Abstract
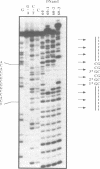
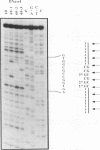
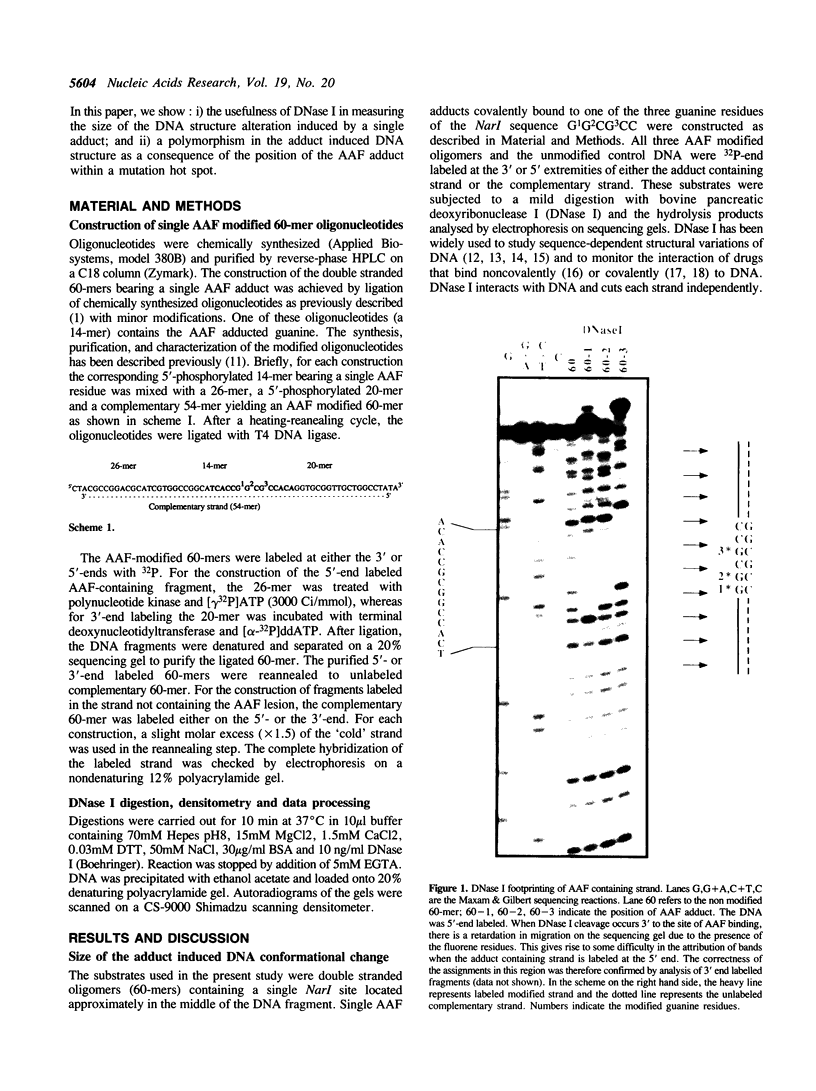
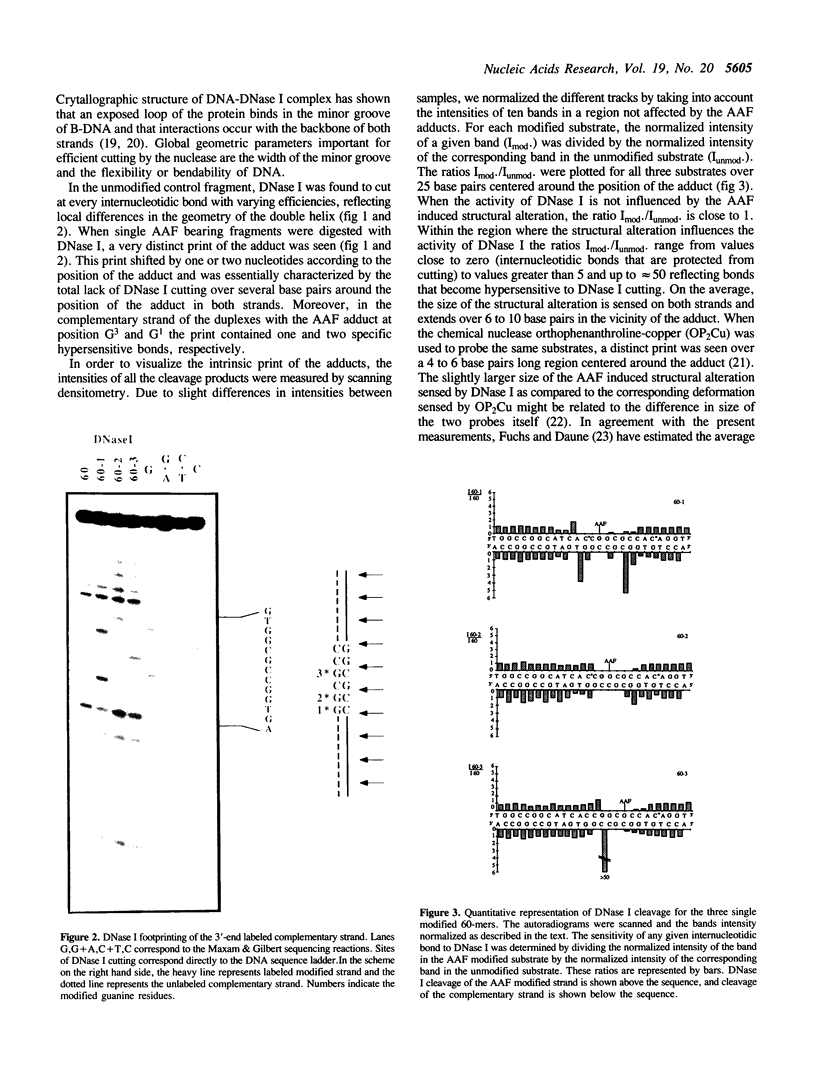
In this paper, we have constructed double stranded helices (60-mers) containing a single N-2-acetylaminofluorene (-AAF) adduct covalently bound to one of the three guanine residues of the Narl site (G1G2CG3CC). This sequence was identified as a strong frameshift mutation hot spot for many carcinogens that bind to the C8 position of guanine. Using DNase I as a probe for DNA conformation we show i) that the average size of the helix deformation extends over 3 to 5 base pairs in both directions from the adduct site, and ii) that there is a strong polymorphism in the adduct induced DNA conformation. The present study supports the idea that adducts induce specific sequence dependent local conformational changes in DNA that are differentially recognized and processed by the enzymatic machineries that lead to repair or mutagenesis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bintz R., Fuchs R. P. Induction of -2 frameshift mutations within alternating GC sequences by carcinogens that bind to the C8 position of guanine residues: development of a specific mutation assay. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 May;221(3):331–338. doi: 10.1007/BF00259396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnouf D., Koehl P., Fuchs R. P. Single adduct mutagenesis: strong effect of the position of a single acetylaminofluorene adduct within a mutation hot spot. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4147–4151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daune M. P., Fuchs R. P., Leng M. Structural modification and protein recognition of DNA modified by N-2-fluorenylacetamide, its 7-iodo derivative, and by N-2-fluorenamine. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1981 Dec;(58):201–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R. Structural specificities of five commonly used DNA nucleases. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 15;176(4):535–557. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Travers A. A. DNA structural variations in the E. coli tyrT promoter. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):491–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90379-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Travers A. A. Structural junctions in DNA: the influence of flanking sequence on nuclease digestion specificities. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4445–4467. