Abstract
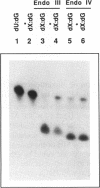
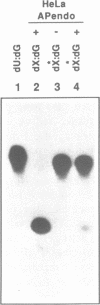
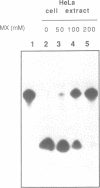
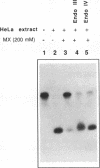
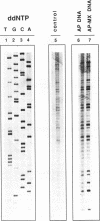
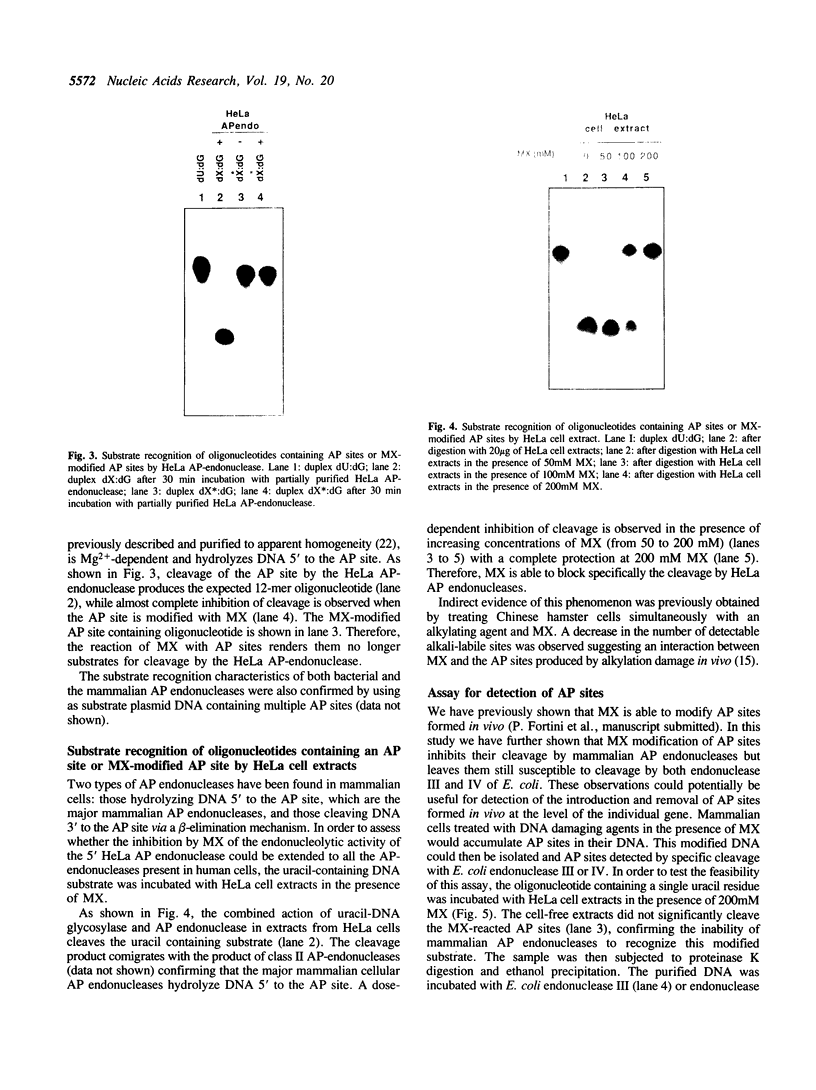
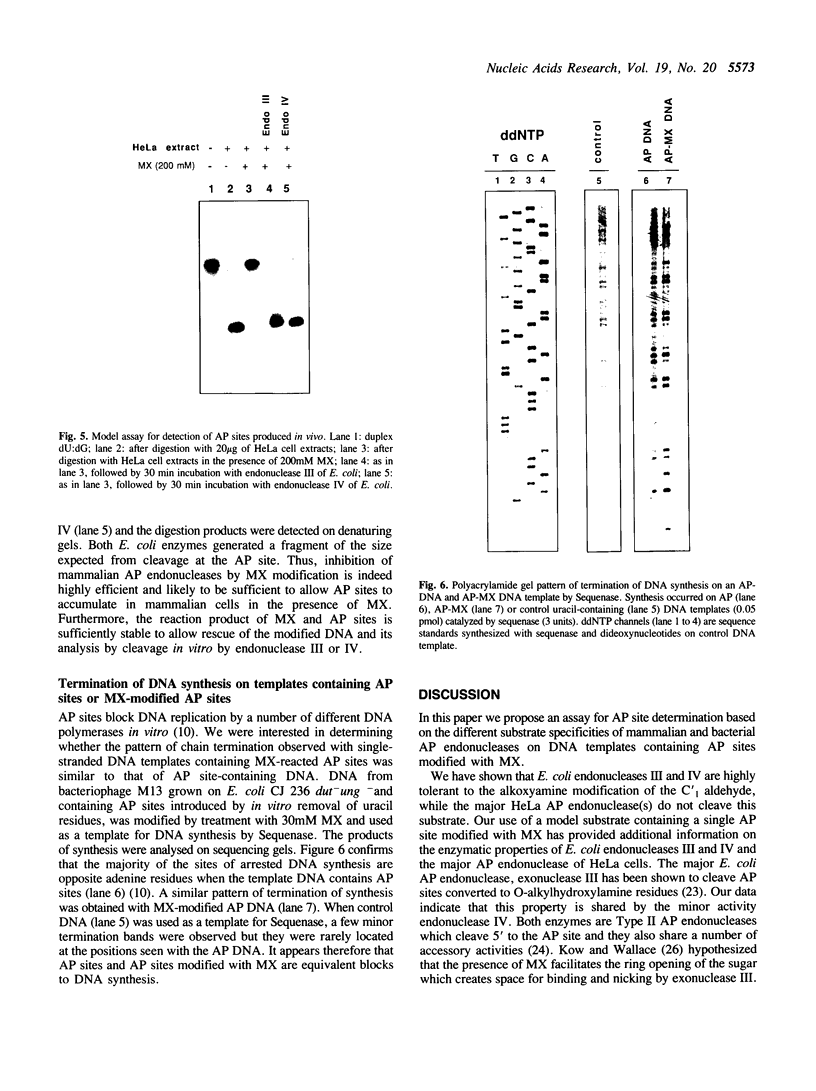
In this study we demonstrate that the different substrate recognition properties of bacterial and human AP endonucleases might be used to quantify and localize apurinic (AP) sites formed in DNA in vivo. By using a model oligonucleotide containing a single AP site modified with methoxyamine (MX), we show that endonuclease III and IV of E. coli are able to cleave the alkoxyamine-adducted site whereas a partially purified HeLa AP endonuclease and crude cell-free extracts from HeLa cells are inhibited by this modification. In addition MX-modified AP sites in a DNA template retain their ability to block DNA synthesis in vitro. Since MX can efficiently react with AP sites formed in mammalian cells in vivo we propose that the MX modified abasic sites thus formed can be quantitated and localized at the level of the individual gene by subsequent site specific cleavage by either E. coli endonuclease III or IV in vitro.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailly V., Sente B., Verly W. G. Bacteriophage-T4 and Micrococcus luteus UV endonucleases are not endonucleases but beta-elimination and sometimes beta delta-elimination catalysts. Biochem J. 1989 May 1;259(3):751–759. doi: 10.1042/bj2590751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailly V., Verly W. G. Escherichia coli endonuclease III is not an endonuclease but a beta-elimination catalyst. Biochem J. 1987 Mar 1;242(2):565–572. doi: 10.1042/bj2420565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bignami M., Lane D. P. O6-methylguanine in the SV40 origin of replication inhibits binding but increases unwinding by viral large T antigen. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):3785–3793. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.3785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohr V. A., Phillips D. H., Hanawalt P. C. Heterogeneous DNA damage and repair in the mammalian genome. Cancer Res. 1987 Dec 15;47(24 Pt 1):6426–6436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohr V. A., Smith C. A., Okumoto D. S., Hanawalt P. C. DNA repair in an active gene: removal of pyrimidine dimers from the DHFR gene of CHO cells is much more efficient than in the genome overall. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):359–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90150-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boiteux S., Laval J. Coding properties of poly(deoxycytidylic acid) templates containing uracil or apyrimidinic sites: in vitro modulation of mutagenesis by deoxyribonucleic acid repair enzymes. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 21;21(26):6746–6751. doi: 10.1021/bi00269a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coombs M. M., Livingston D. C. Reaction of apurinic acid with aldehyde reagents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jan 21;174(1):161–173. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90239-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doetsch P. W., Cunningham R. P. The enzymology of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonucleases. Mutat Res. 1990 Sep-Nov;236(2-3):173–201. