Abstract
The D. melanogaster transposable element copia is structurally similar to retroviral proviruses. We have asked whether copia encodes regulatory functions which have been observed in certain other proviruses. We have introduced reporter constructs based on the copia promoter and other Drosophila promoters into Drosophila cells and asked if copia has any affect on their expression. We find that, whilst copia negatively regulates expression from its own promoter, it also positively regulates expression from the larval serum protein 1 promoter. Analysis of RNA suggests that both regulatory functions occur by post-transcriptional mechanisms.
Full text
PDF
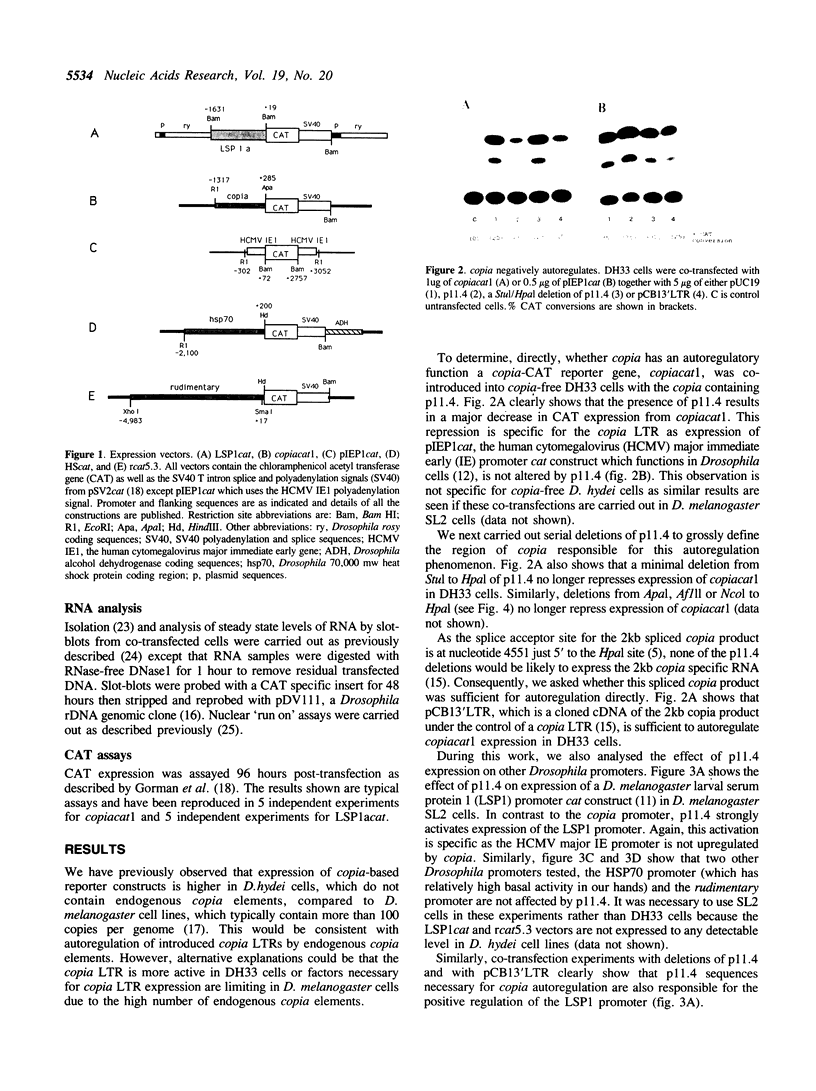


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brierley C., Flavell A. J. The retrotransposon copia controls the relative levels of its gene products post-transcriptionally by differential expression from its two major mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):2947–2951. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.2947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke J. F., Sinclair J. H., Sang J. H., Ish-Horowicz D. An assay for transient gene expression in transfected Drosophila cells, using [3H]guanine incorporation. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2549–2554. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02172.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csink A. K., McDonald J. F. copia expression is variable among natural populations of Drosophila. Genetics. 1990 Oct;126(2):375–385. doi: 10.1093/genetics/126.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Greene W. C. Functions of the auxiliary gene products of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Virology. 1990 Sep;178(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90373-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Trans-activation of human immunodeficiency virus occurs via a bimodal mechanism. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):973–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90696-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delaney S. J., Smith D. F., McClelland A., Sunkel C., Glover D. M. Sequence conservation around the 5' ends of the larval serum protein 1 genes of Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90376-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Nocera P. P., Dawid I. B. Transient expression of genes introduced into cultured cells of Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7095–7098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emori Y., Shiba T., Kanaya S., Inouye S., Yuki S., Saigo K. The nucleotide sequences of copia and copia-related RNA in Drosophila virus-like particles. 1985 Jun 27-Jul 3Nature. 315(6022):773–776. doi: 10.1038/315773a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavell A. J., Levis R., Simon M. A., Rubin G. M. The 5' termini of RNAs encoded by the transposable element copia. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6279–6291. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavell A. J. Role of reverse transcription in the generation of extrachromosomal copia mobile genetic elements. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):514–516. doi: 10.1038/310514a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franz G., Tautz D., Dover G. A. Conservation of major nuclease S1-sensitive sites in the non-conserved spacer region of ribosomal DNA in Drosophila species. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jun 25;183(4):519–527. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90168-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., O'Hare K., Rubin G. M. Effects of transposable element insertions on RNA encoded by the white gene of Drosophila. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):471–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90502-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Wahl G. Hybridization of nucleic acids immobilized on solid supports. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90808-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M., Rubin G. M. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Drosophila transposable element copia: homology between copia and retroviral proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1630–1638. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter S. S., Brorein W. J., Jr, Dunsmuir P., Rubin G. M. Transposition of elements of the 412, copia and 297 dispersed repeated gene families in Drosophila. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):415–427. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90168-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Kidwell M. G., Bingham P. M. The molecular basis of P-M hybrid dysgenesis: the nature of induced mutations. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):987–994. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90462-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders S. E., Rawls J. M., Wardle C. J., Burke J. F. High efficiency expression of transfected genes in a Drosophila melanogaster haploid (1182) cell line. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6205–6216. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair J. H., Burke J. F., Ish-Horowicz D., Sang J. H. Functional analysis of the transcriptional control regions of the copia transposable element. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2349–2354. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04503.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair J. H. The human cytomegalovirus immediate early gene promoter is a strong promoter in cultured Drosophila melanogaster cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2392–2392. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sondermeijer P. J., Derksen J. W., Lubsen N. H. New cell line: established cell lines of Drosophila hydei. In Vitro. 1980 Nov;16(11):913–914. doi: 10.1007/BF02619327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M., Allen J. B., Gartner S., Orenstein J. M., Popovic M., Chenoweth D. E., Arthur L. O., Farrar W. L., Wahl L. M. HIV-1 and its envelope glycoprotein down-regulate chemotactic ligand receptors and chemotactic function of peripheral blood monocytes. J Immunol. 1989 May 15;142(10):3553–3559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka K., Honma H., Zushi M., Kondo S., Togashi S., Miyake T., Shiba T. Virus-like particle formation of Drosophila copia through autocatalytic processing. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):535–541. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08140.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]