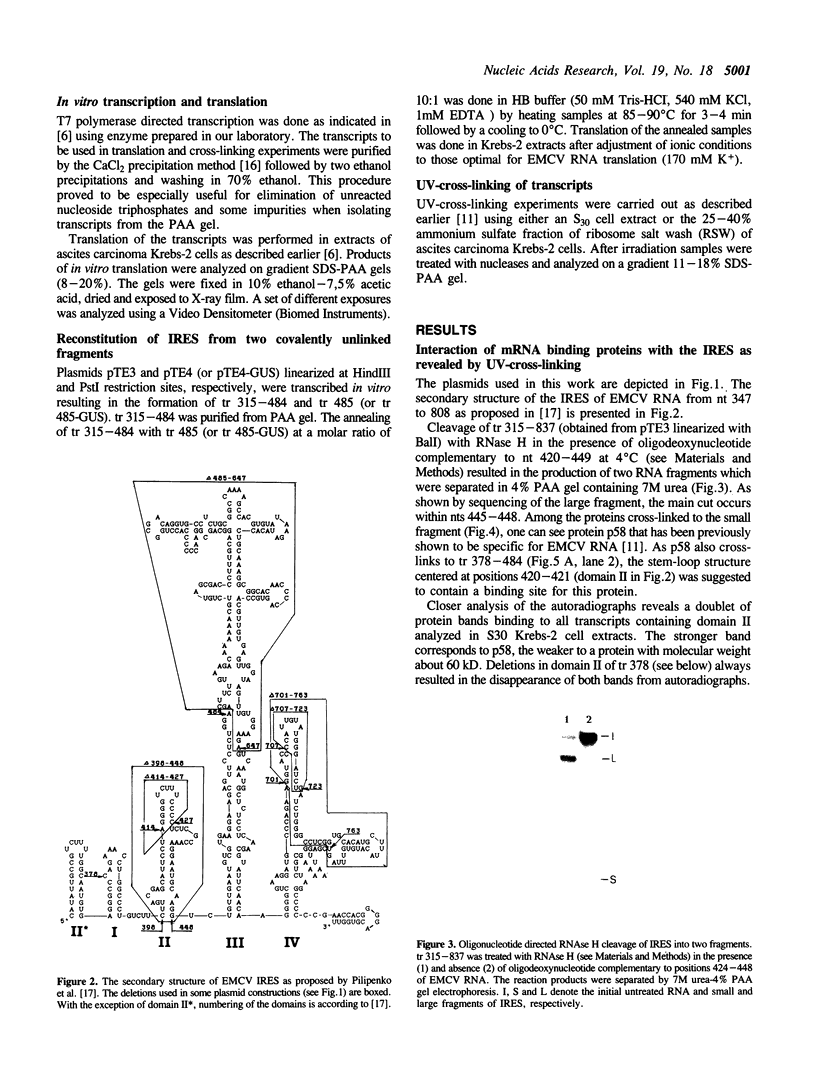
Various derivatives of the internal ribosomal entry site (IRES) of encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV) RNA have been used to analyze by UV-cross-linking its interaction with mRNA binding proteins from ascites carcinoma Krebs-2 cells. A doublet of proteins with Mr 58 and 60 kD bound to two regions of the IRES. One site is centered at nt 420-421 of EMCV RNA whereas the other is located between nt 315-377. Both sites form hairpin structures, the loops of which contain UCUUU motif, conserved among cardio- and aphthoviruses. The interaction of p58 and p60 with IRES is affected by the integrity of the stem-loop structure proximal to the start AUG codon (nts 680-787), although, under similar conditions, cross-linking of these proteins to this region was not detected. Deletions in the main recognition site of p58 strongly reduce the initiation activity of the IRES in vitro. However, elimination of p58 (p60) binding by these mutations does not completely abolish the ability of the IRES to direct polypeptide synthesis starting from the authentic AUG codon. The IRES can be assembled in vitro from two covalently unlinked transcripts, one containing the target site for p58 and the other encompassing the remaining part of the IRES fused to a reporter gene, resulting in considerable restoration of its activity. Implications of these findings for the mechanism of initiation resulting from internal entry of ribosomes are discussed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belsham G. J., Brangwyn J. K. A region of the 5' noncoding region of foot-and-mouth disease virus RNA directs efficient internal initiation of protein synthesis within cells: involvement with the role of L protease in translational control. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5389–5395. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5389-5395.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borovjagin A. V., Evstafieva A. G., Ugarova TYu, Shatsky I. N. A factor that specifically binds to the 5'-untranslated region of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA. FEBS Lett. 1990 Feb 26;261(2):237–240. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80561-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolja V. V., Negruk V. I., Novikov V. K., Atabekov J. G. A simple method for isolating pure RNA preparations after electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gel. Anal Biochem. 1977 Jun;80(2):502–506. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner A. J., Semler B. L., Jackson R. J., Hanecak R., Duprey E., Wimmer E. In vitro translation of poliovirus RNA: utilization of internal initiation sites in reticulocyte lysate. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):507–514. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.507-514.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evstafieva A. G., Ugarova T. Y., Chernov B. K., Shatsky I. N. A complex RNA sequence determines the internal initiation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA translation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 11;19(3):665–671. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.3.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. J., Howell M. T., Kaminski A. The novel mechanism of initiation of picornavirus RNA translation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Dec;15(12):477–483. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90302-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. K., Davies M. V., Kaufman R. J., Wimmer E. Initiation of protein synthesis by internal entry of ribosomes into the 5' nontranslated region of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA in vivo. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1651–1660. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1651-1660.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. K., Kräusslich H. G., Nicklin M. J., Duke G. M., Palmenberg A. C., Wimmer E. A segment of the 5' nontranslated region of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA directs internal entry of ribosomes during in vitro translation. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2636–2643. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2636-2643.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. K., Wimmer E. Cap-independent translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA: structural elements of the internal ribosomal entry site and involvement of a cellular 57-kD RNA-binding protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1560–1572. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminski A., Howell M. T., Jackson R. J. Initiation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA translation: the authentic initiation site is not selected by a scanning mechanism. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3753–3759. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07588.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn R., Luz N., Beck E. Functional analysis of the internal translation initiation site of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4625–4631. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4625-4631.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luz N., Beck E. A cellular 57 kDa protein binds to two regions of the internal translation initiation site of foot-and-mouth disease virus. FEBS Lett. 1990 Sep 3;269(2):311–314. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81182-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meerovitch K., Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. A cellular protein that binds to the 5'-noncoding region of poliovirus RNA: implications for internal translation initiation. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):1026–1034. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. Internal initiation of translation of eukaryotic mRNA directed by a sequence derived from poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):320–325. doi: 10.1038/334320a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilipenko E. V., Blinov V. M., Chernov B. K., Dmitrieva T. M., Agol V. I. Conservation of the secondary structure elements of the 5'-untranslated region of cardio- and aphthovirus RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 25;17(14):5701–5711. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.14.5701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheper G. C., Thomas A. A., Voorma H. O. The 5' untranslated region of encephalomyocarditis virus contains a sequence for very efficient binding of eukaryotic initiation factor eIF-2/2B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jun 13;1089(2):220–226. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90011-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]