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(90)90004-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortini P., Bignami M., Dogliotti E. Evidence for AP site formation related to DNA-oxygen alkylation in CHO cells treated with ethylating agents. Mutat Res. 1990 Jul;236(1):129–137. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(90)90040-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin W. A., Lindahl T. DNA deoxyribophosphodiesterase. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3617–3622. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03240.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentil A., Margot A., Sarasin A. Apurinic sites cause mutations in simian virus 40. Mutat Res. 1984 Nov;129(2):141–147. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(84)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon L. K., Haseltine W. A. Comparison of the cleavage of pyrimidine dimers by the bacteriophage T4 and Micrococcus luteus UV-specific endonucleases. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):12047–12050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane C. M., Linn S. Purification and characterization of an apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease from HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3405–3414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kow Y. W. Mechanism of action of Escherichia coli exonuclease III. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 18;28(8):3280–3287. doi: 10.1021/bi00434a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kow Y. W., Wallace S. S. Mechanism of action of Escherichia coli endonuclease III. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 15;26(25):8200–8206. doi: 10.1021/bi00399a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Shearman C. W., Loeb L. A. Mutagenesis in vitro by depurination of phiX174 dna. Nature. 1981 May 28;291(5813):349–351. doi: 10.1038/291349a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeDoux S. P., Patton N. J., Nelson J. W., Bohr W. A., Wilson G. L. Preferential DNA repair of alkali-labile sites within the active insulin gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):14875–14880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. J., Kelly T. J. Simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro: specificity of initiation and evidence for bidirectional replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1238–1246. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Ljungquist S., Siegert W., Nyberg B., Sperens B. DNA N-glycosidases: properties of uracil-DNA glycosidase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 25;252(10):3286–3294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liuzzi M., Talpaert-Borlé M. A new approach to the study of the base-excision repair pathway using methoxyamine. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5252–5258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liuzzi M., Weinfeld M., Paterson M. C. Selective inhibition by methoxyamine of the apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease activity associated with pyrimidine dimer-DNA glycosylases from Micrococcus luteus and bacteriophage T4. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 16;26(12):3315–3321. doi: 10.1021/bi00386a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungquist S. A new endonuclease from Escherichia coli acting at apurinic sites in DNA. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 10;252(9):2808–2814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb L. A. Apurinic sites as mutagenic intermediates. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):483–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90191-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb L. A., Preston B. D. Mutagenesis by apurinic/apyrimidinic sites. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:201–230. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.001221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon I., Bohr V. A., Smith C. A., Hanawalt P. C. Preferential DNA repair of an active gene in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8878–8882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon I., Hanawalt P. C. Induction of the Escherichia coli lactose operon selectively increases repair of its transcribed DNA strand. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):95–98. doi: 10.1038/342095a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagher D., Strauss B. Insertion of nucleotides opposite apurinic/apyrimidinic sites in deoxyribonucleic acid during in vitro synthesis: uniqueness of adenine nucleotides. Biochemistry. 1983 Sep 13;22(19):4518–4526. doi: 10.1021/bi00288a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakumi K., Sekiguchi M. Structures and functions of DNA glycosylases. Mutat Res. 1990 Sep-Nov;236(2-3):161–172. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(90)90003-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson B. J., Chang C. N., Grollman A. P., Henner W. D. Mechanism of DNA cleavage and substrate recognition by a bovine apurinic endonuclease. Biochemistry. 1989 May 2;28(9):3894–3901. doi: 10.1021/bi00435a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaaper R. M., Glickman B. W., Loeb L. A. Mutagenesis resulting from depurination is an SOS process. Mutat Res. 1982 Nov;106(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(82)90186-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaaper R. M., Kunkel T. A., Loeb L. A. Infidelity of DNA synthesis associated with bypass of apurinic sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):487–491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scicchitano D. A., Hanawalt P. C. Repair of N-methylpurines in specific DNA sequences in Chinese hamster ovary cells: absence of strand specificity in the dihydrofolate reductase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3050–3054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss B., Rabkin S., Sagher D., Moore P. The role of DNA polymerase in base substitution mutagenesis on non-instructional templates. Biochimie. 1982 Aug-Sep;64(8-9):829–838. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(82)80138-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talpaert-Borlé M., Liuzzi M. Reaction of apurinic/apyrimidinic sites with [14C]methoxyamine. A method for the quantitative assay of AP sites in DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Sep 9;740(4):410–416. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(83)90089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]