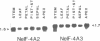Abstract
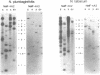
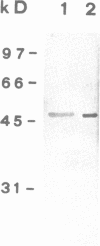
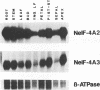
Three cDNA clones coding for eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4A, eIF-4A, were isolated from a Nicotiana plumbaginifolia root cDNA library by heterologous screening. The clones comprise two distinct gene classes as two clones are highly similar while the third is divergent. The genes belong to a highly conserved gene family, the DEAD box supergene family, although the divergent clone contains a DESD box rather than the characteristic DEAD box. The two clones are representatives of separate small multigene families in both N. plumbaginifolia and N. tabacum. Representatives of each family are coordinately expressed in all plant organs examined. The 47 kD polypeptide product of one clone, overexpressed in E. coli, crossreacts immunologically with a rabbit reticulocyte eIF-4A polyclonal antibody. Taken together the data suggest that the two Nicotiana eIF-4A genes encode translation initiation factors. The sequence divergence and the coordinate expression of the two Nicotiana eIF-4A families provide an excellent system to determine if functionally distinct eIF-4A polypeptides are required for translation initiation in plants.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramson R. D., Browning K. S., Dever T. E., Lawson T. G., Thach R. E., Ravel J. M., Merrick W. C. Initiation factors that bind mRNA. A comparison of mammalian factors with wheat germ factors. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5462–5467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum S., Mueller M., Schmid S. R., Linder P., Trachsel H. Translation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: initiation factor 4A-dependent cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6043–6046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boutry M., Chua N. H. A nuclear gene encoding the beta subunit of the mitochondrial ATP synthase in Nicotiana plumbaginifolia. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2159–2165. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03910.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conroy S. C., Dever T. E., Owens C. L., Merrick W. C. Characterization of the 46,000-dalton subunit of eIF-4F. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Nov 1;282(2):363–371. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90130-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalbadie-McFarland G., Abelson J. PRP5: a helicase-like protein required for mRNA splicing in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4236–4240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford M. J., Anton I. A., Lane D. P. Nuclear protein with sequence homology to translation initiation factor eIF-4A. Nature. 1988 Apr 21;332(6166):736–738. doi: 10.1038/332736a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay B., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. A protein component of Drosophila polar granules is encoded by vasa and has extensive sequence similarity to ATP-dependent helicases. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):577–587. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90216-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaramillo M., Browning K., Dever T. E., Blum S., Trachsel H., Merrick W. C., Ravel J. M., Sonenberg N. Translation initiation factors that function as RNA helicases from mammals, plants and yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):134–139. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90154-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katagiri F., Lam E., Chua N. H. Two tobacco DNA-binding proteins with homology to the nuclear factor CREB. Nature. 1989 Aug 31;340(6236):727–730. doi: 10.1038/340727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasko P. F., Ashburner M. The product of the Drosophila gene vasa is very similar to eukaryotic initiation factor-4A. Nature. 1988 Oct 13;335(6191):611–617. doi: 10.1038/335611a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lax S. R., Lauer S. J., Browning K. S., Ravel J. M. Purification and properties of protein synthesis initiation and elongation factors from wheat germ. Methods Enzymol. 1986;118:109–128. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)18068-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroy P., Alzari P., Sassoon D., Wolgemuth D., Fellous M. The protein encoded by a murine male germ cell-specific transcript is a putative ATP-dependent RNA helicase. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):549–559. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90125-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder P., Lasko P. F., Ashburner M., Leroy P., Nielsen P. J., Nishi K., Schnier J., Slonimski P. P. Birth of the D-E-A-D box. Nature. 1989 Jan 12;337(6203):121–122. doi: 10.1038/337121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder P., Slonimski P. P. An essential yeast protein, encoded by duplicated genes TIF1 and TIF2 and homologous to the mammalian translation initiation factor eIF-4A, can suppress a mitochondrial missense mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2286–2290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder P., Slonimski P. P. Sequence of the genes TIF1 and TIF2 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae coding for a translation initiation factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 11;16(21):10359–10359. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.21.10359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowry K. L., Oh R., Steitz J. A. Each of the conserved sequence elements flanking the cleavage site of mammalian histone pre-mRNAs has a distinct role in the 3'-end processing reaction. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):3105–3108. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.3105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen P. J., Trachsel H. The mouse protein synthesis initiation factor 4A gene family includes two related functional genes which are differentially expressed. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2097–2105. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03049.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pain V. M. Initiation of protein synthesis in mammalian cells. Biochem J. 1986 May 1;235(3):625–637. doi: 10.1042/bj2350625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prat A., Schmid S. R., Buser P., Blum S., Trachsel H., Nielsen P. J., Linder P. Expression of translation initiation factor 4A from yeast and mouse in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):140–145. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90155-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads R. E. Cap recognition and the entry of mRNA into the protein synthesis initiation cycle. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Feb;13(2):52–56. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N. Cap-binding proteins of eukaryotic messenger RNA: functions in initiation and control of translation. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1988;35:173–207. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60614-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. B., Gruissem W. Control of plastid gene expression: 3' inverted repeats act as mRNA processing and stabilizing elements, but do not terminate transcription. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1145–1157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90600-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassarman D. A., Steitz J. A. RNA splicing. Alive with DEAD proteins. Nature. 1991 Feb 7;349(6309):463–464. doi: 10.1038/349463a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]