Abstract
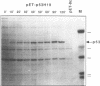
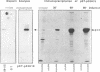
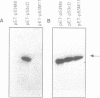
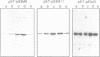
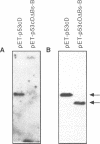
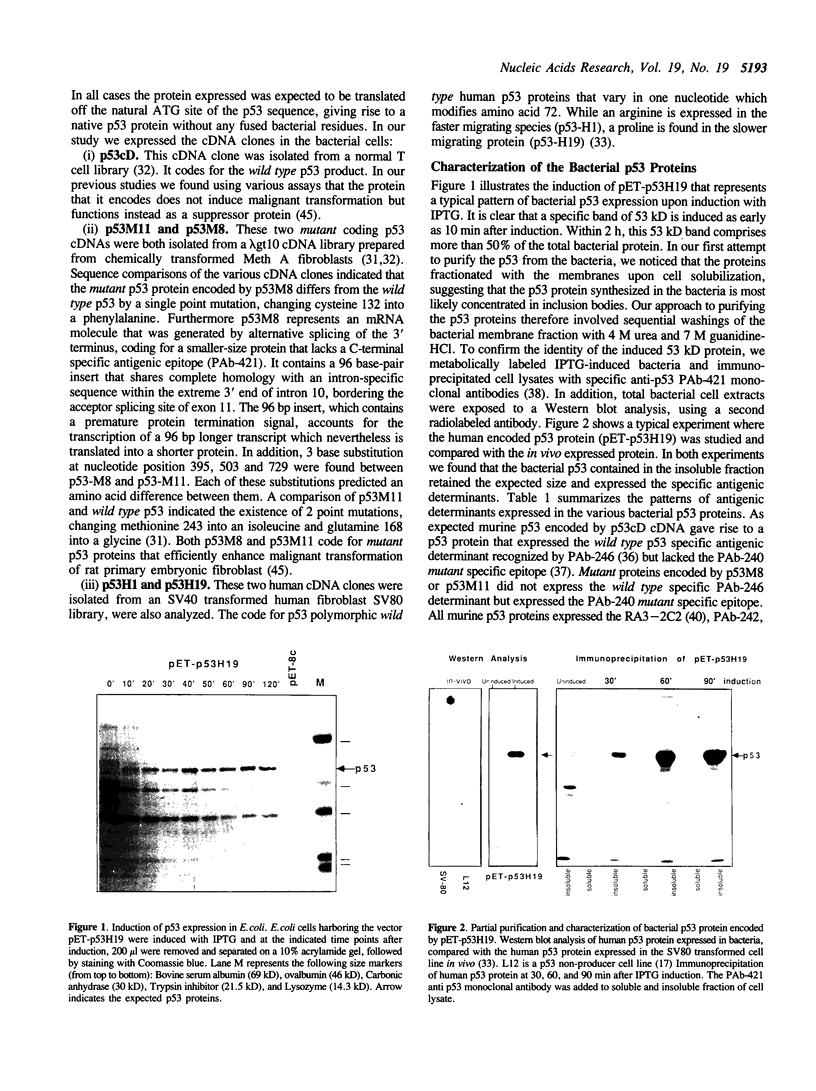
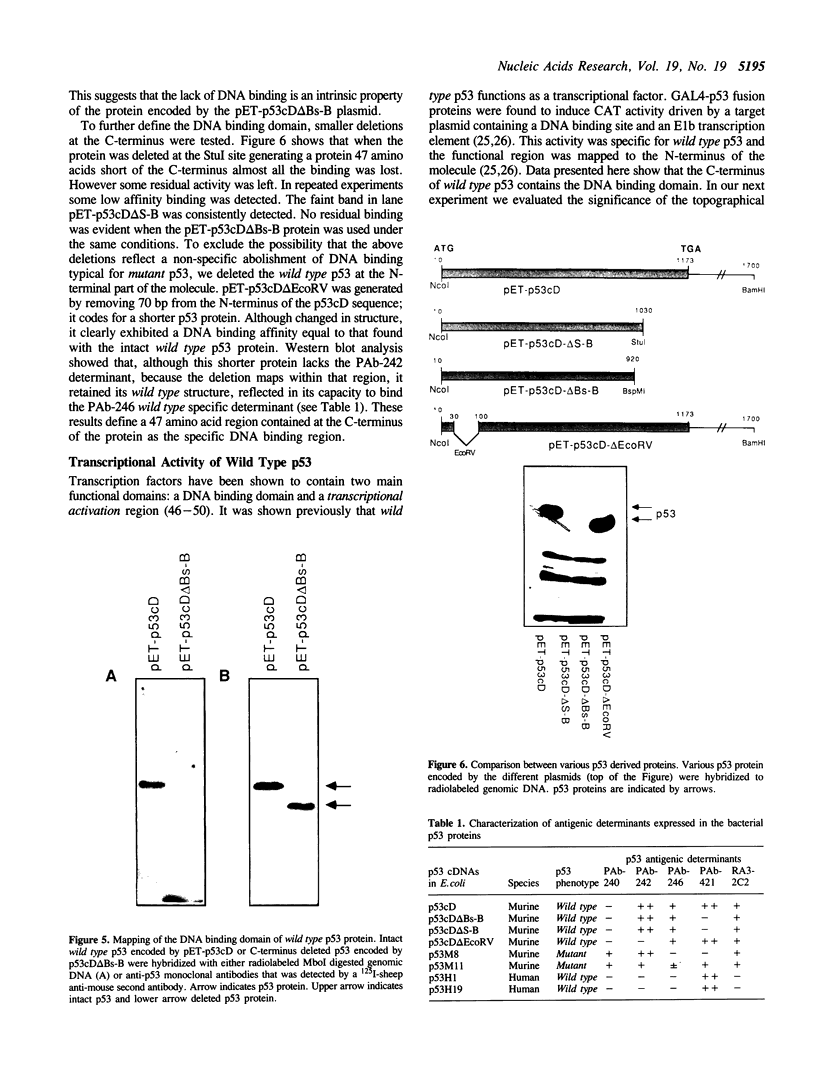
In the present study we evaluated the DNA binding activity of wild type and mutant p53 proteins that were isolated from bacterial expression vectors. A comparison of the binding activities of the various purified p53 proteins, assessed by their ability to bind DNA cellulose columns, indicated that wild type p53 has a higher affinity to DNA than have mutant p53 forms. Furthermore, only wild type p53 was able to bind genomic DNA upon electrophoretic protein blotting. As specific deletion of the C-terminal region of wild type p53 totally abolished binding to genomic DNA, it was concluded that the 47 C-terminal amino acids contain the DNA binding region. The fact that the N-terminus contains a transcription activation region whereas the C-terminus contains a DNA binding domain places p53 in the family of typical transcription factors. Our experiments show that the topographical positioning of these domains plays an important role in the activity of wild type p53.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Addison C., Jenkins J. R., Stürzbecher H. W. The p53 nuclear localisation signal is structurally linked to a p34cdc2 kinase motif. Oncogene. 1990 Mar;5(3):423–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahuja H., Bar-Eli M., Advani S. H., Benchimol S., Cline M. J. Alterations in the p53 gene and the clonal evolution of the blast crisis of chronic myelocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6783–6787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai N., Nomura D., Yokota K., Wolf D., Brill E., Shohat O., Rotter V. Immunologically distinct p53 molecules generated by alternative splicing. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3232–3239. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. J., Fearon E. R., Nigro J. M., Hamilton S. R., Preisinger A. C., Jessup J. M., vanTuinen P., Ledbetter D. H., Barker D. F., Nakamura Y. Chromosome 17 deletions and p53 gene mutations in colorectal carcinomas. Science. 1989 Apr 14;244(4901):217–221. doi: 10.1126/science.2649981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. J., Markowitz S., Fearon E. R., Willson J. K., Vogelstein B. Suppression of human colorectal carcinoma cell growth by wild-type p53. Science. 1990 Aug 24;249(4971):912–915. doi: 10.1126/science.2144057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff J. R., Friedman P. N., Marshak D. R., Prives C., Beach D. Human p53 is phosphorylated by p60-cdc2 and cyclin B-cdc2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4766–4770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Max: a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that forms a sequence-specific DNA-binding complex with Myc. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1211–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.2006410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braithwaite A. W., Sturzbecher H. W., Addison C., Palmer C., Rudge K., Jenkins J. R. Mouse p53 inhibits SV40 origin-dependent DNA replication. Nature. 