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K. R., Waring M. J. DNA structural variations produced by actinomycin and distamycin as revealed by DNAase I footprinting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9271–9285. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs R. P., Bintz R. Activity of carcinogens that bind to the C8 position of guanine residues in an assay specific for the detection of -2 frameshift mutations in a defined hot spot. Environ Health Perspect. 1990 Aug;88:83–87. doi: 10.1289/ehp.908883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs R. P. DNA binding spectrum of the carcinogen N-acetoxy-N-2-acetylaminofluorene significantly differs from the mutation spectrum. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 25;177(1):173–180. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs R. P., Daune M. P. Dynamic structure of DNA modified with the carcinogen N-acetoxy-n-2-acetylaminofluorene. Biochemistry. 1974 Oct 8;13(21):4435–4440. doi: 10.1021/bi00718a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs R., Daune M. Physical studies on deoxyribonucleic acid after covalent binding of a carcinogen. Biochemistry. 1972 Jul 4;11(14):2659–2666. doi: 10.1021/bi00764a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley L. H., Needham-VanDevanter D. R., Lee C. S. Demonstration of the asymmetric effect of CC-1065 on local DNA structure using a site-directed adduct in a 117-base-pair fragment from M13mp1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6412–6416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koehl P., Burnouf D., Fuchs R. P. Construction of plasmids containing a unique acetylaminofluorene adduct located within a mutation hot spot. A new probe for frameshift mutagenesis. J Mol Biol. 1989 May 20;207(2):355–364. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90259-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koehl P., Valladier P., Lefèvre J. F., Fuchs R. P. Strong structural effect of the position of a single acetylaminofluorene adduct within a mutation hot spot. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):9531–9541. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.9531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffel-Schwartz N., Verdier J. M., Bichara M., Freund A. M., Daune M. P., Fuchs R. P. Carcinogen-induced mutation spectrum in wild-type, uvrA and umuC strains of Escherichia coli. Strain specificity and mutation-prone sequences. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 25;177(1):33–51. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90056-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomonossoff G. P., Butler P. J., Klug A. Sequence-dependent variation in the conformation of DNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 15;149(4):745–760. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90356-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramesh N., Brahmachari S. K. Structural alteration from non-B to B-form could reflect DNase I hypersensitivity. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1989 Apr;6(5):899–906. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1989.10506521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage E., Leng M. Conformation of poly(dG-dC) . poly(dG-dC) modified by the carcinogens N-acetoxy-N-acetyl-2-aminofluorene and N-hydroxy-N-2-aminofluorene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4597–4601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santella R. M., Grunberger D., Weinstein I. B., Rich A. Induction of the Z conformation in poly(dG-dC).poly(dG-dC) by binding of N-2-acetylaminofluorene to guanine residues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1451–1455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeberg E., Fuchs R. P. Acetylaminofluorene bound to different guanines of the sequence -GGCGCC- is excised with different efficiencies by the UvrABC excision nuclease in a pattern not correlated to the potency of mutation induction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):191–194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spassky A., Sigman D. S. Nuclease activity of 1,10-phenanthroline-copper ion. Conformational analysis and footprinting of the lac operon. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 31;24(27):8050–8056. doi: 10.1021/bi00348a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suck D., Lahm A., Oefner C. Structure refined to 2A of a nicked DNA octanucleotide complex with DNase I. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):464–468. doi: 10.1038/332464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suck D., Oefner C. Structure of DNase I at 2.0 A resolution suggests a mechanism for binding to and cutting DNA. Nature. 1986 Jun 5;321(6070):620–625. doi: 10.1038/321620a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visse R., de Ruijter M., Brouwer J., Brandsma J. A., van de Putte P. Uvr excision repair protein complex of Escherichia coli binds to the convex side of a cisplatin-induced kink in the DNA. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7609–7617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. D., Miglietta J. J., Kłysik J., Larson J. E., Stirdivant S. M., Zacharias W. Spectroscopic studies on acetylaminofluorene-modified (dT-dG)n . (dC-dA)n suggest a left-handed conformation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10166–10171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]