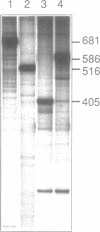
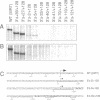
Abstract
Using an in vitro transcription system for Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNA polymerase I, we have analyzed Pol I promoter deletion mutants and mapped the boundaries of the promoter between positions -155 and +27. The 5'-boundary of the minimal core promoter capable of transcription initiation, however, was found to lie between -38 and -26. The 3'-deletion extending to -2 and -5 still allowed some transcription, suggesting that the positioning of Pol I is directed by upstream sequences. The results of in vitro analysis of linker scanning mutants (LSMs) combined with the deletion analysis showed that the promoter consists of three domains: two essential core domains (I: -28 to +8 and II: -76 to -51) and a transcription modulating upstream domain (III: -146 to -91). These results are in general agreement with those obtained in vivo (1). Using a template competition assay we also analyzed these mutant promoters for their ability to form a stable preinitiation complex. We found that the ability of 5'-deletion mutants to sequester an essential factor(s) correlates with their transcriptional activity. In contrast, several 3'-deletions and some LSMs in domain I and II decrease transcription activity greatly without significantly decreasing competition ability. The results indicate that the stimulatory function of domain III is achieved through its interaction with an essential transcription factor(s), although the other domains also participate in this interaction, perhaps directly or through another protein factor.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ammerer G., Hunter C. P., Rothman J. H., Saari G. C., Valls L. A., Stevens T. H. PEP4 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes proteinase A, a vacuolar enzyme required for processing of vacuolar precursors. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2490–2499. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bateman E., Iida C. T., Kownin P., Paule M. R. Footprinting of ribosomal RNA genes by transcription initiation factor and RNA polymerase I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8004–8008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell S. P., Jantzen H. M., Tjian R. Assembly of alternative multiprotein complexes directs rRNA promoter selectivity. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):943–954. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell S. P., Learned R. M., Jantzen H. M., Tjian R. Functional cooperativity between transcription factors UBF1 and SL1 mediates human ribosomal RNA synthesis. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1192–1197. doi: 10.1126/science.3413483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buttgereit D., Pflugfelder G., Grummt I. Growth-dependent regulation of rRNA synthesis is mediated by a transcription initiation factor (TIF-IA). Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 25;13(22):8165–8180. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.22.8165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy B., Haglund R., Rothblum L. I. Regions upstream from the core promoter of the rat ribosomal gene are required for the formation of a stable transcription initiation complex by RNA polymerase I in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jul 14;909(2):133–144. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cizewski V., Sollner-Webb B. A stable transcription complex directs mouse ribosomal RNA synthesis by RNA polymerase I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 25;11(20):7043–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.20.7043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clos J., Buttgereit D., Grummt I. A purified transcription factor (TIF-IB) binds to essential sequences of the mouse rDNA promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):604–608. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clos J., Normann A., Ohrlein A., Grummt I. The core promoter of mouse rDNA consists of two functionally distinct domains. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 10;14(19):7581–7595. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.19.7581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunaway M. A transcription factor, TFIS, interacts with both the promoter and enhancer of the Xenopus rRNA genes. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1768–1778. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion E. A., Warner J. R. An RNA polymerase I enhancer in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2089–2097. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion E. A., Warner J. R. The major promoter element of rRNA transcription in yeast lies 2 kb upstream. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):663–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90473-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haltiner M. M., Smale S. T., Tjian R. Two distinct promoter elements in the human rRNA gene identified by linker scanning mutagenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):227–235. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haltiner M., Kempe T., Tjian R. A novel strategy for constructing clustered point mutations. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):1015–1025. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida C. T., Kownin P., Paule M. R. Ribosomal RNA transcription: proteins and DNA sequences involved in preinitiation complex formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1668–1672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen H. M., Admon A., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Nucleolar transcription factor hUBF contains a DNA-binding motif with homology to HMG proteins. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):830–836. doi: 10.1038/344830a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato H., Nagamine M., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Formation of the transcription initiation complex on mammalian rDNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3418–3427. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempers-Veenstra A. E., Musters W., Dekker A. F., Klootwijk J., Planta R. J. Deletion mapping of the yeast Pol I promoter. Curr Genet. 1985;10(4):253–260. doi: 10.1007/BF00365621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempers-Veenstra A. E., Oliemans J., Offenberg H., Dekker A. F., Piper P. W., Planta R. J., Klootwijk J. 3'-End formation of transcripts from the yeast rRNA operon. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2703–2710. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04554.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempers-Veenstra A. E., van Heerikhuizen H., Musters W., Klootwijk J., Planta R. J. Transcription of an artificial ribosomal RNA gene in yeast. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1377–1382. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01980.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kownin P., Bateman E., Paule M. R. Effects of single-base substitutions within the Acanthamoeba castellanii rRNA promoter on transcription and on binding of transcription initiation factor and RNA polymerase I. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):747–753. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kownin P., Bateman E., Paule M. R. Eukaryotic RNA polymerase I promoter binding is directed by protein contacts with transcription initiation factor and is DNA sequence-independent. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):693–699. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90327-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kownin P., Iida C. T., Brown-Shimer S., Paule M. R. The ribosomal RNA promoter of Acanthamoeba castellanii determined by transcription in a cell-free system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 11;13(17):6237–6248. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.17.6237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulkens T., van Heerikhuizen H., Klootwijk J., Oliemans J., Planta R. J. A yeast ribosomal DNA-binding protein that binds to the rDNA enhancer and also close to the site of Pol I transcription initiation is not important for enhancer functioning. Curr Genet. 1989 Dec;16(5-6):351–359. doi: 10.1007/BF00340714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Cordes S., Tjian R. Purification and characterization of a transcription factor that confers promoter specificity to human RNA polymerase I. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1358–1369. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Learned T. K., Haltiner M. M., Tjian R. T. Human rRNA transcription is modulated by the coordinate binding of two factors to an upstream control element. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):847–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90559-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lue N. F., Kornberg R. D. Accurately initiated, enhancer-dependent transcription by RNA polymerase I in yeast extracts. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18091–18094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahajan P. B., Thompson E. A. Hormonal regulation of transcription of rDNA. Purification and characterization of the hormone-regulated transcription factor IC. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16225–16233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. G., Tower J., Sollner-Webb B. A complex control region of the mouse rRNA gene directs accurate initiation by RNA polymerase I. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):554–562. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishima Y., Financsek I., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Fractionation and reconstitution of factors required for accurate transcription of mammalian ribosomal RNA genes: identification of a species-dependent initiation factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6659–6670. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow B. E., Johnson S. P., Warner J. R. Proteins that bind to the yeast rDNA enhancer. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):9061–9068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow B. E., Ju Q., Warner J. R. Purification and characterization of the yeast rDNA binding protein REB1. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):20778–20783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musters W., Knol J., Maas P., Dekker A. F., van Heerikhuizen H., Planta R. J. Linker scanning of the yeast RNA polymerase I promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):9661–9678. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.9661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagamine M., Kishimoto T., Aono J., Kato H., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Sequestration analysis for RNA polymerase I transcription factors with various deletion and point mutations reveals different functional regions of the mouse rRNA gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1486–1495. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Mahony D. J., Rothblum L. I. Identification of two forms of the RNA polymerase I transcription factor UBF. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3180–3184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikaard C. S., McStay B., Schultz M. C., Bell S. P., Reeder R. H. The Xenopus ribosomal gene enhancers bind an essential polymerase I transcription factor, xUBF. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1779–1788. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H. rRNA synthesis in the nucleolus. Trends Genet. 1990 Dec;6(12):390–395. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90298-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs D. L., Nomura M. Specific transcription of Saccharomyces cerevisiae 35 S rDNA by RNA polymerase I in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7596–7603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnapp A., Clos J., Hädelt W., Schreck R., Cvekl A., Grummt I. Isolation and functional characterization of TIF-IB, a factor that confers promoter specificity to mouse RNA polymerase I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 25;18(6):1385–1393. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.6.1385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnapp A., Pfleiderer C., Rosenbauer H., Grummt I. A growth-dependent transcription initiation factor (TIF-IA) interacting with RNA polymerase I regulates mouse ribosomal RNA synthesis. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2857–2863. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07475.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz M. C., Choe S. Y., Reeder R. H. Specific initiation by RNA polymerase I in a whole-cell extract from yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):1004–1008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. D., Oriahi E., Lowe D., Yang-Yen H. F., O'Mahony D., Rose K., Chen K., Rothblum L. I. Characterization of factors that direct transcription of rat ribosomal DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3105–3116. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Mougey E. B. News from the nucleolus: rRNA gene expression. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Feb;16(2):58–62. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90025-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Tower J. Transcription of cloned eukaryotic ribosomal RNA genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:801–830. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tower J., Culotta V. C., Sollner-Webb B. Factors and nucleotide sequences that direct ribosomal DNA transcription and their relationship to the stable transcription complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3451–3462. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tower J., Sollner-Webb B. Transcription of mouse rDNA is regulated by an activated subform of RNA polymerase I. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):873–883. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90514-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wandelt C., Grummt I. Formation of stable preinitiation complexes is a prerequisite for ribosomal DNA transcription in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 11;11(11):3795–3809. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.11.3795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R. Synthesis of ribosomes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;53(2):256–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.2.256-271.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windle J. J., Sollner-Webb B. Two distant and precisely positioned domains promote transcription of Xenopus laevis rRNA genes: analysis with linker-scanning mutants. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4585–4593. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Sande C. A., Kulkens T., Kramer A. B., de Wijs I. J., van Heerikhuizen H., Klootwijk J., Planta R. J. Termination of transcription by yeast RNA polymerase I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9127–9146. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]