1987 Oct 1;329(6138):458–460. doi: 10.1038/329458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull P., Morley K. L., Hoekstra M. F., Hunter T., Verma I. M. The mouse c-rel protein has an N-terminal regulatory domain and a C-terminal transcriptional transactivation domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5473–5485. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. L., Chen Y. M., Bookstein R., Lee W. H. Genetic mechanisms of tumor suppression by the human p53 gene. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1576–1580. doi: 10.1126/science.2274789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):222–245. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang C. V., Lee W. M. Nuclear and nucleolar targeting sequences of c-erb-A, c-myb, N-myc, p53, HSP70, and HIV tat proteins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):18019–18023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diller L., Kassel J., Nelson C. E., Gryka M. A., Litwak G., Gebhardt M., Bressac B., Ozturk M., Baker S. J., Vogelstein B. p53 functions as a cell cycle control protein in osteosarcomas. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5772–5781. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dippold W. G., Jay G., DeLeo A. B., Khoury G., Old L. J. p53 transformation-related protein: detection by monoclonal antibody in mouse and human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1695–1699. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Goldfinger N., Pinhasi-Kimhi O., Shaulsky G., Skurnik Y., Arai N., Rotter V., Oren M. Meth A fibrosarcoma cells express two transforming mutant p53 species. Oncogene. 1988 Sep;3(3):313–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Michalovitz D., Eliyahu S., Pinhasi-Kimhi O., Oren M. Wild-type p53 can inhibit oncogene-mediated focus formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8763–8767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Jang S. K. Presence of a potent transcription activating sequence in the p53 protein. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1046–1049. doi: 10.1126/science.2144363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A., Hinds P. W., Levine A. J. The p53 proto-oncogene can act as a suppressor of transformation. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1083–1093. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon J. V., Greaves R., Iggo R., Lane D. P. Activating mutations in p53 produce a common conformational effect. A monoclonal antibody specific for the mutant form. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1595–1602. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08279.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. p53 and DNA polymerase alpha compete for binding to SV40 T antigen. Nature. 1987 Oct 1;329(6138):456–458. doi: 10.1038/329456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg D., Michael-Michalovitz D., Ginsberg D., Oren M. Induction of growth arrest by a temperature-sensitive p53 mutant is correlated with increased nuclear localization and decreased stability of the protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):582–585. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Crawford L. V., Pim D. C., Williamson N. M. Monoclonal antibodies specific for simian virus 40 tumor antigens. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):861–869. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.861-869.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris N., Brill E., Shohat O., Prokocimer M., Wolf D., Arai N., Rotter V. Molecular basis for heterogeneity of the human p53 protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4650–4656. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelman Z., Prokocimer M., Peller S., Kahn Y., Rechavi G., Manor Y., Cohen A., Rotter V. Rearrangements in the p53 gene in Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood. 1989 Nov 15;74(7):2318–2324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Kinzler K. W., Baker S. J., Nigro J. M., Rotter V., Levine A. J., Friedman P., Prives C., Vogelstein B. Mutant p53 proteins bind DNA abnormally in vitro. Oncogene. 1991 Jan;6(1):131–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Green M. R. Transcription activation by the adenovirus E1a protein. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):39–44. doi: 10.1038/338039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez J., Georgoff I., Martinez J., Levine A. J. Cellular localization and cell cycle regulation by a temperature-sensitive p53 protein. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):151–159. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer W. E., Shields M. T., Amin M., Sauve G. J., Appella E., Romano J. W., Ullrich S. J. Negative growth regulation in a glioblastoma tumor cell line that conditionally expresses human wild-type p53. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6166–6170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalovitz D., Halevy O., Oren M. Conditional inhibition of transformation and of cell proliferation by a temperature-sensitive mutant of p53. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):671–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90113-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan L. M., Matlashewski G. J., Scrable H. J., Cavenee W. K. Mechanisms of p53 loss in human sarcomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5863–5867. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigro J. M., Baker S. J., Preisinger A. C., Jessup J. M., Hostetter R., Cleary K., Bigner S. H., Davidson N., Baylin S., Devilee P. Mutations in the p53 gene occur in diverse human tumour types. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):705–708. doi: 10.1038/342705a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Ziff E. B. DNA-binding motif. Nature. 1989 Oct 5;341(6241):392–392. doi: 10.1038/341392a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Gann A. A. Activators and targets. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):329–331. doi: 10.1038/346329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raycroft L., Wu H. Y., Lozano G. Transcriptional activation by wild-type but not transforming mutants of the p53 anti-oncogene. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1049–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.2144364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues N. R., Rowan A., Smith M. E., Kerr I. B., Bodmer W. F., Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. p53 mutations in colorectal cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7555–7559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. H., Lade B. N., Chui D. S., Lin S. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Vectors for selective expression of cloned DNAs by T7 RNA polymerase. Gene. 1987;56(1):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter V., Abutbul H., Ben-Ze'ev A. P53 transformation-related protein accumulates in the nucleus of transformed fibroblasts in association with the chromatin and is found in the cytoplasm of non-transformed fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1983;2(7):1041–1047. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01543.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter V., Witte O. N., Coffman R., Baltimore D. Abelson murine leukemia virus-induced tumors elicit antibodies against a host cell protein, P50. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):547–555. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.547-555.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuermann M., Neuberg M., Hunter J. B., Jenuwein T., Ryseck R. P., Bravo R., Müller R. The leucine repeat motif in Fos protein mediates complex formation with Jun/AP-1 and is required for transformation. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):507–516. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90253-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaulsky G., Ben-Ze'ev A., Rotter V. Subcellular distribution of the p53 protein during the cell cycle of Balb/c 3T3 cells. Oncogene. 1990 Nov;5(11):1707–1711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaulsky G., Goldfinger N., Ben-Ze'ev A., Rotter V. Nuclear accumulation of p53 protein is mediated by several nuclear localization signals and plays a role in tumorigenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6565–6577. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmeyer K., Deppert W. DNA binding properties of murine p53. Oncogene. 1988 Nov;3(5):501–507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stürzbecher H. W., Maimets T., Chumakov P., Brain R., Addison C., Simanis V., Rudge K., Philp R., Grimaldi M., Court W. p53 interacts with p34cdc2 in mammalian cells: implications for cell cycle control and oncogenesis. Oncogene. 1990 Jun;5(6):795–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Nau M. M., Chiba I., Birrer M. J., Rosenberg R. K., Vinocour M., Levitt M., Pass H., Gazdar A. F., Minna J. D. p53: a frequent target for genetic abnormalities in lung cancer. Science. 1989 Oct 27;246(4929):491–494. doi: 10.1126/science.2554494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E. H., Friedman P. N., Prives C. The murine p53 protein blocks replication of SV40 DNA in vitro by inhibiting the initiation functions of SV40 large T antigen. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):379–392. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90913-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Flores P., Begue A., Leprince D., Stehelin D. The c-ets proto-oncogenes encode transcription factors that cooperate with c-Fos and c-Jun for transcriptional activation. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):191–193. doi: 10.1038/346191a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf D., Harris N., Goldfinger N., Rotter V. Isolation of a full-length mouse cDNA clone coding for an immunologically distinct p53 molecule. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):127–132. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yewdell J. W., Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. Monoclonal antibody analysis of p53 expression in normal and transformed cells. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):444–452. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.444-452.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]